Multiparametric Renal Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Prediction and Annual Monitoring of the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease over Two Years
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Clinical Assessment and Protocol
2.3. Multiparametric Renal MRI
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
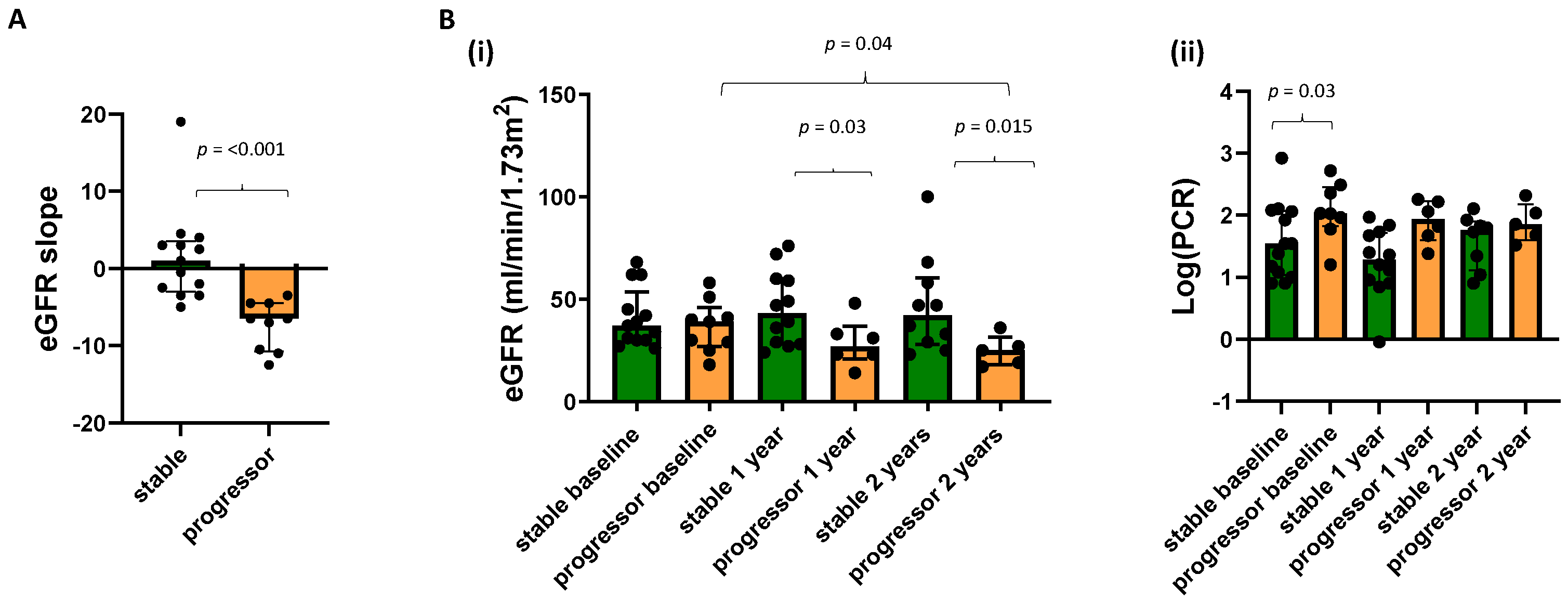
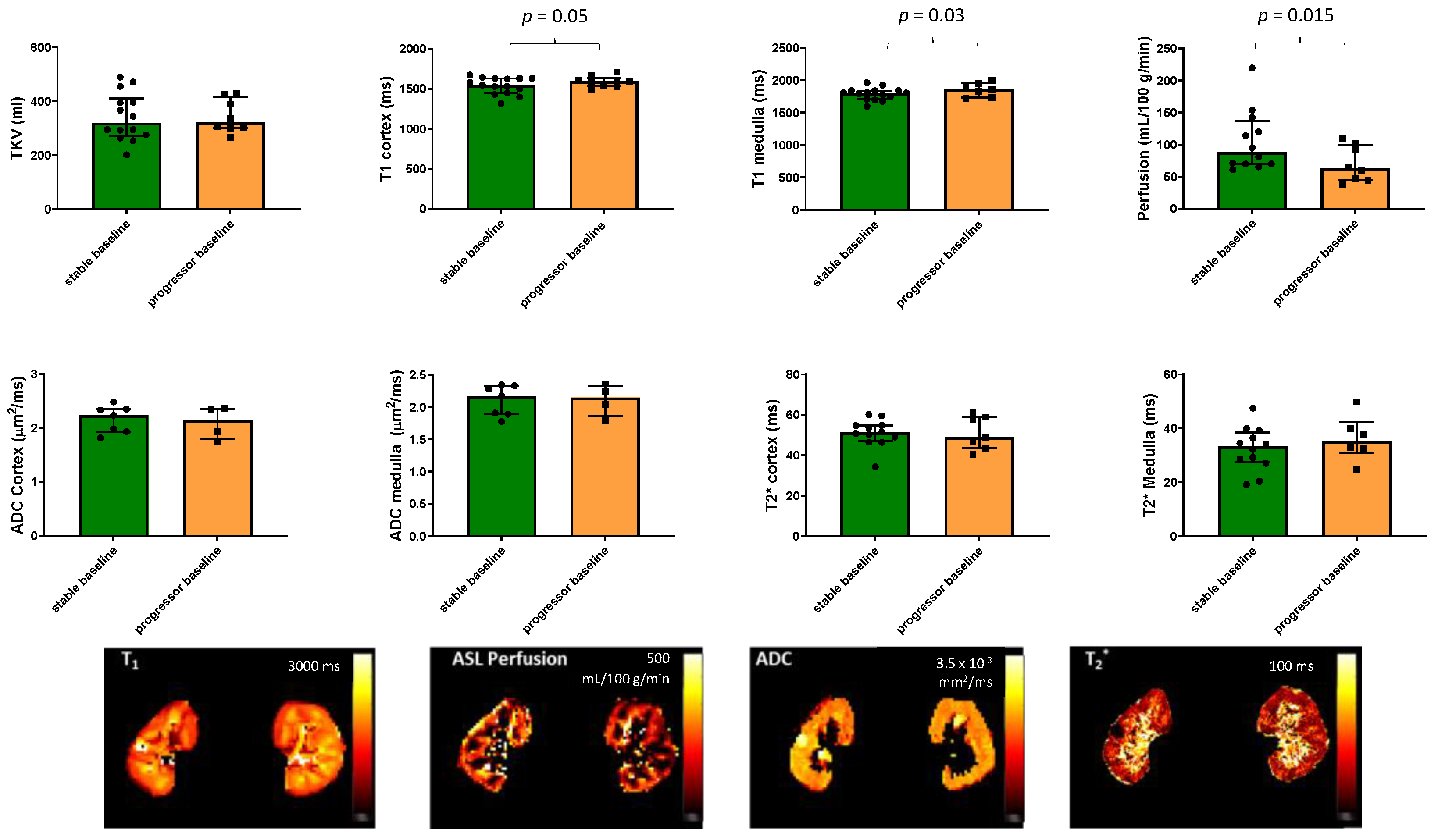
3.1. Prognostic Value of the Baseline MRI and Clinical Measures
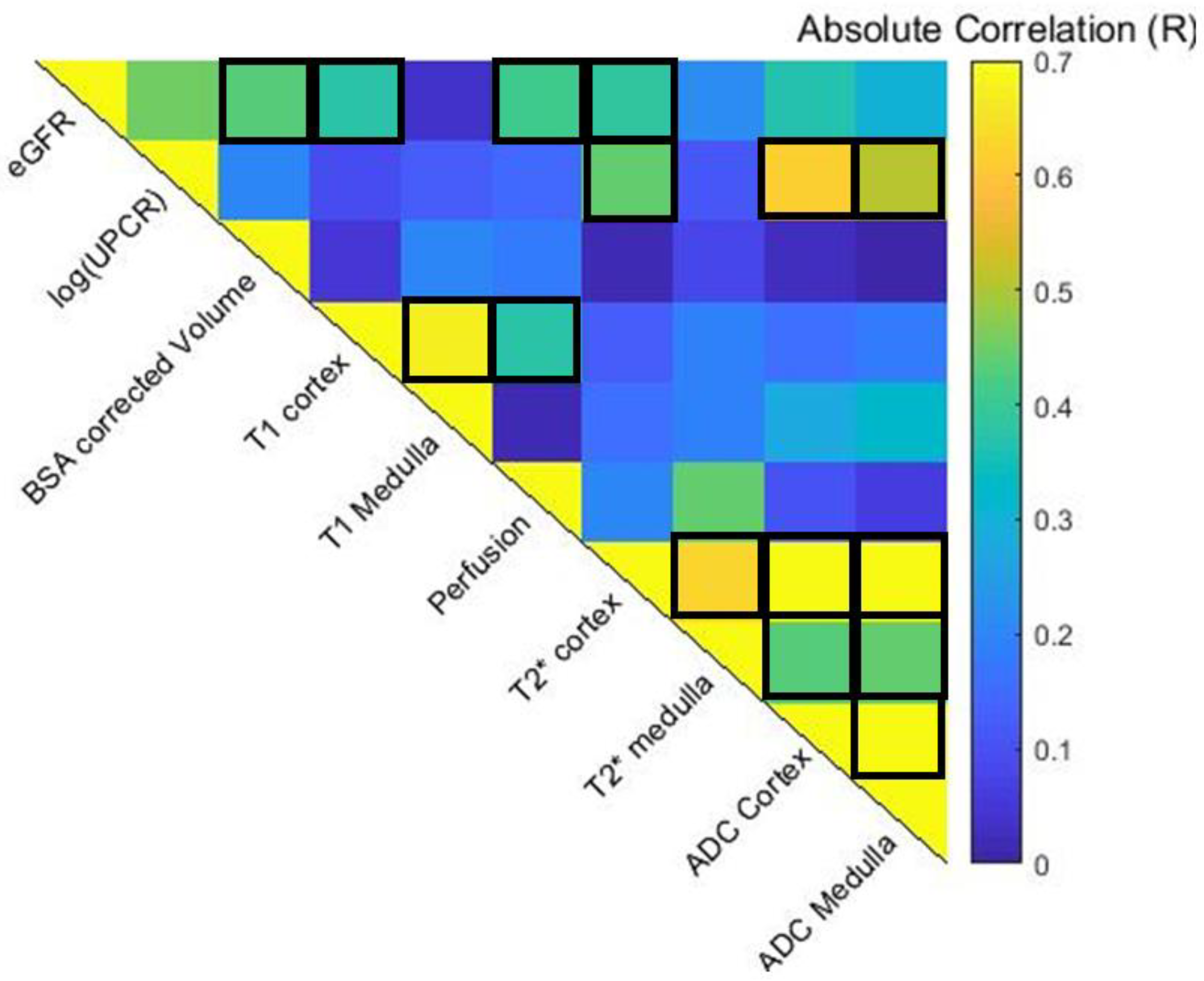
3.2. Association between MRI Data and Biochemical Measures
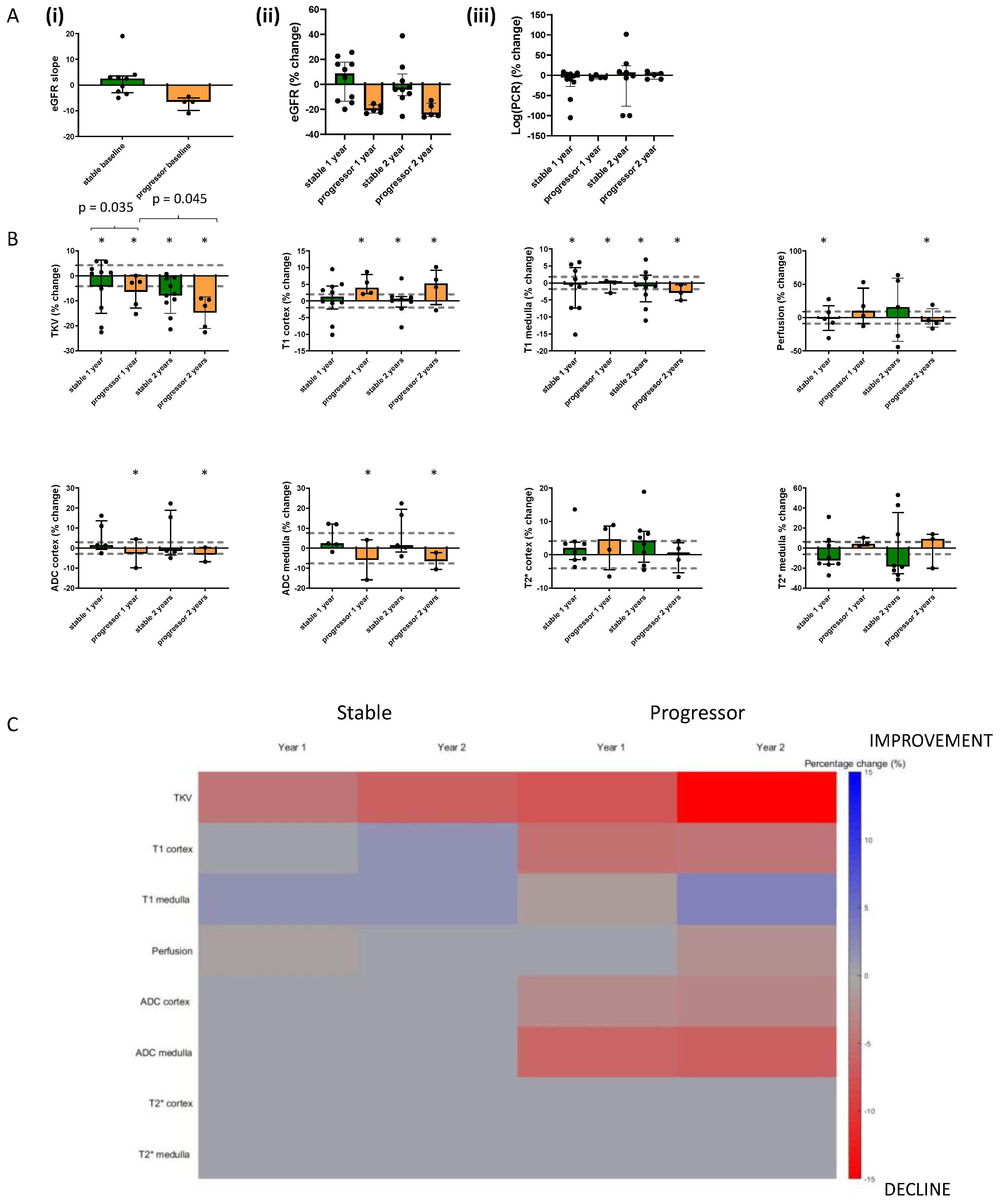
3.3. Monitoring CKD Progression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Francis, S.T.; Selby, N.M.; Taal, M.W. Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Evaluate Kidney Structure, Function, and Pathology: Moving Toward Clinical Application. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2023, 82, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, E.F.; Buchanan, C.E.; Bradley, C.R.; Prestwich, B.; Mahmoud, H.; Taal, M.; Selby, N.M.; Francis, S.T. Multiparametric Renal Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Validation, Interventions, and Alterations in Chronic Kidney Disease. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendichovszky, I.; Pullens, P.; Dekkers, I.; Nery, F.; Bane, O.; Pohlmann, A.; de Boer, A.; Ljimani, A.; Odudu, A.; Buchanan, C.; et al. Technical recommendations for clinical translation of renal MRI: A consensus project of the Cooperation in Science and Technology Action PARENCHIMA. Magn. Reson. Mater. Physics Biol. Med. 2019, 33, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, P.V.; Li, L.-P.; Thacker, J.M.; Li, W.; Hack, B.; Kohn, O.; Sprague, S.M. Cortical Perfusion and Tubular Function as Evaluated by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlates with Annual Loss in Renal Function in Moderate Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2019, 49, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, P.V. Update on renal blood oxygenation level–dependent MRI to assess intrarenal oxygenation in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 778–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.V.; Li, W.; Raj, D.S.; Carr, J.; Carr, M.; Thacker, J.; Li, L.-P.; Wang, C.; Sprague, S.M.; Ix, J.H.; et al. Multicenter Study Evaluating Intrarenal Oxygenation and Fibrosis Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Individuals with Advanced CKD. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 3, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham-Brown, M.P.; Singh, A.; Wormleighton, J.; Brunskill, N.J.; McCann, G.P.; Barratt, J.; Burton, J.O.; Xu, G. Association between native T1 mapping of the kidney and renal fibrosis in patients with IgA nephropathy. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedli, I.; Crowe, L.A.; Berchtold, L.; Moll, S.; Hadaya, K.; de Perrot, T.; Vesin, C.; Martin, P.-Y.; de Seigneux, S.; Vallée, J.-P. New Magnetic Resonance Imaging Index for Renal Fibrosis Assessment: A Comparison between Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and T1 Mapping with Histological Validation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.; Shang, F.; Wang, Y.; Lu, H.; Gu, H.; Dou, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Native T1 Mapping in Assessing Kidney Fibrosis for Patients with Chronic Glomerulonephritis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillis, K.A.; McComb, C.; Patel, R.K.; Stevens, K.K.; Schneider, M.P.; Radjenovic, A.; Morris, S.T.; Roditi, G.H.; Delles, C.; Mark, P.B. Non-Contrast Renal Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Assess Perfusion and Corticomedullary Differentiation in Health and Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephron 2016, 133, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoeny, H.C.; De Keyzer, F. Extracranial applications of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2007, 17, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoeny, H.C.; De Keyzer, F.; Oyen, R.H.; Peeters, R.R. Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of Kidneys in Healthy Volunteers and Patients with Parenchymal Diseases: Initial Experience. Radiology 2005, 235, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Fang, W.; Ling, H.; Chai, W.; Chen, K. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of kidneys in patients with chronic kidney disease: Initial study. Eur. Radiol. 2010, 20, 978–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togao, O.; Doi, S.; Kuro-O, M.; Masaki, T.; Yorioka, N.; Takahashi, M. Assessment of Renal Fibrosis with Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging: Study with Murine Model of Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction. Radiology 2010, 255, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yan, F. Diffusion-weighted imaging in assessing renal pathology of chronic kidney disease: A preliminary clinical study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Li, S.; Li, Y. Assessment of renal fibrosis in chronic kidney disease using diffusion-weighted MRI. Clin. Radiol. 2014, 69, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Palmer, S.L.; Lin, X.; Li, W.; Chen, K.; Yan, F.; Li, X. Diffusion-weighted imaging and pathology of chronic kidney disease: Initial study. Abdom. Imaging 2018, 43, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Stevens, P.E.; Bilous, R.W.; Coresh, J.; De Francisco, A.L.M.; De Jong, P.E.; Griffith, K.E.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Iseki, K.; Lamb, E.J.; et al. Kidney disease: Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) CKD work group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guide-line for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Cockwell, P.; Fisher, L.-A. The global burden of chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2020, 395, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccali, C.; Vanholder, R.; Massy, Z.A.; Ortiz, A.; Sarafidis, P.; Dekker, F.W.; Fliser, D.; Fouque, D.; Heine, G.H.; Jager, K.J.; et al. The systemic nature of CKD. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, C.E.; Mahmoud, H.; Cox, E.F.; McCulloch, T.; Prestwich, B.L.; Taal, M.W.; Selby, N.M.; Francis, S.T. Quantitative assessment of renal structural and functional changes in chronic kidney disease using multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 35, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillman, J.R.; Benoit, S.W.; Gandhi, D.B.; Trout, A.T.; Tkach, J.A.; VandenHeuvel, K.; Devarajan, P. Multiparametric quantitative renal MRI in children and young adults: Comparison between healthy individuals and patients with chronic kidney disease. Abdom. Imaging 2022, 47, 1840–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchtold, L.; Friedli, I.; Crowe, L.A.; Martinez, C.; Moll, S.; Hadaya, K.; De Perrot, T.; Combescure, C.; Martin, P.-Y.; Vallée, J.-P.; et al. Validation of the corticomedullary difference in magnetic resonance imaging-derived apparent diffusion coefficient for kidney fibrosis detection: A cross-sectional study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruijm, M.; Milani, B.; Pivin, E.; Podhajska, A.; Vogt, B.; Stuber, M.; Burnier, M. Reduced cortical oxygenation predicts a progressive decline of renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, K.; Inoue, T.; Kozawa, E.; Ishikawa, M.; Shimada, A.; Kobayashi, N.; Tanaka, J.; Okada, H. Reduced oxygenation but not fibrosis defined by functional magnetic resonance imaging predicts the long-term progression of chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Cai, X.; Lee, J.; Li, W.; Larive, B.; Kendrick, C.; Gassman, J.J.; Middleton, J.P.; Carr, J.; Raphael, K.L.; et al. Kidney Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Change in eGFR in Individuals with CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-P.; Thacker, J.M.; Li, W.; Hack, B.; Wang, C.; Kohn, O.; Sprague, S.M.; Prasad, P.V. Medullary Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent MRI Index (R2*) is Associated with Annual Loss of Kidney Function in Moderate CKD. Am. J. Nephrol. 2021, 51, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A. Estimating GFR Using the CKD Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) Creatinine Equation: More Accurate GFR Estimates, Lower CKD Prevalence Estimates, and Better Risk Predictions. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 55, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A New Equation to Estimate Glomerular Filtration Rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Inker, L.A.; Matsushita, K.; Greene, T.; Willis, K.; Lewis, E.; de Zeeuw, D.; Cheung, A.K.; Coresh, J. GFR Decline as an End Point for Clinical Trials in CKD: A Scientific Workshop Sponsored by the National Kidney Foundation and the US Food and Drug Administration. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 64, 821–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Weldegiorgis, M.; Inker, L.A.; Gansevoort, R.; Parving, H.-H.; Dwyer, J.P.; Mondal, H.; Coresh, J.; Greene, T.; Levey, A.S.; et al. Estimated GFR Decline as a Surrogate End Point for Kidney Failure: A Post Hoc Analysis from the Reduction of End Points in Non–Insulin-Dependent Diabetes With the Angiotensin II Antagonist Losartan (RENAAL) Study and Irbesartan Diabetic Nephropathy Trial (IDNT). Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coresh, J.; Turin, T.C.; Matsushita, K.; Sang, Y.; Ballew, S.H.; Appel, L.J.; Arima, H.; Chadban, S.J.; Cirillo, M.; Djurdjev, O.; et al. Decline in Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate and Subsequent Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease and Mortality. JAMA 2014, 311, 2518–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taal, M.W.; Lucas, B.; Roderick, P.; Cockwell, P.; Wheeler, D.C.; Saleem, M.A.; Fraser, S.D.S.; Banks, R.E.; Johnson, T.; Hale, L.J.; et al. Associations with age and glomerular filtration rate in a referred population with chronic kidney disease: Methods and baseline data from a UK multicentre cohort study (NURTuRE-CKD). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38, 2617–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inker, L.A.; Collier, W.; Greene, T.; Miao, S.; Chaudhari, J.; Appel, G.B.; Badve, S.V.; Caravaca-Fontán, F.; Del Vecchio, L.; Floege, J.; et al. A meta-analysis of GFR slope as a surrogate endpoint for kidney failure. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, M.; Ding, Y.; Qu, L.; Chen, C.; Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Fu, C.; Gu, F. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging for the assessment of renal fibrosis of chronic kidney disease: A preliminary study. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 47, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollner, F.G.; Kocinski, M.; Hansen, L.; Golla, A.-K.; Trbalic, A.S.; Lundervold, A.; Materka, A.; Rogelj, P. Kidney Segmentation in Renal Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Current Status and Prospects. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 71577–71605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, A.J.; Buchanan, C.E.; Allcock, T.; Scerri, D.; Cox, E.F.; Prestwich, B.L.; Francis, S.T. Automated renal segmentation in healthy and chronic kidney disease subjects using a convolutional neural network. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 86, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, S.T.; Guo, J.; Bruns, A.; Dürr, M.; Braun, J.; Hamm, B.; Sack, I.; Garcia, S.R.M. Multiparametric Quantitative MRI for the Detection of IgA Nephropathy Using Tomoelastography, DWI, and BOLD Imaging. Investig. Radiol. 2019, 54, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Application of Functional Renal MRI to Improve Assessment of Chronic Kidney Disease (AFiRM). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04238299. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04238299 (accessed on 19 October 2023).
- Sir Peter Mansfield Imaging Centre UK Renal Imaging Network (UKRIN): MRI Acquisition and Processing Standardisation (MAPS). Available online: https://www.nottingham.ac.uk/research/groups/spmic/research/uk-renal-imaging-network/ukrin-maps.aspx (accessed on 19 October 2023).
| Baseline | Year 1 | Year 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Progressors (n = 9) | Stable (n = 13) | Progressors (n = 6) | Stable (n = 12) | Progressors (n = 5) | Stable (n = 10) | |
| Ethnicity (no. Caucasian] | 7 | 11 | 4 | 10 | 4 | 8 |
| Gender (no. male) | 7 | 10 | 4 | 10 | 4 | 7 |
| Age (years) | 58 ± 16 | 57 ± 18 | 62 ± 38 | 59 ± 17 | 58 ± 19 | 60 ± 13 |
| Height (m) | 174 ± 9 | 274 ± 9 | 171 ± 7 | 173 ± 9 | 174 ± 7 | 172 ± 9 |
| Weight (kg) | 85 ± 11 | 89 ± 14 | 90 ± 16 | 87 ± 11 | 88 ± 16 | 88(20) |
| BMl (kg/m2) | 28 ± 3 | 30 ± 6 | 29 ± 4 | 29 ± 4 | 29 ± 3 | 28 ± 3 |
| Serum creatinine (umol/L) | 160 ± 37 | 176 ± 37 | 207 ± 44 | 150 ± 39 * | 231 ± 28 | 149 ± 47 * |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 37(13) | 41 ± 14 | 29 + 12 | 46 + 18 * | 25 ± 7 | 47 ± 24 * |
| Urine PCR (mg/mmol) | 160 + 168 | 35(107) * | 100 ± 64 | 30 ± 29 | 94 ± 70 | 55 ± 41 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 142 + 17 | 136 ± 18 | 132 ± 11 | 140 ± 18 | 140 ± 20 | 142 ± 15 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 81 ± 8 | 82 ± 9 | 76 ± 12 | 76 ± 10 | 78 ± 10 | 83 ± 14 |
| Primary Renal Diagnosis, n (%) | ||||||
| Glomerular disease | 5 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 3 |
| Tubulointerstitial disease | 2 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Ischaemic nephropathy | 2 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 4 |
| Fibrosis score at baseline (n) | 4(5), 3(2), 2(1), 0(1) | 4(6), 3(3), 2(2), 0(2) | 4(3), 3(1), 2(1), 0(1) | 4(6), 3(2), 2(2), 0(2) | 4(3), 3(1), 2(1) | 4(4), 3(2), 2(2), 0(2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buchanan, C.E.; Mahmoud, H.; Cox, E.F.; Prestwich, B.L.; Noble, R.A.; Selby, N.M.; Taal, M.W.; Francis, S.T. Multiparametric Renal Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Prediction and Annual Monitoring of the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease over Two Years. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7282. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237282
Buchanan CE, Mahmoud H, Cox EF, Prestwich BL, Noble RA, Selby NM, Taal MW, Francis ST. Multiparametric Renal Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Prediction and Annual Monitoring of the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease over Two Years. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(23):7282. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237282
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuchanan, Charlotte E., Huda Mahmoud, Eleanor F. Cox, Benjamin L. Prestwich, Rebecca A. Noble, Nicholas M. Selby, Maarten W. Taal, and Susan T. Francis. 2023. "Multiparametric Renal Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Prediction and Annual Monitoring of the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease over Two Years" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 23: 7282. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237282
APA StyleBuchanan, C. E., Mahmoud, H., Cox, E. F., Prestwich, B. L., Noble, R. A., Selby, N. M., Taal, M. W., & Francis, S. T. (2023). Multiparametric Renal Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Prediction and Annual Monitoring of the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease over Two Years. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(23), 7282. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237282






