Remdesivir-Induced Bradycardia and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Potential Risk Factors Assessment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Guidelines
2.2. Database Search and Identified Manuscripts
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Methodological Quality Appraisal
2.5. Primary Outcomes
2.6. Secondary Outcomes
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
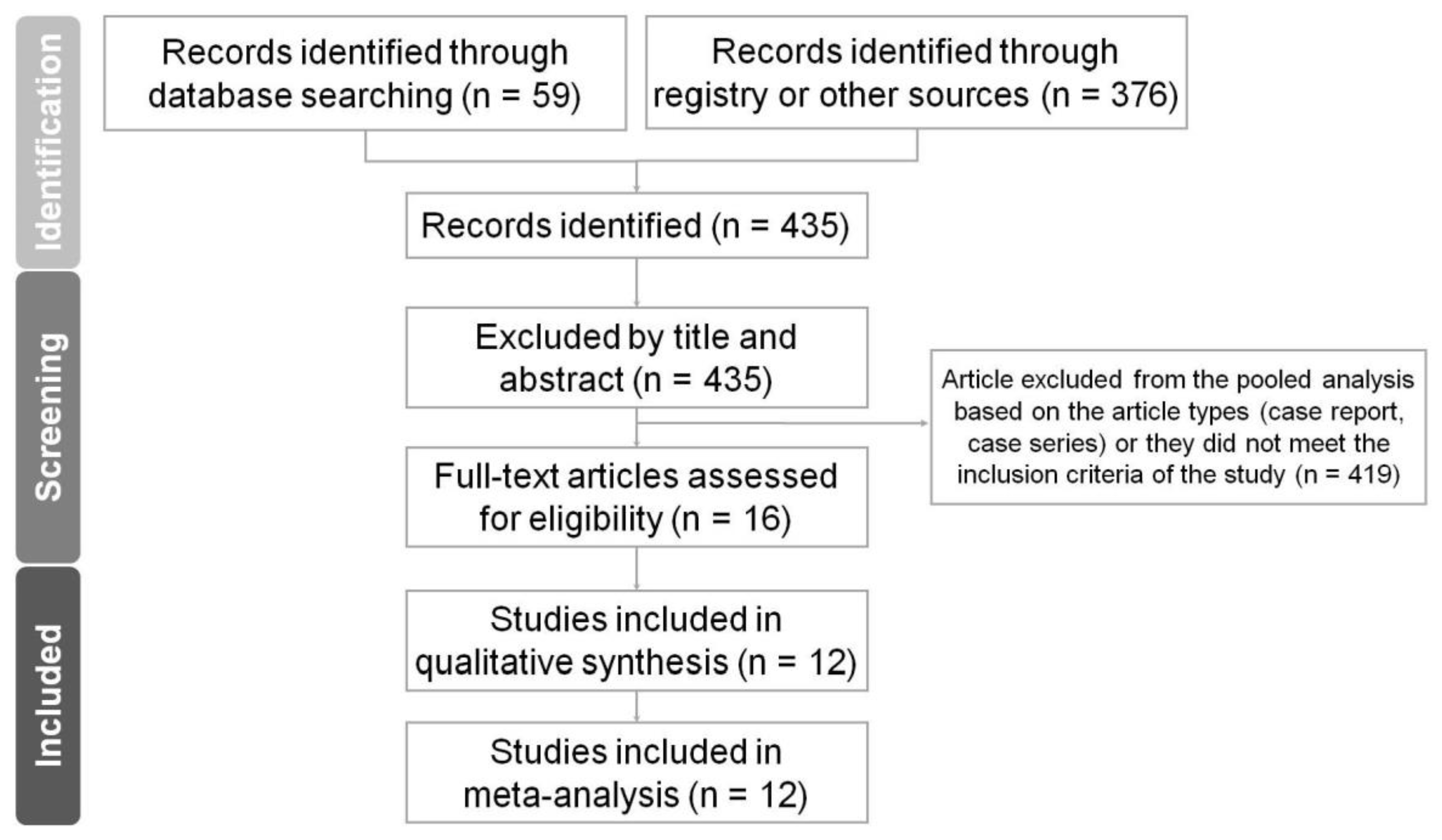
3.1. Study Identification and Selection
3.2. Primary Outcome: The Association between Mortality and Remdesivir-Induced Bradycardia
3.3. Secondary Outcomes: Risk Factor of Remdesivir-Induced Bradycardia
3.4. Trial Sequential Analysis (TSA) of Remdesivir-Induced Bradycardia and Remdesivir-Induced Bradycardia-Related Mortality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenberg, K. Remdesivir in The Treatment of COVID-19. Am. J. Nurs. 2021, 121, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Solidarity Trial Consortium. Remdesivir and three other drugs for hospitalised patients with COVID-19: Final results of the WHO Solidarity randomised trial and updated meta-analyses. Lancet 2022, 399, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.C.; Chao, C.M.; Hsueh, P.R. Clinical efficacy of antiviral agents against coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2021, 54, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghjoo, M.; Golipra, R.; Kheirkhah, J.; Golabchi, A.; Shahabi, J.; Oni-Heris, S.; Sami, R.; Tajmirriahi, M.; Saravi, M.; Khatami, M.; et al. Effect of COVID-19 medications on corrected QT interval and induction of torsade de pointes: Results of a multicenter national survey. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Jammali, S.; Al-Zakhari, R.; Sheets, N.; Mahtani, A.; Stefanishina, V.; Isber, N. Bradyarrhythmia After Remdesivir Administration in SARS-CoV-2: A Review of Literature and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology. Cardiol. Res. 2022, 13, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barstow, C.; McDivitt, J.D. Cardiovascular Disease Update: Bradyarrhythmias. FP Essent. 2017, 454, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Graudins, A.; Lee, H.M.; Druda, D. Calcium channel antagonist and beta-blocker overdose: Antidotes and adjunct therapies. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 81, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanagala, S.G.; Dholiya, H.; Jhajj, P.; Patel, M.A.; Gupta, V.; Gupta, S.; Wu, S.-I.; Jain, R. Remdesivir-Induced Bradycardia. South. Med. J. 2023, 116, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.Y.; Yang, C. Remdesivir-Induced Bradycardia and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. 2023. Available online: https://inplasy.com/inplasy-2023-6-0066/ (accessed on 21 June 2023).
- Bae, J.M. A suggestion for quality assessment in systematic reviews of observational studies in nutritional epidemiology. Epidemiol. Health 2016, 38, e2016014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, J.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chapter 10: Analysing Data and Undertaking Meta-Analyses. 2022. Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current/chapter-10 (accessed on 16 January 2022).
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Rothstein, H.R.; Introduction to Meta-Analysis. Chapter 13: Fixed-Effect versus Random-Effects Models. 2009. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9780470743386.ch13 (accessed on 11 March 2009).
- Hedges, L.V. Distribution theory for Glass’s estimator of effect size and related estimators. J. Educ. Stat. 1981, 6, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chapter 13: Assessing Risk of Bias Due to Missing Results in a Synthesis. 2022. Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current/chapter-13 (accessed on 16 January 2022).
- Attena, E.; Albani, S.; Maraolo, A.E.; Mollica, M.; De Rosa, A.; Pisapia, R.; Fiorentino, G.; Parrella, R.; Severino, S.; Russo, V. Remdesivir-induced bradycardia in COVID-19: A single center prospective study. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2021, 14, e009811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotto, C.; Blanc, P.; Esperti, S.; Suardi, L.R.; Gabbuti, A.; Vichi, F.; Mecocci, L.; Degli Esposti, A.; Pierotti, P.; Attala, L.; et al. Remdesivir treatment and transient bradycardia in patients with coronavirus diseases 2019 (COVID-19). J. Infect. 2021, 83, 237–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallotto, C.; Suardi, L.R.; Gabbuti, A.; Esperti, S.; Mecocci, L.; Blanc, P. Potential remdesivir-related transient bradycardia in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bistrovic, P.; Manola, S.; Lucijanic, M. Bradycardia during remdesivir treatment might be associated with improved survival in patients with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study on 473 patients from a tertiary centre. Postgrad. Med. J. 2022, 98, 501–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantazopoulos, I.; Mavrovounis, G.; Dimeas, G.; Zikos, N.; Pitsikou, M.; Rousogianni, E.; Mermiri, M.; Michou, A.; Spanos, M.; Maniotis, C.; et al. Remdesivir-induced bradycardia is not associated with worse outcome in patients with COVID-19: A retrospective analysis. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2022, 22, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, A.; Bauzon, J.S.; Batra, K.; Mohammed, S.; Lee, K.; Houshmand, N.; Pham, U.; Cosme, C.; Inciong, K.; Al-Taweel, O.; et al. Clinical characteristics and implications of bradycardia in COVID-19 patients treated with remdesivir: A single-center retrospective cohort study. Clin. Drug Investig. 2022, 42, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeh, C.; Giberson, C.; Kumar, S.; Aseri, M.; Barve, P. A multicenter retrospective analysis on the etiology of bradycardia in COVID-19 patients. Cureus 2022, 14, e21294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsowaida, Y.S.; Shehadeh, F.; Kalligeros, M.; Mylonakis, E. Incidence and potential risk factors for remdesivir-associated bradycardia in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1106044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attena, E.; Caturano, A.; Annunziata, A.; Maraolo, A.E.; De Rosa, A.; Fusco, F.M.; Halasz, G.; Dall’Ospedale, V.; Conte, M.; Parisi, V.; et al. Remdesivir treatment and clinical outcome in non-severe hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A propensity score matching multicenter Italian hospital experience. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 79, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filtz, A.; Carandina, A.; Fasiello, A.; Barbetta, L.; Lombardi, R.; Cinque, F.; Rizzi, G.; Ceriani, E.; Furlan, L.; Bellocchi, C.; et al. Remdesivir-induced bradycardia in patients hospitalized with SARS-CoV2 infection: A possible vagally-mediated mechanism. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2023, 18, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajimoradi, M.; Sharif Kashani, B.; Dastan, F.; Aghdasi, S.; Abedini, A.; Naghashzadeh, F.; Mohamadifar, A.; Keshmiri, M.S.; Noorali, S.; Lookzadeh, S.; et al. Remdesivir associated sinus bradycardia in patients with COVID-19: A prospective longitudinal study. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 13, 1107198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umeh, C.A.; Maguwudze, S.; Kaur, H.; Dimowo, O.; Naderi, N.; Safdarpour, A.; Hussein, T.; Gupta, R. Bradycardia and Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients on Remdesivir: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Cardiol. Res. 2023, 14, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubitosa, J.C.; Kakar, P.; Gerula, C.; Nossa, H.; Finkel, D.; Wong, K.; Khatri, M.; Ali, H. Marked sinus bradycardia associated with remdesivir in COVID-19: A case and literature review. Case Rep. 2020, 2, 2260–2264. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, A.; Ohira, S.; Kato, Y.; Ikuta, T.; Yanagida, S.; Mi, X.; Ishii, Y.; Kanda, Y.; Nishida, M.; Inoue, A.; et al. Activation of the urotensin-II receptor by remdesivir induces cardiomyocyte dysfunction. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wettschureck, N.; Offermanns, S. Mammalian G proteins and their cell type specific functions. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 1159–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingsley, R.; Rohlman, C.; Otto, A.; Chaudhary, R.; Phelan, D.; Kirchoff, R. Remdesivir-induced conduction abnormalities: A molecular model-based explanation. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 26, 11208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Arcuri, C.; Chaudhuri, S.; Gupta, R.; Aseri, M.; Barve, P.; Shah, S. A novel study on SARS-CoV-2 virus associated bradycardia as a predictor of mortality-retrospective multicenter analysis. Clin. Cardiol. 2021, 44, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, L.B.; Abdel-Qadir, H.; Fralick, M. Bradycardia associated with remdesivir therapy for COVID-19 in a 59-year-old man. CMAJ 2021, 193, E612–E615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, S.C.; Kebriaei, R.; Dresser, L.D. Remdesivir: Review of pharmacology, pre-clinical data, and emerging clinical experience for COVID-19. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2020, 40, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layland, J.; Carrick, D.; Lee, M.; Oldroyd, K.; Berry, C. Adenosine: Physiology, pharmacology, and clinical applications. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2014, 7, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shryock, J.C.; Belardinelli, L. Adenosine and adenosine receptors in the cardiovascular system: Biochemistry, physiology, and pharmacology. Am. J. Cardiol. 1997, 79, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The U.S. Food; Drug Administration (FDA). Fact Sheet for Health Care Providers Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) of Remdesivir (GS-5734™). 2020. Available online: https://www.nursingworld.org/~49e5d3/globalassets/covid19/remdessivir-fact-sheet-health-care-providers.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Bhimraj, A.; Morgan, R.L.; Shumaker, A.H.; Baden, L.; Chi-Chung Cheng, V.; Edwards, K.M.; Gandhi, R.T.; Gallagher, J.C.; Muller, W.J.; O’Horo, J.C.; et al. Lessons Learned from Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) therapies: Critical perspectives from the infectious diseases society of America (IDSA) COVID-19 treatment guideline panel. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 1691–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, M.J.; Abernethy, D.R.; Greenblatt, D.J. Effect of obesity on the pharmacokinetics of drugs in humans. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2010, 49, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Poirier, P.; Burke, L.E.; Després, J.P.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Lear, S.A.; Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Sanders, P.; et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e984–e1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, Y.; Inokuchi, Y.; Hayama, T.; Hirai, T.; Nishiyama, M.; Sueyasu, Y.; Yokoo, K. Exploration of the optimal GS-441524 trough concentration for treating COVID-19. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 62, 106892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishisaka, Y.; Aikawa, T.; Malik, A.; Kampaktsis, P.N.; Briasoulis, A.; Kuno, T. Association of Remdesivir use with bradycardia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e29018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| First Author | Year | S1 1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | C1 2 | E1 3 | E2 | E3 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attena, E. [16] | 2021 | * | * | * | ** | * | * | * | 8 | |
| Pallotto, C. [17] | 2021 | * | * | * | ** | * | * | * | 8 | |
| Pallotto, C. [18] | 2021 | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | * | 9 |
| Bistrovic, P. [19] | 2022 | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Pantazopoulos [20] | 2022 | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 8 |
| Schreiber [21] | 2022 | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 8 |
| Umeh, C. [22] | 2022 | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | * | 9 |
| Alsowaida, Y.S. [23] | 2023 | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Attena, E. [24]. | 2023 | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | * | 9 |
| Filtz, A. [25] | 2023 | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | * | 9 |
| Hajimoradi, M. [26] | 2023 | * | * | * | * | * | * | * | 7 | |
| Umeh, C. [27] | 2023 | * | * | * | * | ** | * | * | * | 9 |
| First Author and Year | Country | Population | Participants | Dosage | Duration | Incidence 1 | Bradycardia Definition (Beat/min) | Study Design | Additional Therapies | Quality Assessment | Funding/Grants/ Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attena, E. 2021 [16] | Italy | Hospitalized adult patients | RDV: 100 Control: 66 | LD: 200 mg MD: 100 mg | 5–10 days were allowed | 21/100 (21%) | HR < 50 | Prospective Cohort study | Azithromycin, Dexamethasone, Heparin | 8 | N/A |
| Pallotto, C. 2021 [17] | Italy | Hospitalized adult patients | RDV: 62 Control: 79 | LD: 200 mg MD: 100 mg | 5 days | 29/62 (46.8%) | 2 HR < 60 × 2 or HR < 50 × 1 | Retrospective Cohort Study | Steroids, LMWH | 8 | N/A |
| Pallotto, C. 2021 [18] | Italy | Hospitalized adult patients | RDV: 20 Control: 26 | LD: 200 mg MD: 100 mg | 5 days | 12/20 (60.0%) | Compared pre and post △HR | Retrospective Cohort Study | Dexamethasone, LMWH | 9 | N/A |
| Bistrovic, P. 2022 [19] | Croatia | Hospitalized adult patients | RDV: 473 | LD: 200 mg MD: 100 mg | 5 days: 455/473 (96.2%) >5 days: 18/473 (3.8%) | 79/473 (16.8%) | HR < 60 | Retrospective Cohort Study | Steroids, LMWH | 7 | N/A |
| Pantazopoulos 2022 [20] | Greece | Hospitalized adult patients | RDV: 160 | LD: 200 mg MD: 100 mg | 5 days | 118/160 (73.8%) | HR < 60 | Retrospective Cohort Study | Dexamethasone, LMWH | 8 | N/A |
| Schreiber 2022 [21] | USA | Hospitalized adult patients | RDV: 375 | LD: 200 mg MD: 100 mg | 5 days | 182/375 (48.5%) | HR < 60 | Retrospective Cohort Study | Not mention | 8 | N/A |
| Umeh, C. 2022 [22] | USA | Hospitalized adult patients | RDV: 507 Control: 609 | LD: 200 mg MD: 100 mg | 5 days | 218/507 (43.0%) | HR < 60 | Retrospective Cohort Study | Dexamethasone, Methylprednisolone | 9 | N/A |
| Alsowaida, Y.S. 2023 [23] | USA | Hospitalized adult patients | RDV: 1635 | LD: 200 mg MD: 100 mg | 10 days | 606/1635 (37.1%) | HR < 60 | Retrospective Cohort Study | Dexamethasone | 7 | N/A |
| Attena, E. 2023 [24] | Italy | Hospitalized adult patients | RDV: 200 Control: 200 | LD: 200 mg MD: 100 mg | 5 days | 40/200 (20.0%) | HR < 50 | Retrospective Cohort Study | Azithromycin, Dexamethasone | 9 | Università degli Studi della Campania Luigi Vanvitelli within the CRUI-CARE Agreement |
| Filtz, A. 2023 [25] | Italy | Hospitalized adult patients | RDV: 71 Control: 54 | LD: 200 mg MD: 100 mg | 5 days | 40/71 (56.0%) | HR < 60 | Retrospective Cohort Study | Any other additional therapeutic according to guideline was allowed | 9 | Italian Ministry of Health |
| Hajimoradi, M. 2023 [26] | Iran | Outpatients/ Hospitalized adult patients | RDV: 177 | LD: 200 mg MD: 100 mg | 5 days | 48/177 (27.3%) | HR < 60 | Prospective Cohort study | Tocilizumab, Dexamethasone | 7 | N/A |
| Umeh, C. 2023 [27] | USA | Hospitalized adult patients | RDV: 1493 Control: 1367 | LD: 200 mg MD: 100 mg | 5 days | 801/1254 (63.9%) | 3 HR < 60 × 2 | Retrospective Cohort Study | Dexamethasone | 9 | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ai, M.-Y.; Chang, W.-L.; Yang, C.-J. Remdesivir-Induced Bradycardia and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Potential Risk Factors Assessment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7518. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247518
Ai M-Y, Chang W-L, Yang C-J. Remdesivir-Induced Bradycardia and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Potential Risk Factors Assessment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(24):7518. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247518
Chicago/Turabian StyleAi, Ming-Ying, Wei-Lun Chang, and Chia-Jui Yang. 2023. "Remdesivir-Induced Bradycardia and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Potential Risk Factors Assessment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 24: 7518. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247518
APA StyleAi, M.-Y., Chang, W.-L., & Yang, C.-J. (2023). Remdesivir-Induced Bradycardia and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Potential Risk Factors Assessment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(24), 7518. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247518








