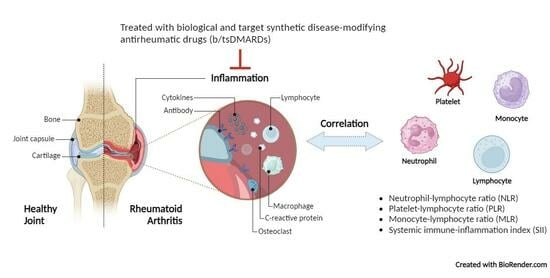
Correlation of Hematological Indices and Acute-Phase Reactants in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort
2.2. Demographic and Laboratory Data
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
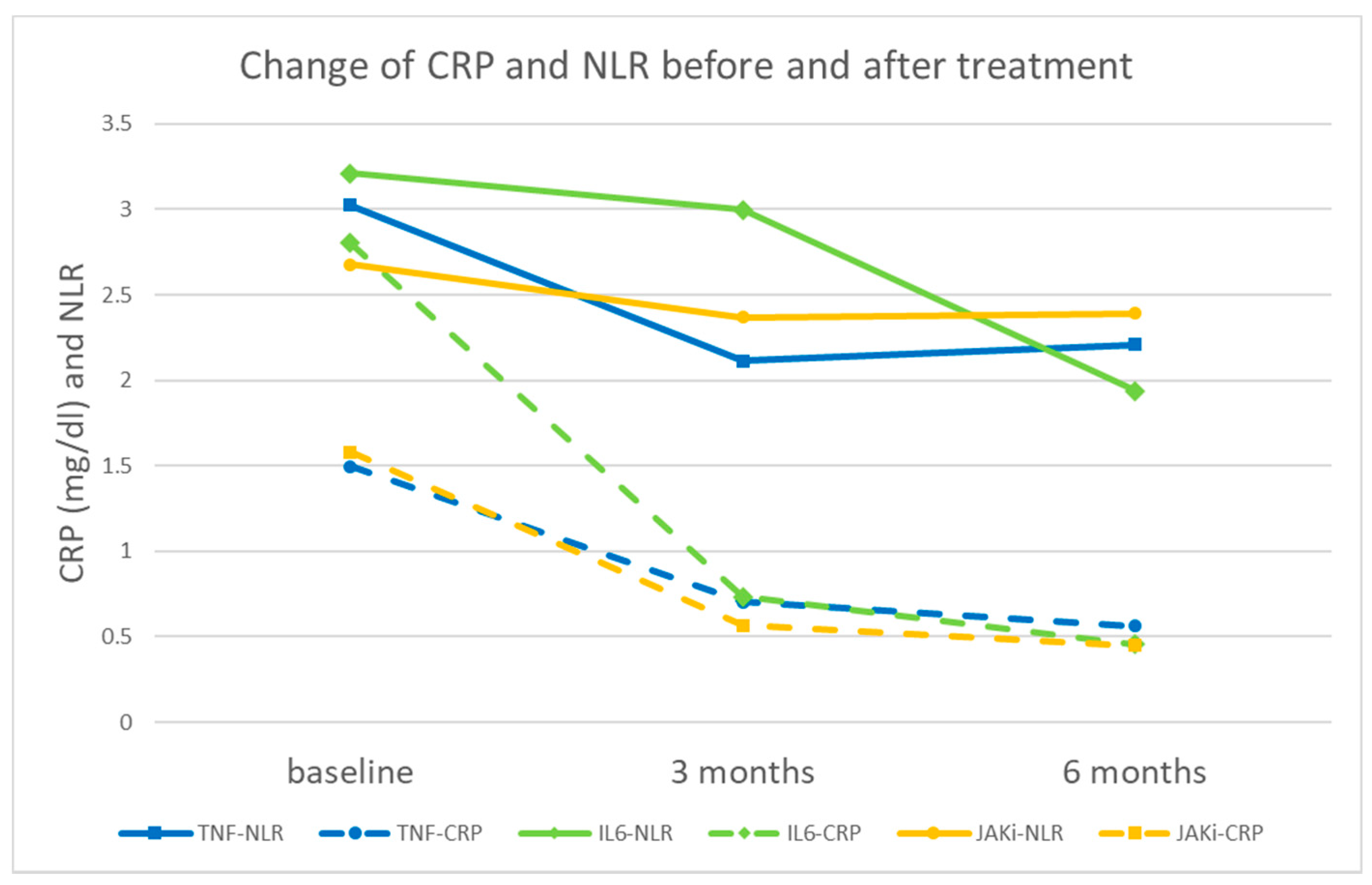
3.1. Characteristics and Laboratory Data of Patients before and after Treatment
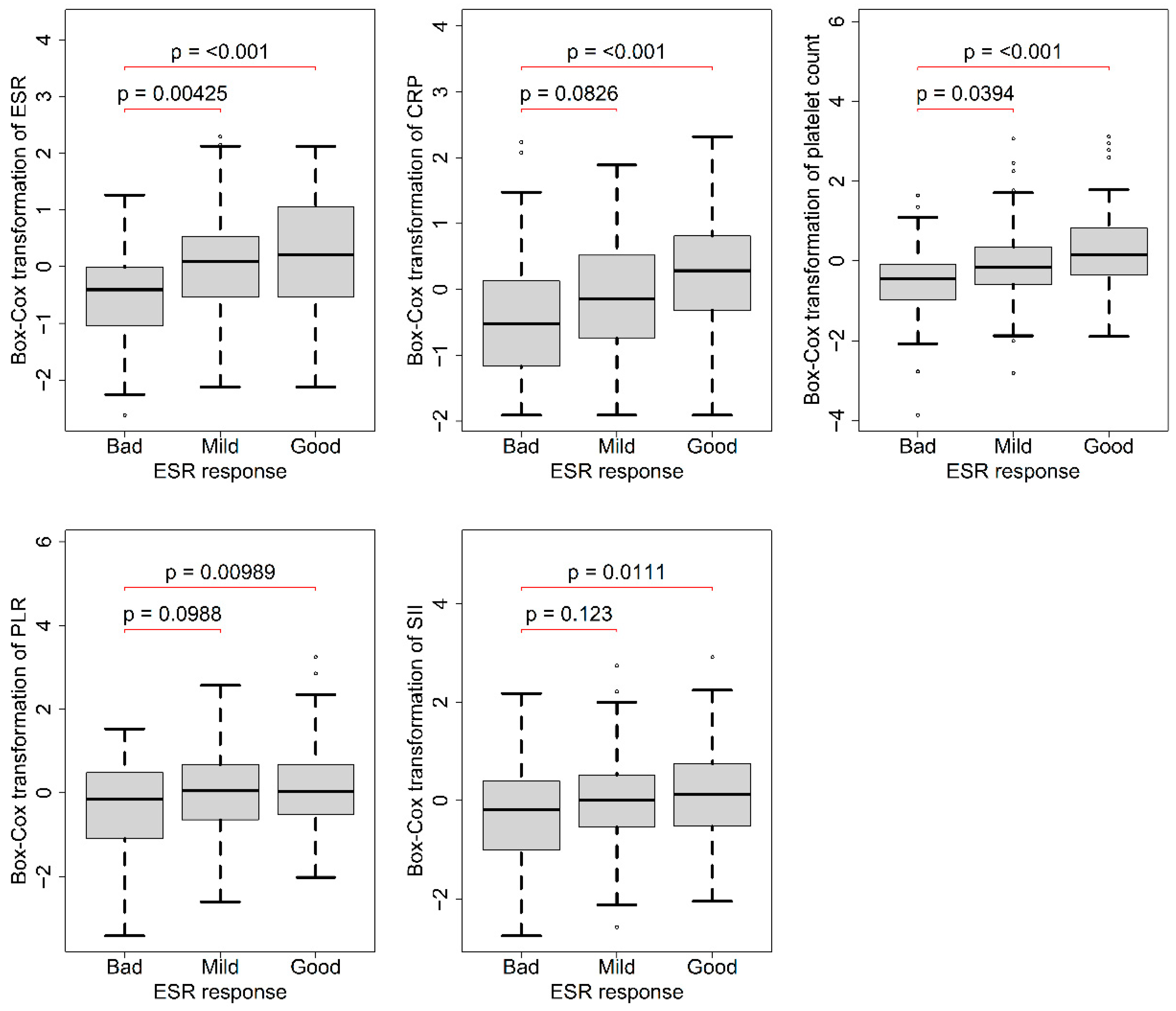
3.2. Association of Baseline Data with ESR Response 3 Months after Treatment
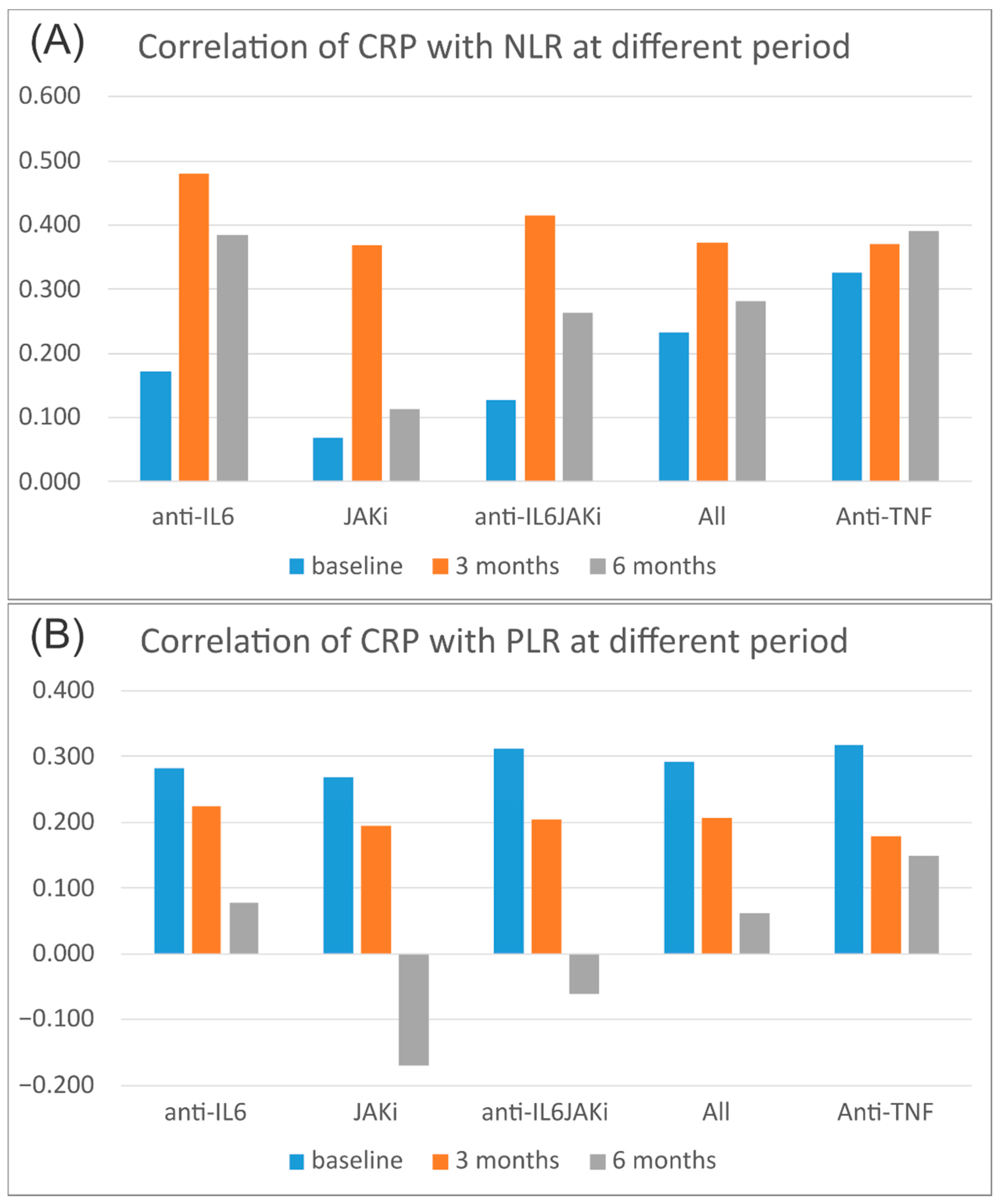
3.3. Correlation of Acute-Phase Reactants with Hematological Indices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.B.M.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Burmester, G.R.; Dougados, M.; Kerschbaumer, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Sepriano, A.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; de Wit, M.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Compán, V.; Gherghe, A.M.; Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Landewé, R.; van der Heijde, D. Relationship between disease activity indices and their individual components and radiographic progression in RA: A systematic literature review. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 994–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevoo, M.L.; van’t Hof, M.A.; Kuper, H.H.; van Leeuwen, M.A.; van de Putte, L.B.; van Riel, P.L. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995, 38, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seppen, B.; Wiegel, J.; Ter Wee, M.M.; van Schaardenburg, D.; Roorda, L.D.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Boers, M.; Bos, W.H. Smartphone-Assisted Patient-Initiated Care Versus Usual Care in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Low Disease Activity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 1737–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, D.; Mai, A.; Klaassen-Mielke, R.; Timmesfeld, N.; Trampisch, U.; Rudolf, H.; Baraliakos, X.; Schmitz, E.; Fendler, C.; Klink, C.; et al. The Efficacy of Short-Term Bridging Strategies with High- and Low-Dose Prednisolone on Radio-graphic and Clinical Outcomes in Active Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 1628–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekara, S.; Sachin, S. Measures in rheumatoid arthritis: Are we measuring too many parameters. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 15, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, C.K.; Najm, A.; Young, F.; McGarry, T.; Biniecka, M.; Fearon, U.; Veale, D.J. The Utility and Limitations of CRP, ESR and DAS28-CRP in Appraising Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Li, D.; Wu, D.; Zhang, N. The Relationship between Hematological Indices and Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases (ARDs), a Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erre, G.L.; Paliogiannis, P.; Castagna, F.; Mangoni, A.A.; Carru, C.; Passiu, G.; Zinellu, A. Meta-analysis of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 49, e13037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xie, L. Correlation between NLR, PLR, and LMR and Disease Activity, Efficacy Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 4433141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijuan, W.; Yuting, Z.; Chaoyang, L.; Ju, Y. Neutrophil-lymphocyte, platelet-lymphocyte and lymphocyte-monocyte ratios may not be useful markers to assess disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: A STROBE-compliant article. Medicine 2021, 100, e27631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; He, H.; Zang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Hu, H.; Cui, J.; Wang, W.; Gao, Y.; Wei, H.; Wang, Z. Systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) as a novel biomarker in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A multi-center retrospective study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 41, 1989–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; van der Heijde, D.; Machold, K.P.; Aletaha, D.; Landewé, R. Proposal for a new nomenclature of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Findeisen, K.E.; Sewell, J.; Ostor, A.J.K. Biological Therapies for Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Overview for the Clinician. Biologics 2021, 15, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mélet, J.; Mulleman, D.; Goupille, P.; Ribourtout, B.; Watier, H.; Thibault, G. Rituximab-induced T cell depletion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Association with clinical response. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 2783–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmester, G.R.; Blanco, R.; Charles-Schoeman, C.; Wollenhaupt, J.; Zerbini, C.; Benda, B.; Gruben, D.; Wallenstein, G.; Krishnaswami, S.; Zwillich, S.H.; et al. Tofacitinib (CP-690,550) in combination with methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to tumour necrosis factor inhibitors: A randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereckova, J.; Martiniakova, S.; Payer, J.; Falk, M.; Killinger, Z.; Perecko, T. Analysis of hematological parameters in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving biological therapy: Contribution to prevention of avoidable hematological complications. EXCLI J. 2022, 21, 580–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Xiao, D.M.; Qin, W.; Xie, B.H.; Wang, T.H.; Huang, H.; Zhao, B.J.; Han, X.; Sun, Q.Q.; Wu, X.D.; et al. The clinical value of hematological markers in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with tocilizumab. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, J.Y.; Kim, S.K. Association between Hematological Indicesand Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Janus Kinase Inhibitors for 24 Weeks. Medicina 2022, 58, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silman, A.J. The 1987 revised American Rheumatism Association criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1988, 27, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, K.P.; Zhang, Q. The association between systemic immune-inflammation index and rheumatoid arthritis: Evidence from NHANES 1999–2018. Arthritis. Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M. R-software: A Newer Tool in Epidemiological Data Analysis. Indian J. Community Med. 2013, 38, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, K.; Preacher, K.J. On effect size. Psychol. Methods 2012, 17, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diedenhofen, B.; Musch, J. cocor: A comprehensive solution for the statistical comparison of correlations. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoglu, H. User’s guide to correlation coefficients. Turk. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 18, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.W.; Kim, A.R.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, G.T.; Ahn, E.Y.; So, M.W.; Lee, S.G. Diagnostic Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte, Platelet-to-Lymphocyte, and Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratios for the Assessment of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Patients with Undifferentiated Inflammatory Arthritis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Cai, G.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.; Yao, S.; Zhuang, L.; Ren, M.; Wang, Q.; Yu, X. The value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as complementary diagnostic tools in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis: A multicenter retrospective study. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targońska-Stępniak, B.; Zwolak, R.; Piotrowski, M.; Grzechnik, K.; Majdan, M. The Relationship between Hematological Markers of Systemic Inflammation (Neutrophil-To-Lymphocyte, Platelet-To-Lymphocyte, Lymphocyte-To-Monocyte Ratios) and Ultrasound Disease Activity Parameters in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mititelu, R.R.; Pădureanu, R.; Băcănoiu, M.; Pădureanu, V.; Docea, A.O.; Calina, D.; Barbulescu, A.L.; Buga, A.M. Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Markers-Mirror Tools in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, D.Y.; Xu, X.Z.; Liu, Y.Y.; Yin, T.T.; Li, D. Platelet/Lymphocyte, Lymphocyte/Monocyte, and Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratios as Biomarkers in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 6474–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Hao, D.; Song, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Wang, Q.; Yu, X. Systemic inflammatory response index as an independent risk factor for ischemic stroke in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A retrospective study based on propensity score matching. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 3919–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercader-Salvans, J.; García-González, M.; Quevedo-Abeledo, J.C.; Quevedo-Rodríguez, A.; Romo-Cordero, A.; Ojeda-Bruno, S.; Gómez-Bernal, F.; López-Mejías, R.; Martín-González, C.; González-Gay, M.; et al. Blood Composite Scores in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Sierra, M.; Quevedo-Rodríguez, A.; Romo-Cordero, A.; González-Chretien, G.; Quevedo-Abeledo, J.C.; de Vera-González, A.; González-Delgado, A.; Martín-González, C.; González-Gay, M.; Ferraz-Amaro, I. Relationship of Blood Inflammatory Composite Markers with Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Life 2023, 13, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuno, H. Remarkable efficacy of tocilizumab for treating rheumatoid arthritis in patients with high platelet counts. Mod. Rheumatol. 2015, 25, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, R.M.; Davis, P.; Jayson, M.I. Thrombocytosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1976, 35, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukasik, Z.M.; Makowski, M.; Makowska, J.S. From blood coagulation to innate and adaptive immunity: The role of platelets in the physiology and pathology of autoimmune disorders. Rheumatol. Int. 2018, 38, 959–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargin, G.; Senturk, T.; Yavasoglu, I.; Kose, R. Relationship between neutrophil-lymphocyte, platelet-lymphocyte ratio and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis treated with rituximab. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 2122–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
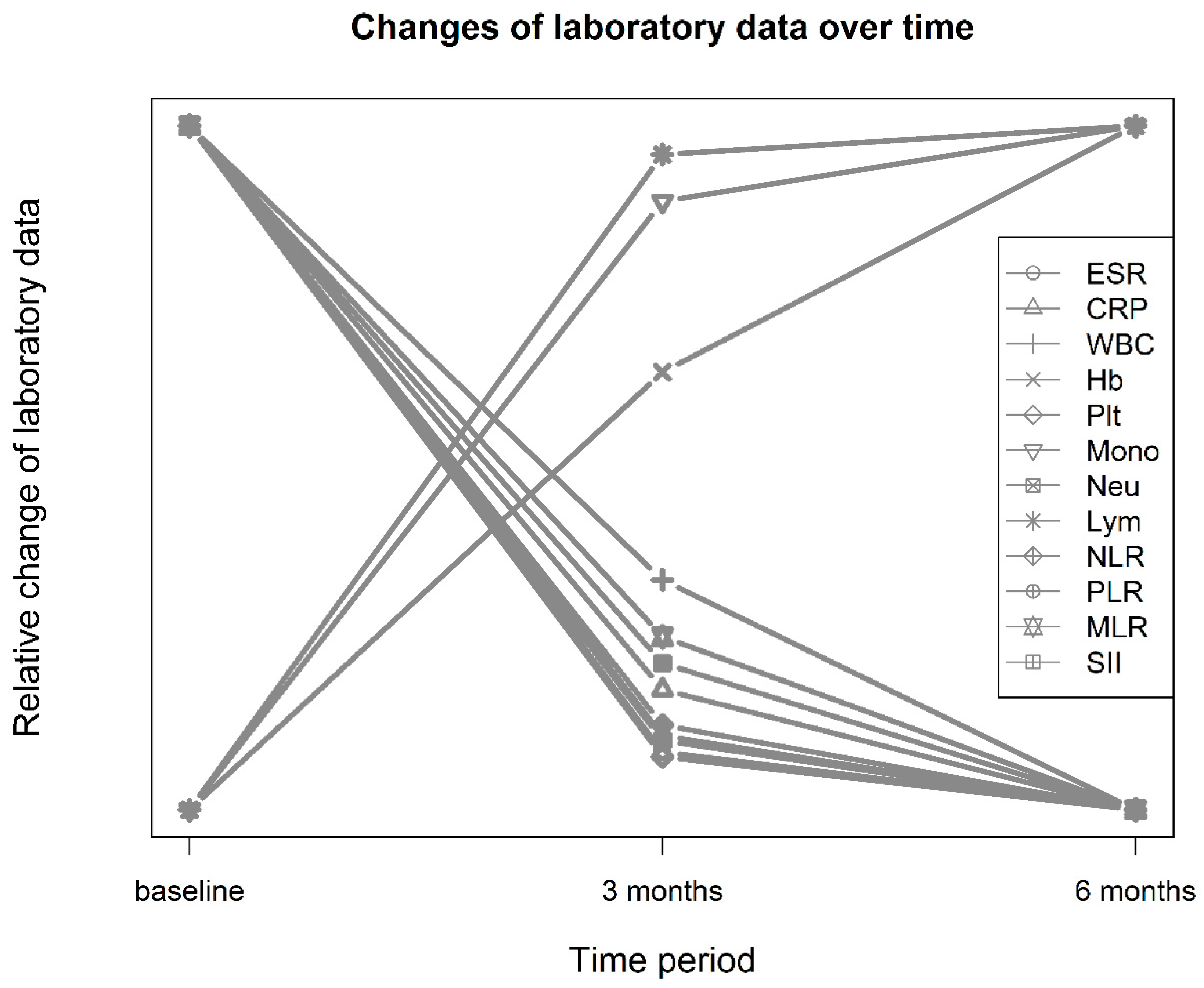
| Baseline a (N = 273) | 3 Months after b | 6 Months after c | F Value | p-Value ¶ | Cohen’s d * | η2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 57.2 ± 12.4 | ||||||
| Male: female | 71: 202 (26:74%) | ||||||
| Lab data | |||||||
| ESR (mm/h) | 45.9 ± 27.7 | 30.3 ± 24.1 | 28.5 ± 22.6 | 93.4 | <0.001 | 0.60 | 0.087 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 17.0 ± 22.7 | 7.74 ± 13.9 | 5.73 ± 10.8 | 50.1 | <0.001 | 0.49 | 0.08 |
| White blood cells (109/L) | 6.73 ± 2.28 | 6.46 ± 2.34 | 6.35 ± 2.17 | 4.0 | 0.019 | 0.12 | 0.004 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 118 ± 16.4 | 122 ± 15.8 | 124 ± 15.6 | 59.8 | <0.001 | −0.25 | 0.028 |
| Platelets (109/L) | 277.1 ± 87.1 | 249 ± 74.5 | 248 ± 73.8 | 37.5 | <0.001 | 0.35 | 0.028 |
| Monocytes (109/L) | 0.46 ± 0.20 | 0.462 ± 0.206 | 0.463 ± 0.199 | 0.4 | 0.691 | −0.01 | 0.000485 |
| Neutrophils (109/L) | 4.40 ± 1.99 | 3.90 ± 1.91 | 3.76 ± 1.87 | 14.4 | <0.001 | 0.26 | 0.019 |
| Lymphocytes (109/L) | 1.68 ± 0.63 | 1.90 ± 0.739 | 1.93 ± 0.688 | 26.5 | <0.001 | −0.32 | 0.027 |
| Hematological indices | |||||||
| NLR | 2.99 ± 1.83 | 2.33 ± 1.55 | 2.21 ± 1.47 | 26.8 | <0.001 | 0.39 | 0.042 |
| PLR | 187 ± 87.3 | 150 ± 76.0 | 146 ± 75.6 | 46.0 | <0.001 | 0.45 | 0.049 |
| MLR | 0.300 ± 0.144 | 0.273 ± 0.189 | 0.263 ± 0.140 | 5.5 | 0.006 | 0.16 | 0.008 |
| SII | 847 ± 615 | 600 ± 482 | 571 ± 493 | 33.9 | <0.001 | 0.45 | 0.05 |
| Good (N = 129) | Mild (N = 81) | Bad (N = 53) | p-Value * | η2 * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lab data | |||||
| ESR (mm/h) | 50.9 ± 29.4 | 46.4 ± 26.7 | 33.0 ± 21.8 | <0.001 ** | 0.0600 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 20.8 ± 24.5 | 14.8 ± 19.3 | 12.5 ± 23.6 | <0.001 ** | 0.0700 |
| WBC (109/L) | 6.91 ± 2.28 | 6.66 ± 2.51 | 6.43 ± 1.96 | 0.404 | 0.0070 |
| Hb (g/L) | 119 ± 15.2 | 115 ± 15.3 | 120 ± 19.2 | 0.135 | 0.0200 |
| PLT (109/L) | 298 ± 85.7 | 266 ± 86.3 | 234 ± 76.1 | <0.001 ** | 0.0900 |
| Monocyte (%) | 0.467 ± 0.20 | 0.443 ± 0.20 | 0.445 ± 0.18 | 0.524 | 0.0050 |
| Neutrophil (%) | 4.54 ± 1.95 | 4.44 ± 2.26 | 4.13 ± 1.76 | 0.405 | 0.0069 |
| Lymphocyte (%) | 1.71 ± 0.61 | 1.60 ± 0.57 | 1.69 ± 0.77 | 0.445 | 0.0062 |
| Hematological indices | |||||
| NLR | 2.91 ± 1.48 | 3.17 ± 2.16 | 3.05 ± 2.16 | 0.706 | 0.0058 |
| PLR | 196 ± 91.0 | 187 ± 87.8 | 164 ± 75.2 | 0.021 ** | 0.0300 |
| MLR | 0.30 ± 0.15 | 0.297 ± 0.14 | 0.297 ± 0.14 | 0.993 | 0.0001 |
| SII | 895 ± 603 | 866 ± 676 | 725 ± 571 | 0.023 ** | 0.0300 |
| Correlation | p-Value | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NLR | PLR | MLR | SII | NLR | PLR | MLR | SII | ||
| ESR | Baseline | 0.141 | 0.273 | 0.206 | 0.226 | 0.020 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 3 months | 0.211 | 0.250 | 0.177 | 0.227 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.004 | <0.001 | |
| 6 months | 0.160 | 0.170 | 0.134 | 0.179 | 0.0096 | 0.006 | 0.031 | 0.004 | |
| CRP | Baseline | 0.233 | 0.291 | 0.187 | 0.361 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 | <0.001 |
| 3 months | 0.373 | 0.207 | 0.250 | 0.394 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| 6 months | 0.280 | 0.062 | 0.187 | 0.313 | <0.001 | 0.318 | 0.003 | <0.001 | |
| Comparison of Correlation at Baseline with | NLR p-Value | PLR p-Value | MLR p-Value | SII p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESR | 3 months | 0.238 | 0.826 | 0.782 | 0.827 |
| 6 months | 0.706 | 0.073 | 0.328 | 0.509 | |
| CRP | 3 months | 0.037 | 0.310 | 0.329 | 0.537 |
| 6 months | 0.418 | 0.004 | 0.964 | 0.464 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Y.-J.; Su, K.-Y.; Shen, C.-L.; Wu, Y.-F. Correlation of Hematological Indices and Acute-Phase Reactants in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7611. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247611
Pan Y-J, Su K-Y, Shen C-L, Wu Y-F. Correlation of Hematological Indices and Acute-Phase Reactants in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(24):7611. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247611
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Yu-Jen, Kuei-Ying Su, Chih-Lung Shen, and Yi-Feng Wu. 2023. "Correlation of Hematological Indices and Acute-Phase Reactants in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 24: 7611. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247611
APA StylePan, Y.-J., Su, K.-Y., Shen, C.-L., & Wu, Y.-F. (2023). Correlation of Hematological Indices and Acute-Phase Reactants in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(24), 7611. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12247611