The Effect of Semaglutide on Blood Pressure in Patients without Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
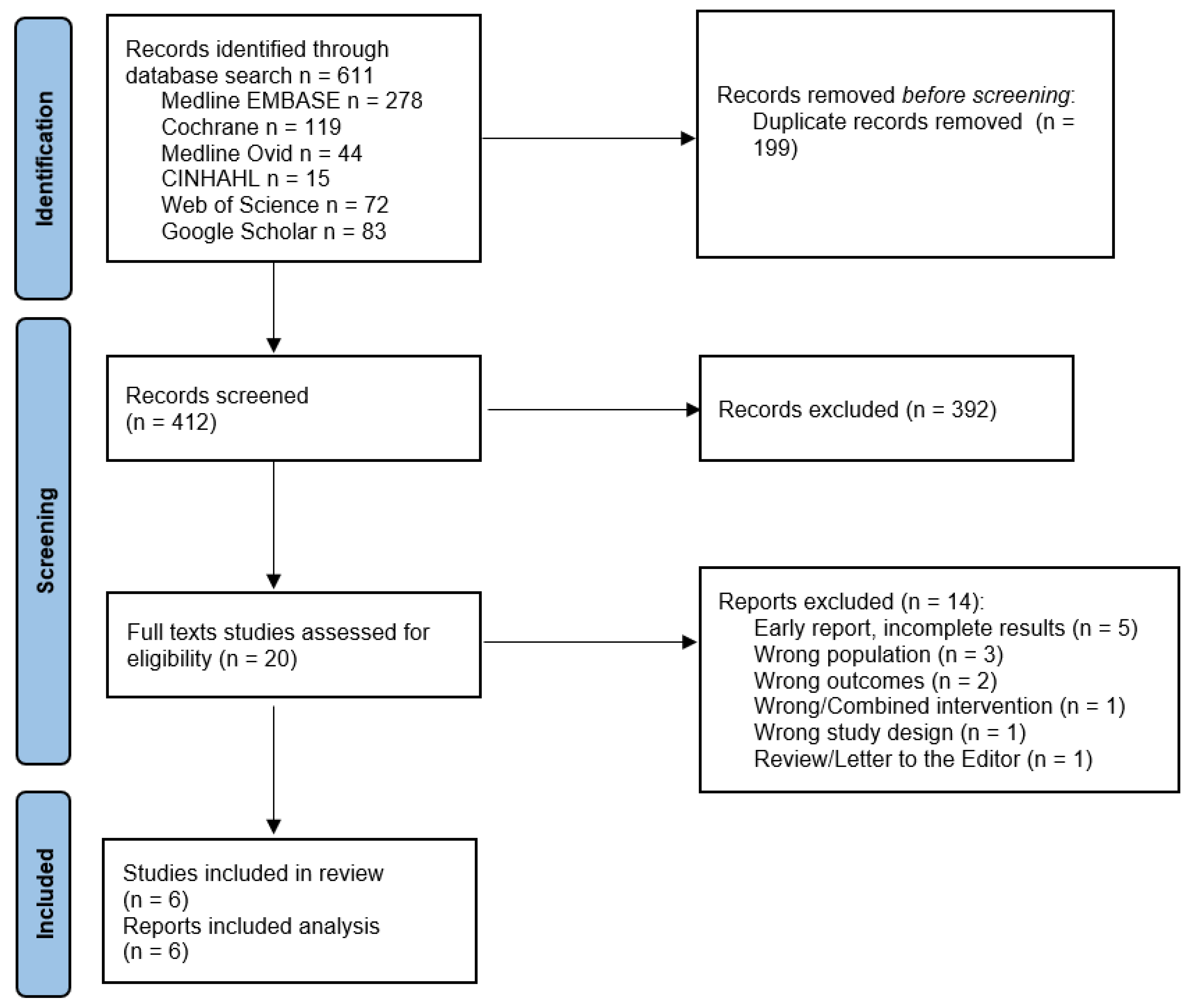
3.1. Flow and Characteristics of the Included Studies
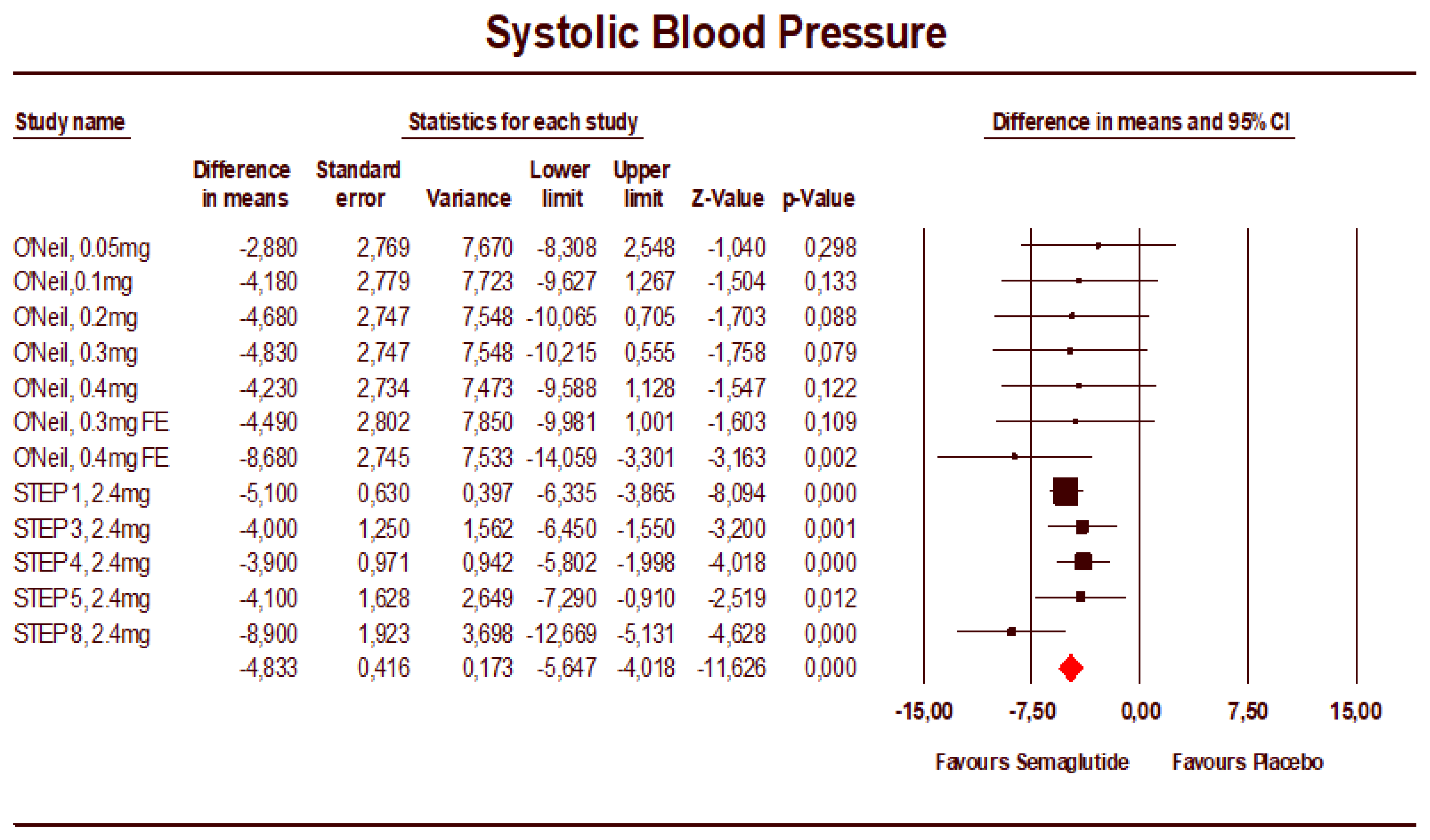
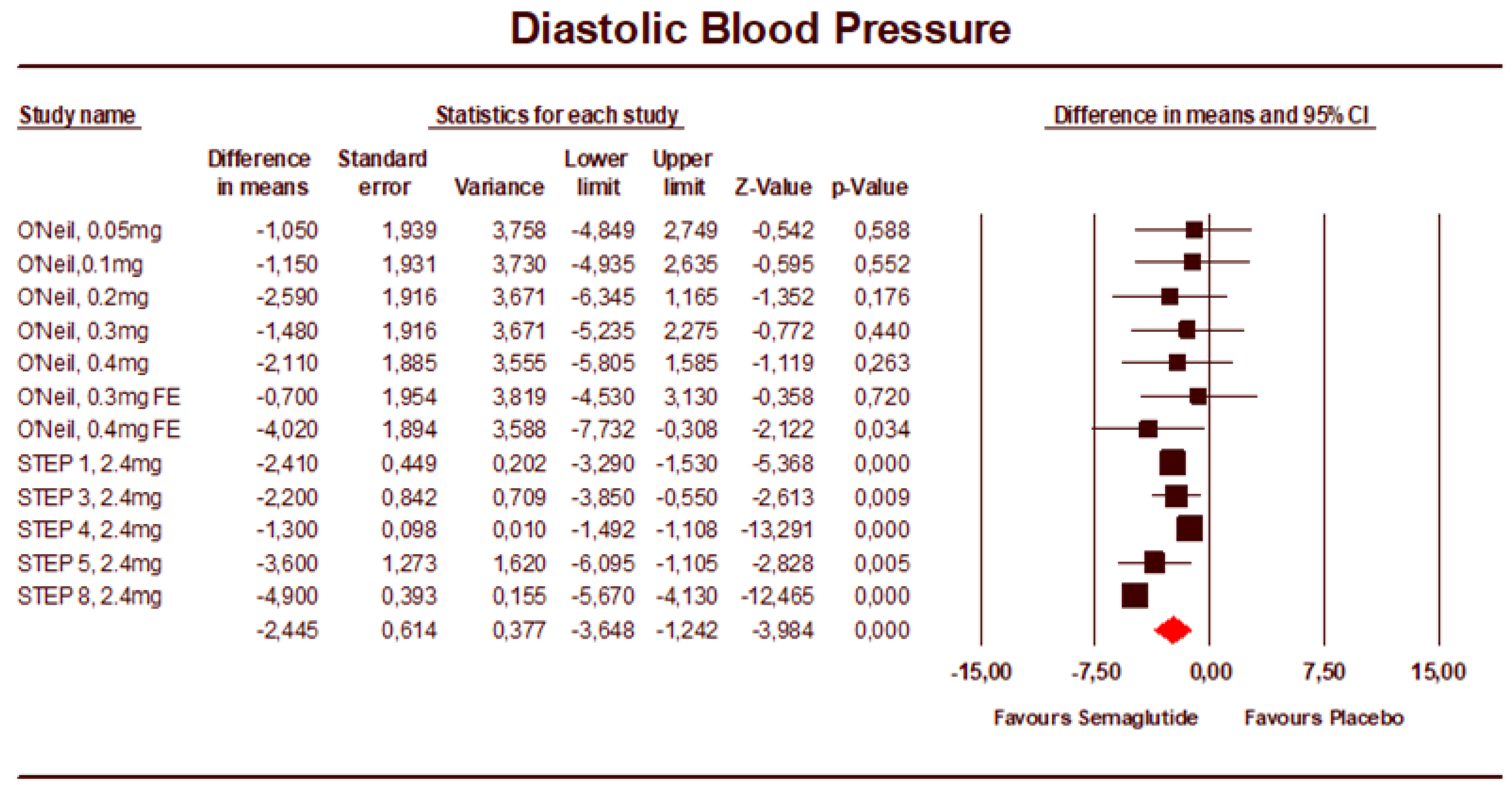
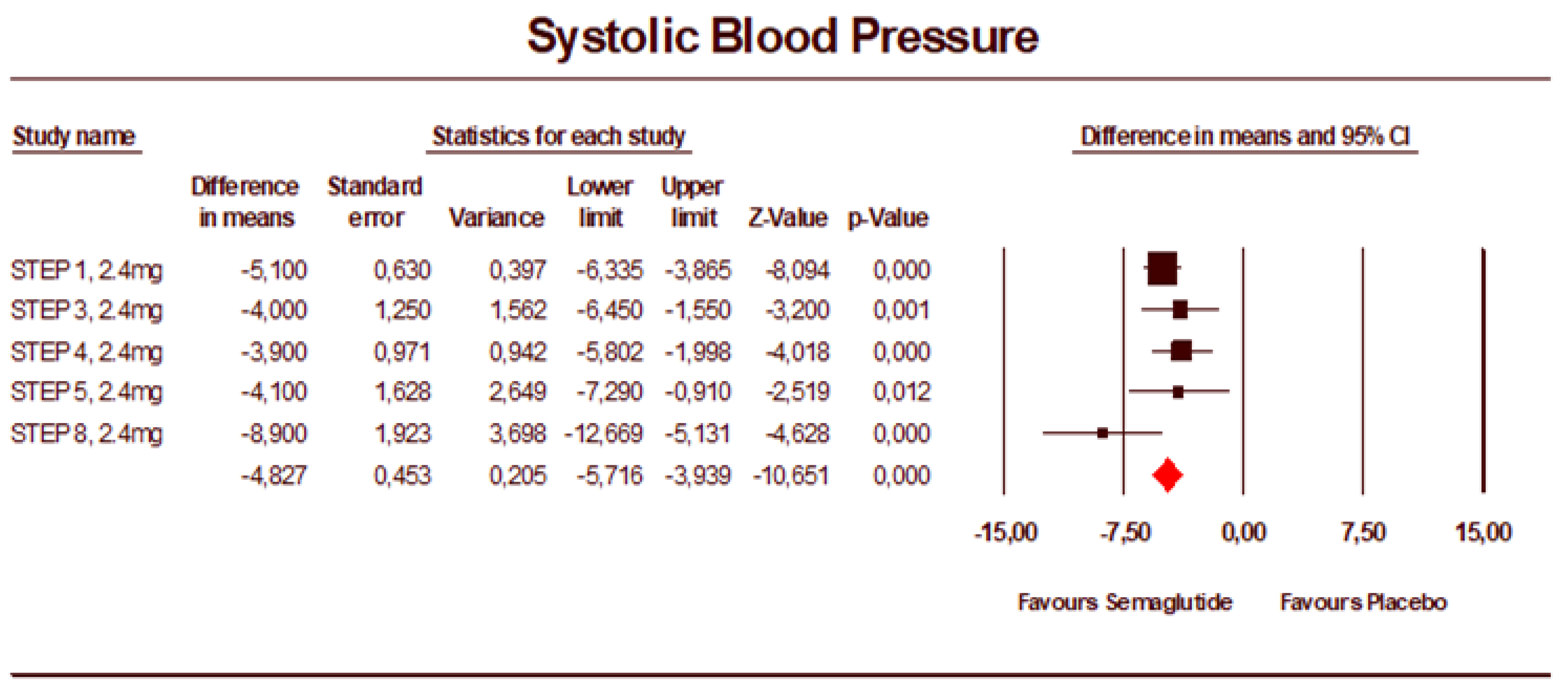
3.2. Meta-Analysis Results
3.3. Risk of Bias Assessment
3.4. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swinburn, B.A.; Kraak, V.I.; Allender, S.; Atkins, V.J.; Baker, P.I.; Bogard, J.R.; Brinsden, H.; Calvillo, A.; De Schutter, O.; Devarajan, R.; et al. The Global Syndemic of Obesity, Undernutrition, and Climate Change: The Lancet Commission report. Lancet 2019, 393, 791–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Must, A.; Spadano, J.; Coakley, E.H.; Field, A.E.; Colditz, G.; Dietz, W.H. The Disease Burden Associated With Overweight and Obesity. JAMA 1999, 282, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C.; Farnan, R.; Stinson, J.; Hall, M.; Hemeryck, L.; O’Connor, P.; Hennessy, M.; Barry, M. Referrals to, and characteristics of patients attending a specialist hypertension clinic. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2021, 36, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Moran, A.E. Trends in the Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment, and Control of Hypertension Among Young Adults in the United States, 1999 to 2014. Hypertension 2017, 70, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.E.; do Carmo, J.M.; da Silva, A.A.; Wang, Z.; Hall, M.E. Obesity-Induced Hypertension: Interaction of neurohumoral and renal mechanisms. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 991–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.E.; Cohen, J.B.; Ard, J.D.; Egan, B.M.; Hall, J.E.; Lavie, C.J.; Ma, J.; Ndumele, C.E.; Schauer, P.R.; Shimbo, D. Weight-Loss Strategies for Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2021, 78, e38–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, A.J.; West, N.P.; Cripps, A.W. Obesity, inflammation, and the gut microbiota. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neter, J.E.; Stam, B.E.; Kok, F.J.; Grobbee, D.E.; Geleijnse, J.M. Influence of Weight Reduction on Blood Pressure. Hypertension 2003, 42, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebenhofer, A.; Winterholer, S.; Jeitler, K.; Horvath, K.; Berghold, A.; Krenn, C.; Semlitsch, T. Long-term effects of weight-reducing drugs in people with hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2021, CD007654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.B.; Gadde, K.M. Weight Loss Medications in the Treatment of Obesity and Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2019, 21, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Batterham, R.L.; Calanna, S.; Davies, M.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Lingvay, I.; McGowan, B.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Tran, M.T.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadden, T.A.; Bailey, T.S.; Billings, L.K.; Davies, M.; Frias, J.P.; Koroleva, A.; Lingvay, I.; O’Neil, P.M.; Rubino, D.M.; Skovgaard, D.; et al. Effect of Subcutaneous Semaglutide vs Placebo as an Adjunct to Intensive Behavioral Therapy on Body Weight in Adults With Overweight or Obesity. JAMA 2021, 325, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubino, D.; Abrahamsson, N.; Davies, M.; Hesse, D.; Greenway, F.L.; Jensen, C.; Lingvay, I.; Mosenzon, O.; Rosenstock, J.; Rubio, M.A.; et al. Effect of Continued Weekly Subcutaneous Semaglutide vs Placebo on Weight Loss Maintenance in Adults With Overweight or Obesity. JAMA 2021, 325, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savović, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Green, S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neil, P.M.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; McGowan, B.; Mosenzon, O.; Pedersen, S.D.; Wharton, S.; Carson, C.G.; Jepsen, C.H.; Kabisch, M.; Wilding, J.P.H. Efficacy and safety of semaglutide compared with liraglutide and placebo for weight loss in patients with obesity: A randomised, double-blind, placebo and active controlled, dose-ranging, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, W.T.; Batterham, R.; Bhatta, M.; Buscemi, S.; Christensen, L.; Frias, J.; Jódar, E.; Kandler, K.; Rigas, G.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Two-year effect of semaglutide 2.4 mg vs placebo in adults with overweight or obesity: STEP 5. Obesity 2021, 29, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Rubino, D.M.; Greenway, F.L.; Khalid, U.; O’Neil, P.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Sørrig, R.; Wadden, T.A.; Wizert, A.; Garvey, W.T.; STEP 8 Investigators; et al. Effect of Weekly Subcutaneous Semaglutide vs Daily Liraglutide on Body Weight in Adults With Overweight or Obesity Without Diabetes. JAMA 2022, 327, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C.; Ali, O.; Farnan, R.; Hall, M.; Stinson, J.; O’Connor, P.; Hennessy, M.; Barry, M. Is it time to reconsider the treatment paradigm for obese patients with hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2021, 36, 482–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakos, C.I.; Papadopoulos, D.P.; Sanidas, E.A.; Markou, M.I.; Hatziagelaki, E.E.; Grassos, C.A.; Velliou, M.L.; Barbetseas, J.D. Blood Pressure-Lowering Effect of Newer Antihyperglycemic Agents (SGLT-2 Inhibitors, GLP-1 Receptor Agonists, and DPP-4 Inhibitors). Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2021, 21, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Wu, H.; Hu, N.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Xiao, F.; Wang, T.; Jiang, H.; Xu, S.; Huang, B.; et al. Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on body weight in adults with obesity without diabetes mellitus—a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Obes. Rev. 2022, 23, e13435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, P.; Zeng, H.; Huang, M.; Fu, W.; Chen, Z. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity: A meta-analysis. Endocrine 2022, 75, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semlitsch, T.; Krenn, C.; Jeitler, K.; Berghold, A.; Horvath, K.; Siebenhofer, A. Long-term effects of weight-reducing diets in people with hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2021, CD008274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, F.M.; Svetkey, L.P.; Vollmer, W.M.; Appel, L.J.; Bray, G.A.; Harsha, D.; Obarzanek, E.; Conlin, P.R.; Miller, E.R.; Simons-Morton, D.G.; et al. Effects on Blood Pressure of Reduced Dietary Sodium and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) Diet. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berndt, J.; Ooi, S.; Pak, S. What Is the Mechanism Driving the Reduction of Cardiovascular Events from Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists?—A Mini Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buse, J.B.; Bain, S.C.; Mann, J.F.; Nauck, M.A.; Nissen, S.E.; Pocock, S.; Poulter, N.R.; Pratley, R.E.; Linder, M.; Fries, T.M.; et al. Cardiovascular Risk Reduction With Liraglutide: An Exploratory Mediation Analysis of the LEADER Trial. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1546–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanami, D.; Takashi, Y. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Clinical Outcomes to Mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Ahmad, N.N.; Wharton, S.; Connery, L.; Alves, B.; Kiyosue, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author, Year | Study | Design | Main Inclusion Criteria | Follow-Up | Study Group | Enrolled Individuals (N) | Men |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O’Neil PM, 2018 [18] | Randomized, double-blind, placebo and active-controlled, dose-ranging, phase 2 trial | Adults without diabetes and with a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or greater | 52 weeks | Semaglutide 0.05 mg | 103 | 36 (35%) | |
| Semaglutide 0.1 mg | 102 | 36 (35%) | |||||
| Semaglutide 0.2 mg | 103 | 37 (36%) | |||||
| Semaglutide 0.3 mg | 103 | 37 (36%) | |||||
| Semaglutide 0.4 mg | 102 | 36 (35%) | |||||
| Semaglutide 0.3 mg FE | 102 | 36 (35%) | |||||
| Semaglutide 0.4 mg FE | 103 | 36 (35%) | |||||
| Placebo | 136 | 48 (35%) | |||||
| Wilding JPH, 2021 [12] | STEP-1 | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial | Adults without diabetes and with a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or greater OR a BMI of 27 kg/m2 or greater with one or more treated or untreated weight-related coexisting conditions | 68 weeks | Semaglutide 2.4 mg | 1306 | 351 (26.9%) |
| Placebo | 655 | 157 (24%) | |||||
| Wadden TA, 2021 [13] | STEP-3 | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial | Adults without diabetes and with a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or greater OR a BMI of 27 kg/m2 or greater with at least one comorbidity | 68 weeks | Semaglutide 2.4 mg | 407 | 92 (22.6%) |
| Placebo | 204 | 24 (11.8%) | |||||
| Rubino D, 2021 [14] | STEP-4 | Randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3a trial | Adults without diabetes and with a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or greater OR a BMI of 27 kg/m2 or greater with at least one comorbidity | 48 weeks | Semaglutide 2.4 mg | 535 | 106 (19.8%) |
| Placebo | 368 | 63 (23.5%) | |||||
| Garvey WT, 2021 [19] | STEP-5 | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial | Adults without diabetes and with a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or greater OR a BMI of 27 kg/m2 or greater with at least one comorbidity | 104 weeks | Semaglutide 2.4 mg | 152 | 29 (19.1%) |
| Placebo | 152 | 39 (25.7%) | |||||
| Rubino DM, 2022 [20] | STEP-8 | Randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3b trial | Adults without diabetes and with a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or greater OR a BMI of 27 kg/m2 or greater with at least one comorbidity | 68 weeks | Semaglutide 2.4 mg | 126 | 24 (19%) |
| Placebo | 85 | 19 (22.4%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kennedy, C.; Hayes, P.; Salama, S.; Hennessy, M.; Fogacci, F. The Effect of Semaglutide on Blood Pressure in Patients without Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030772
Kennedy C, Hayes P, Salama S, Hennessy M, Fogacci F. The Effect of Semaglutide on Blood Pressure in Patients without Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(3):772. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030772
Chicago/Turabian StyleKennedy, Cormac, Peter Hayes, Sulafa Salama, Martina Hennessy, and Federica Fogacci. 2023. "The Effect of Semaglutide on Blood Pressure in Patients without Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 3: 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030772
APA StyleKennedy, C., Hayes, P., Salama, S., Hennessy, M., & Fogacci, F. (2023). The Effect of Semaglutide on Blood Pressure in Patients without Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(3), 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030772







