Validation of Physical Activity Correlates Questionnaire from Social Ecological Model in College Students
Abstract
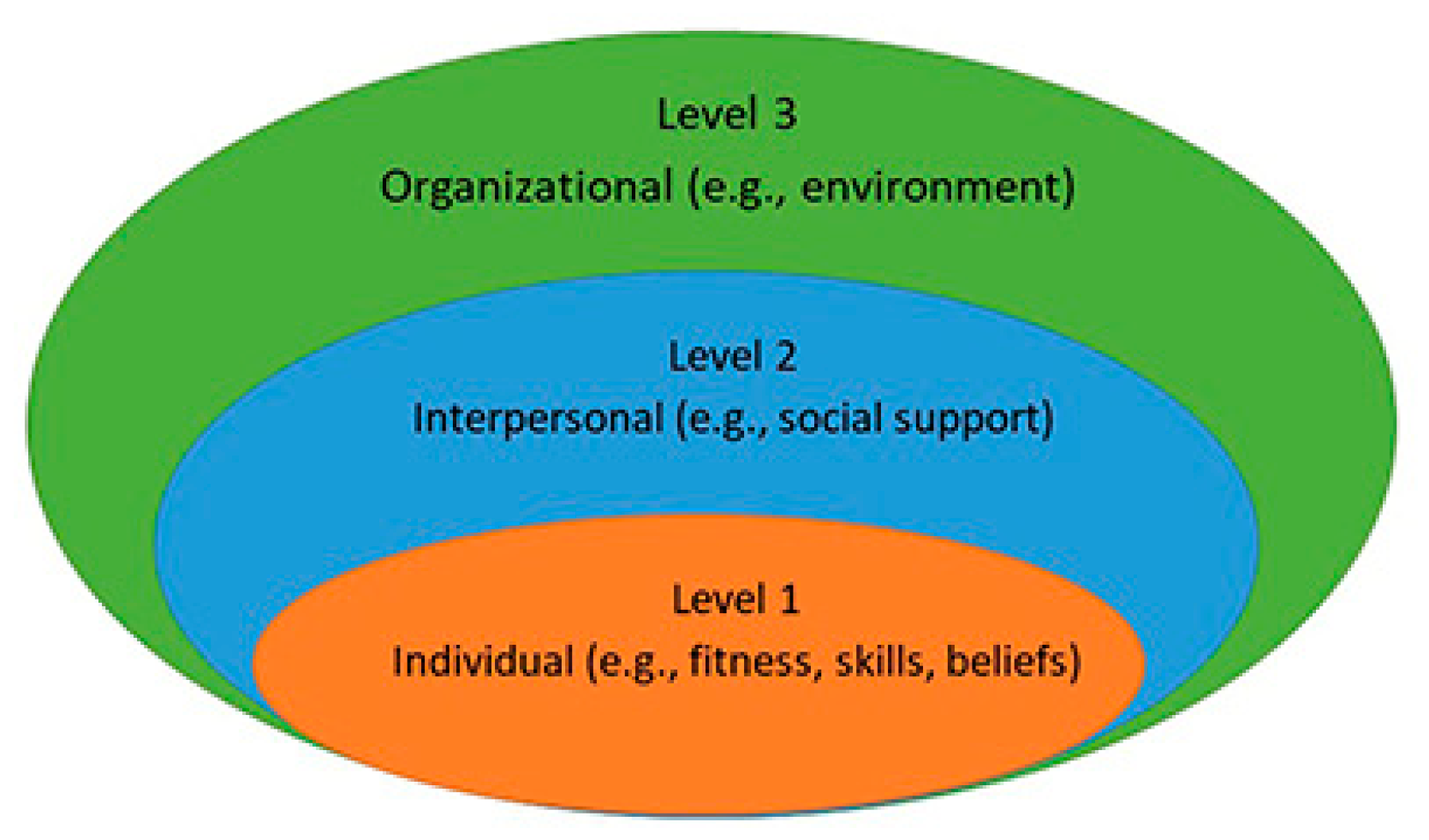
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Questionnaire Development
2.3. Content Validation
2.4. Construct Validation
2.5. Data Collection
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Questionnaire Development and Content Validation
3.2. Construct Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pinto, A.J.; Roschel, H.; de Sá Pinto, A.L.; Lima, F.R.; Pereira, R.M.R.; Silva, C.A.; Bonfá, E.; Gualano, B. Physical inactivity and sedentary behavior: Overlooked risk factors in autoimmune rheumatic diseases? Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American College Health Association. American College Health Association-National College Health Assessment III: Reference Group Data Report, Fall 2021; American College Health Association: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.Y. Investigation on college students’ sports attitude and behavior. J. Tianjin Univ. Sport 2003, 3, 89–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.C. Behavioral and Sociocultural Influences on Physical Activity among Asian-American Youth. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, T.F.; Liu, J.W.; Li, D.M. Research on spare-time physical training behavior of university students in Jiangxi province and influential factors. J. Shanghai Univ. Sport 2006, 3, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.S. Study on the Effects of College Sports Environment on the Sport Behavior of College Students in Guangzhou. Master’s Thesis, Guangzhou University, Guangzhou, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, K.; Liu, W.; Xiong, S.; Ken, L.; Zeng, N.; Peng, Q.; Yan, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Lei, M.; et al. Associations between self-determined motivation, accelerometer-determined physical activity, and quality of life in Chinese college students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.P. The relationship between family intimacy, physical self-esteem and college students’ physical activity at home. J. Tianjin Inst. Phys. Educ. 2021, 563–568, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.C.; Gong, Z.L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.T.; Zhou, M.Q.; Li, R.Q.; Zhuo, Q. The relationship between physical activity, sedentary time and waist circumference and body fat rate of college students—An isochronous replacement model. Health Res. 2022, 51, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.H.; Chen, J.C. A survey on the current status of physical activity of college freshmen: Taking Central China Normal University as an example. Hubei Sport. Sci. Technol. 2020, 39, 554–557. [Google Scholar]
- van Sluijs, E.M.F.; Ekelund, U.; Crochemore-Silva, I.; Guthold, R.; Ha, A.; Lubans, D.; Oyeymi, A.L.; Ding, D.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Physical activity behaviours in adolescence: Current evidence and opportunities for intervention. Lancet 2021, 398, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Every Move Counts towards Better Health—Says WHO. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/25-11-2020-every-move-counts-towards-better-health-says-who (accessed on 25 November 2020).
- Guo, Q.; Wang, X.Z.; Jiang, J.B. Physical activity and sedentary behavior of children and adolescents in my country Research on pattern characteristics. Sport. Sci. 2017, 37, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Cao, Z.B. Results from the China 2018 Report Card on physical activity for children and youth. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2019, 17, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yuan, Q.; Zeng, N.; Tao, K.; Peng, Q.; Gao, Z. Relationships among college students’ sedentary behavior, sleep quality, and body mass index. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.Z.; A, Y.G.; Chen, P.Y.; Wang, Z.Y. Correlates of Physical Activity of Children and Adolescents: A System Review of Studies in Recent 25 Years. China Sport Sci. Technol. 2022, 58, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.L.; Gao, Y.L.; Fu, D.J.; Zu, S.M.; Tan, R.L.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of the current situation and influencing factors of physical activity of college students in a medical college. Chin. J. Sch. Health 2014, 35, 1136–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Li, Z.H.; Li, Y.M.; Tang, X.Q.; Zhu, X.X.; Liu, J. Research on the physical activity level and influencing factors of college students based on GT9X measurement in the post-epidemic era. In Proceedings of the 12th National A Compilation of Abstracts of Sports Science Conference Papers—Poster Exchange, Online, 13–15 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Oyibo, K.; Orji, R.; Vassileva, J. Developing culturally relevant design guidelines for encouraging physical activity: A social cognitive theory perspective. J. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2018, 2, 319–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How Many College Students in China. 2022. Available online: https://zhidao.baidu.com/question/561499838767480652.html (accessed on 29 July 2022).
- Humpel, N.; Owen, N.; Leslie, E. Environmental factors associated with adults’ participation in physical activity: A review. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2002, 22, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallis, J.F.; Owen, N.; Fisher, E.B. Ecological models of health behavior. In Health Behavior and Health Education: Theory, Research, and Practice; Glanz, K., Rimer, B., Viswanath, K., Eds.; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 465–485. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Solmon, M. Integrating self-determination theory with the social ecological model to understand students’ physical activity behaviors. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2013, 6, 54–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenson, K.R.; Birnbaum, A.S.; Bedimo-Rung, A.L.; Sallis, J.F.; Voorhees, C.C.; Ring, K.; Elder, J.P. Girls’ perception of physical environmental factors and transportation: Reliability and association with physical activity and active transport to school. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2006, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleury, J.; Lee, S.M. The social ecological model and physical activity in African American women. Am. J. Community Psychol. 2006, 37, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Podlog, L.; Harrison, L. College students’ goal orientations, situational motivation and effort/persistence in physical activity. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2012, 31, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Essiet, I.A.; Baharom, A.; Shahar, H.K.; Uzochukwu, B. Application of the socio-ecological model to predict physical activity behaviour among Nigerian University students. Pan. Afr. Med. J. 2017, 26, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Dunn, J.; Morrow, J.; Greenleaf, C. Ecological analysis of college women’s physical activity and health-related quality of life. Women Health 2018, 58, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, C.; Kellou, N.; Dugas, J.; Platat, C.; Copin, N.; Schweitzer, B.; Hausser, F.; Bergouignan, A.; Lefai, E.; Blanc, S. A socio-ecological approach promoting physical activity and limiting sedentary behavior in adolescence showed weight benefits maintained 2.5 years after intervention cessation. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luque-Vara, T.; Linares-Manrique, M.; Fernández-Gómez, E.; Martín-Salvador, A.; Sánchez-Ojeda, M.A.; Enrique-Mirón, C. Content validation of an Instrument for the Assessment of School Teachers’ Levels of Knowledge of Diabetes through expert judgment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronbach, L.J.; Meehl, P.E. Construct validity in psychological tests. Psychol. Bull. 1955, 52, 281–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westen, D.; Rosenthal, R. Quantifying construct validity: Two simple measures. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2003, 84, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagozzi, R.P.; Tybout, A.M.; Craig, C.S.; Sternthal, B. The Construct Validity of the Tripartite Classification of Attitudes. SAGE Publ. 1979, 16, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Cattell, R.B. The scree test for the number of factors. Multivar. Behav. Res. 1966, 1, 245–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, H.F. Directional statistical decisions. Psychol. Rev. 1960, 67, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollen, K.A.; Stine, R. Bootstrapping Goodness of Fit Measures in Structural Equation Model. Sociol. Methods Res. 1992, 21, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E.; Tatham, R.L. Multivariate Data Analysis; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bagozzi, R.P.; Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Canonical correlation analysis as a special case of a structural relations model. Multivar. Behav. Res. 1981, 16, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lance, C.E.; Vandenberg, R.J.; Self, R.M. Latent growth models of individual change: The case of newcomer adjustment. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 2000, 83, 107–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, G.W.; Rensvold, R.B. Evaluating goodness-of-fit indexes for testing measurement invariance. Struct. Equ. Model. 2002, 9, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyland, P.; Shevlin, M.; Adamson, G.; Boduszek, D. The role of trauma-specific irrational beliefs and sociodemographic risk factors in posttraumatic stress responses. J. Ration.-Emot. Cogn.-Behav. Ther. 2013, 31, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raykov, T. Satisfying a simplex structure is simpler than it should be: A latent curve analysis revisit. Multivariate Behav Res. 1998, 33, 343–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.C.; Zhang, S.L.; Luo, J.; Zhou, C.L.; Ping, J.; Zhou, L.; Lv, W.G.; Tan, Y.; Yin, H.C.; Jin, Y.H.; et al. Research Report on the Status-quo and Restrictive Factors on the Extracurricular Physical Exercise of the Teenagers in China. China Sport Sci. 2012, 32, 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Si, Q.; Wang, L.Z.; Kim, J.S.; Zhu, M.L. Research on Determinants of Adolescents in-school Extracurriculum Physical Activities Based on Inter personal and Organizational Level Factors of Social Ecological Mode. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2017, 259–264, 279. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.R. Research on the effectiveness and improvement strategy of college students’ Mixing Sports into Life System. J. Sport. Sci. 2018, 39, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, D.J.; Schneider, M.; Dickerson, S.S. Environmental resources moderate the relationship between social support and school sports participation among adolescents: A cross-sectional analysis. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanchard, C.; Fisher, J.; Sparling, P.; Nehl, E.; Rhodes, R.; Courneya, K.; Baker, F. Understanding physical activity behavior in African American and Caucasian college students: An application of the theory of planned behavior. J. Am. Coll. Health 2008, 56, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Rosenzweig, A. Exercise and cardiovascular protection: Update and future. J. Sport Health Sci. 2021, 10, 607–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzatvar, Y.; Izquierdo, M.; Núñez, J.; Calatayud, J.; Ramírez-Vélez, R.; García-Hermoso, A. Cardiorespiratory fitness measured with cardiopulmonary exercise testing and mortality in patients with cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Sport Health Sci. 2021, 10, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, M.; Yang, J.; Bao, M.; Chen, T.; Cai, R.; Zhang, N.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Wu, X.; Zhang, B.; et al. The relationships between step count and all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events: A dose-response meta-analysis. J. Sport Health Sci. 2021, 10, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, M. What’s new in the 2020 World Health Organization Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior? J. Sport Health Sci. 2021, 10, 288–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesinovic, J.; Jansons, P.; Zengin, A.; de Courten, B.; Rodriguez, A.J.; Daly, R.M.; Ebeling, P.R.; Scott, D. Exercise attenuates bone mineral density loss during diet-induced weight loss in adults with overweight and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Sport Health Sci. 2021, 10, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mañas, A.; Del Pozo Cruz, B.; Ekelund, U.; Losa Reyna, J.; Rodríguez Gómez, I.; Carnicero Carreño, J.A.; Rodríguez Mañas, L.; García García, F.J.; Ara, I. Association of accelerometer-derived step volume and intensity with hospitalizations and mortality in older adults: A prospective cohort study. J. Sport Health Sci. 2022, 11, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, D.J.; Pope, Z.C.; Zeng, N.; Lee, J.; Gao, Z. Comparison of college students’ energy expenditure, physical activity, and enjoyment during exergaming and traditional exercise. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factors | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| Interest | ||||||
| 1 I think physical exercise is fun (int1) | 0.70 | |||||
| 24 I feel very happy doing physical exercises (int2) | 0.76 | |||||
| 31 I think physical exercise can make me happy (int3) | 0.69 | |||||
| 5 I think physical exercise can promote my interaction with other people (int4) | 0.52 | |||||
| 10 I feel physical exercise makes me very energetic (int5) | 0.68 | |||||
| Social Support | ||||||
| 3 My classmates and friends often do physical exercises (soc1) | 0.75 | |||||
| 11 When I am with my classmates and friends, my classmates or friends often do physical exercises with me (soc2) | 0.69 | |||||
| 13 My classmates and friends often discuss topics related to physical exercise activities with me (soc3) | 0.68 | |||||
| 22 My classmates and friends often encourage me to keep exercising (soc4) | 0.60 | |||||
| Media | ||||||
| 2 Publicity on physical exercise in social media affects my physical exercise (med1) | 0.57 | |||||
| 25 Publicity about physical exercise on school website, radio station, campus slogan, etc. promotes me to exercise (med2) | 0.70 | |||||
| 32 The promotion of physical exercise on social network platforms such as WeChat, Weibo, and QQ promotes me to exercise (med3) | 0.59 | |||||
| Facilities | ||||||
| 9 It doesn’t take long to reach my school’s sports facilities (fac1) | 0.45 | |||||
| 15 The school sports venues and facilities can meet my needs for physical exercise (fac2) | 0.56 | |||||
| 26 Sports facilities of our school include indoor stadiums, outdoor stadiums, swimming pools/halls, tennis courts, etc. (fac3) | 0.57 | |||||
| 30 I have convenient transportation to school sports facilities (fac4) | 0.77 | |||||
| Traditional culture | ||||||
| 16 In order to study, I hardly have time for physical exercise (tra2) | 0.52 | |||||
| 19 I think people who exercise regularly have relatively well-developed limbs and simple minds (tra3) | 0.73 | |||||
| 21 I think learning is more important than physical exercise (tra4) | 0.45 | |||||
| Environment | ||||||
| 6 I don’t do physical exercises if it’s too cold or too hot (env1) | 0.46 | |||||
| 20 I don’t do physical exercises in severe weather such as wind, rain and snow (env4) | 0.69 | |||||
| 27 I don’t do physical exercises if the air quality is not good (env6) | 0.62 | |||||
| Items | Factors | Standardized Factor Loadings | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 I think physical exercise is fun (int1) | <--- | Interest | 0.70 |
| 24 I feel very happy doing physical exercises (int2) | <--- | Interest | 0.76 |
| 31 I think physical exercise can make me happy (int3) | <--- | Interest | 0.80 |
| 5 I think physical exercise can promote my interaction with other people (int4) | <--- | Interest | 0.64 |
| 10 I feel physical exercise makes me very energetic (int5) | <--- | Interest | 0.71 |
| 3 My classmates and friends often do physical exercises (soc1) | <--- | Social support | 0.71 |
| 11 When I am with my classmates and friends, my classmates or friends often do physical exercises with me (soc2) | <--- | Social support | 0.78 |
| 13 My classmates and friends often discuss topics related to physical exercise activities with me (soc3) | <--- | Social support | 0.79 |
| 22 My classmates and friends often encourage me to keep exercising (soc4) | <--- | Social support | 0.62 |
| 2 Publicity on physical exercise in social media affects my physical exercise (med1) | <--- | Media | 0.65 |
| 25 Publicity about physical exercise on school website, radio station, campus slogan, etc. promotes me to exercise (med2) | <--- | Media | 0.68 |
| 32 The promotion of physical exercise on social network platforms such as WeChat, Weibo, and QQ promotes me to exercise (med3) | <--- | Media | 0.70 |
| 9 It doesn’t take long to reach my school’s sports facilities (fac1) | <--- | Facilities | 0.49 |
| 15 The school sports venues and facilities can meet my needs for physical exercise (fac2) | <--- | Facilities | 0.67 |
| 26 Sports facilities of our school include indoor stadiums, outdoor stadiums, swimming pools/halls, tennis courts, etc. (fac3) | <--- | Facilities | 0.54 |
| 30 I have convenient transportation to school sports facilities (fac4) | <--- | Facilities | 0.66 |
| 16 In order to study, I hardly have time for physical exercise (tra2) | <--- | Traditional culture | 0.67 |
| 19 I think people who exercise regularly have relatively well-developed limbs and simple minds (tra3) | <--- | Traditional culture | 0.52 |
| 21 I think learning is more important than physical exercise (tra4) | <--- | Traditional culture | 0.52 |
| 6 I don’t do physical exercises if it’s too cold or too hot (env1) | <--- | Environment | 0.60 |
| 20 I don’t do physical exercises in severe weather such as wind, rain and snow (env4) | <--- | Environment | 0.75 |
| 27 I don’t do physical exercises if the air quality is not good (env6) | <--- | Environment | 0.55 |
| Environment | Traditional Culture | Facilities | Media | Social Support | Interest | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environment | 0.63 | |||||
| Traditional culture | 0.34 | 0.57 | ||||
| Facilities | 0.09 | −0.35 | 0.59 | |||
| Media | −0.13 | −0.16 | 0.47 | 0.68 | ||
| Social support | −0.30 | −0.20 | 0.44 | 0.72 | 0.73 | |
| Interest | −0.17 | −0.36 | 0.56 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.72 |
| X2/df | CFI | RMSEA | ΔCFI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Invariance across gender | ||||
| Configural level | 3.07 | 0.905 | 0.041 | |
| Full metric level | 3.02 | 0.903 | 0.040 | 0.002 |
| Full scalar level | 3.49 | 0.874 | 0.045 | 0.029 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, M.; Sun, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Adams, K.; Gao, Z. Validation of Physical Activity Correlates Questionnaire from Social Ecological Model in College Students. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030777
Huang M, Sun H, Chen H, Zhang Y, Adams K, Gao Z. Validation of Physical Activity Correlates Questionnaire from Social Ecological Model in College Students. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(3):777. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030777
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Meirong, Haichun Sun, Han Chen, Yanping Zhang, Kaitlyn Adams, and Zan Gao. 2023. "Validation of Physical Activity Correlates Questionnaire from Social Ecological Model in College Students" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 3: 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030777
APA StyleHuang, M., Sun, H., Chen, H., Zhang, Y., Adams, K., & Gao, Z. (2023). Validation of Physical Activity Correlates Questionnaire from Social Ecological Model in College Students. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(3), 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030777






