Acute Localized Exanthematous Pustulosis (ALEP) Caused by Topical Application of Minoxidil
Abstract
1. Introduction
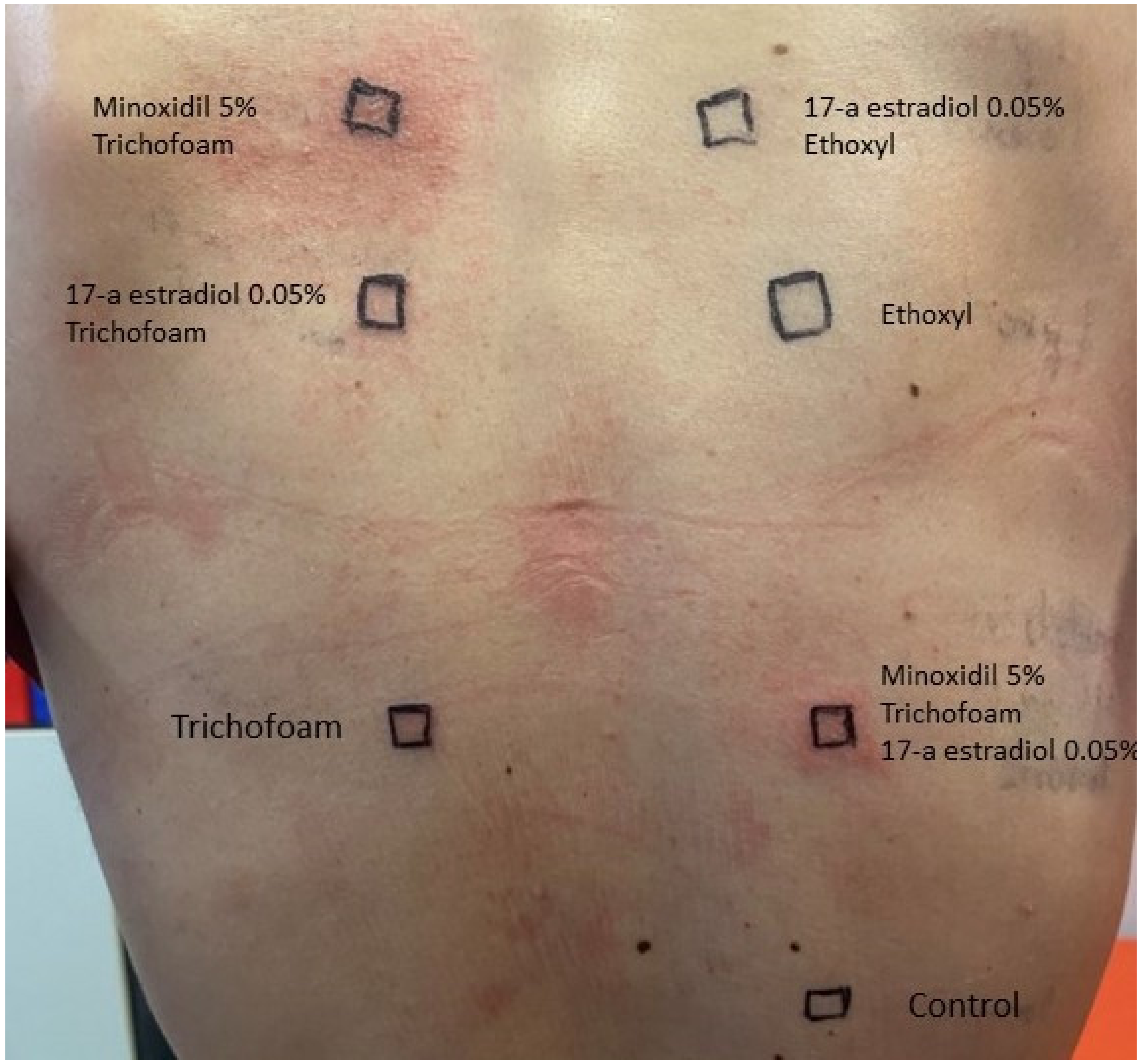
2. Case Description
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Safa, I.; Ines, L.; Noureddine, L.; Meriem, J.; Manel, N.; Belhajali, H.; Faten, Z.; Zili, J. Acute localized exanthematous pustulosis: Clinical features, pathophysiology, and therapy. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e15087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, A.; Baldo, A.; De Fata Salvatores, G.; Desiato, V.; Ayala, F.; Donadio, C. Acute Localized Exanthematous Pustulosis (ALEP): Review of Literature with Report of Case Caused by Amoxicillin-Clavulanic Acid. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 7, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumi, R.; Yoshida, Y.; Adachi, K.; Nanba, E.; Yamamoto, O. Acute localized exanthematous pustulosis caused by a herbal medicine, dai-kenchu-to. Contact Dermat. 2018, 79, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbayrak, A.; Yazar, C.; Alev Deresoy, F.; Sencan, M.; Yildiz Seckin, H.; Kutlu, O. Acute localized exanthematous pustulosis because of cefixime in a child: Case report and review of pediatric cases. Int. J. Dermatol. 2022, 61, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prange, B.; Marini, A.; Kalke, A.; Hodzic-Avdagic, N.; Ruzicka, T.; Hengge, U.R. Acute localized exanthematous pustulosis (ALEP). J. Dtschen Dermatol. Ges. 2005, 3, 210–212. [Google Scholar]
- Sidoroff, A.; Halevy, S.; Bavinck, J.N.; Vaillant, L.; Roujeau, J.C. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)—A clinical reaction pattern. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2001, 28, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, E.N.C.; Perkins, W. Acute localised exanthematous pustulosis: Case report, review of the literature and proposed diagnostic criteria. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2018, 59, 226–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidoroff, A.; Dunant, A.; Viboud, C.; Halevy, S.; Bavinck, J.N.; Naldi, L.; Mockenhaupt, M.; Fagot, J.P.; Roujeau, J.C. Risk factors for acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)-results of a multinational case-control study (EuroSCAR). Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 157, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, S.; Modi, M.; Dhawan, V. Acute localized exanthematous pustulosis (ALEP) caused by Ibuprofen. A case report. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 47, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osché, M.; Gusdorf, L.; Cribier, B.; Scrivener, J.N. Acute localized exanthematous pustulosis following heparin calcium injections. Ann. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 147, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.P.; Yang, C.S.; Shen, J.L.; Chen, Y.J. Sorafenib-induced acute localized exanthematous pustulosis in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165, 443–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tresch, S.; Cozzio, A.; Kamarashev, J.; Harr, T.; Schmid-Grendelmeier, P.; French, L.E.; Feldmeyer, L. T cell-mediated acute localized exanthematous pustulosis caused by finasteride. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Torrijos, E.; Cortina de la Calle, M.P.; Méndez Díaz, Y.; Moreno Lozano, L.; Extremera Ortega, A.; Galindo Bonilla, P.A.; Alfaya Arias, T.; García Rodríguez, R. Acute Localized Exanthematous Pustulosis Due to Bemiparin. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 27, 328–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senilă, S.; Seicean, A.; Fechete, O.; Grad, A.; Ungureanu, L. Infliximab-induced acne and acute localized exanthematous pustulosis: Case report. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betto, P.; Germi, L.; Bonoldi, E.; Bertazzoni, M. Acute localized exanthematous pustulosis (ALEP) caused by amoxicillin-clavulanic acid. Int. J. Dermatol. 2008, 47, 295–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostaki, M.; Polydorou, D.; Adamou, E.; Chasapi, V.; Antoniou, C.; Stratigos, A. Acute localized exanthematous pustulosis due to metronidazole. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, e109–e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Lee, U.H.; Jang, S.J.; Park, H.S.; Kang, Y.S. Acute localized exanthematous pustulosis induced by docetaxel. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 63, e44–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Cantisani, C.; Melis, L.; Iorio, A.; Scali, E.; Calvieri, S. Minoxidil use in dermatology, side effects and recent patents. Recent Pat. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2012, 6, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Anzalone, A.; Fortuna, M.C.; Caro, G.; Garelli, V.; Pranteda, G.; Carlesimo, M. Multi-therapies in androgenetic alopecia: Review and clinical experiences. Dermatol. Ther. 2016, 29, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, E.S.; Friedman, P.M.; Cohen, D.E.; Washenik, K. Allergic contact dermatitis to topical minoxidil solution: Etiology and treatment. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2002, 46, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Anzi, O.; Hassam, B. Pustular dermatosis of the scalp due to topical minoxidil 5. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2018, 30, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BinJadeed, H.; Almudimeegh, A.M.; Alomran, S.A.; Alshathry, A.H. A Case of Contact Allergic Dermatitis to Topical Minoxidil. Cureus 2021, 13, e12510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, S.; Kuechler, P.C.; Britschgi, M.; Steiner, U.C.; Yawalkar, N.; Limat, A.; Baltensperger, K.; Braathen, L.; Pichler, W.J. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: Role of cytotoxic T cells in pustule formation. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 161, 2079–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldmeyer, L.; Heidemeyer, K.; Yawalkar, N. Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis: Pathogenesis, Genetic Background, Clinical Variants and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, W.J. Delayed drug hypersensitivity reactions. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 139, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, T.V. The Gell-Coombs classification of hypersensitivity reactions: A re-interpretation. Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.A.; Valeyrie-Allanore, L.; Wolkenstein, P.; Chosidow, O. Severe cutaneous adverse reactions to drugs. Lancet 2017, 390, 1996–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaud, A.; Collet, E.; Milpied, B.; Assier, H.; Staumont, D.; Avenel-Audran, M.; Grange, A.; Amarger, S.; Girardin, P.; Guinnepain, M.T.; et al. A multicentre study to determine the value and safety of drug patch tests for the three main classes of severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 168, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, S.L. Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2012, 53, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, A.; Coutinho, I.; Gameiro, A.; Gouveia, M.; Gonçalo, M. Patch testing—A valuable tool for investigating non-immediate cutaneous adverse drug reactions to antibiotics. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabashima, R.; Sugita, K.; Sawada, Y.; Hino, R.; Nakamura, M.; Tokura, Y. Increased circulating Th17 frequencies and serum IL-22 levels in patients with acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarov, A.; Livni, E.; Halevy, S. Generalized pustular drug eruptions: Confirmation by in vitro tests. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 1998, 10, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makris, M.; Kanelleas, A.; Papapostolou, N.; Pisimisi, M.; Katoulis, A.C. Acute Localized Exanthematous Pustulosis (ALEP) Caused by Topical Application of Minoxidil. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030831
Makris M, Kanelleas A, Papapostolou N, Pisimisi M, Katoulis AC. Acute Localized Exanthematous Pustulosis (ALEP) Caused by Topical Application of Minoxidil. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(3):831. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030831
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakris, Michael, Antonios Kanelleas, Niki Papapostolou, Maria Pisimisi, and Alexander C. Katoulis. 2023. "Acute Localized Exanthematous Pustulosis (ALEP) Caused by Topical Application of Minoxidil" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 3: 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030831
APA StyleMakris, M., Kanelleas, A., Papapostolou, N., Pisimisi, M., & Katoulis, A. C. (2023). Acute Localized Exanthematous Pustulosis (ALEP) Caused by Topical Application of Minoxidil. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(3), 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030831






