Research on Establishing Corneal Edema after Phacoemulsification Prediction Model Based on Variable Selection with Copula Entropy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Clinical Outcome and Predictors
2.3. Model Development
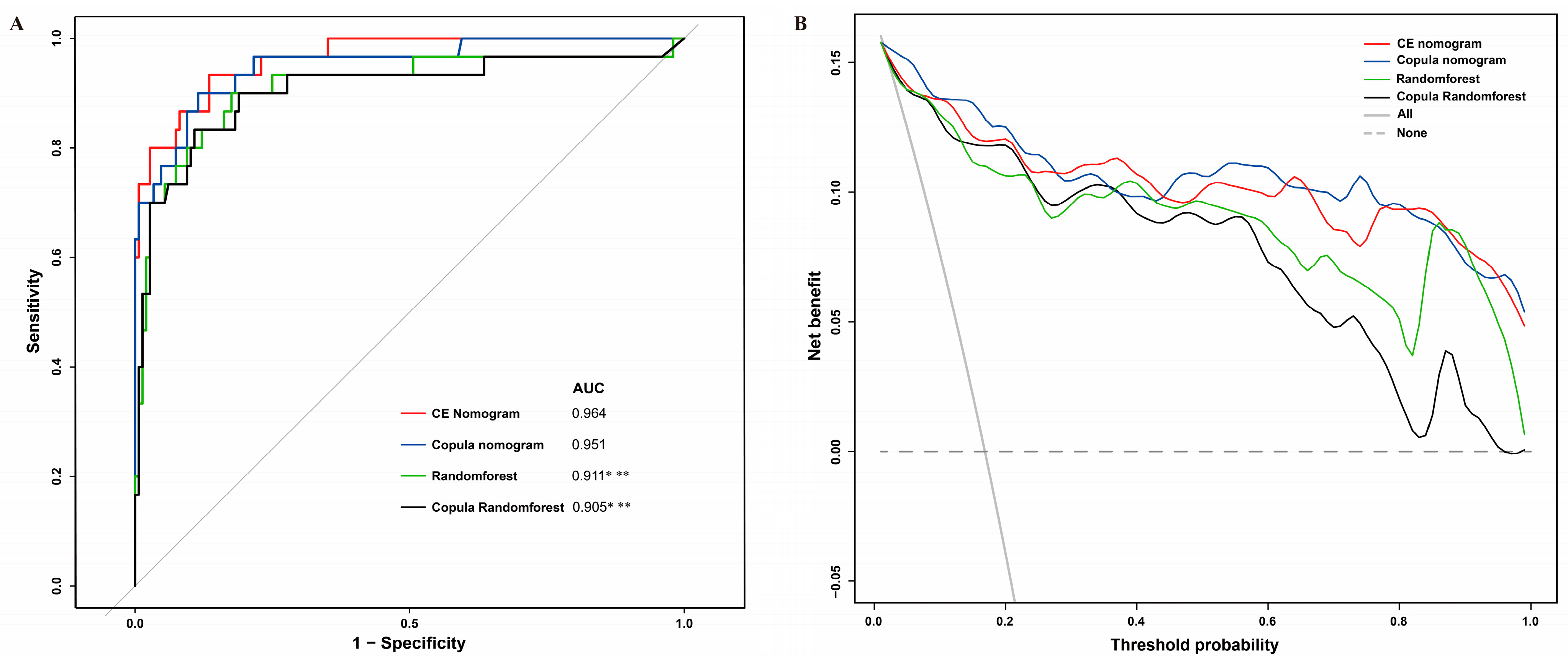
2.4. Model Evaluation
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
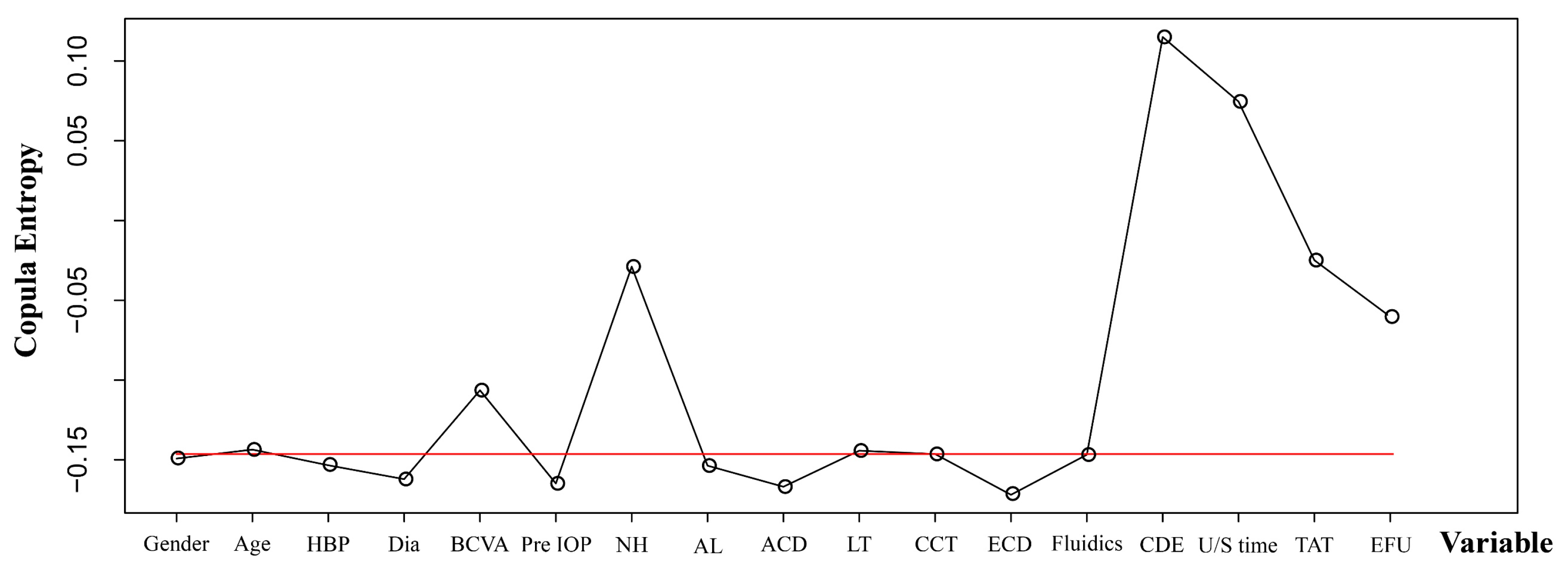
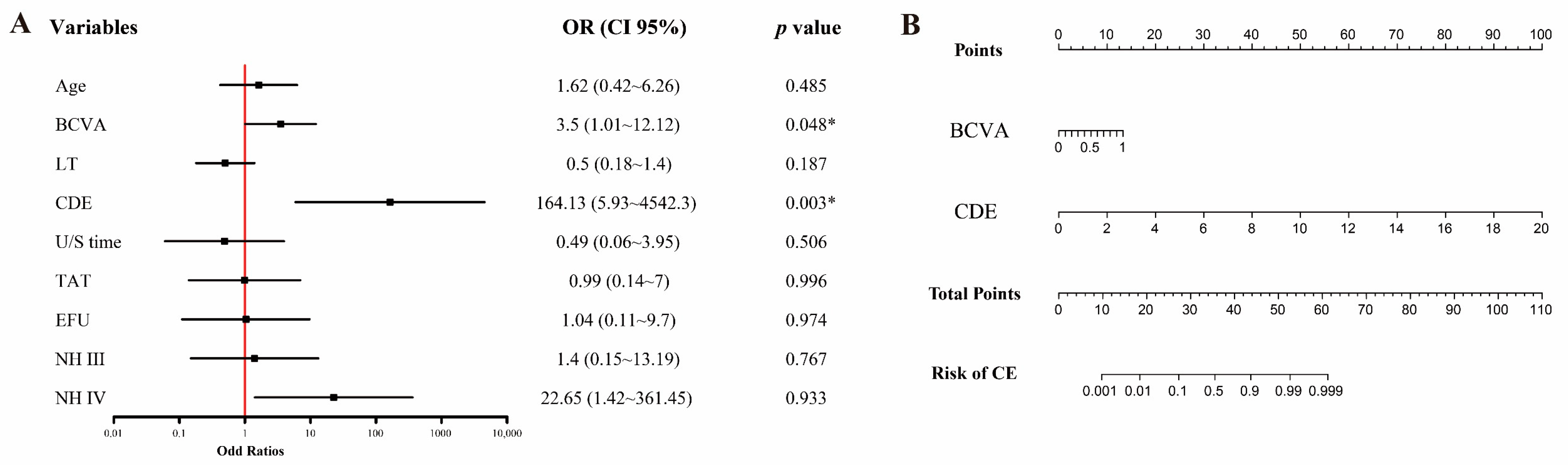
3.1. Clinical Outcomes and Predictors
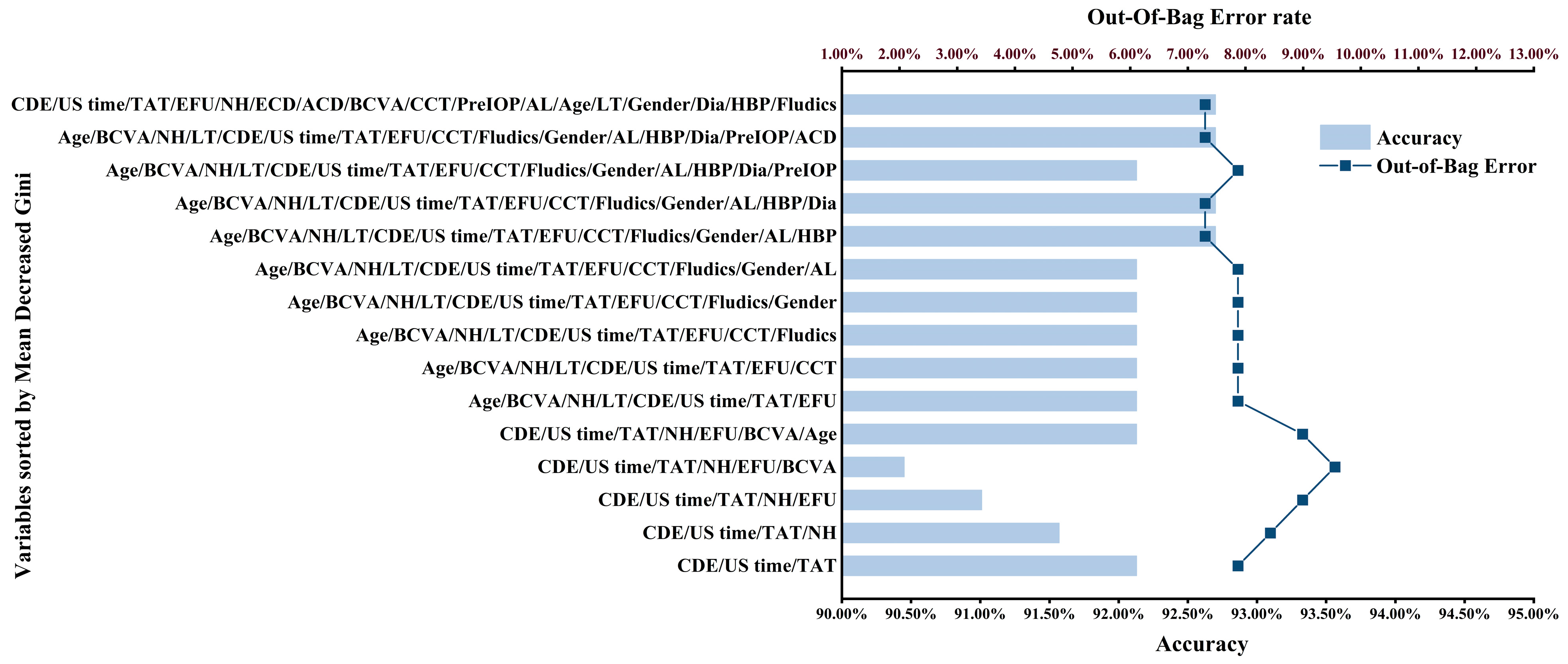
3.2. Model Development
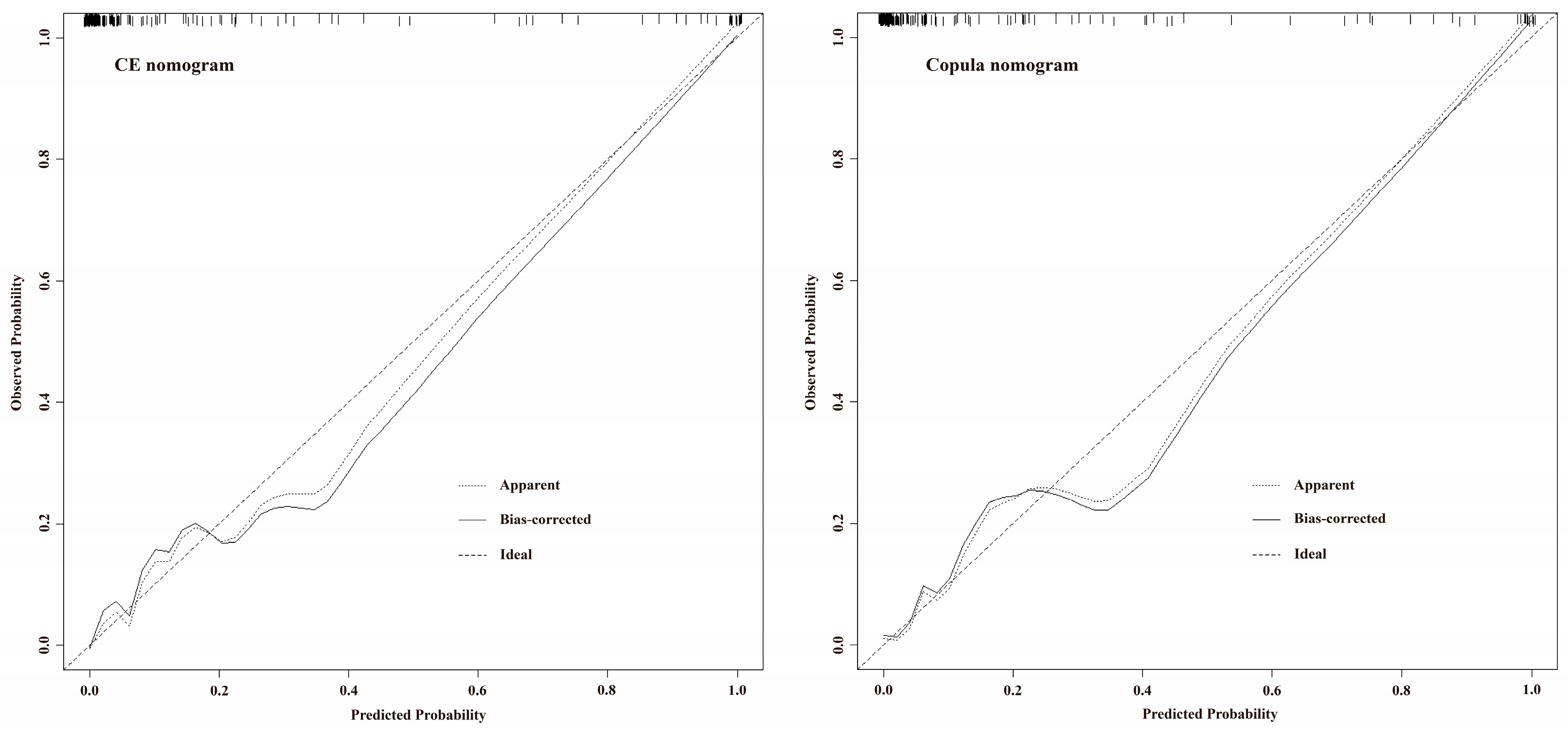
3.3. Model Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lundstrom, M.; Barry, P.; Henry, Y.; Rosen, P.; Stenevi, U. Evidence-based guidelines for cataract surgery: Guidelines based on data in the European registry of quality outcomes for cataract and refractive surgery database. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2012, 38, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Silva, S.R.; Riaz, Y.; Evans, J.R. Phacoemulsification with posterior chamber intraocular lens versus extracapsular cataract extraction (ECCE) with posterior chamber intraocular lens for age-related cataract. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, CD008812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Singhal, D.; Nair, S.P.; Sahay, P.; Sreeshankar, S.S.; Maharana, P.K. Corneal edema after phacoemulsification. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 65, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrentino, F.S.; Matteini, S.; Imburgia, A.; Bonifazzi, C.; Sebastiani, A.; Parmeggiani, F. Torsional phacoemulsification: A pilot study to revise the “harm scale” evaluating the endothelial damage and the visual acuity after cataract surgery. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, B.; Jonsson, M.; Behndig, A. Postoperative corneal swelling correlates strongly to corneal endothelial cell loss after phacoemulsification cataract surgery. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 139, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Han, Y.K. Long-term (≥10 years) results of corneal endothelial cell loss after cataract surgery. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 54, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, W.M. Biology of the corneal endothelium in health and disease. Eye 2003, 17, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C.; Huang, C.W.; Yeh, L.K.; Hsiao, F.C.; Hsueh, Y.J.; Meir, Y.J.; Chen, K.J.; Cheng, C.M.; Wu, W.C. Accelerated corneal endothelial cell loss after phacoemulsification in patients with mildly low endothelial cell density. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2270. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J. Variable selection with copula entropy. Chin. J. Appl. Probab. Stat. 2021, 37, 405–420. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Han, X.; Zhang, J.; Shang, X.; Ha, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Luo, L.; He, M. Predicting the 10-year risk of cataract surgery using machine learning techniques on questionnaire data: Findings from the 45 and up study. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 106, 1503–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Tabuchi, H.; Takase, K.; Masumoto, H. Use of a machine learning method in predicting refraction after cataract surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Schneider, M.J.; Vardhan, S.A.; Ravilla, T. Use of predictive models to identify patients who are likely to benefit from refraction at a follow-up visit after cataract surgery. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 69, 2695–2701. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, D.; Bai, T.; Luo, J.; Wood, J.; Vashisht, A.; Zhang, S.; Xuan, J.; Kattan, M.; Coplan, P. Using machine learning to predict post-operative depth of focus after cataract surgery with implantation of tecnis symfony. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 31, 2938–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, W.; Gao, Y.; Ma, T.; Ye, Z.; Li, Z. A prospective randomized clinical trial of active-fluidics versus gravity-fluidics system in phacoemulsification for age-related cataract (AGSPC). Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 1977–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, W.; Gao, Y.; Ma, T.; Ye, Z.; Li, Z. Active-fluidics versus gravity-fluidics system in phacoemulsification for age-related cataract (AGSPC): Study protocol for a prospective, randomised, double-blind, controlled clinical trial. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e059062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chylack, L.T., Jr.; Leske, M.C.; McCarthy, D.; Khu, P.; Kashiwagi, T.; Sperduto, R. Lens opacities classification system II (LOCS II). Arch. Ophthalmol. 1989, 107, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Huang, C.; Chen, B.; Lam, D.S.; Zhang, S.; Congdon, N. Determinants of postoperative corneal edema and impact on goldmann intraocular pressure. Cornea 2011, 30, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perone, J.M.; Boiche, M.; Lhuillier, L.; Ameloot, F.; Premy, S.; Jeancolas, A.L.; Goetz, C.; Neiter, E. Correlation between postoperative central corneal thickness and endothelial damage after cataract surgery by phacoemulsification. Cornea 2018, 37, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhuillier, L.; Jeancolas, A.L.; Renaudin, L.; Goetz, C.; Ameloot, F.; Premy, S.; Ouamara, N.; Perone, J.M. Impact of ophthalmic surgeon experience on early postoperative central corneal thickness after cataract surgery. Cornea 2017, 36, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrekar, J.N. Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1315–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, A.J.; Elkin, E.B. Decision curve analysis: A novel method for evaluating prediction models. Med. Decis. Mak. 2006, 26, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Sun, Z. Mutual information is copula entropy. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2011, 16, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Jung, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.; Ahn, M. Diagnostic classification and biomarker identification of Alzheimer’s disease with random forest algorithm. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Fan, X.S.; Jin, Y.; He, J.X.; Gui, Y.; Song, L.Y.; Song, Y.; Sun, Q.; Chen, W. Development of heart failure risk prediction models based on a multi-marker approach using random forest algorithms. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Tan, X.; Tang, X.; Zhang, F.; Xia, M.; Chen, G.; He, L.; Zhou, L.; et al. Prediction of ESRD in IgA Nephropathy Patients from an Asian Cohort: A Random Forest Model. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2018, 43, 1852–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulesteix, A.L.; Bender, A.; Lorenzo Bermejo, J.; Strobl, C. Random forest Gini importance favours SNPs with large minor allele frequency: Impact, sources and recommendations. Brief Bioinform. 2012, 13, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesiar, R.; Sheikhi, A. Nonlinear random forest classification, a copula-based approach. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Anderson, E.; Hill, G.; Chen, J.J.; Patrianakos, T. Comparison of cumulative dissipated energy between the Infiniti and Centurion phacoemulsification systems. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2015, 9, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesilirmak, N.; Diakonis, V.F.; Sise, A.; Waren, D.P.; Yoo, S.H.; Donaldson, K.E. Differences in energy expenditure for conventional and femtosecond-assisted cataract surgery using 2 different phacoemulsification systems. J. Cataract. Refract Surg. 2017, 43, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, L.J.; Nguyen, C.L.; Wong, E.; Wang, S.S.Y.; Francis, I.C. Prospective study of Centurion® versus Infiniti® phacoemulsification systems: Surgical and visual outcomes. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 10, 1698–1702. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.; Xu, G.; Li, H.; Ma, T.; Ye, Z.; Li, Z. Research on Establishing Corneal Edema after Phacoemulsification Prediction Model Based on Variable Selection with Copula Entropy. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041290
Luo Y, Xu G, Li H, Ma T, Ye Z, Li Z. Research on Establishing Corneal Edema after Phacoemulsification Prediction Model Based on Variable Selection with Copula Entropy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(4):1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041290
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yu, Guangcan Xu, Hongyu Li, Tianju Ma, Zi Ye, and Zhaohui Li. 2023. "Research on Establishing Corneal Edema after Phacoemulsification Prediction Model Based on Variable Selection with Copula Entropy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 4: 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041290
APA StyleLuo, Y., Xu, G., Li, H., Ma, T., Ye, Z., & Li, Z. (2023). Research on Establishing Corneal Edema after Phacoemulsification Prediction Model Based on Variable Selection with Copula Entropy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(4), 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041290





