Evaluation of Dose Requirements Using Weight-Based versus Non-Weight-Based Dosing of Norepinephrine to Achieve a Goal Mean Arterial Pressure in Patients with Septic Shock
Abstract
1. Introduction
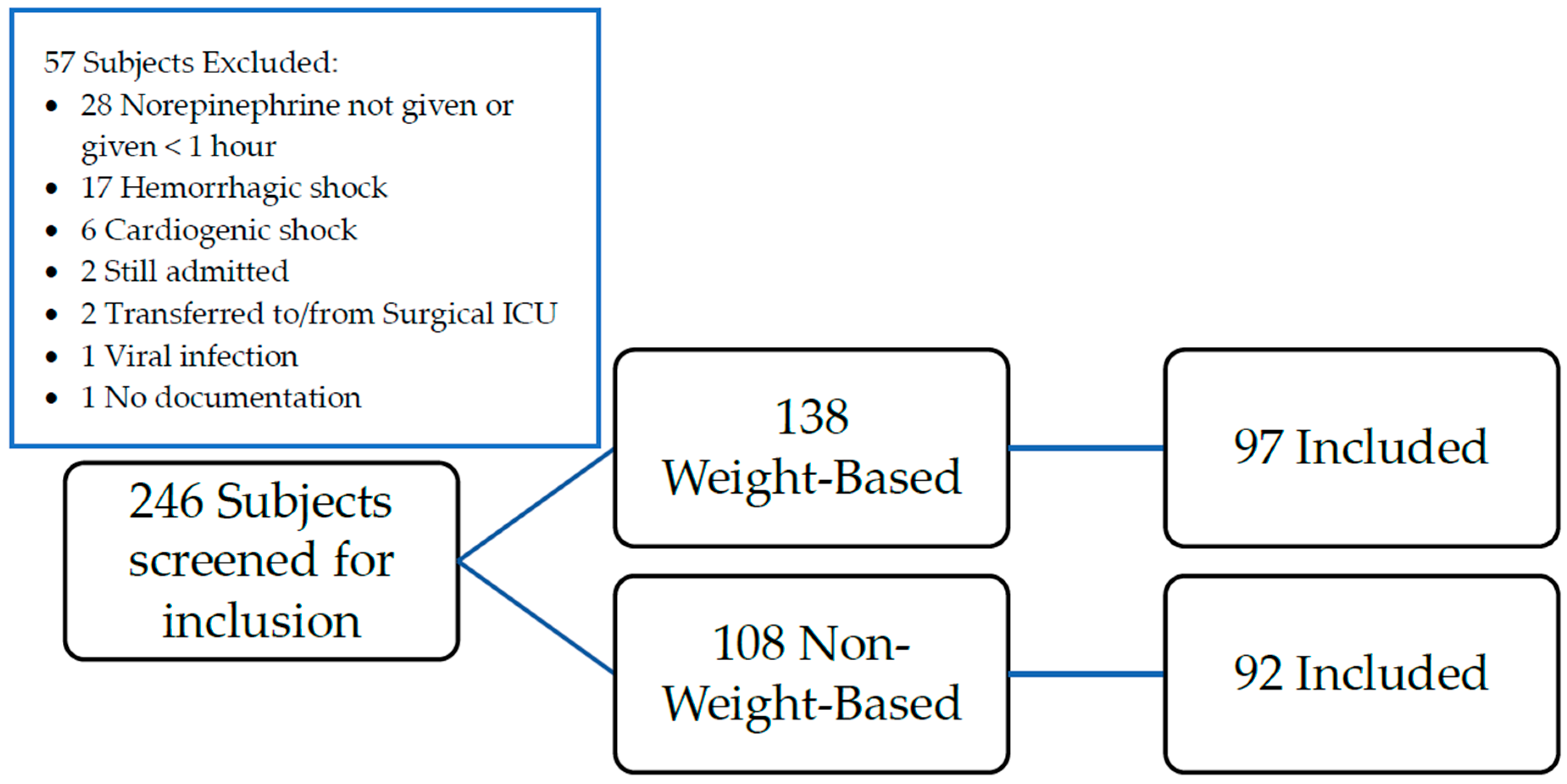
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; Mcintyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, e1063–e1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Backer, D.; Biston, P.; Devriendt, J.; Madl, C.; Chochrad, D.; Aldecoa, C.; Brasseur, A.; Defrance, P.; Gottignies, P.; Vincent, J.L. Comparison of dopamine and norepinephrine in the treatment of shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oba, Y.; Lone, N.A. Mortality benefit of vasopressor and inotropic agents in septic shock: A Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Crit. Care 2014, 29, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, C.C.; Tabrizchi, R. The effects of noradrenaline, B-HT 920, methoxamine, angiotensin II and vasopressin on mean circulatory filling pressure in conscious rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1986, 89, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klem, C.; Dasta, J.F.; Reilley, T.E.; Flancbaum, L.J. Variability in dobutamine pharmacokinetics in unstable critically ill surgical patients. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 22, 1926–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, A.J.; Steiner, L.A.; O’Connell, M.; Chatfield, D.A.; Gupta, A.K.; Menon, D.K. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dopamine and norepinephrine in critically ill head-injured patients. Intensive Care Med. 2004, 30, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beloeil, H.; Mazoit, J.X.; Benhamou, D.; Duranteau, J. Norepinephrine kinetics and dynamics in septic shock and trauma patients. Br. J. Anaesth. 2005, 95, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abboud, I.; Lerolle, N.; Urien, S.; Tadie, J.M.; Leviel, F.; Fagon, J.Y.; Faisy, C. Pharmacokinetics of epinephrine in patients with septic shock: Modelization and interaction with endogenous neurohormonal status. Crit. Care 2009, 13, R120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, P.; Xu, A. Interplay between adipose tissue and blood vessels in obesity and vascular dysfunction. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2013, 14, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radosevich, J.J.; Patanwala, A.E.; Erstad, B.L. Norepinephrine dosing in obese and nonobese patients with septic shock. Am. J. Crit. Care 2016, 25, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadiei, N.; Daley, M.J.; Murthy, M.S.; Shuman, C.S. Impact of norepinephrine weight-based dosing compared with non-weight-based dosing in achieving time to goal mean arterial pressure in obese patients with septic shock. Ann. Pharmacother. 2017, 51, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotecha, A.A.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Apala, D.R.; Frazee, E.; Iyer, V.N. Clinical outcomes of weight-based norepinephrine dosing in underweight and morbidly obese patients: A propensity-matched analysis. J. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 35, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, J.A.; Walley, K.R.; Singer, J.; Gordon, A.C.; Hébert, P.C.; Cooper, D.J.; Holmes, C.L.; Mehta, S.; Granton, J.T.; Storms, M.M.; et al. Vasopressin versus norepinephrine infusion in patients with septic shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.E.; Newsome, A.S.; Tackett, R.L. Prescribing of pressor agents in septic shock: A survey of critical care pharmacists. J. Pharm. Technol. 2019, 35, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabi, Y.M.; Dara, S.I.; Tamim, H.M.; Rishu, A.H.; Bouchama, A.; Khedr, M.K.; Feinstein, D.; Parrillo, J.E.; Wood, K.E.; Keenan, S.P.; et al. Clinical characteristics, sepsis interventions and outcomes in the obese patients with septic shock: An international multicenter cohort study. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.J.; Pandya, K.A.; Flannery, A.H. Evaluating the impact of obesity on safety and efficacy of weight-based norepinephrine dosing in septic shock: A single-center, retrospective study. Intensive Crit. Care Nurs. 2017, 41, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, T.J.; Johnson, A.E.W.; Raffa, J.D.; Celi, L.A.; Mark, R.G.; Badawi, O. The eICU Collaborative Research Database, a freely available multi-center database for critical care research. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | Weight-Based (n = 97) | Non-Weight-Based (n = 92) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), median [IQR] | 71 [63–75] | 71 [63.5–75] | 0.99 |
| Male, n (%) | 91 (93.8%) | 90 (97.8%) | 0.17 |
| Weight (kg), median [IQR] | 83.4 [69.7–99.1] | 81.6 [69.3–100.4] | 0.95 |
| Obese (Body Mass Index ≥ 30 kg/m2), n (%) | 29 (29.9) | 29 (31.9) | 0.77 |
| Race, n (%) | 0.23 | ||
| Caucasian | 55 (56.7) | 59 (64.1) | |
| African American | 38 (39.2) | 31 (33.7) | |
| Latino | 4 (4.1) | 2 (2.2) | |
| Admission source, n (%) | 0.33 | ||
| Emergency Department | 79 (81.4) | 77 (83.7) | |
| Outside Hospital | 10 (10.3) | 5 (5.4) | |
| Outpatient/Clinic | 6 (6.2) | 10 (10.9) | |
| Other | 2 (2.1) | 0 (0) | |
| qSOFA, n (%) | 0.03 | ||
| 0 | 10 (10.3) | 23 (25.0) | |
| 1 | 50 (51.6) | 42 (45.7) | |
| 2 | 26 (26.8) | 23 (25.0) | |
| 3 | 11 (11.3) | 4 (4.3) | |
| qSOFA, median [IQR] | 1 [1–2] | 1 [0.5–2] | 0.02 |
| APACHE II score, median [IQR] | 18 [13–23] | 16.5 [12.5–24] | 0.79 |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index, median [IQR] | 7 [5–9] | 6 [5–8] | 0.23 |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index % 10-year survival, median [IQR] | 0 [0–21] | 2 [0–21] | 0.54 |
| Initial lactate (mmol/L), median [IQR] | 2.3 [1.3–3.7] | 2.3 [1.2–4.8] | 0.54 |
| Intravenous fluid resuscitation documented, n (%) | 34 (35) | 39 (42.4) | 0.19 |
| Intravenous fluid given, n (%) | |||
| 0.9% Sodium chloride | 19 (19.6) | 20 (21.7) | 0.72 |
| Lactated ringer’s | 16 (16.5) | 19 (20.7) | 0.58 |
| Albumin | 0 (0) | 2 (2.1) | 0.17 |
| First MAP documented in ICU (mmHg), median [IQR] | 79 [65–93] | 78 [67–95.5] | 0.57 |
| Last MAP when norepinephrine started (mmHg), median [IQR] | 58 [54–64] | 59 [53–64] | 0.86 |
| SCr (mg/dL) at baseline (prior to admission), median [IQR] | 1.02 [0.82–1.24] | 1.13 [0.91–1.50] | 0.05 |
| BUN (mg/dL) at baseline (prior to admission), median [IQR] | 15 [11–21] | 18 [13–29] | 0.01 |
| SCr (mg/dL) on admission to ICU, median [IQR] | 2 [1.23–3.38] | 1.68 [1.19–2.9] | 0.22 |
| BUN (mg/dL) on admission to ICU, median [IQR] | 32 [19–54] | 29.5 [19–47.5] | 0.43 |
| Additional agents, n (%) | 38 (39.2) | 44 (47.8) | 0.23 |
| Vasopressin | 29 (29.9) | 37 (40.7) | |
| Epinephrine | 12 (12.4) | 13 (14.3) | |
| Dopamine | 2 (2.1) | 6 (6.5) | |
| Phenylephrine | 2 (2.1) | 2 (2.2) | |
| Dobutamine | 5 (5.2) | 4 (4.3) | |
| Milrinone | 0 (0) | 6 (6.5) |
| Weight-Based (n = 71) | Non-Weight-Based (n = 65) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Norepinephrine dose at goal MAP (mcg/kg/min), median [IQR] | 0.05 [0.02–0.07] | 0.07 [0.05–0.13] | <0.001 |
| Norepinephrine dose at goal MAP (mcg/min), median [IQR] | 4.18 [1.52–5.91] | 5.30 [4.04–11.56] | <0.001 |
| Time to goal MAP (min), median [IQR] | 30 [15–60] | 30 [15–60] | 0.75 |
| Duration of norepinephrine (days), median [IQR] | 3 [2–4] | 2 [1–3] | 0.002 |
| Weight-Based (n = 97) | Non-Weight-Based (n = 92) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial norepinephrine dose (mcg/kg/min), median [IQR] | 0.02 [0.01–0.05] | 0.062 [0.04–0.12] | <0.001 |
| Duration of norepinephrine (days), median [IQR] | 2 [2–4] | 2 [1–3] | 0.02 |
| Duration of mechanical ventilation (days), median [IQR] | 2 [0–7] | 2 [0–5.5] | 0.57 |
| Incidence of acute kidney injury, n (%) | 71 (50.7) | 69 (49.3) | 0.86 |
| Required CRRT during admission, n (%) | 26 (26.8) | 11 (12) | 0.01 |
| ICU Length of stay (days), median [IQR] | 7 [4–13] | 9 [5–16.5] | 0.21 |
| Hospital length of stay (days), median [IQR] | 15 [8–29] | 15.5 [8.5–26] | 0.94 |
| In-hospital mortality, n (%) | 44 (45.4) | 49 (53.3) | 0.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Selby, A.R.; Khan, N.S.; Dadashian, T.; Hall 2nd, R.G. Evaluation of Dose Requirements Using Weight-Based versus Non-Weight-Based Dosing of Norepinephrine to Achieve a Goal Mean Arterial Pressure in Patients with Septic Shock. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041344
Selby AR, Khan NS, Dadashian T, Hall 2nd RG. Evaluation of Dose Requirements Using Weight-Based versus Non-Weight-Based Dosing of Norepinephrine to Achieve a Goal Mean Arterial Pressure in Patients with Septic Shock. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(4):1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041344
Chicago/Turabian StyleSelby, Ashley R., Nida S. Khan, Tara Dadashian, and Ronald G. Hall 2nd. 2023. "Evaluation of Dose Requirements Using Weight-Based versus Non-Weight-Based Dosing of Norepinephrine to Achieve a Goal Mean Arterial Pressure in Patients with Septic Shock" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 4: 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041344
APA StyleSelby, A. R., Khan, N. S., Dadashian, T., & Hall 2nd, R. G. (2023). Evaluation of Dose Requirements Using Weight-Based versus Non-Weight-Based Dosing of Norepinephrine to Achieve a Goal Mean Arterial Pressure in Patients with Septic Shock. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(4), 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041344






