Comparing Motor-Evoked Potential Characteristics of NEedle versus suRFACE Recording Electrodes during Spinal Cord Monitoring—The NERFACE Study Part I
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patients
2.3. Anesthesia
2.4. Muscle-Recorded Transcranial Electrical Stimulation Motor Evoked Potentials
2.4.1. Stimulation Parameters
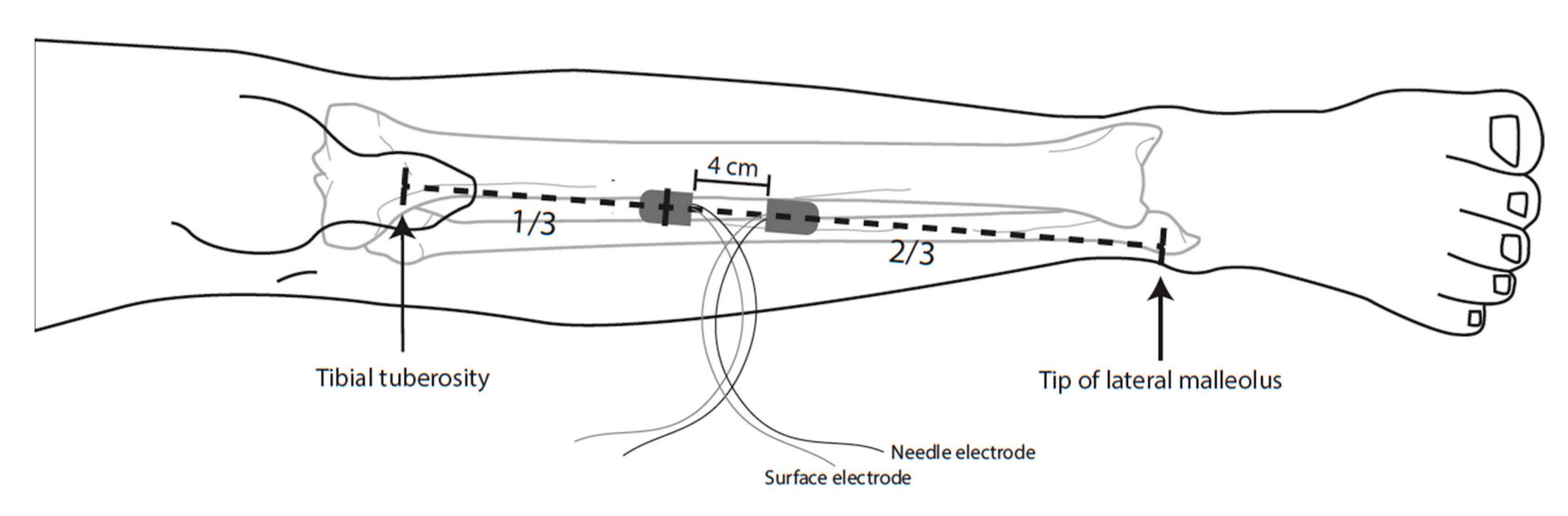
2.4.2. Recording Method
- Subcutaneous needle electrode: 13 mm length × 0.40 mm width (27 G), noncoated, straight, (Medtronic, Xomed, Jacksonville, FL, USA);
- Surface electrode: 20 × 27 mm, adhesive surface pad electrodes (Medtronic, Xomed, Jacksonville, FL, USA).
2.4.3. Elicitability
2.4.4. Motor Threshold
2.4.5. Amplitude and Area under the Curve
2.4.6. Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
2.4.7. Variability
2.5. Data Collection
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. mTc-MEP Parameters
3.2.1. Elicitability
3.2.2. Motor Threshold
3.2.3. Amplitude, Area under the Curve and Amplitude Difference
3.2.4. Signal-to-Noise Ratio
3.2.5. Variability
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fehlings, M.G.; Brodke, D.S.; Norvell, D.C.; Dettori, J.R. The Evidence for Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring in Spine Surgery: Does It Make a Difference? Spine 2010, 35, S37–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.B. Intraoperative Motor Evoked Potential Monitoring: Overview and Update. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2006, 20, 347–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, F.; Palandri, G.; Basso, E.; Lanteri, P.; Deletis, V.; Faccioli, F.; Bricolo, A. Motor Evoked Potential Monitoring Improves Outcome after Surgery for Intramedullary Spinal Cord Tumors: A Historical Control Study. Neurosurgery 2006, 58, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deletis, V.; Sala, F. Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring of the Spinal Cord during Spinal Cord and Spine Surgery: A Review Focus on the Corticospinal Tracts. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.B.; Skinner, S.; Shils, J.; Yingling, C. American Society of Neurophysiological Monitoring Intraoperative Motor Evoked Potential Monitoring—A Position Statement by the American Society of Neurophysiological Monitoring. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 124, 2291–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.B.; Dong, C.; Quatrale, R.; Sala, F.; Skinner, S.; Soto, F.; Szelényi, A. Recommendations of the International Society of Intraoperative Neurophysiology for Intraoperative Somatosensory Evoked Potentials. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deletis, V. Intraoperative Neurophysiology and Methodologies Used to Monitor the Functional Integrity of the Motor System. Riv. Med. 2002, 14, 25–51. [Google Scholar]
- Langeloo, D.D.; Lelivelt, A.; Louis Journée, H.; Slappendel, R.; de Kleuver, M. Transcranial Electrical Motor-Evoked Potential Monitoring During Surgery for Spinal Deformity. Spine 2003, 28, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gath, I.; Stålberg, E. The Calculated Radial Decline of the Extracellular Action Potential Compared with in Situ Measurements in the Human Brachial Biceps. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1978, 44, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegeman, D.F.; Dumitru, D.; King, J.C.; Roeleveld, K. Near- and Far-Fields: Source Characteristics and the Conducting Medium in Neurophysiology. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1997, 14, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drost, G.; Stegeman, D.F.; van Engelen, B.G.M.; Zwarts, M.J. Clinical Applications of High-Density Surface EMG: A Systematic Review. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2006, 16, 586–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, S.A.; Transfeldt, E.E.; Savik, K. Surface Electrodes Are Not Sufficient to Detect Neurotonic Discharges: Observations in a Porcine Model and Clinical Review of Deltoid Electromyographic Monitoring Using Multiple Electrodes. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2008, 22, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.A.; Cheongsiatmoy, J.; Shilian, P.; Parikh, P. Comparison of Transcranial Motor Evoked Potential Amplitude Responses between Intramuscular and Subcutaneous Needles in Proximal Thigh Muscle. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 35, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, D.B. Overview on Criteria for MEP Monitoring. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 34, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahinovic, M.M.; Gadella, M.C.; Shils, J.; Dulfer, S.E.; Drost, G. Anesthesia and Intraoperative Neurophysiological Spinal Cord Monitoring. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2021, 34, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuwer, M.R.; Comi, G.; Emerson, R.; Fuglsang-Frederiksen, A.; Guerit, M.; Hinrichs, H.; Ikeda, A.; Luccas, F.J.C.; Rappelsburger, P. IFCN Standards for Digital Recording of Clinical EEG. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 106, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstedt, J.; Nilsson, G.; Stalberg, E. Calculation of the Electromyographic Jitter. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1974, 37, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegeman, D.F.; Zwarts, M.J.; Anders, C.; Hashimoto, T. Chapter 20 Multi-Channel Surface EMG in Clinical Neurophysiology. Suppl. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2000, 53, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Journée, S.L.; Journée, H.L.; Reed, S.M.; Berends, H.I.; de Bruijn, C.M.; Delesalle, C.J.G. Extramuscular Recording of Spontaneous EMG Activity and Transcranial Electrical Elicited Motor Potentials in Horses: Characteristics of Different Subcutaneous and Surface Electrode Types and Practical Guidelines. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Journée, H.L.; Berends, H.I.; Kruyt, M.C. The Percentage of Amplitude Decrease Warning Criteria for Transcranial MEP Monitoring. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 34, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shekhlee, A.; Shapiro, B.E.; Preston, D.C. Iatrogenic Complications and Risks of Nerve Conduction Studies and Needle Electromyography. Muscle Nerve 2003, 27, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besomi, M.; Hodges, P.W.; Van Dieën, J.; Carson, R.G.; Clancy, E.A.; Disselhorst-Klug, C.; Holobar, A.; Hug, F.; Kiernan, M.C.; Lowery, M.; et al. Consensus for Experimental Design in Electromyography (CEDE) Project: Electrode Selection Matrix. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2019, 48, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mateen, F.J.; Grant, I.A.; Sorenson, E.J. Needlestick Injuries among Electromyographers. Muscle Nerve 2008, 38, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, J.G.; van der Kamp, W.; Tjon-A-Tsien, A. CMAP Variability as a Function of Electrode Site and Size. Muscle Nerve 1995, 18, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Characteristics | Patients n = 185 |
|---|---|
| Median age in years (IQR) | 18 (15–46) |
| Female N (%) | 120 (64.9) |
| Diagnosis N (%) | |
| Orthopedic surgery | 115 (62.2) |
| Idiopathic scoliosis | 82 (64.9) |
| Syndromic scoliosis | 13 (7.0) |
| Neuromuscular scoliosis | 16 (8.7) |
| Congenital scoliosis | 1 (0.5) |
| Kyphosis | 3 (1.6) |
| Neurosurgery | 54 (29.2) |
| Intramedullary tumor | 12 (6.5) |
| Intradural extramedullary tumor | 21 (11.4) |
| Intradural cauda equina tumor | 9 (4.9) |
| Thoracic HNP with spinal cord compression | 3 (1.6) |
| Transdural | 1 (0.5) |
| Extradural | 2 (1.1) |
| Tethered spinal cord | 3 (1.6) |
| Spinal nerve root tumor | 3 (1.6) |
| Transdural | 1 (0.5) |
| Extradural | 2 (1.1) |
| ATSCH | 1 (0.5) |
| Trauma with spinal cord compression (extradural) | 1 (0.5) |
| Degenerative spine instability (extradural) | 1 (0.5) |
| Vascular surgery (endovascular aneurysm surgery) | 16 (8.7) |
| Mean surgery time in minutes (SD) | 326.21 (100.8) |
| TA strength prior to surgery N (%) | |
| Right | |
| MRC < 5 | 20 (10.8) |
| MRC = 5 | 165 (89.2) |
| Left | |
| MRC < 5 | 21 (11.4) |
| MRC = 5 | 164 (88.67) |
| TA strength after surgery N (%) | |
| Right | |
| MRC < 5 | 17 (9.2) |
| MRC = 5 | 168 (90.8) |
| Left | |
| MRC < 5 | 18 (9.7) |
| MRC = 5 | 167 (90.3) |
| Patient | % Not Elicitable TASL | % Not Elicitable TANL | % Not Elicitable TASR | % Not Elicitable TANR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25.0 | 25.0 | ||
| 2 | 18.2 | 18.2 | ||
| 3 | 79.3 | 79.3 | ||
| 4 | 75.7 | 75.7 | ||
| 5 | 13.1 | 13.1 | ||
| 6 | 9.9 | 11.6 | ||
| 7 | 13.7 | 13.7 | ||
| 8 | 29.0 | 32.3 | ||
| 9 | 19.6 | 19.0 | 20.7 | 21.2 |
| 10 | 74.1 | 77.8 | 68.5 | 68.5 |
| 11 | 7.8 | 7.8 | 15.5 | 26.2 |
| 12 | 78.1 | 78.1 | 71.9 | 71.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gadella, M.C.; Dulfer, S.E.; Absalom, A.R.; Lange, F.; Scholtens-Henzen, C.H.M.; Groen, R.J.M.; Wapstra, F.H.; Faber, C.; Tamási, K.; Sahinovic, M.M.; et al. Comparing Motor-Evoked Potential Characteristics of NEedle versus suRFACE Recording Electrodes during Spinal Cord Monitoring—The NERFACE Study Part I. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041404
Gadella MC, Dulfer SE, Absalom AR, Lange F, Scholtens-Henzen CHM, Groen RJM, Wapstra FH, Faber C, Tamási K, Sahinovic MM, et al. Comparing Motor-Evoked Potential Characteristics of NEedle versus suRFACE Recording Electrodes during Spinal Cord Monitoring—The NERFACE Study Part I. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(4):1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041404
Chicago/Turabian StyleGadella, Maria C., Sebastiaan E. Dulfer, Anthony R. Absalom, Fiete Lange, Carola H. M. Scholtens-Henzen, Rob J. M. Groen, Frits H. Wapstra, Christopher Faber, Katalin Tamási, Marko M. Sahinovic, and et al. 2023. "Comparing Motor-Evoked Potential Characteristics of NEedle versus suRFACE Recording Electrodes during Spinal Cord Monitoring—The NERFACE Study Part I" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 4: 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041404
APA StyleGadella, M. C., Dulfer, S. E., Absalom, A. R., Lange, F., Scholtens-Henzen, C. H. M., Groen, R. J. M., Wapstra, F. H., Faber, C., Tamási, K., Sahinovic, M. M., & Drost, G. (2023). Comparing Motor-Evoked Potential Characteristics of NEedle versus suRFACE Recording Electrodes during Spinal Cord Monitoring—The NERFACE Study Part I. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(4), 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041404









