Roles of Bilirubin in Hemorrhagic Transformation of Different Types and Severity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Data Collection and Group Stratification
2.3. Definition and Classification of HT Subtypes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Patients with and without HT in the Two Cohorts
3.2. Baseline Characteristics according to TBIL Quartiles
3.3. Association between TBIL Level and HT after AIS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khatri, R.; McKinney, A.M.; Swenson, B.; Janardhan, V. Blood-brain barrier, reperfusion injury, and hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke. Neurology 2012, 79 (Suppl. S1), S52–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lo, E.H. Triggers and mediators of hemorrhagic transformation in cerebral ischemia. Mol. Neurobiol. 2003, 28, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciaroni, M.; Agnelli, G.; Corea, F.; Ageno, W.; Alberti, A.; Lanari, A.; Caso, V.; Micheli, S.; Bertolani, L.; Venti, M.; et al. Early hemorrhagic transformation of brain infarction: Rate, predictive factors, and influence on clinical outcome: Results of a prospective multicenter study. Stroke 2008, 39, 2249–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, N.M.; Levine, S.R.; Gornbein, J.A.; Saver, J.L. Defining clinically relevant cerebral hemorrhage after thrombolytic therapy for stroke: Analysis of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke tissue-type plasminogen activator trials. Stroke 2014, 45, 2728–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Sun, H.; Xing, Y. Hemorrhagic transformation after cerebral infarction: Current concepts and challenges. Ann. Transl. Med. 2014, 2, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracard, S.; Ducrocq, X.; Mas, J.L.; Soudant, M.; Oppenheim, C.; Moulin, T.; Guillemin, F. Mechanical thrombectomy after intravenous alteplase versus alteplase alone after stroke (THRACE): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacke, W.; Kaste, M.; Fieschi, C.; von Kummer, R.; Davalos, A.; Meier, D.; Larrue, V.; Bluhmki, E.; Davis, S.; Donnan, G.; et al. Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of thrombolytic therapy with intravenous alteplase in acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS II). Second European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study Investigators. Lancet 1998, 352, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucchiara, B.; Tanne, D.; Levine, S.R.; Demchuk, A.M.; Kasner, S. A risk score to predict intracranial hemorrhage after recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2008, 17, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, M.; Leira, R.; Serena, J.; Pumar, J.M.; Lizasoain, I.; Castillo, J.; Dávalos, A. Plasma metalloproteinase-9 concentration predicts hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2003, 34, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciaroni, M.; Agnelli, G.; Caso, V.; Corea, F.; Ageno, W.; Alberti, A.; Lanari, A.; Micheli, S.; Bertolani, L.; Venti, M.; et al. Acute hyperglycemia and early hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2009, 28, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Muramatsu, M.; Kojima, T.; Taki, W. Intracranial heme metabolism and cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 2003, 34, 2796–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau, C.; Métivier, S.; D’Amico, M.; Péron, J.M.; Otal, P.; Pagan, J.C.; Chabbert, V.; Chagneau-Derrode, C.; Procopet, B.; Rousseau, H.; et al. Serum bilirubin and platelet count: A simple predictive model for survival in patients with refractory ascites treated by TIPS. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, C.J.; Pyne-Geithman, G.J.; Jauch, E.C.; Shukla, R.; Wagner, K.R.; Clark, J.F.; Zuccarello, M. Bilirubin as a cerebrospinal fluid marker of sentinel subarachnoid hemorrhage: A preliminary report in pigs. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 101, 1026–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Sun, M.; Dang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Bilirubin: A novel predictor of hemorrhagic transformation and symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage after mechanical thrombectomy. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Lei, C.; Hao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, R.; Liu, M. Liver function may play an uneven role in haemorrhagic transformation for stroke subtypes after acute ischaemic stroke. Eur. J. Neurol. 2016, 23, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, H.P., Jr.; Bendixen, B.H.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biller, J.; Love, B.B.; Gordon, D.L.; Marsh, E.E., 3rd. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 1993, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacke, W.; Kaste, M.; Fieschi, C.; Toni, D.; Lesaffre, E.; von Kummer, R.; Boysen, G.; Bluhmki, E.; Höxter, G.; Mahagne, M.H.; et al. Intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute hemispheric stroke: The European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS). JAMA 1995, 274, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larrue, V.; von Kummer, R.R.; Müller, A.; Bluhmki, E. Risk factors for severe hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke patients treated with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator: A secondary analysis of the European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study (ECASS II). Stroke 2001, 32, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Wang, Y.; Song, Q.; Liu, J.; Wei, C.; Liu, M. Association Between Coagulation Function and Spontaneous Hemorrhagic Transformation in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2020, 17, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Meng, D.; Liu, Z.; Hua, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Qian, Z.; Xu, X. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio Is a Therapeutic Biomarker for Spontaneous Hemorrhagic Transformation. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 38, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.T.; Campbell, B.C.; Christensen, S.; Desmond, P.M.; De Silva, D.A.; Parsons, M.W.; Churilov, L.; Lansberg, M.G.; Mlynash, M.; Olivot, J.M.; et al. Worse stroke outcome in atrial fibrillation is explained by more severe hypoperfusion, infarct growth, and hemorrhagic transformation. Int. J. Stroke 2015, 10, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrade, J.B.C.; Mohr, J.P.; Lima, F.O.; Carvalho, J.J.F.; de Farias, V.A.E.; Oliveira-Filho, J.; Pontes-Neto, O.M.; Bazan, R.; Merida, K.L.B.; Franciscato, L.; et al. Predicting hemorrhagic transformation in patients not submitted to reperfusion therapies. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 104940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zeng, J.; Wang, F.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X.; Miao, J. Risk factors of hemorrhagic transformation after intravenous thrombolysis with rt-PA in acute cerebral infarction. QJM 2019, 112, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Li, G.; Xing, Y.; Nie, D.; Liu, X. Influencing factors of hemorrhagic transformation in non-thrombolysis patients with cerebral infarction. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2019, 181, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Pan, H.; Qiao, Y.; Huang, P.; Su, J.; Liu, J. Fibrinogen Level Combined with Platelet Count for Predicting Hemorrhagic Transformation in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients Treated with Mechanical Thrombectomy. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 716020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, D.W.; Legrand, J.; Krafft, P.R.; Flores, J.; Klebe, D.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H. Acute Hyperglycemia Is Associated with Immediate Brain Swelling and Hemorrhagic Transformation After Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Rats. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2016, 121, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.J.; Sharp, F.R. Implications of MMP9 for Blood Brain Barrier Disruption and Hemorrhagic Transformation Following Ischemic Stroke. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desilles, J.P.; Syvannarath, V.; Ollivier, V.; Journé, C.; Delbosc, S.; Ducroux, C.; Boisseau, W.; Louedec, L.; Di Meglio, L.; Loyau, S.; et al. Exacerbation of Thromboinflammation by Hyperglycemia Precipitates Cerebral Infarct Growth and Hemorrhagic Transformation. Stroke 2017, 48, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; He, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Cai, Z.; Guo, Z.; Meng, P.; Ji, N.; He, X.; Pang, L. Hemoglobin A1c predicts hemorrhagic transformation and poor outcomes after acute anterior stroke. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 1432-e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, T.W.; Chou, C.H.; Wang, C.C.; Chou, C.C.; Hu, J.; Chen, W.L. Associations between serum total bilirubin levels and functional dependence in the elderly. Intern. Med. J. 2012, 42, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineda, S.; Bang, O.Y.; Saver, J.L.; Starkman, S.; Yun, S.W.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Kim, D.; Ali, L.K.; Shah, S.H.; Ovbiagele, B. Association of serum bilirubin with ischemic stroke outcomes. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2008, 17, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Li, J.W.; Lu, Z.J.; Wang, C.; Guan, D.N.; Xu, Y. Serum bilirubin after acute ischemic stroke is associated with stroke severity. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2012, 9, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Cheng, Z.; Yun, H.J.; Cai, L.; Tong, Y.; Han, Z.; Geng, X.; Ding, Y. Serum Bilirubin Associated with Stroke Severity and Prognosis: Preliminary Findings on Liver Function after Acute Ischemic Stroke. Neurol. Res. 2022, 45, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurzepa, J.; Bielewicz, J.; Stelmasiak, Z.; Bartosik-Psujek, H. Serum bilirubin and uric acid levels as the bad prognostic factors in the ischemic stroke. Int. J. Neurosci. 2009, 119, 2243–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.E.; Foresti, R.; Green, C.J.; Motterlini, R. Dynamics of haem oxygenase-1 expression and bilirubin production in cellular protection against oxidative stress. Biochem. J. 2000, 348 Pt 3, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doré, S.; Takahashi, M.; Ferris, C.D.; Zakhary, R.; Hester, L.D.; Guastella, D.; Snyder, S.H. Bilirubin, formed by activation of heme oxygenase-2, protects neurons against oxidative stress injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 2445–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftspring, M.C.; Wurster, W.L.; Pyne-Geithman, G.J.; Clark, J.F. An in vitro model of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: Oxidation of unconjugated bilirubin by cytochrome oxidase. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 1990–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Q.; Li, L.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Sun, Y.Y.; Wu, J. Research Progress in Understanding the Relationship Between Heme Oxygenase-1 and Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, C.; Hou, L.; He, M.; Song, G.; Ren, S.; Han, C. Higher Level of Serum Heme Oxygenase-1 in Patients With Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Int. Surg. 2015, 100, 1220–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Zhu, H.; Liang, R.; Gu, Y.; Pang, Y.; Qi, J.; Wu, H.; et al. Distinct role of heme oxygenase-1 in early- and late-stage intracerebral hemorrhage in 12-month-old mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Doré, S. Heme oxygenase-1 exacerbates early brain injury after intracerebral haemorrhage. Brain 2007, 130 Pt 6, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyne-Geithman, G.J.; Nair, S.G.; Stamper, D.N.; Clark, J.F. Role of bilirubin oxidation products in the pathophysiology of DIND following SAH. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2013, 115, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.F.; Loftspring, M.; Wurster, W.L.; Beiler, S.; Beiler, C.; Wagner, K.R.; Pyne-Geithman, G.J. Bilirubin oxidation products, oxidative stress, and intracerebral hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2008, 105, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakovic, K.; Ai, J.; D’Abbondanza, J.; Tariq, A.; Sabri, M.; Alarfaj, A.K.; Vasdev, P.; Macdonald, R.L. Bilirubin and its oxidation products damage brain white matter. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, N.V.; Wharton, J.A.; Leclerc, J.L.; Blackburn, S.L.; Douglas-Escobar, M.V.; Weiss, M.D.; Seubert, C.N.; Doré, S. Clinical Implications of Bilirubin-Associated Neuroprotection and Neurotoxicity. Int. J. Clin. Anesthesiol. 2013, 1, 2–4. [Google Scholar]
- Doré, S. Decreased activity of the antioxidant heme oxygenase enzyme: Implications in ischemia and in Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 32, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grojean, S.; Koziel, V.; Vert, P.; Daval, J.L. Bilirubin induces apoptosis via activation of NMDA receptors in developing rat brain neurons. Exp. Neurol. 2000, 166, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit, Y.; Cashore, W.; Schiff, D. Studies of bilirubin toxicity at the synaptosome and cellular levels. Semin. Perinatol. 1992, 16, 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- Notter, M.F.; Kendig, J.W. Differential sensitivity of neural cells to bilirubin toxicity. Exp. Neurol. 1986, 94, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.F.; Rodrigues, C.M.; Brites, D. Bilirubin-induced apoptosis in cultured rat neural cells is aggravated by chenodeoxycholic acid but prevented by ursodeoxycholic acid. J. Hepatol. 2001, 34, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumral, A.; Genc, S.; Genc, K.; Duman, N.; Tatli, M.; Sakizli, M.; Ozkan, H. Hyperbilirubinemic serum is cytotoxic and induces apoptosis in murine astrocytes. Biol. Neonate. 2005, 87, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genc, S.; Genc, K.; Kumral, A.; Baskin, H.; Ozkan, H. Bilirubin is cytotoxic to rat oligodendrocytes in vitro. Brain. Res. 2003, 985, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Leak, R.K.; Keep, R.F.; Chen, J. Translational Stroke Research on Blood-Brain Barrier Damage: Challenges, Perspectives, and Goals. Transl. Stroke Res. 2016, 7, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arba, F.; Piccardi, B.; Palumbo, V.; Biagini, S.; Galmozzi, F.; Iovene, V.; Giannini, A.; Testa, G.D.; Sodero, A.; Nesi, M.; et al. Blood-brain barrier leakage and hemorrhagic transformation: The Reperfusion Injury in Ischemic StroKe (RISK) study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 3147–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, M.; Menon, B.K.; van Zwam, W.H.; Dippel, D.W.; Mitchell, P.J.; Demchuk, A.M.; Dávalos, A.; Majoie, C.B.; van der Lugt, A.; de Miquel, M.A.; et al. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet 2016, 387, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Cai, Q.; Xiao, L.; Gu, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, W.; Xu, G.; Liu, X. Influence of procedure time on outcome and hemorrhagic transformation in stroke patients undergoing thrombectomy. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 2560–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Yang, D.; Wang, H.; Zi, W.; Zhang, M.; Geng, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, W.; Xu, H.; Tian, X.; et al. Predictors for Symptomatic Intracranial Hemorrhage After Endovascular Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2017, 48, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, M.; Hashimoto, H.; Kosaka, F. Histological changes of neuronal damage in vegetative dogs induced by 18 minutes of complete global brain ischemia: Two-phase damage of Purkinje cells and hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. Acta Neuropathol. 1990, 80, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, P.M.; Steinberg, G.K. Novel Stroke Therapeutics: Unraveling Stroke Pathophysiology and Its Impact on Clinical Treatments. Neuron 2015, 87, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jickling, G.C.; Liu, D.; Stamova, B.; Ander, B.P.; Zhan, X.; Lu, A.; Sharp, F.R. Hemorrhagic transformation after ischemic stroke in animals and humans. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
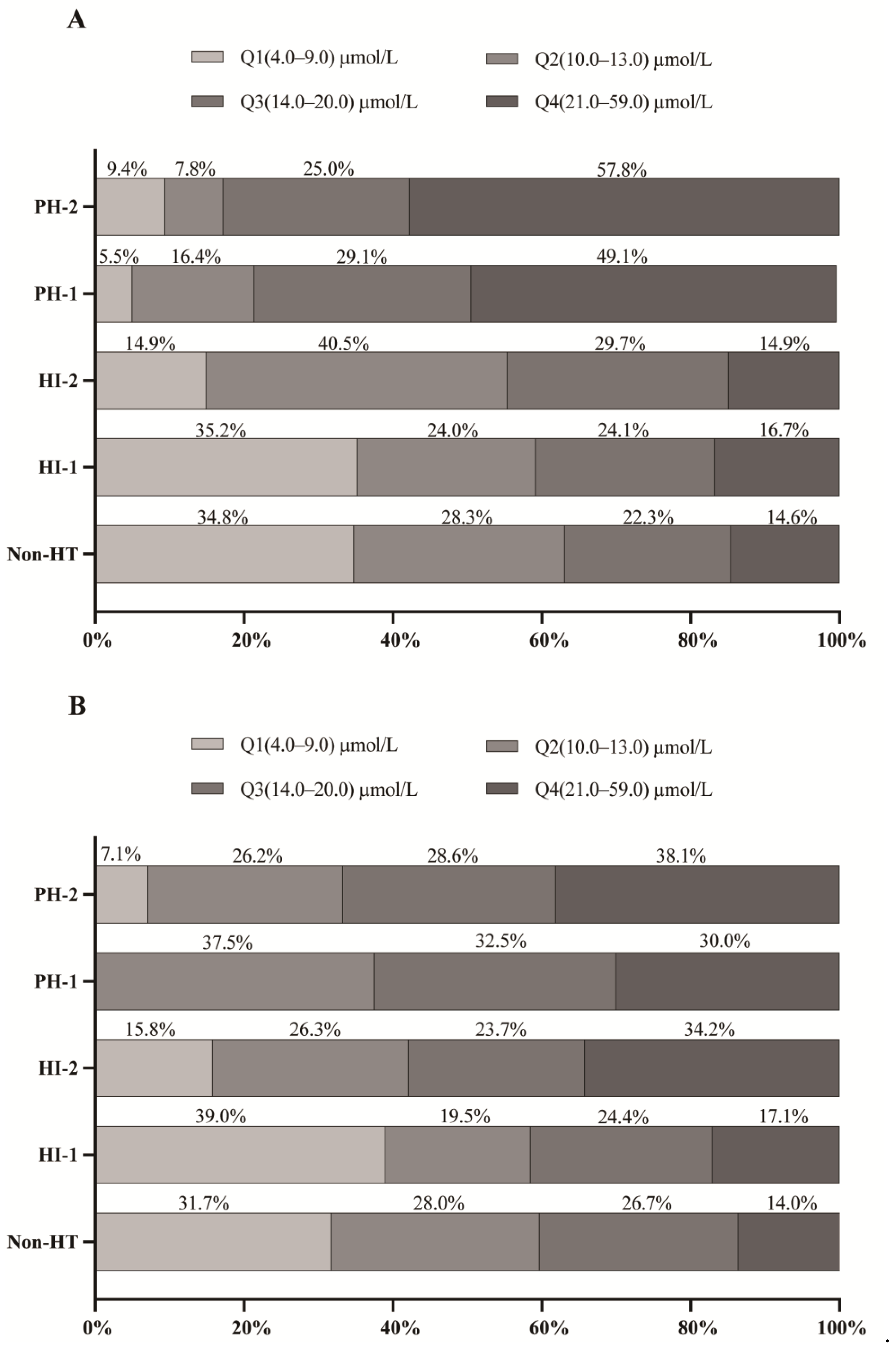

| sHT Cohort (n = 494) | tHT Cohort (n = 332) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Non-HT (n = 247) | HT (n = 247) | p Value * | Non-HT (n = 161) | HT (n = 161) | p Value * |
| Demographic parameters | ||||||
| Age (years) | 67 (58–73) | 68 (58.5–76) | 0.121 | 69 (61–76) | 70 (61–77) | 0.918 |
| Sex (Male, n%) | 176 (71.3%) | 176 (71.3%) | 1 | 113 (34%) | 113 (34%) | 1 |
| Vascular risk factors | ||||||
| History of atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 23 (9.3%) | 43 (17.4%) | 0.008 | 61 (37.9%) | 65 (40.4%) | 0.732 |
| History of hypertension, n (%) | 151 (61.1%) | 151 (61.1%) | 1 | 111 (68.9%) | 109 (67.7%) | 0.905 |
| History of diabetes, n (%) | 67 (27.1%) | 63 (25.5%) | 0.683 | 32 (19.9%) | 36 (22.4) | 0.682 |
| History of coronary heart disease, n (%) | 21 (8.5%) | 23 (9.3%) | 0.578 | 20 (12.4%) | 21 (13%) | 1 |
| Current smoking, n (%) | 163 (66.0%) | 162 (65.6%) | 0.924 | 66 (41%) | 59 (36.6%) | 0.493 |
| Current drinking, n (%) | 77 (31.2%) | 70 (28.3%) | 0.555 | 53 (32.9%) | 58 (36%) | 0.639 |
| mRS on admission, median (IQR) | 2 (1–3) | 3 (2–4) | <0.001 | 5 (4–5) | 5 (4–5) | 0.076 |
| NIHSS on admission, median (IQR) | 5.0 (2.0–10.5) | 9.0 (5.0–13.0) | <0.001 | 16 (10–20) | 16 (12–24) | 0.143 |
| Biochemistry and vital signs on admission | ||||||
| RBC | 4.5 (4.18–4.805) | 4.44 (4.105–4.760) | 0.153 | 4.03±0.61 | 4.13±0.61 | 0.118 |
| WBC | 6.37 (5.37–7.60) | 8.05 (6.43–10.26) | <0.001 | 8.95 (7.09–11.2) | 10.25 (8.44–12.39) | <0.001 |
| Hb | 139 (128–147) | 136 (126–145) | 0.104 | 124 (110–135) | 128 (113–140) | 0.032 |
| PLT | 198 (173–230) | 189 (150–231) | 0.009 | 191 (155–243) | 176 (144–219) | 0.026 |
| Glucose | 5 (4.45–6.4) | 5.8 (4.8–7.2) | <0.001 | 6.4 (5.5–8) | 7.7 (6.3–10.075) | <0.001 |
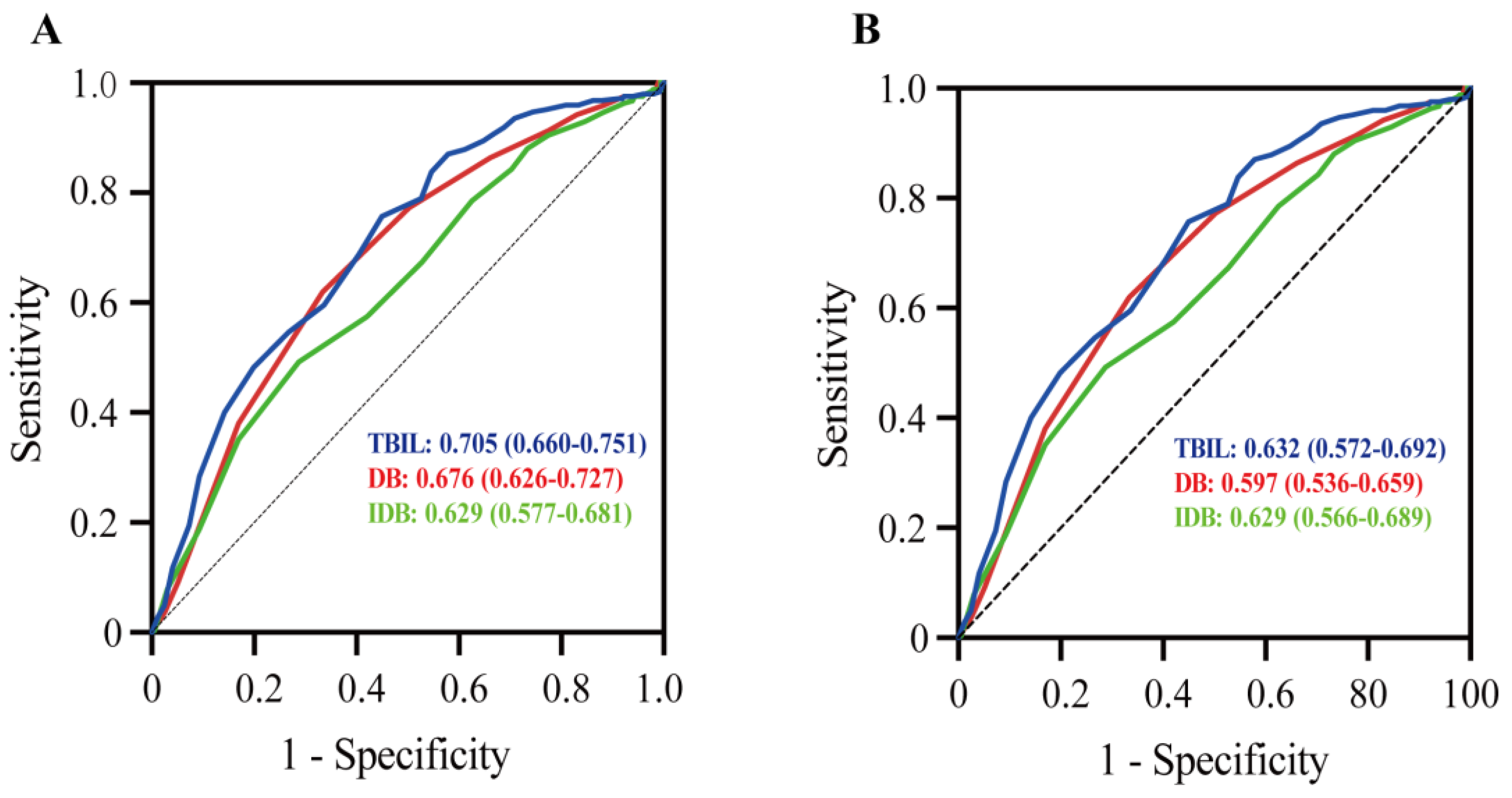
| TBIL | 11 (8–14) | 15 (11–24) | <0.001 | 13 (9–17) | 15 (11–21) | <0.001 |
| DB | 4 (3–5) | 5 (4–7) | <0.001 | 4 (3–7) | 5 (4–7) | 0.002 |
| IDB | 7 (5–9) | 8 (6–12) | <0.001 | 8 (5–11) | 10 (7–14) | <0.001 |
| ALT | 19 (14–26.75) | 19 (13–29) | 0.911 | 16 (11–23) | 19 (13.75–30.25) | 0.002 |
| AST | 22 (19–31) | 25 (20–32) | 0.010 | 22 (19–28) | 25 (21–34) | 0.005 |
| AKP | 82 (69–94) | 83 (70.25–98) | 0.214 | 72 (62.75–89) | 78 (62–93) | 0.219 |
| γ-GT | 30 (20–46) | 40.5 (23.35–58.5) | 0.002 | 30 (18–48) | 33 (23.5–50.5) | 0.122 |
| Stroke mechanisms | 0.493 | 0.284 | ||||
| Atherosclerotic, n (%) | 213 (86.2%) | 217 (87.9%) | 79 (49.1%) | 68 (42.2%) | ||
| Cardioembolic, n (%) | 23 (9.3%) | 25 (10.1%) | 63 (39.1%) | 78 (48.4%) | ||
| Lacunar, n (%) | 5 (2.0%) | 2 (0.8%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (0.6%) | ||
| Other causes, n (%) | 6 (2.4%) | 3 (1.2%) | 19 (11.8%) | 14 (8.7%) | ||
| Initial treatment in hospital | ||||||
| Anticoagulants | 45 (18.2%) | 67 (27.1%) | 0.018 | 78 (48.4%) | 81 (50.3%) | 0.824 |
| Antiplatelets | 220 (89.1%) | 136 (55.1%) | <0.001 | 107 (66.5%) | 93 (57.8%) | 0.135 |
| Variables | All Patients | TBIL Quartiles | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartile 1 n = 125 (4.0–9.0 μmol/L) | Quartile 2 n = 127 (10.0–13.0 μmol/L) | Quartile 3 n = 122 (14.0–20.0 μmol/L) | Quartile 4 n = 120 (21.0–59.0 μmol/L) | p-Value * | ||
| HT | 247 (50.0%) | 39 (31.2%) | 57 (44.9%) | 67 (54.9%) | 84 (70%) | <0.001 |
| Demographic parameters | ||||||
| Age (years) | 67 (58–74.75) | 65 (61.5–75) | 72 (59–76) | 63 (56.5–76.5) | 68.5 (58.75–76) | 0.191 |
| Sex (Male) | 352 (71.3%) | 92 (73.6%) | 80 (63.0%) | 88 (72.1%) | 92 (76.7%) | 0.097 |
| Vascular risk factors | ||||||
| History of atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 66 (13.4%) | 13 (10.4) | 15 (11.8%) | 19 (15.6%) | 19 (15.8%) | 0.501 |
| History of hypertension, n (%) | 302 (61.1%) | 72 (57.6%) | 78 (61.4%) | 78 (63.9%) | 74 (61.7%) | 0.782 |
| History of diabetes, n (%) | 130 (26.3%) | 42 (33.6%) | 31 (24.4%) | 30 (24.6%) | 27 (22.5%) | 0.191 |
| History of coronary heart disease, n (%) | 44 (8.9%) | 6 (4.8%) | 12 (9.4%) | 14 (11.5%) | 12 (10.0%) | 0.694 |
| Current smoking, n (%) | 169 (34.2%) | 55 (44%) | 39 (30.7%) | 23 (18.9%) | 52 (43.3%) | <0.001 |
| Current drinking, n (%) | 147 (29.8%) | 28 (24.3%) | 29 (22.8%) | 51 (41.8%) | 39 (32.5%) | 0.002 |
| mRS on admission, median (IQR) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (2–3) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (2–3) | 3 (2–3.5) | 0.172 |
| NIHSS on admission, median (IQR) | 7 (3–11) | 6 (3–10) | 6 (2–11) | 7 (3–11) | 8 (4–11) | 0.110 |
| Biochemistry and vital signs on admission | ||||||
| RBC | 4.465 (4.15–4.78) | 4.42 (4.15–4.74) | 4.42 (4.15–4.735) | 4.585 (4.18–4.89) | 4.54 (4.145–4.856) | 0.118 |
| WBC | 7.115 (5.735–8.886) | 7.27 (6.15–8.41) | 7.31 (6.03–8.93) | 7.6 (5.85–8.723) | 7.42 (6.25–9.255) | 0.858 |
| Hb | 138 (127–146) | 137 (128–144) | 135 (125.5–145) | 139 (127–150) | 139 (128–148.25) | 0.143 |
| PLT | 195 (162–230.75) | 208 (179.5–249) | 191 (163–222) | 195 (157–227) | 183 (152–213.5) | <0.001 |
| Glucose | 5.4 (4.6–6.8) | 5.1 (4.6–6.4) | 5.35 (4.8–6.9) | 5.2 (4.4–6.675) | 5.55 (4.7–6.975) | 0.219 |
| TBIL | 13 (9–19) | 8 (6–9) | 11 (10–13) | 15 (14–17.75) | 25 (21–29) | <0.001 |
| DB | 5 (3–7) | 3 (3–3) | 4 (4–5) | 6 (5–7) | 8 (5.75–10) | <0.001 |
| IDB | 8 (6–12) | 5 (4–5) | 7 (6–8) | 9 (8–11) | 14.5 (9–17.25) | <0.001 |
| ALT | 19 (14–28) | 18 (13–28) | 18 (14–26.75) | 20 (14–28) | 19 (14–28.75) | 0.706 |
| AST | 7 (5–10) | 22 (18–29) | 23 (19–30.75) | 28 (20–33) | 25.5 (20–32.75) | 0.022 |
| AKP | 83 (69–97) | 88 (77–102) | 83 (68–95) | 78 (67–94.5) | 81.5 (70.25–96) | 0.178 |
| γ-GT | 34 (22–53.25) | 29.5 (20–46.5) | 31 (19–43.75) | 40.5 (22.25–63) | 42.5 (26.75–58.25) | 0.003 |
| Stroke mechanisms | 0.306 | |||||
| Atherosclerotic, n (%) | 430 (87%) | 110 (88%) | 112 (88.2%) | 102 (83.6%) | 106 (88.3%) | |
| Cardioembolic, n (%) | 48 (9.7%) | 9 (7.2%) | 10 (7.9%) | 17 (13.9%) | 12 (10%) | |
| Lacunar, n (%) | 7 (1.4%) | 4 (3.2%) | 1 (0.8%) | 2 (1.6%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Other causes, n (%) | 9 (1.8%) | 2 (1.6%) | 4 (3.1%) | 1 (0.8%) | 2 (1.7%) | |
| Initial treatment in hospital | ||||||
| Anticoagulants | 112 (22.7%) | 30 (24.0%) | 31 (24.4%) | 24 (19.7%) | 27 (22.5) | 0.808 |
| Antiplatelets | 117 (23.7%) | 29 (23.2%) | 33 (26.0%) | 31 (25.4%) | 24 (20.0%) | 0.685 |
| Variables | All Patients | TBIL Quartiles | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartile 1 n = 76 (4.0–9.0 μmol/L) | Quartile 2 n = 89 (10.0–13.0 μmol/L) | Quartile 3 n = 87 (14.0–20.0 μmol/L) | Quartile 4 n = 70 (21.0–59.0 μmol/L) | p-Value * | ||
| HT | 161 (50.0%) | 25 (32.9%) | 44 (49.4%) | 44 (50.6%) | 48 (68.6%) | <0.001 |
| Demographic parameters | ||||||
| Age (years) | 70 (61–76.75) | 70 (61.75–76.25) | 69 (61–76) | 69 (62.5–77.5) | 70.5 (61–76) | 0.988 |
| Sex (Male) | 226 (70.2%) | 53 (69.7%) | 57 (64.0%) | 63 (72.4%) | 53 (75.7%) | 0.417 |
| Vascular risk factors | ||||||
| History of atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 126 (39.1%) | 24 (31.6%) | 29 (32.6%) | 35 (40.2%) | 38 (54.3%) | 0.017 |
| History of hypertension, n (%) | 220 (68.3%) | 49 (64.5%) | 66 (74.2%) | 61 (70.1%) | 44 (62.9%) | 0.386 |
| History of diabetes, n (%) | 68 (21.1%) | 17 (22.4%) | 24 (27.0%) | 14 (16.1%) | 13 (18.6%) | 0.987 |
| History of coronary heart disease, n (%) | 41 (12.7%) | 9 (11.8%) | 9 (10.1%) | 9 (10.3%) | 14 (20.0%) | 0.189 |
| Current smoking, n (%) | 125 (38.8%) | 34 (44.7%) | 33 (37.1%) | 35 (40.2%) | 23 (32.9%) | 0.502 |
| Current drinking, n (%) | 111 (34.5) | 30 (39.5%) | 23 (25.8%) | 36 (41.4%) | 22 (31.4%) | 0.117 |
| mRS on admission, median (IQR) | 5 (3–5) | 5 (4–5) | 4.5 (4–5) | 5 (4–5) | 5 (4–5) | 0.212 |
| NIHSS on admission, median (IQR) | 16 (11–22) | 17 (11–23.75) | 15 (10.25–18.75) | 16 (11.5–22) | 17 (11.5–24) | 0.491 |
| Biochemistry and vital signs on admission | ||||||
| RBC | 4.09 (3.65–4.47) | 3.84 (3.43–4.34) | 4.15 (3.67–4.46) | 4.13 (3.76–4.44) | 4.20 (3.90–4.74) | 0.006 |
| WBC | 9.635 (7.690–11.845) | 9.14 (7.12–11.03) | 10.04 (8.02–12.53) | 9.16 (7.43–11.86) | 10.62 (8.52–12.35) | 0.015 |
| Hb | 125 (112–138) | 115 (104–131.25) | 120 (109–136) | 129 (117.5–139.5) | 129.5 (121–142) | <0.001 |
| PLT | 181.75 (149.5–231) | 197 (155.75–253.5) | 190 (165–238) | 175 (143.5–222.5) | 166.5 (139.25–211.5) | 0.012 |
| Glucose | 7 (5.8–8.9) | 6.65 (5.6–8.65) | 7.05 (6.1–8.63) | 6.9 (5.8–8.95) | 7.7 (6.03–9.2) | 0.402 |
| TBIL | 14 (10–19) | 8 (6–9) | 11 (10–12) | 17 (15–18) | 25.5 (22–30.75) | <0.001 |
| DB | 4 (3–7) | 3 (2–3) | 4 (3–5) | 6 (4–7) | 8 (7–11) | <0.001 |
| IDB | 9 (6–13) | 5 (4–6) | 7 (6–8) | 10 (9–12) | 17 (15–20.75) | <0.001 |
| ALT | 17 (12–26) | 17 (12.75–26) | 16 (12–24.25) | 16 (13–28) | 19.5 (12–28.75) | 0.624 |
| AST | 24 (20–31) | 23 (20–30) | 23 (18–30) | 24 (20–33.5) | 25 (21–34) | 0.416 |
| AKP | 76 (63–91) | 67.5 (58–85.5) | 82 (70.75–94.25) | 76 (65–92) | 71.5 (57–89) | 0.010 |
| γ-GT | 31 (20.75–51) | 32 (20–49) | 31 (23–50.5) | 28.5 (18.75–44) | 33.5 (23.75–55) | 0.587 |
| Stroke mechanisms | 0.240 | |||||
| Atherosclerotic, n (%) | 147 (44.3%) | 42 (55.3%) | 45 (50.6%) | 33 (37.9%) | 27 (38.6%) | |
| Cardioembolic, n (%) | 141 (42.5%) | 28 (28.9%) | 34 (38.2%) | 42 (48.3%) | 37 (52.9%) | |
| Lacunar, n (%) | 1 (0.3%) | 1 (1.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Other causes, n (%) | 33 (20%) | 5 (5.1%) | 10 (12.6%) | 12 (13.8%) | 6 (8.6%) | |
| Initial treatment in hospital | ||||||
| Anticoagulants | 159 (48%) | 37 (38.1%) | 37 (41.5%) | 41 (46.1%) | 44 (62.9%) | 0.059 |
| Antiplatelets | 200 (40.5%) | 53 (54.6%) | 58 (65.2%) | 48 (55.2%) | 41 (58.6%) | 0.365 |
| sHT Cohort | tHT Cohort | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 * | Model 2 † | Model 3 # | Model 1 * | Model 2 † | Model 3 $ | |||||||
| Adjusted OR a (95%CI) | p-Value | Adjusted OR a (95%CI) | p-Value | Adjusted OR a (95%CI) | p-Value | Adjusted OR a (95%CI) | p-Value | Adjusted OR a (95%CI) | p-Value | Adjusted OR a (95%CI) | p-Value | |
| TBIL | ||||||||||||
| Q1 | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref | ||||||
| Q2 | 1.777 (1.148–2.735) | 0.030 | 1.917 (1.192–3.083) | 0.024 | 1.473 (0.799–2.720) | 0.298 | 1.985 (1.167–3.379) | 0.034 | 2.272 (1.214–4.251) | 0.031 | 1.703 (0.874–3.317) | 0.189 |
| Q3 | 2.697 (1.743–4.173) | <0.001 | 2.866 (1.782–4.493) | <0.001 | 2.092 (1.099–33.979) | 0.059 | 2.085 (1.223–3.556) | 0.023 | 2.172 (1.148–4.108) | 0.045 | 1.819 (0.920–3.598) | 0.149 |
| Q4 | 5.122 (3.245–8.084) | <0.001 | 5.285 (3.223–8.667) | <0.001 | 3.924 (2.051–7.505) | <0.001 | 4.443 (2.479–7.963) | <0.001 | 6.226 (3.073–12.614) | <0.001 | 3.557 (1.662–7.611) | 0.006 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Long, J.; Chen, Y.; He, J.; Huang, G. Roles of Bilirubin in Hemorrhagic Transformation of Different Types and Severity. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041471
Chen J, Chen Y, Lin Y, Long J, Chen Y, He J, Huang G. Roles of Bilirubin in Hemorrhagic Transformation of Different Types and Severity. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(4):1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041471
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jiahao, Yiting Chen, Yisi Lin, Jingfang Long, Yufeng Chen, Jincai He, and Guiqian Huang. 2023. "Roles of Bilirubin in Hemorrhagic Transformation of Different Types and Severity" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 4: 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041471
APA StyleChen, J., Chen, Y., Lin, Y., Long, J., Chen, Y., He, J., & Huang, G. (2023). Roles of Bilirubin in Hemorrhagic Transformation of Different Types and Severity. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(4), 1471. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041471




