Predicting Hepatotoxicity Associated with Low-Dose Methotrexate Using Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
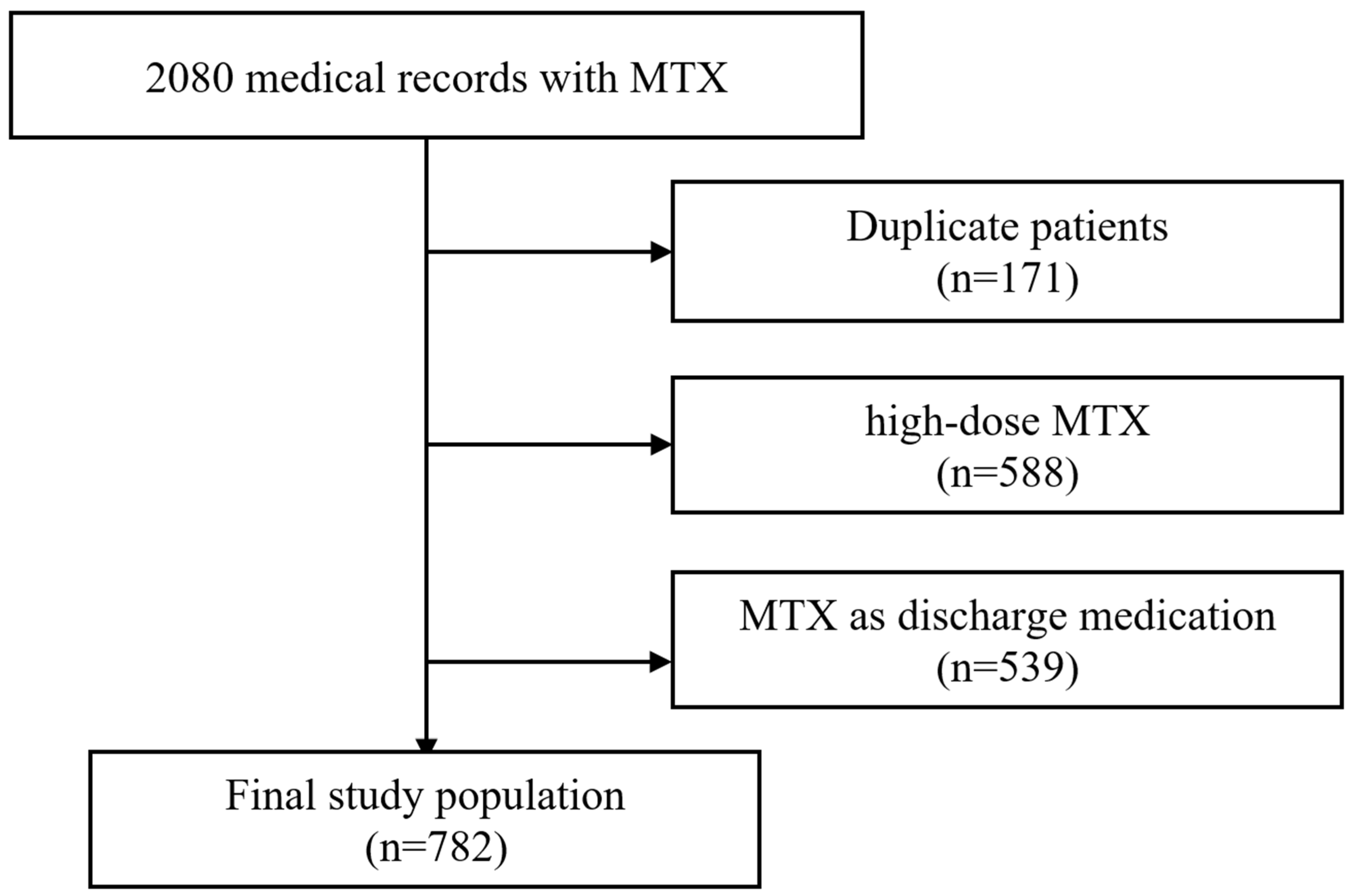
2.1. Study Setting and the Study Population
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Model Development
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Model Performance
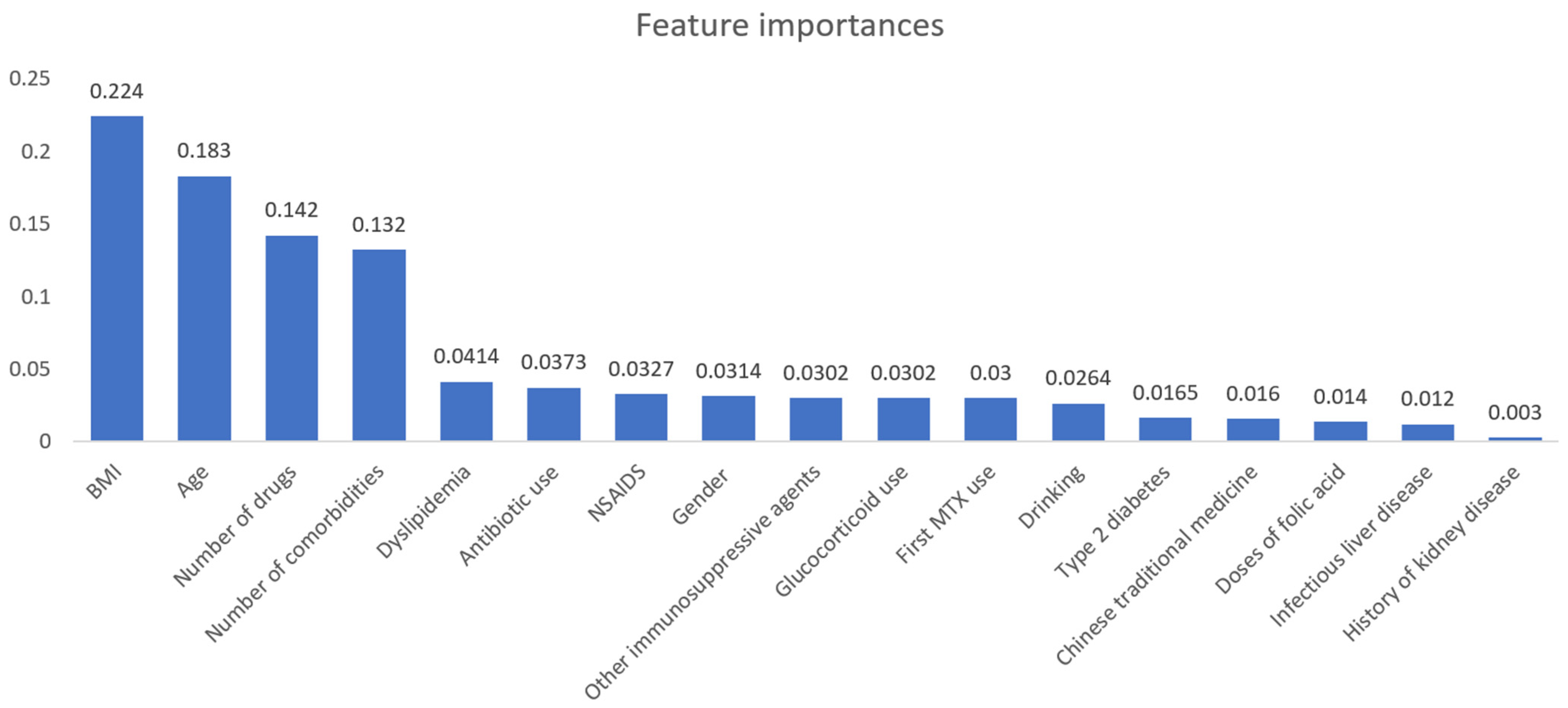
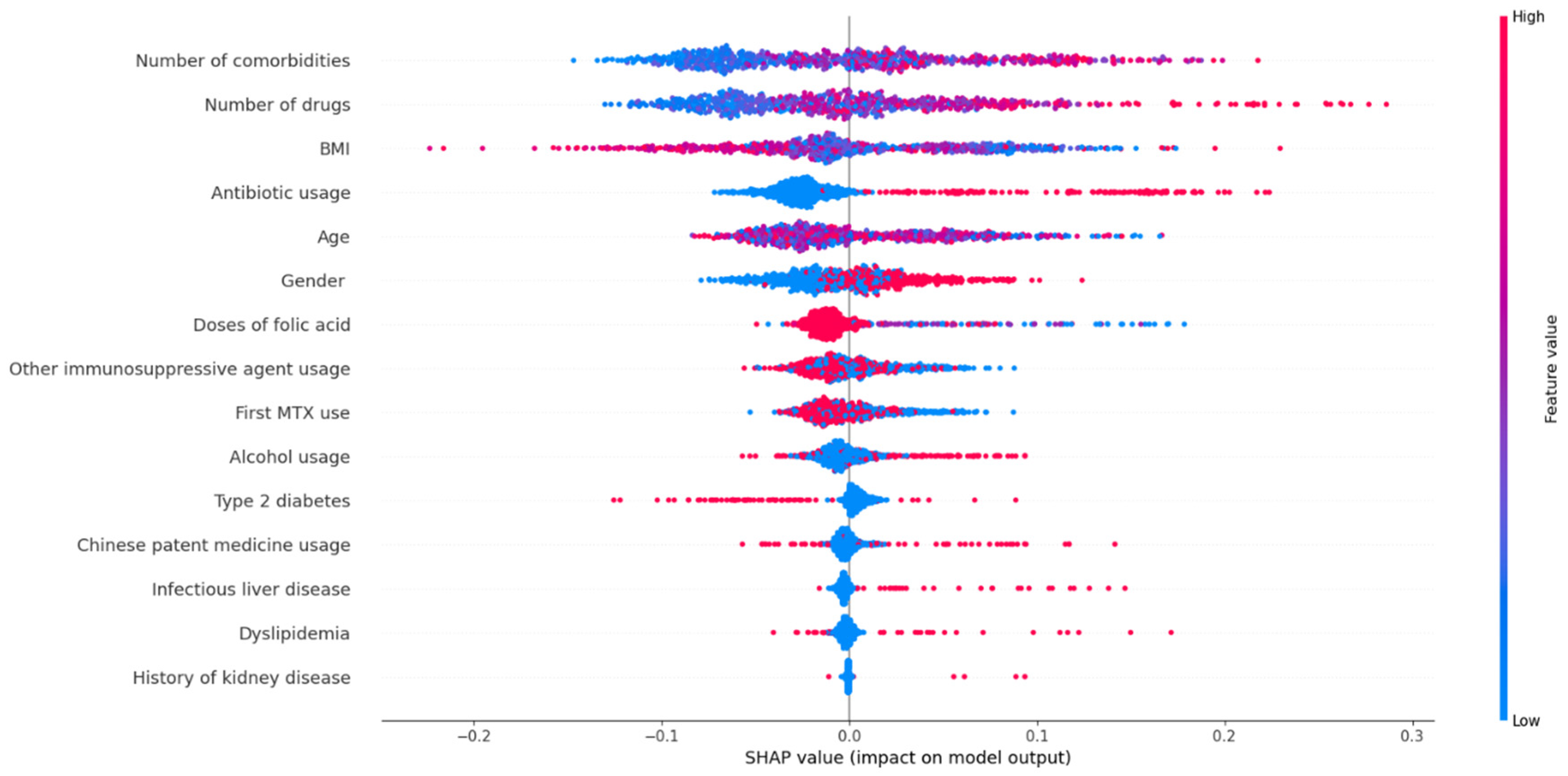
3.3. Hepatotoxicity and Risk Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- West, S.G. Methotrexate hepatotoxicity. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 1997, 23, 883–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farber, S. Chemotherapy in the treatment of leukemia and Wilm’s tumor. JAMA 1996, 198, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saag, K.G.; Teng, G.G.; Patkar, N.M.; Anuntiyo, J.; Finney, C.; Curtis, J.R.; Paulus, H.E.; Mudano, A.; Pisu, M.; Elkins-Melton, M.; et al. American college of rheumatology 2008 recommendations for the use of nonbiologic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2010, 59, 762–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, M.; Smith, E.; Hoy, D.; Carmona, L.; Wolfe, F.; Vos, T.; Williams, B.; Gabriel, S.; Lassere, M.; Johns, N.; et al. The global burden of rheumatoid arthritis: Estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 73, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, T.M.; Boytsov, N.N.; Zhang, X.; Schroeder, K.; Michaud, K.; Araujo, A.B. Prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in the United States adult population in healthcare claims databases, 2004–2014. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 37, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasoedova, E.; Crowson, C.S.; Kremers, H.M.; Therneau, T.M.; Gabriel, S.E. Is the incidence of rheumatoid arthritis rising?: Results from Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1955–2007. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 62, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icen, M.; Crowson, C.S.; McEvoy, M.T.; Dann, F.J.; Gabriel, S.E.; Maradit Kremers, H. Trends in incidence of adult-onset psoriasis over three decades: A population-based study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 60, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek, I.M.; Loring, B.; John, S.M. A systematic review of worldwide epidemiology of psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.S.; Chia, F.; Dans, L.; Harrison, A.; Hsieh, T.Y.; Jain, R.; Jung, S.M.; Kishimoto, M.; Kumar, A.; Leong, K.P.; et al. 2018 update of the APLAR recommendations for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameda, H.; Fujii, T.; Nakajima, A.; Koike, R.; Sagawa, A.; Kanbe, K.; Tomita, T.; Harigai, M.; Suzuki, Y. Japan college of rheumatology guideline for the use of methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2019, 29, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.A.; Guyatt, G.; Ogdie, A.; Gladman, D.D.; Deal, C.; Deodhar, A.; Dubreuil, M.; Dunham, J.; Husni, M.E.; Kenny, S.; et al. Special Article: 2018 American college of rheumatology/national psoriasis foundation guideline for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2019, 71, 2–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, A.; Aberer, E.; Bata-Csörgő, Z.; Caproni, M.; Dreher, A.; Frances, C.; Gläser, R.; Klötgen, H.W.; Landmann, A.; Marinovic, B.; et al. S2k guideline for treatment of cutaneous lupus erythematosus—Guided by the european dermatology forum (edf) in cooperation with the european academy of dermatology and venereology (eadv). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nast, A.; Spuls, P.I.; van der Kraaij, G.; Gisondi, P.; Paul, C.; Ormerod, A.D.; Saiag, P.; Smith, C.H.; Dauden, E.; de Jong, E.M.; et al. European S3-Guideline on the systemic treatment of psoriasis vulgaris—Update Apremilast and Secukinumab—EDF in cooperation with EADV and IPC. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 1951–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warris, L.T.; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.; Aarsen, F.K.; Pluijm, S.M.; Bierings, M.B.; van den Bos, C.; Zwaan, C.M.; Thygesen, H.H.; Tissing, W.J.; Veening, M.A.; et al. Hydrocortisone as an intervention for dexamethasone-induced adverse effects in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Results of a double-blind, randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2287–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakase, H.; Uchino, M.; Shinzaki, S.; Matsuura, M.; Matsuoka, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Saruta, M.; Hirai, F.; Hata, K.; Hiraoka, S.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for inflammatory bowel disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 305–353. [Google Scholar]
- Ramanan, A.V.; Dick, A.D.; Jones, A.P.; McKay, A.; Williamson, P.R.; Compeyrot-Lacassagne, S.; Hardwick, B.; Hickey, H.; Hughes, D.; Woo, P.; et al. Adalimumab plus Methotrexate for Uveitis in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1637–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bosch, F.; Kruithof, E.; Baeten, D.; De Keyser, F.; Mielants, H.; Veys, E.M. Effects of a loading dose regimen of three infusions of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor α (infliximab) in spondyloarthropathy: An open pilot study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2000, 59, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, B.; Kivelevitch, D.; Campa, M.; Menter, A. Palmoplantar pustular psoriasis unresponsive to the interleukin-1β antagonist canakinumab. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 41, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Li, G.G.; Liu, Q.; Niu, X.; Li, R.; Ma, H. Short-term efficacy and safety of IL-17, IL-12/23, and IL-23 inhibitors brodalumab, secukinumab, ixekizumab, ustekinumab, guselkumab, tildrakizumab, and risankizumab for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 10, 2546161. [Google Scholar]
- Kremer, J.M.; Kaye, G.I.; Kaye, N.W.; Ishak, K.G.; Axiotis, C.A. Light and electron microscopic analysis of sequential liver biopsy samples from rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving long-term methotrexate therapy. Followup over long treatment intervals and correlation with clinical and laboratory variables. Arthritis Rheum. 1995, 8, 1194–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, J.R.; Beukelman, T.; Onofrei, A.; Cassell, S.; Greenberg, J.D.; Kavanaugh, A.; Reed, G.; Strand, V.; Kremer, J.M. Elevated liver enzyme tests among patients with rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis treated with methotrexate and/or leflunomide. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Choe, J.Y.; Kim, S.K. Assessment of liver fibrosis by transient elastography in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with methotrexate. Joint Bone Spine 2010, 77, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiting-O’Keefe, Q.E.; Fye, K.H.; Sack, K.D. Methotrexate and histologic hepatic abnormalities: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Med. 1991, 90, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalb, R.E.; Strober, B.; Weinstein, G.; Lebwohl, M. Methotrexate and psoriasis: National Psoriasis Foundation Consensus Conference. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009, 60, 824–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clary, D.D.; Reid, A.T.; Kiani, R.; Fanciullo, J. Methotrexate Hepatotoxicity Monitoring Guidelines in Psoriasis and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Is There a Consensus? South Dak. Med. 2021, 74, 363–366. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospect. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteva, A.; Kuprel, B.; Novoa, R.A.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Blau, H.M.; Thrun, S. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 2017, 542, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunčar, G.; Kukar, M.; Notar, M.; Brvar, M.; Černelč, P.; Notar, M.; Notar, M. An application of machine learning to haematological diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Yu, H.Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Yao, Q.; Wu, S.N.; Yin, C.; Fu, B.; Zhu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xing, Y.; et al. Electronic health record driven prediction for gestational diabetes mellitus in early pregnancy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, R.C. Machine learning in medicine. Circulation 2015, 132, 1920–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, B.A.; Navar, A.M.; Carter, R.E. Moving beyond regression techniques in cardiovascular risk prediction: Applying machine learning to address analytic challenges. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 1805–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.; Zverinski, D.; Pfahringer, B.; Kempfert, J.; Kuehne, T.; Sündermann, S.H.; Stamm, C.; Hofmann, T.; Falk, V.; Eickhoff, C. Machine learning for real-time prediction of complications in critical care: A retrospective study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazaud, C.; Fardet, L. Relative risk of and determinants for adverse events of methotrexate prescribed at a low dose: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N.P.; Maddur, H.; Russo, M.W.; Wong, R.J.; Reddy, K.R.; Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, 878–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekhoven, D.J.; Buhlmann, P. MissForest–nonparametric missing value imputation for mixed-type data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jung, C. GBDT-MO: Gradient-Boosted Decision Trees for Multiple Outputs. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 3156–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Su, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, B.; Sun, Y.; Gao, W.; Fu, Y. Real-time biomechanical modelling of the liver using LightGBM model. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2022, 18, e2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, J.T.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. CatBoost for big data: An interdisciplinary review. J. Big Data 2020, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, S.; Yang, J. Adaboost Algorithm in Artificial Intelligence for Optimizing the IRI Prediction Accuracy of Asphalt Concrete Pavement. Sensors 2021, 21, 5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Q.; Peng, D.; Lin, H.; Zhan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhuo, S. Rapid identification of human ovarian cancer in second harmonic generation images using radiomics feature analyses and tree-based pipeline optimization tool. J. Biophotonics 2020, 13, e202000050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Zhang, K.C.; Wei, B.; Chen, L. Status quo and future prospects of artificial neural network from the perspective of gastroenterologists. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 2681–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, C.M.; Chong, V.H.; Earnest, A.; Yang, W.L. Prevalence and risk factors for methotrexate hepatoxicity in Asian patients with psoriasis. World J. Hepatol. 2013, 5, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amital, H.; Arnson, Y.; Chodick, G.; Shalev, V. Hepatotoxicity rates do not differ in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis treated with methotrexate. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanoh, S. In Vitro and in Vivo Assessments of Drug-induced Hepatotoxicity and Drug Metabolism in Humans. Yakugaku Zasshi 2015, 135, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballet, F. Hepatotoxicity in drug development: Detection, significance and solutions. J. Hepatol. 1997, 2, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, Y.; Duran, H.E.; Durmaz, L.; Taslimi, P.; Beydemir, Ş.; Gulçin, İ. The Influence of Some Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs on Metabolic Enzymes of Aldose Reductase, Sorbitol Dehydrogenase, and α-Glycosidase: A Perspective for Metabolic Disorders. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 190, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcum, Z.A.; Arbogast, K.L.; Behrens, M.C.; Logsdon, M.W.; Francis, S.D.; Jeffery, S.M.; Aspinall, S.L.; Hanlon, J.T.; Handler, S.M. The utility of an adverse drug event trigger tool in veterans affairs nursing facilities. Consult. Pharm. 2013, 28, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Qin, Z.; Zhan, M.; Chen, Z.; Wu, B.; Xu, T. Validating the Chinese geriatric trigger tool and analysing adverse drug event associated risk factors in elderly Chinese patients: A retrospective review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232095. [Google Scholar]
- Einar, S.B. Drug-induced liver injury due to antibiotics. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 617–623. [Google Scholar]
- Leitner, J.M.; Graninger, W.; Thalhammer, F. Hepatotoxicity of antibacterials: Pathomechanisms and clinical. Infection 2010, 38, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mindikoglu, A.L.; Magder, L.S.; Regev, A. Outcome of liver transplantation for drug-induced acute liver failure in the United States: Analysis of the United Network for Organ Sharing database. Liver Transplant. 2009, 15, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornsson, E.; Olsson, R. Outcome and prognostic markers in severe drug-induced liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 42, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, R.J.; Lucena, M.I.; Fernández, M.C.; Pelaez, G.; Pachkoria, K.; García-Ruiz, E.; García-Muñoz, B.; González-Grande, R.; Pizarro, A.; Durán, J.A.; et al. Drug-induced liver injury: An analysis of 461 incidences submitted to the Spanish registry over a 10-year period. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, A.; Lunt, M.; Verstappen, S. Quantifying the hepatotoxic risk of alcohol consumption in patients with rheumatoid arthritis taking methotrexate. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1509–1514. [Google Scholar]
- Kremer, J.M.; Alarcón, G.S.; Lightfoot, R.W., Jr.; Willkens, R.F.; Furst, D.E.; Williams, H.J.; Dent, P.B.; Weinblatt, M.E. Methotrexate for rheumatoid arthritis. Suggested guidelines for monitoring liver toxicity. Arthritis Rheum. 1994, 37, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, K.; McDonald, H.; Pullar, T.; Taggart, A.; Chalmers, R.; Oliver, S.; Mooney, J.; Somerville, M.; Bosworth, A.; Kennedy, T.; et al. BSR/BHPR guideline for disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) therapy in consultation with the British Association of Dermatologists. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 924–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, S.M.; Fisher, J.; Clarke, S.; Montgomery, B.; Jones, P.W.; Saklatvala, J.; Dawes, P.T.; Shadforth, M.F.; Hothersall, T.E.; Hassell, A.B.; et al. Do patients with rheumatoid arthritis established on methotrexate and folic acid 5 mg daily need to continue folic acid supplements long term? Rheumatology 2000, 39, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.A.; Furst, D.E.; Bharat, A.; Curtis, J.R.; Kavanaugh, A.F.; Kremer, J.M.; Moreland, L.W.; O’Dell, J.; Winthrop, K.L.; Beukelman, T.; et al. 2012 Update of the 2008 American College of Rheumatology Recommendations for the Use of Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs and Biologic Agents in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, D.A.; Will, R.K.; Hoffman, D.M.; Laing, B.; Blackbourn, S.J. Exacerbation of rheumatoid arthritis in patients treated with methotrexate after administration of folinic acid. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1991, 50, 913–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tishler, M.; Caspi, D.; Fishel, B.; Yaron, M. The effects of leucovorin (folinic acid) on methotrexate therapy in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1988, 31, 906–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, B.F.; Hanson, D.E.; Sheaff, A.K. Strength training as a countermeasure to aging muscle and chronic disease. Sport. Med. 2011, 41, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alım, Z.; Kılıç, D.; Demir, Y. Some indazoles reduced the activity of human serum paraoxonase 1, an antioxidant enzyme: In vitro inhibition and molecular modeling studies. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 125, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lee, D.S.; An, T.H.; Park, H.J.; Kim, W.K.; Bae, K.H.; Oh, K.J. Metabolic Spectrum of Liver Failure in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: From NAFLD to NASH to HCC. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sever, B.; Altıntop, M.D.; Demir, Y.; Akalın-Çiftçi, G.; Beydemir, Ş.; Özdemir, A. Design, synthesis, in vitro and in silico investigation of aldose reductase inhibitory effects of new thiazole-based compounds. Bioorganic Chem. 2020, 102, 104110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langman, G.; Hall, P.M.; Todd, G. Role of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in methotrexate-induced liver injury. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2001, 16, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaudié, H.; Sbidian, E.; Paul, C.; Maza, A.; Gallini, A.; Aractingi, S.; Aubin, F.; Bachelez, H.; Cribier, B.; Joly, P.; et al. Methotrexate in psoriasis: A systematic review of treatment modalities, incidence, risk factors and monitoring of liver toxicity. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25 (Suppl. S2), 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Total (n = 782) | Training Set (n = 625) | Testing Set (n = 157) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatotoxicity | ||||
| Yes | 279 | 223 | 56 | 1.00 |
| No | 503 | 402 | 101 | |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 352 | 281 | 71 | 1.00 |
| Female | 430 | 344 | 86 | |
| Age (years) | 47.85 ± 15.56 (10–87) | 47.67 ± 15.63 (14–78) | 48.58 ± 15.33 (10–87) | 0.40 |
| First time taking MTX | ||||
| Yes | 501 | 400 | 101 | 1.00 |
| No | 272 | 225 | 56 | |
| Body mass index * (kg/m2) | Original data | |||
| 729 | 586 | 143 | ||
| 22.72 ± 3.91 (13.27–41.14) | 22.78 ± 3.94 (13.27–41.14) | 22.45 ± 3.77 (13.74–37.13) | 0.71 | |
| Processed data | ||||
| 22.68 ± 3.81 (13.27–41.14) | 22.77 ± 3.86 (13.27–41.14) | 22.38 ± 3.23 (13.74–37.13) | 0.37 | |
| Alcohol use | ||||
| Yes | 164 | 130 | 34 | 0.83 |
| No | 618 | 495 | 123 | |
| History of kidney disease | ||||
| Yes | 6 | 5 | 1 | 1.00 |
| No | 776 | 620 | 156 | |
| History of liver disease | ||||
| Yes | 32 | 23 | 9 | 0.26 |
| No | 750 | 602 | 148 | |
| Number of comorbidities | 4.98 ± 2.97 (1–17) | 4.90 ± 2.90 (1–17) | 5.28 ± 3.23 (1–16) | 0.69 |
| Type 2 diabetes | ||||
| Yes | 69 | 59 | 10 | 0.27 |
| No | 713 | 566 | 147 | |
| Hyperlipidemia | ||||
| Yes | 41 | 30 | 11 | 0.32 |
| No | 741 | 595 | 146 | |
| Folate supplementation | ||||
| Yes | 723 | 575 | 148 | 0.40 |
| No | 59 | 50 | 9 | |
| Doses of folic acid/week | 9.19 ± 3.33 (0–35) | 9.16 ± 3.39 (0–35) | 9.29 ± 3.07 (0–15) | 0.05 |
| NSAIDs use | ||||
| Yes | 276 | 231 | 45 | 0.06 |
| No | 506 | 394 | 112 | |
| Glucocorticoid use | ||||
| Yes | 441 | 350 | 91 | 0.72 |
| No | 341 | 275 | 66 | |
| Antibiotics use | ||||
| Yes | 153 | 117 | 36 | 0.26 |
| No | 629 | 508 | 121 | |
| Other immunosuppressive agent use | ||||
| Yes | 446 | 351 | 95 | 0.37 |
| No | 336 | 274 | 62 | |
| Number of medications | 5.91 ± 2.93 (0–24) | 5.97 ± 2.93 (0–24) | 5.67 ± 2.92 (0–18) | 0.92 |
| Chinese patent medicines use | ||||
| Yes | 68 | 56 | 12 | 0.75 |
| No | 714 | 569 | 145 | |
| Models | Precision | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LightGBM | 40.00% | 59.87% | 25.00% | 20.79% | 25.00% | 30.77% |
| GBDT | 50.94% | 59.24% | 41.07% | 30.69% | 41.07% | 41.82% |
| Adaboost | 51.35% | 64.33% | 33.93% | 17.81% | 33.93% | 40.86% |
| Catboost | 42.86% | 60.51% | 32.14% | 23.76% | 32.14% | 36.73% |
| XGboost | 43.18% | 60.51% | 33.93% | 24.75% | 33.93% | 38.00% |
| Random Forest | 50.00% | 64.33% | 32.14% | 17.82% | 32.14% | 39.13% |
| TPOT | 43.90% | 61.15% | 32.14% | 22.77% | 32.14% | 37.11% |
| ANN | 36.36% | 62.42% | 7.14% | 6.93% | 7.14% | 11.94% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Q.; Wang, H.; Xu, T. Predicting Hepatotoxicity Associated with Low-Dose Methotrexate Using Machine Learning. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041599
Hu Q, Wang H, Xu T. Predicting Hepatotoxicity Associated with Low-Dose Methotrexate Using Machine Learning. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(4):1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041599
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Qiaozhi, Hualing Wang, and Ting Xu. 2023. "Predicting Hepatotoxicity Associated with Low-Dose Methotrexate Using Machine Learning" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 4: 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041599
APA StyleHu, Q., Wang, H., & Xu, T. (2023). Predicting Hepatotoxicity Associated with Low-Dose Methotrexate Using Machine Learning. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(4), 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041599






