Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Monitoring
Abstract
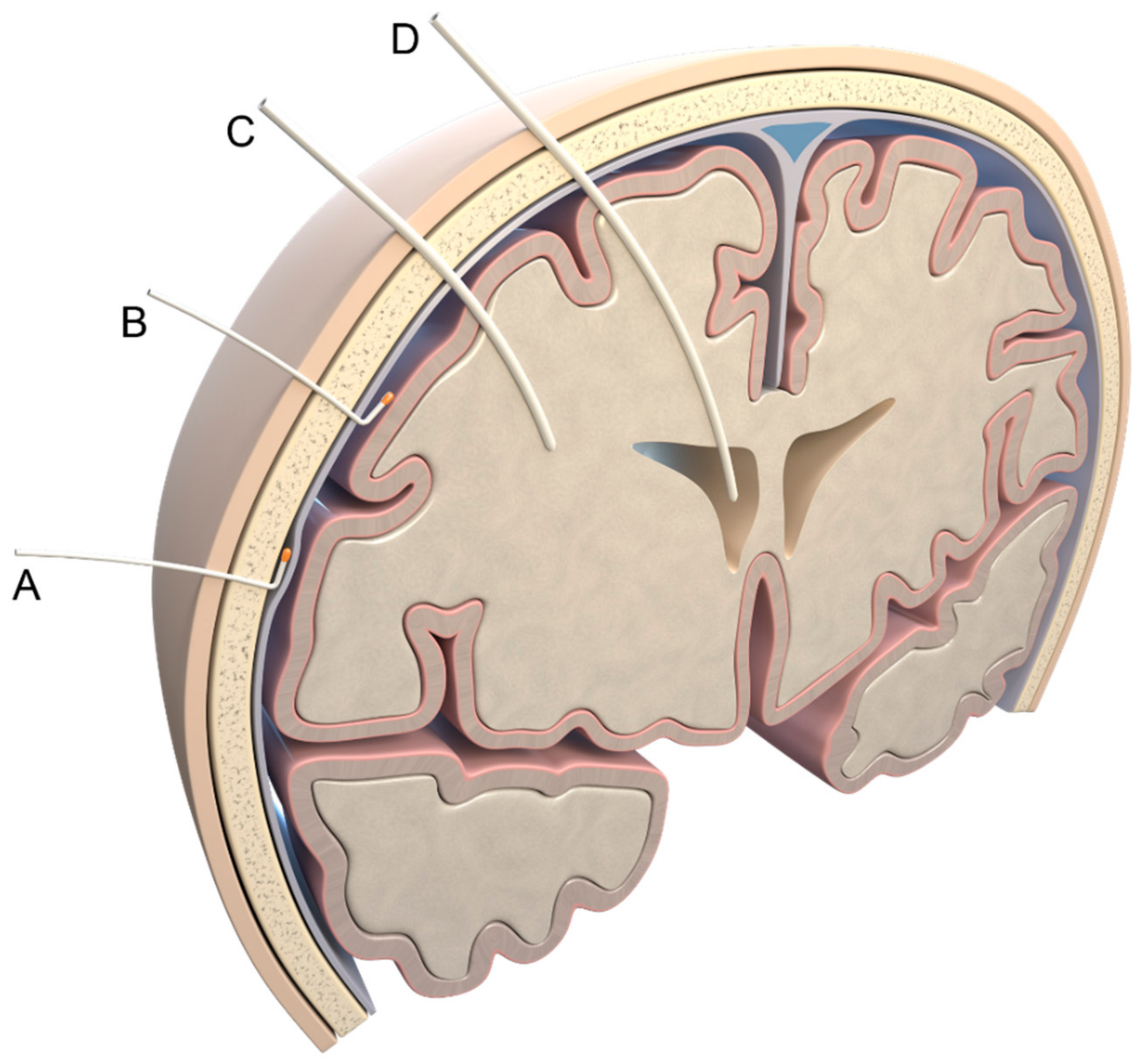
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Approaches of Non-Invasive Measurements
3.1. Methods Based on Physiological Parameters and Ultrasound/Doppler
3.1.1. Transcranial Doppler
3.1.2. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
3.1.3. Combined Methods
3.1.4. Fontanelle in Newborns and Infants
3.1.5. CO2
3.1.6. Micromotions of the Skull/Mechanical Extensometer
3.1.7. Other Approaches: Eigenfrequency, Microwaves, and Ultrasound
3.2. Computed Tomography (CT) and MR (Magnet Resonance) Imaging-Based Methods
3.2.1. CT
3.2.2. MR Methods
3.3. Electrophysiological Properties
3.3.1. Dielectric/Electric Impedance Methods
3.3.2. Electroencephalography (EEG)
3.4. Ophthalmic Methods
3.4.1. Ophthalmic Artery and Ophthalmic Arterioles
3.4.2. Retinal Vein Pulsation
3.4.3. Ultrasound of ONSD
3.4.4. CT and MRI of ONSD
3.4.5. Ophthalmoscopy
3.4.6. Optical Coherence Tomography
3.4.7. Visual-Evoked Potentials
3.4.8. Pupils
3.5. Otic Methods
3.5.1. Tympanic Membrane and Cochlear Microphonic Potential
3.5.2. Otic Transcranial Acoustic Signals
3.6. Short Summary of Instruments and Devices Tested in Clinical Practice
4. Conclusions
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Research Gaps
4.3. Future Perspectives
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Monro, A. Observations on the Structure and Function of the Nervous System, (Folio, Creech, Edinb. Johnson). Lond. Med. J. 1783, 4, 113–135. [Google Scholar]
- Weed, L.H. Some limitations of the monro-kellie hypothesis. Arch. Surg. 1929, 18, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harary, M.; Dolmans, R.G.; Gormley, W. Intracranial Pressure Monitoring—Review and Avenues for Development. Sensors 2018, 18, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janny, P. La Pression Intracranienne Chez l’homme: Méthode d’enregistrement: Etude de Ses Variations et de Ses Rapports Avec Les Signes Cliniques et Ophtalmologiques. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Paris, Paris, France, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Guillaume, J.; Janny, P. Continuous intracranial manometry; importance of the method and first results. Rev. Neurol. 1951, 84, 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, N. Continuous Recording and Control of Ventricular Fluid Pressure in Neurosurgical Practice. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. Suppl. 1960, 36, 1–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldensohn, E.S.; Whitehead, R.W.; Parry, T.M.; Spencer, J.N.; Grover, R.F.; Draper, W.B. Studies on Diffusion Respiration: IX. Effect of Diffusion Respiration and High Concentrations of CO2 on Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure of Anesthetized Dogs. Am. J. Physiol.-Leg. Content 1951, 165, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, H.W.; Espey, F.F.; Kristoff, F.V.; Evans, J.P. Observations on the Interrelationships of Intracranial Pressure and Cerebral Blood Flow. J. Neurosurg. 1951, 8, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.P. Experimental and clinical observations on rising intracranial pressure. Arch. Surg. 1951, 63, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.P. Increased Intracranial Pressure: Its Physiology and Management. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 1956, 36, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czosnyka, M. Monitoring and Interpretation of Intracranial Pressure. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, R. External Ventricular Drains: Management and Complications. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2015, 6, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, V.M.; O’Neill, B.R.; Jho, D.; Whiting, D.M.; Oh, M.Y. The History of External Ventricular Drainage: Historical Vignette. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 120, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, W.; Cheng, F.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, J.; Hu, J.; Ren, G. External Ventricular Drains versus Intraparenchymal Intracranial Pressure Monitors in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Prospective Observational Study. World Neurosurg. 2015, 83, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, L.A.; Andrews, P.J.D. Monitoring the Injured Brain: ICP and CBF. Br. J. Anaesth. 2006, 97, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, A.; Pandit, V.; Fennell, V.; Jones, T.; Joseph, B.; O’Keeffe, T.; Friese, R.S.; Rhee, P. Intracranial Pressure Monitor in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 194, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocchetti, N.; Picetti, E.; Berardino, M.; Buki, A.; Chesnut, R.M.; Fountas, K.N.; Horn, P.; Hutchinson, P.J.; Iaccarino, C.; Kolias, A.G.; et al. Clinical Applications of Intracranial Pressure Monitoring in Traumatic Brain Injury: Report of the Milan Consensus Conference. Acta Neurochir. 2014, 156, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli, S.; Peitz, G.; Ares, W.; Hafeez, S.; Grandhi, R. Complications of Invasive Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Devices in Neurocritical Care. Neurosurg. Focus 2017, 43, E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Servadei, F.; Picetti, E. Intracranial Pressure Monitoring and Outcome in Traumatic Brain Injury: The Probe Does Matter? World Neurosurg. 2015, 83, 732–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Du, H.; Yin, L.; He, M.; Hao, B.; Chen, L. Which Side of Lateral Ventricles to Choose during External Ventricular Drainage in Patients with Intraventricular Hemorrhage: Ipsilateral or Contralateral? J. Surg. Res. 2013, 183, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, M.; Antes, S.; Leonhardt, S.; Schmitt, M.; Orakcioglu, B.; Sakowitz, O.W.; Eymann, R. Telemetric ICP Measurement with the First CE-Approved Device: Data from Animal Experiments and Initial Clinical Experiences. In Intracranial Pressure and Brain Monitoring XIV; Schuhmann, M.U., Czosnyka, M., Eds.; Acta Neurochirurgica Supplementum; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2012; Volume 114, pp. 111–116. ISBN 978-3-7091-0955-7. [Google Scholar]
- Lilja, A.; Andresen, M.; Hadi, A.; Christoffersen, D.; Juhler, M. Clinical Experience with Telemetric Intracranial Pressure Monitoring in a Danish Neurosurgical Center. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2014, 120, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.J.; Freimann, F.B.; von der Brelie, C.; Rohde, V.; Schatlo, B. Test-Retest Reliability of Outpatient Telemetric Intracranial Pressure Measurements in Shunt-Dependent Patients with Hydrocephalus and Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension. World Neurosurg. 2019, 131, e74–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antes, S.; Stadie, A.; Müller, S.; Linsler, S.; Breuskin, D.; Oertel, J. Intracranial Pressure–Guided Shunt Valve Adjustments with the Miethke Sensor Reservoir. World Neurosurg. 2018, 109, e642–e650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shellock, F.G.; Knebel, J.; Prat, A.D. Evaluation of MRI Issues for a New Neurological Implant, the Sensor Reservoir. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 31, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Koo, B.-N.; Choi, S.H.; Park, K.; Kim, M.-S. Ultrasonographic Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter for Predicting Elevated Intracranial Pressure during Laparoscopic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Surg. Endosc. 2018, 32, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistical Methods for Assessing Agreement between Two Methods of Clinical Measurement. Lancet Lond. Engl. 1986, 1, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlin, T.; Murray-Krezan, C.; Yonas, H. Comparison of Parenchymal and Ventricular Intracranial Pressure Readings Utilizing a Novel Multi-Parameter Intracranial Access System. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Talving, P.; Karamanos, E.; Teixeira, P.G.; Skiada, D.; Lam, L.; Belzberg, H.; Inaba, K.; Demetriades, D. Intracranial Pressure Monitoring in Severe Head Injury: Compliance with Brain Trauma Foundation Guidelines and Effect on Outcomes: A Prospective Study: Clinical Article. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 119, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padayachy, L.C. Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Assessment. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2016, 32, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagher, O. Editorial: Treatment Guidelines from the Brain Trauma Foundation. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 119, 1246–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alali, A.S.; Fowler, R.A.; Mainprize, T.G.; Scales, D.C.; Kiss, A.; de Mestral, C.; Ray, J.G.; Nathens, A.B. Intracranial Pressure Monitoring in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: Results from the American College of Surgeons Trauma Quality Improvement Program. J. Neurotrauma 2013, 30, 1737–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koizumi, H.; Suehiro, E.; Fujiyama, Y.; Sugimoto, K.; Inoue, T.; Suzuki, M. Update on Intensive Neuromonitoring for Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury: A Review of the Literature and the Current Situation. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2014, 54, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eide, P.; Holm, S.; Sorteberg, W. Simultaneous Monitoring of Static and Dynamic Intracranial Pressure Parameters from Two Separate Sensors in Patients with Cerebral Bleeds: Comparison of Findings. Biomed. Eng. OnLine 2012, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reid, A.; Marchbanks, R.J.; Bateman, D.E.; Martin, A.M.; Brightwell, A.P.; Pickard, J.D. Mean Intracranial Pressure Monitoring by a Non-Invasive Audiological Technique: A Pilot Study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1989, 52, 610–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reid, A.; Marchbanks, R.J.; Burge, D.M.; Martin, A.M.; Bateman, D.E.; Pickard, J.D.; Brightwell, A.P. The Relationship between Intracranial Pressure and Tympanic Membrane Displacement. Br. J. Audiol. 1990, 24, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mládek, A.; Gerla, V.; Šeba, P.; Kolář, V.; Skalický, P.; Whitley, H.; Lhotská, L.; Beneš, V.; Bradáč, O. From Head Micro-Motions towards CSF Dynamics and Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullan, J.T.; Knight, W.A.; Clark, J.F.; Beyette, F.R.; Pancioli, A. Time-Critical Neurological Emergencies: The Unfulfilled Role for Point-of-Care Testing. Int. J. Emerg. Med. 2010, 3, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salman, M.S. Can Intracranial Pressure Be Measured Non-Invasively? Lancet 1997, 350, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firsching, R.; Schütze, M.; Motschmann, M.; Behrens-Baumann, W.; Meyer-Schwickerath, R. Non-Invasive Measurement of Intracranial Pressure. Lancet 1998, 351, 523–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayreh, S.S. Non-Invasive Measurement of Intracranial Pressure. Lancet 1998, 351, 524–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A. Non-Invasive Measurement of Intracranial Pressure. Lancet 1998, 351, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, T.H.; Gibson, C.R.; Pass, A.F.; Kramer, L.A.; Lee, A.G.; Fogarty, J.; Tarver, W.J.; Dervay, J.P.; Hamilton, D.R.; Sargsyan, A.; et al. Optic Disc Edema, Globe Flattening, Choroidal Folds, and Hyperopic Shifts Observed in Astronauts after Long-Duration Space Flight. Ophthalmology 2011, 118, 2058–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alperin, N.; Bagci, A.M. Spaceflight-Induced Visual Impairment and Globe Deformations in Astronauts Are Linked to Orbital Cerebrospinal Fluid Volume Increase. In Intracranial Pressure & Neuromonitoring XVI; Heldt, T., Ed.; Acta Neurochirurgica Supplement; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 126, pp. 215–219. ISBN 978-3-319-65797-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ocamoto, G.N.; Russo, T.L.; Mendes Zambetta, R.; Frigieri, G.; Hayashi, C.Y.; Brasil, S.; Rabelo, N.N.; Spavieri Júnior, D.L. Intracranial Compliance Concepts and Assessment: A Scoping Review. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 756112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raboel, P.H.; Bartek, J.; Andresen, M.; Bellander, B.M.; Romner, B. Intracranial Pressure Monitoring: Invasive versus Non-Invasive Methods—A Review. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 950393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evensen, K.B.; Eide, P.K. Measuring Intracranial Pressure by Invasive, Less Invasive or Non-Invasive Means: Limitations and Avenues for Improvement. Fluids Barriers CNS 2020, 17, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robba, C.; Bacigaluppi, S.; Cardim, D.; Donnelly, J.; Bertuccio, A.; Czosnyka, M. Non-Invasive Assessment of Intracranial Pressure. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2016, 134, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbachev, V.I.; Likholetova, N.V. Non-invasive monitoring of intracranial pressure. Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. Im. S. S. Korsakova 2014, 114, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Hawryluk, G.W.J.; Citerio, G.; Hutchinson, P.; Kolias, A.; Meyfroidt, G.; Robba, C.; Stocchetti, N.; Chesnut, R. Intracranial Pressure: Current Perspectives on Physiology and Monitoring. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 48, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, D.S.; Sahu, S.; Swain, A.; Kant, S. Intracranial Pressure Monitoring: Gold Standard and Recent Innovations. World J. Clin. Cases 2019, 7, 1535–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, D.G.; Czosnyka, M. Brain Monitoring: Do We Need a Hole? An Update on Invasive and Noninvasive Brain Monitoring Modalities. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 795762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, J.B.; Shiloh, A.L.; Savel, R.H.; Eisen, L.A. Non-Invasive Methods of Estimating Intracranial Pressure. Neurocrit. Care 2011, 15, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robba, C.; Frigieri, G.; Brasil, S.; Taccone, F.S. Early Prognostic Value of Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Methods in Brain-Injured Patients. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 48, 1812–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, S.M.; Tran, A.; Cheng, W.; Rochwerg, B.; Taljaard, M.; Kyeremanteng, K.; English, S.W.; Sekhon, M.S.; Griesdale, D.E.G.; Dowlatshahi, D.; et al. Diagnosis of Elevated Intracranial Pressure in Critically Ill Adults: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ 2019, 366, l4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cardim, D.; Griesdale, D.E.; Ainslie, P.N.; Robba, C.; Calviello, L.; Czosnyka, M.; Smielewski, P.; Sekhon, M.S. A Comparison of Non-Invasive versus Invasive Measures of Intracranial Pressure in Hypoxic Ischaemic Brain Injury after Cardiac Arrest. Resuscitation 2019, 137, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, M.J.; Rosner, S.D.; Johnson, A.H. Cerebral Perfusion Pressure: Management Protocol and Clinical Results. J. Neurosurg. 1995, 83, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dias, C.; Silva, M.J.; Pereira, E.; Monteiro, E.; Maia, I.; Barbosa, S.; Silva, S.; Honrado, T.; Cerejo, A.; Aries, M.J.H.; et al. Optimal Cerebral Perfusion Pressure Management at Bedside: A Single-Center Pilot Study. Neurocrit. Care 2015, 23, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteley, W.; Al-Shahi, R.; Warlow, C.P.; Zeidler, M.; Lueck, C.J. CSF Opening Pressure: Reference Interval and the Effect of Body Mass Index. Neurology 2006, 67, 1690–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenfeldt, N.; Koskinen, L.-O.D.; Bergenheim, A.T.; Malm, J.; Eklund, A. CSF Pressure Assessed by Lumbar Puncture Agrees with Intracranial Pressure. Neurology 2007, 68, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treggiari, M.M.; Schutz, N.; Yanez, N.D.; Romand, J.-A. Role of Intracranial Pressure Values and Patterns in Predicting Outcome in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review. Neurocrit. Care 2007, 6, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evensen, K.B.; O’Rourke, M.; Prieur, F.; Holm, S.; Eide, P.K. Non-Invasive Estimation of the Intracranial Pressure Waveform from the Central Arterial Blood Pressure Waveform in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klingelhöfer, J.; Conrad, B.; Benecke, R.; Sander, D. Intracranial Flow Patterns at Increasing Intracranial Pressure. Klin. Wochenschr. 1987, 65, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingelhöfer, J.; Conrad, B.; Benecke, R.; Sander, D.; Markakis, E. Evaluation of Intracranial Pressure from Transcranial Doppler Studies in Cerebral Disease. J. Neurol. 1988, 235, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranevicius, O.; Bertasius, K.; Pranevicius, M.; Jarzemskas, E. Non-Invasive Dynamic Assessment of the Elasticity of Intracranial Structures. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1992, 86, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajauskas, S.; Antanaitis, S.; Pranevicius, M.; Pranevicius, O.; Bertasius, K. Ultrasound Transcranial Propagation Time Measurement in Neurodiagnostics. Z. Für Med. Phys. 1994, 4, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czosnyka, M.; Guazzo, E.; Iyer, V.; Kirkpatrick, P.; Smielewski, P.; Whitehouse, H.; Pickard, J.D. Testing of Cerebral Autoregulation in Head Injury by Waveform Analysis of Blood Flow Velocity and Cerebral Perfusion Pressure. In Brain Edema IX; Ito, U., Baethmann, A., Hossmann, K.-A., Kuroiwa, T., Marmarou, A., Reulen, H.-J., Takakura, K., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1994; pp. 468–471. ISBN 978-3-7091-9336-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ursino, M.; Giulioni, M.; Lodi, C.A. Relationships among Cerebral Perfusion Pressure, Autoregulation, and Transcranial Doppler Waveform: A Modeling Study. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 89, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, E.A.; Czosnyka, M.; Matta, B.F.; Gooskens, I.; Piechnik, S.; Pickard, J.D. Non-Invasive Cerebral Perfusion Pressure (NCPP): Evaluation of the Monitoring Methodology in Head Injured Patients. In Brain Edema XI; Mendelow, A.D., Baethmann, A., Czernicki, Z., Hoff, J.T., Ito, U., James, H.E., Kuroiwa, T., Marmarou, A., Marshall, L.F., Reulen, H.-J., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2000; pp. 451–452. ISBN 978-3-7091-7257-5. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, E.A. Preliminary Experience of the Estimation of Cerebral Perfusion Pressure Using Transcranial Doppler Ultrasonography. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2001, 70, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardim, D.; Robba, C.; Bohdanowicz, M.; Donnelly, J.; Cabella, B.; Liu, X.; Cabeleira, M.; Smielewski, P.; Schmidt, B.; Czosnyka, M. Non-Invasive Monitoring of Intracranial Pressure Using Transcranial Doppler Ultrasonography: Is It Possible? Neurocrit. Care 2016, 25, 473–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behrens, A.; Lenfeldt, N.; Ambarki, K.; Malm, J.; Eklund, A.; Koskinen, L.-O. Transcranial Doppler Pulsatility Index: Not an Accurate Method to Assess Intracranial Pressure. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Legrand, M.; Lukaszewicz, A.-C.; Charlier, P.; Mateo, J.; Payen, D. Transcranial Doppler Monitoring May Be Misleading in Prediction of Elevated ICP in Brain-Injured Patients. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 39, 1150–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penson, R.P.; Allen, R. Intracranial Pressure Monitoring by Time Domain Analysis. J. R. Soc. Promot. Health 1998, 118, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czosnyka, M.; Brady, K.; Reinhard, M.; Smielewski, P.; Steiner, L.A. Monitoring of Cerebrovascular Autoregulation: Facts, Myths, and Missing Links. Neurocrit. Care 2009, 10, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursino, M. A Mathematical Study of Human Intracranial Hydrodynamics Part 2—Simulation of Clinical Tests. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 1988, 16, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ursino, M.; Di Giammarco, P. A Mathematical Model of the Relationship between Cerebral Blood Volume and Intracranial Pressure Changes: The Generation of Plateau Waves. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 1991, 19, 15–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursino, M.; Lodi, C.A. A Simple Mathematical Model of the Interaction between Intracranial Pressure and Cerebral Hemodynamics. J. Appl. Physiol. 1997, 82, 1256–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashif, F.M.; Verghese, G.C.; Novak, V.; Czosnyka, M.; Heldt, T. Model-Based Noninvasive Estimation of Intracranial Pressure from Cerebral Blood Flow Velocity and Arterial Pressure. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 129ra44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.J.; Park, C.; Oh, J.; Lee, B. Non-Invasive Detection of Intracranial Hypertension Using a Simplified Intracranial Hemo- and Hydro-Dynamics Model. Biomed. Eng. OnLine 2015, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Bolondi, L.; Duck, F.; Evans, D.H.; Ewertsen, C.; Fraser, A.G.; Gilja, O.H.; Jenssen, C.; Merz, E.; Nolsoe, C.; et al. History of Ultrasound in Medicine from Its Birth to Date (2022), on Occasion of the 50 Years Anniversary of EFSUMB. A Publication of the European Federation of Societies for Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology (EFSUMB), Designed to Record the Historical Development of Medical Ultrasound. Med. Ultrason. 2022, 24, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budohoski, K.P.; Schmidt, B.; Smielewski, P.; Kasprowicz, M.; Plontke, R.; Pickard, J.D.; Klingelhöfer, J.; Czosnyka, M. Non-Invasively Estimated ICP Pulse Amplitude Strongly Correlates with Outcome After TBI. In Intracranial Pressure and Brain Monitoring XIV; Schuhmann, M.U., Czosnyka, M., Eds.; Acta Neurochirurgica Supplementum; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2012; Volume 114, pp. 121–125. ISBN 978-3-7091-0955-7. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.; Ryu, S.J.; Jeong, B.H.; Lee, S.P.; Hong, C.-K.; Kim, Y.B.; Lee, B. Real-Time Noninvasive Intracranial State Estimation Using Unscented Kalman Filter. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 1931–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, B.; Bocklisch, S.F.; Päßler, M.; Czosnyka, M.; Schwarze, J.J.; Klingelhöfer, J. Fuzzy Pattern Classification of Hemodynamic Data Can Be Used to Determine Noninvasive Intracranial Pressure. In Intracranial Pressure and Brain Monitoring XII; Poon, W.S., Chan, M.T.V., Goh, K.Y.C., Lam, J.M.K., Ng, S.C.P., Marmarou, A., Avezaat, C.J.J., Pickard, J.D., Czosnyka, M., Hutchinson, P.J.A., et al., Eds.; Acta Neurochirurgica Supplementum; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2005; Volume 95, pp. 345–349. ISBN 978-3-211-24336-7. [Google Scholar]
- Chacón, M.; Pardo, C.; Puppo, C.; Curilem, M.; Landerretche, J. Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Estimation Using Support Vector Machine. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; pp. 996–999. [Google Scholar]
- Robba, C.; Cardim, D.; Tajsic, T.; Pietersen, J.; Bulman, M.; Donnelly, J.; Lavinio, A.; Gupta, A.; Menon, D.K.; Hutchinson, P.J.A.; et al. Ultrasound Non-Invasive Measurement of Intracranial Pressure in Neurointensive Care: A Prospective Observational Study. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.; Czosnyka, M.; Cardim, D.; Czosnyka, Z.; Rosengarten, B. Is Lumbar Puncture Needed?—Noninvasive Assessment of ICP Facilitates Decision Making in Patients with Suspected Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension. Ultraschall Med. Eur. J. Ultrasound 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, H.J.; Cairns, C.; Fillipo, D.; Jöbsis-Vander Vliet, F.F. Near Infrared Spectrophotometry: Potential Role During Increased Intracranial Pressure. In Oxygen Transport to Tissue VII; Kreuzer, F., Cain, S.M., Turek, Z., Goldstick, T.K., Eds.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1985; Volume 191, pp. 863–871. ISBN 978-1-4684-3293-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kampfl, A.; Pfausler, B.; Denchev, D.; Jaring, H.P.; Schmutzhard, E. Near Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) in Patients with Severe Brain Injury and Elevated Intracranial Pressure: A Pilot Study. In Brain Edema X; James, H.E., Marshall, L.F., Raulen, H.J., Baethmann, A., Marmarou, A., Ito, U., Hoff, J.T., Kuroiwa, T., Czernicki, Z., Eds.; Acta Neurochirurgica Supplements; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1997; Volume 70, pp. 112–114. ISBN 978-3-7091-7418-0. [Google Scholar]
- Weerakkody, R.A.; Czosnyka, M.; Zweifel, C.; Castellani, G.; Smielewski, P.; Keong, N.; Haubrich, C.; Pickard, J.; Czosnyka, Z. Slow Vasogenic Fluctuations of Intracranial Pressure and Cerebral near Infrared Spectroscopy—An Observational Study. Acta Neurochir. 2010, 152, 1763–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerakkody, R.A.; Czosnyka, M.; Zweifel, C.; Castellani, G.; Smielewski, P.; Brady, K.; Pickard, J.D.; Czosnyka, Z. Near Infrared Spectroscopy as Possible Non-Invasive Monitor of Slow Vasogenic ICP Waves. In Intracranial Pressure and Brain Monitoring XIV; Schuhmann, M.U., Czosnyka, M., Eds.; Acta Neurochirurgica Supplementum; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2012; Volume 114, pp. 181–185. ISBN 978-3-7091-0955-7. [Google Scholar]
- Zweifel, C.; Castellani, G.; Czosnyka, M.; Helmy, A.; Manktelow, A.; Carrera, E.; Brady, K.M.; Hutchinson, P.J.A.; Menon, D.K.; Pickard, J.D.; et al. Noninvasive Monitoring of Cerebrovascular Reactivity with Near Infrared Spectroscopy in Head-Injured Patients. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 1951–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diedler, J.; Zweifel, C.; Budohoski, K.P.; Kasprowicz, M.; Sorrentino, E.; Haubrich, C.; Brady, K.M.; Czosnyka, M.; Pickard, J.D.; Smielewski, P. The Limitations of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy to Assess Cerebrovascular Reactivity: The Role of Slow Frequency Oscillations. Anesth. Analg. 2011, 113, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruesch, A.; Schmitt, S.; Yang, J.; Smith, M.A.; Kainerstorfer, J.M. Fluctuations in Intracranial Pressure Can Be Estimated Non-Invasively Using near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Non-Human Primates. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2020, 40, 2304–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, D.; Yıldızdaş, D.; Horoz, Ö.Ö.; Aslan, N.; İncecik, F. Evaluation of the Relationship between NIRS (near-Infrared Spectroscopy) and Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Measurement in Children with Increased Intracranial Pressure: A Pilot Study. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durduran, T.; Yodh, A.G. Diffuse Correlation Spectroscopy for Non-Invasive, Micro-Vascular Cerebral Blood Flow Measurement. NeuroImage 2014, 85, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, J.B.; Ghouse, A.; Tagliabue, S.; Maruccia, F.; Rey-Perez, A.; Báguena, M.; Cano, P.; Zucca, R.; Weigel, U.M.; Sahuquillo, J.; et al. Non-Invasive Estimation of Intracranial Pressure by Diffuse Optics: A Proof-of-Concept Study. J. Neurotrauma 2020, 37, 2569–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán, M.; Abay, T.Y.; Kyriacou, P.A. Non-Invasive Techniques for Multimodal Monitoring in Traumatic Brain Injury: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Neurotrauma 2020, 37, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mufti, F.; Smith, B.; Lander, M.; Damodara, N.; Nuoman, R.; El-Ghanem, M.; Kamal, N.; Al-Marsoummi, S.; Alzubaidi, B.; Nuoaman, H.; et al. Novel Minimally Invasive Multi-Modality Monitoring Modalities in Neurocritical Care. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 390, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watad, A.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Bacigaluppi, S.; Amital, H.; Watad, S.; Sharif, K.; Bisharat, B.; Siri, A.; Mahamid, A.; Abu Ras, H.; et al. Artificial Neural Networks Can Be Effectively Used to Model Changes of Intracranial Pressure (ICP) during Spinal Surgery Using Different Non Invasive ICP Surrogate Estimators. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.; Weinhold, M.; Czosnyka, M.; May, S.A.; Steinmeier, R.; Klingelhöfer, J. Accuracy of Non-Invasive ICP Assessment Can Be Increased by an Initial Individual Calibration. In Acta Neurochirurgica Supplements; Steiger, H.-J., Ed.; Acta Neurochirurgica Supplementum; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2008; Volume 102, pp. 49–52. ISBN 978-3-211-85577-5. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, B.; Cardim, D.; Weinhold, M.; Streif, S.; McLeod, D.D.; Czosnyka, M.; Klingelhöfer, J. Comparison of Different Calibration Methods in a Non-Invasive ICP Assessment Model. In Intracranial Pressure & Neuromonitoring XVI; Heldt, T., Ed.; Acta Neurochirurgica Supplement; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 126, pp. 79–84. ISBN 978-3-319-65797-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hornero, R.; Aboy, M.; Abásolo, D. Analysis of Intracranial Pressure during Acute Intracranial Hypertension Using Lempel–Ziv Complexity: Further Evidence. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2007, 45, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Liu, X. A Multi-Parameters Fusion Model for Non-Invasive Detection of Intracranial Pressure. In Proceedings of the 2014 36th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 August 2014; Volume 2014, pp. 1743–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smielewski, P.; Czosnyka, Z.; Kasprowicz, M.; Pickard, J.D.; Czosnyka, M. ICM+: A Versatile Software for Assessment of CSF Dynamics. In Intracranial Pressure and Brain Monitoring XIV; Schuhmann, M.U., Czosnyka, M., Eds.; Acta Neurochirurgica Supplementum; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2012; Volume 114, pp. 75–79. ISBN 978-3-7091-0955-7. [Google Scholar]
- Horbar, J.D.; Yeager, S.; Philip, A.G.; Lucey, J.F. Effect of Application Force on Noninvasive Measurements of Intracranial Pressure. Pediatrics 1980, 66, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; Wright, B.M.; Shore, C. Clinical fontanometry in the newborn. Lancet 1988, 331, 754–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, A.M.; Whitelaw, A.G. Non-Invasive Monitoring of Intracranial Pressure--Fact or Fancy? Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1987, 29, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, E.; Hayashi, T.; Masajima, T.; Anegawa, S.; Kuramoto, S.; Kikukawa, T. A New Instrument for Non-Invasive Measurement of Intracranial Pressure via the Anterior Fontanelle. Neurol. Med. Chir. 1982, 22, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honda, E.; Hayashi, T.; Kuramoto, S. Fontanelle Pressure (ICP) in Infantile Hydrocephalus Investigation of ICP in 6 Cases of Hydrocephalus with Normal Head Circumference and without Shunting Operation. Kurume Med. J. 1984, 31, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Kuramoto, S.; Honda, E.; Anegawa, S. A New Instrument for Noninvasive Measurement of Intracranial Pressure through the Anterior Fontanel: I. Preliminary Report. Childs Nerv. Syst. 1987, 3, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, P.J.; Rochefort, M.; Rolfe, P.; Goddard, P.J. Development of a Sensor for Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Measurement in the Newborn. J. Biomed. Eng. 1988, 10, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, A.I. The Rotterdam Teletransducer: State of the Device. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1985, 40, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, A.I.R.; de Jong, D.A. The Rotterdam Teletransducer: State of the Device. Acta Neurochir. 1986, 79, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behmanesh, B.; Setzer, M.; Noack, A.; Bartels, M.; Quick-Weller, J.; Seifert, V.; Freiman, T.M. Noninvasive Epicutaneous Transfontanelle Intracranial Pressure Monitoring in Children under the Age of 1 Year: A Novel Technique. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2016, 18, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Behmanesh, B.; Gessler, F.; Dubinski, D.; Quick-Weller, J.; Cattani, A.; Schubert-Bast, S.; Seifert, V.; Konczalla, J.; Freiman, T.M. First Clinical Experience with the New Noninvasive Transfontanelle ICP Monitoring Device in Management of Children with Premature IVH. Neurosurg. Rev. 2020, 43, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Huang, Z.; Song, H.; Kim, H.S.; Park, J. Wearable Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Sensor for Infants. Biosensors 2021, 11, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurazumi, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Yanagida, R.; Morisaki, H.; Iwasaki, K.-I. Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Estimation During Combined Exposure to CO₂ and Head-Down Tilt. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2018, 89, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, T.; Ballard, R.E.; Shuer, L.M.; Cantrell, J.H.; Yost, W.T.; Hargens, A.R. Noninvasive Measurement of Pulsatile Intracranial Pressure Using Ultrasound. In Intracranial Pressure and Neuromonitoring in Brain Injury; Marmarou, A., Bullock, R., Avezaat, C., Baethmann, A., Becker, D., Brock, M., Hoff, J., Nagai, H., Reulen, H.-J., Teasdale, G., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1998; pp. 66–69. ISBN 978-3-7091-7331-2. [Google Scholar]
- Bollela, V.R.; Frigieri, G.; Vilar, F.C.; Spavieri Jr, D.L.; Tallarico, F.J.; Tallarico, G.M.; Andrade, R.A.P.; de Haes, T.M.; Takayanagui, O.M.; Catai, A.M.; et al. Noninvasive Intracranial Pressure Monitoring for HIV-Associated Cryptococcal Meningitis. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2017, 50, e6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frigieri, G.; Andrade, R.A.P.; Dias, C.; Spavieri, D.L.; Brunelli, R.; Cardim, D.A.; Wang, C.C.; Verzola, R.M.M.; Mascarenhas, S. Analysis of a Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Method in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury. In Intracranial Pressure & Neuromonitoring XVI; Heldt, T., Ed.; Acta Neurochirurgica Supplement; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 126, pp. 107–110. ISBN 978-3-319-65797-4. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaese, T.M.; Welling, L.C.; Koscianski, A.M.; Frigeri, G.; Auada, J.; Rabelo, N.N.; Figueiredo, E.G. Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Monitoring in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension and Lumbar Puncture in Pediatric Patient: Case Report. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2021, 12, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr Arias, M.V.; Conceição, R.T.; Guimarães, F.C.; Cardoso, G.S.; Rocha, N.L.F.C. Preliminary Evaluation of a Non-Invasive Device for Monitoring Intracranial Pressure Waveforms in Dogs. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2022, 63, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassett, C.E.; Uysal, S.P.; Butler, R.; Moore, N.Z.; Cardim, D.; Gomes, J.A. Assessment of Cerebral Autoregulation Using Invasive and Noninvasive Methods of Intracranial Pressure Monitoring. Neurocrit. Care 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulos, V.; Douzinas, E.E.; Kypriades, E.M.; Pappas, Y.Z. A New Method for the Early Diagnosis of Brain Edema/Brain Swelling. An Experimental Study in Rabbits. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 2958–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, T.; Furihata, K.; Hongo, K. Natural Resonance Frequency of the Brain Depends on Only Intracranial Pressure: Clinical Research. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redzwan, S.; Velander, J.; Perez, M.D.; Asan, N.B.; Rajabi, M.; Niklaus, F.; Nowinski, D.; Lewen, A.; Enblad, P.; Augustine, R. Initial In-Vitro Trial for Intra-Cranial Pressure Monitoring Using Subdermal Proximity-Coupled Split-Ring Resonator. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Microwave Biomedical Conference (IMBioC), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 14–15 June 2018; pp. 73–75. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; He, W.; Chen, W.; Zhu, L. Research on Simulation and Experiment of Noninvasive Intracranial Pressure Monitoring Based on Acoustoelasticity Effects. Med. Devices Evid. Res. 2013, 6, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petkus, V.; Preiksaitis, A.; Krakauskaite, S.; Bartusis, L.; Chomskis, R.; Hamarat, Y.; Zubaviciute, E.; Vosylius, S.; Rocka, S.; Ragauskas, A. Non-Invasive Cerebrovascular Autoregulation Assessment Using the Volumetric Reactivity Index: Prospective Study. Neurocrit. Care 2019, 30, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alperin, N.J.; Lee, S.H.; Loth, F.; Raksin, P.B.; Lichtor, T. MR-Intracranial Pressure (ICP): A Method to Measure Intracranial Elastance and Pressure Noninvasively by Means of MR Imaging: Baboon and Human Study. Radiology 2000, 217, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burman, R.; Shah, A.H.; Benveniste, R.; Jimsheleishvili, G.; Lee, S.H.; Loewenstein, D.; Alperin, N. Comparing Invasive with MRI-Derived Intracranial Pressure Measurements in Healthy Elderly and Brain Trauma Cases: A Pilot Study: Comparing LPOP and MR-ICP in Controls. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 50, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mase, M.; Miyati, T.; Yamada, K.; Kasai, H.; Hara, M.; Shibamoto, Y. Non-Invasive Measurement of Intracranial Compliance Using Cine MRI in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2005, 95, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-H.; Chen, H.-C.; Tung, H.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Chen, H.-M.; Pan, K.-J.; Cheng, D.-C.; Chen, J.-H.; Chen, C.C.-C.; Chai, J.-W.; et al. Noninvasive Assessment of Intracranial Elastance and Pressure in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension by MRI: MR Intracranial Pressure for SIH. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 48, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muehlmann, M.; Koerte, I.K.; Laubender, R.P.; Steffinger, D.; Lehner, M.; Peraud, A.; Heinen, F.; Kiefer, M.; Reiser, M.; Ertl-Wagner, B. Magnetic Resonance–Based Estimation of Intracranial Pressure Correlates with Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Valve Opening Pressure Setting in Children With Hydrocephalus. Investig. Radiol. 2013, 48, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringstad, G.; Lindstrøm, E.K.; Vatnehol, S.A.S.; Mardal, K.-A.; Emblem, K.E.; Eide, P.K. Non-Invasive Assessment of Pulsatile Intracranial Pressure with Phase-Contrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kollmeier, J.M.; Gürbüz-Reiss, L.; Sahoo, P.; Badura, S.; Ellebracht, B.; Keck, M.; Gärtner, J.; Ludwig, H.-C.; Frahm, J.; Dreha-Kulaczewski, S. Deep Breathing Couples CSF and Venous Flow Dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, I.L.; Heide, M.; Hofer, S.; Dechent, P.; Fiss, I.; von der Brelie, C.; Rohde, V.; Frahm, J.; Bähr, M.; Liman, J. High Periventricular T1 Relaxation Times Predict Gait Improvement After Spinal Tap in Patients with Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2022, 32, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.J.; Khadhraoui, E.; Voit, D.; Riedel, C.H.; Frahm, J.; Ernst, M. First Clinical Application of a Novel T1 Mapping of the Whole Brain. Neuroradiol. J. 2022, 35, 197140092210842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, T.; Voit, D.; Kollmeier, J.M.; Kalentev, O.; van Zalk, M.; Frahm, J. FLASHlight MRI in Real Time—A Step towards Star Trek Medicine. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2023, 13, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzler, E.; Lehmann, G. Über ein neues Verfahren zur Darstellung der Herztätigkeit (Dielektrographie). Arbeitsphysiologie 1932, 5, 636–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkner, F.L. Rheoencephalography: A Method for the Continuous Registration of Cerebrovascular Changes; American lecture series; Thomas: Waukesha, WI, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Waltz, A.G. Inadequacy of “Rheoencephalography”: A Clinical Study of Impedance Cephalography for Evaluation of Cerebrovascular Disorders. Arch. Neurol. 1967, 16, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russegger, L.; Ennemoser, O. Atraumatic measurement of intracranial pressure. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 1990, 102, 543–547. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, G.; Neubauer, G.; Mazal, P.R. Dielectric Properties of Human Brain Tissue Measured Less than 10 h Postmortem at Frequencies from 800 to 2450 MHz. Bioelectromagnetics 2003, 24, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodo, M.; Pearce, F.J.; Baranyi, L.; Armonda, R.A. Changes in the Intracranial Rheoencephalogram at Lower Limit of Cerebral Blood Flow Autoregulation. Physiol. Meas. 2005, 26, S1–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffith, J.; Cluff, K.; Eckerman, B.; Aldrich, J.; Becker, R.; Moore-Jansen, P.; Patterson, J. Non-Invasive Electromagnetic Skin Patch Sensor to Measure Intracranial Fluid-Volume Shifts. Sensors 2018, 18, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grant, P.F.; Lowery, M.M. Simplified Parametric Models of the Dielectric Properties of Brain and Muscle Tissue during Electrical Stimulation. Med. Eng. Phys. 2019, 65, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Li, W.; You, F.; Huo, X.; Xu, C.; Ji, Z.; Liu, R.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Fu, F.; et al. High-Precision Electrical Impedance Tomography Data Acquisition System for Brain Imaging. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 5974–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, B.; Xu, C.; Hu, S.; Dai, M.; Xia, J.; Luo, P.; Shi, X.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, X.; et al. Comparison of Electrical Impedance Tomography and Intracranial Pressure during Dehydration Treatment of Cerebral Edema. NeuroImage Clin. 2019, 23, 101909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawthorne, C.; Shaw, M.; Piper, I.; Moss, L.; Kinsella, J. Transcranial Bioimpedance Measurement as a Non-Invasive Estimate of Intracranial Pressure. In Intracranial Pressure & Neuromonitoring XVI; Heldt, T., Ed.; Acta Neurochirurgica Supplement; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 126, pp. 89–92. ISBN 978-3-319-65797-4. [Google Scholar]
- Brehmer, S. Wertigkeit der Schädelrheographie zur nicht-invasiven Hirndruckmessung. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Ulm, Ulm, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, M.; Jin, G.; Xu, J.; Qin, M. Experimental Study on the Detection of Cerebral Hemorrhage in Rabbits Based on Broadband Antenna Technology. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2019, 24, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Zhao, S.; Bai, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liao, Q.; He, M.; Zhuang, W.; Chen, M.; et al. Noninvasive Real-Time Assessment of Intracranial Pressure after Traumatic Brain Injury Based on Electromagnetic Coupling Phase Sensing Technology. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yin, S.; Jian, M.; Chen, J.; Zeng, L.; Bai, Z.; Zhuang, W.; Xu, B.; He, S.; Sun, J.; et al. Early Assessment of Acute Ischemic Stroke in Rabbits Based on Multi-Parameter near-Field Coupling Sensing. Biomed. Eng. OnLine 2022, 21, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-García, A.; Pérez-Romero, M.; Pastor, J.; Sola, R.G.; Vega-Zelaya, L.; Monasterio, F.; Torrecilla, C.; Vega, G.; Pulido, P.; Ortega, G.J. Identifying Causal Relationships between EEG Activity and Intracranial Pressure Changes in Neurocritical Care Patients. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 066029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz García, A.; Pérez Romero, M.; Pastor Gómez, J.; García de Sola, R.; Vega Zelaya, L.; Monasterio, F.; Torrecilla López, C.; Vega, G.; Pulido Rivas, P.; Ortega Rabbione, G.J. ¿Es posible obtener información de la presión intracraneal a partir de la actividad electroencefalográfica? Rev. Neurol. 2019, 68, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kim, H.; Song, K.-J.; Shin, S.-D.; Kim, H.-C.; Lim, H.-J.; Kim, Y.; Kang, H.-J.; Hong, K.-J. Prediction of Increased Intracranial Pressure in Traumatic Brain Injury Using Quantitative Electroencephalogram in a Porcine Experimental Model. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Fan, Y. A Review of the Methods of Non-Invasive Assessment of Intracranial Pressure through Ocular Measurement. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.A.; Grzybowski, A.; Eikenberry, J.; Januleviciene, I.; Verticchio Vercellin, A.C.; Mathew, S.; Siesky, B.; Harris, A. Review of Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Measurement Techniques for Ophthalmology Applications. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 104, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wan, C. Non-Invasive Detection of Intracranial Pressure Related to the Optic Nerve. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 2823–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragauskas, A.; Daubaris, G.; Dziugys, A.; Azelis, V.; Gedrimas, V. Innovative Non-Invasive Method for Absolute Intracranial Pressure Measurement without Calibration. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2005, 95, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragauskas, A.; Matijosaitis, V.; Zakelis, R.; Petrikonis, K.; Rastenyte, D.; Piper, I.; Daubaris, G. Clinical Assessment of Noninvasive Intracranial Pressure Absolute Value Measurement Method. Neurology 2012, 78, 1684–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusbaum, D.M. Two-Depth Transcranial Doppler: A Novel Approach for Non-Invasive Absolute Intracranial Pressure Measurement. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2011, 82, 1080–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauskaite, S.; Petkus, V.; Bartusis, L.; Zakelis, R.; Chomskis, R.; Preiksaitis, A.; Ragauskas, A.; Matijosaitis, V.; Petrikonis, K.; Rastenyte, D. Accuracy, Precision, Sensitivity, and Specificity of Noninvasive ICP Absolute Value Measurements. In Intracranial Pressure and Brain Monitoring XV; Ang, B.-T., Ed.; Acta Neurochirurgica Supplement; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 122, pp. 317–321. ISBN 978-3-319-22532-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ragauskas, A.; Bartusis, L.; Piper, I.; Zakelis, R.; Matijosaitis, V.; Petrikonis, K.; Rastenyte, D. Improved Diagnostic Value of a TCD-Based Non-Invasive ICP Measurement Method Compared with the Sonographic ONSD Method for Detecting Elevated Intracranial Pressure. Neurol. Res. 2014, 36, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinen, L.-O.D.; Malm, J.; Zakelis, R.; Bartusis, L.; Ragauskas, A.; Eklund, A. Can Intracranial Pressure Be Measured Non-Invasively Bedside Using a Two-Depth Doppler-Technique? J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2017, 31, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucinskas, P.; Deimantavicius, M.; Bartusis, L.; Zakelis, R.; Misiulis, E.; Dziugys, A.; Hamarat, Y. Human Ophthalmic Artery as a Sensor for Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Monitoring: Numerical Modeling and in Vivo Pilot Study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siaudvytyte, L.; Januleviciene, I.; Ragauskas, A.; Bartusis, L.; Siesky, B.; Harris, A. Update in Intracranial Pressure Evaluation Methods and Translaminar Pressure Gradient Role in Glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015, 93, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamarat, Y.; Bartusis, L.; Deimantavicius, M.; Siaudvytyte, L.; Januleviciene, I.; Ragauskas, A.; Bershad, E.M.; Fandino, J.; Kienzler, J.; Remonda, E.; et al. Graphical and Statistical Analyses of the Oculocardiac Reflex during a Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Measurement. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, M.S.; Pedersen, C.B.; Poulsen, F.R. A New Novel Method for Assessing Intracranial Pressure Using Non-Invasive Fundus Images: A Pilot Study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobstein, A.; Nordmann, J. Modern Ophthalmodynamometry. Doc. Ophthalmol. 1959, 13, 397–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Schwickerath, R.; Stodtmeister, R.; Hartmann, K. Non-invasive determination of intracranial pressure. Physiological basis and practical procedure. Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 2004, 221, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Rahman, A.; Morgan, W.; Jo Khoo, Y.; Lind, C.; Kermode, A.; Carroll, W.; Yu, D.-Y. Linear Interactions between Intraocular, Intracranial Pressure, and Retinal Vascular Pulse Amplitude in the Fourier Domain. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Rahman, A.; Morgan, W.; Yu, D.-Y. A Machine Learning Approach in the Non-Invasive Prediction of Intracranial Pressure Using Modified Photoplethysmography. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querfurth, H.W.; Lieberman, P.; Arms, S.; Mundell, S.; Bennett, M.; van Horne, C. Ophthalmodynamometry for ICP Prediction and Pilot Test on Mt. Everest. BMC Neurol. 2010, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonas, J.B.; Pfeil, K.; Chatzikonstantinou, A.; Rensch, F. Ophthalmodynamometric Measurement of Central Retinal Vein Pressure as Surrogate of Intracranial Pressure in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2008, 246, 1059–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, W.H.; Abdul-Rahman, A.; Yu, D.-Y.; Hazelton, M.L.; Betz-Stablein, B.; Lind, C.R.P. Objective Detection of Retinal Vessel Pulsation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, L.; Zhao, D.; Ayton, L.; Grayden, D.; Bui, B.; Morokoff, A.; John, S. Non-Invasive Measurement of Intracranial Pressure Through Application of Venous Ophthalmodynamometry. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Guadalajara, Mexico, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 6771–6774. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, W.H.; Hazelton, M.L.; Yu, D.-Y. Retinal Venous Pulsation: Expanding Our Understanding and Use of This Enigmatic Phenomenon. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2016, 55, 82–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, W.H.; Vukmirovic, A.; Abdul-Rahman, A.; Khoo, Y.J.; Kermode, A.G.; Lind, C.R.; Dunuwille, J.; Yu, D.Y. Zero Retinal Vein Pulsation Amplitude Extrapolated Model in Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Estimation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, H.E. Retinal Vein Changes as a Biomarker to Guide Diagnosis and Management of Elevated Intracranial Pressure. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 751370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golzan, S.M.; Avolio, A.; Graham, S.L. Non-Invasive Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure Estimation Using Multi-Layer Perceptron Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 5278–5281. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Kahn, M. Measurement and Relationship of Subarachnoid Pressure of the Optic Nerve to Intracranial Pressures in Fresh Cadavers. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1993, 116, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatos, T.; Chatzimichail, K.; Papathanasiou, M.; Gouliamos, A. Optic Nerve Sonography: A New Window for the Non-Invasive Evaluation of Intracranial Pressure in Brain Injury. Emerg. Med. J. EMJ 2009, 26, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziarz, A.; Sne, N.; Kegel, F.; Alhazzani, W.; Nath, S.; Badhiwala, J.H.; Rice, T.; Engels, P.; Samir, F.; Healey, A.; et al. Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Sonography for the Diagnosis of Increased Intracranial Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocol. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziarz, A.; Sne, N.; Kegel, F.; Nath, S.; Badhiwala, J.H.; Nassiri, F.; Mansouri, A.; Yang, K.; Zhou, Q.; Rice, T.; et al. Bedside Optic Nerve Ultrasonography for Diagnosing Increased Intracranial Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goeres, P.; Zeiler, F.A.; Unger, B.; Karakitsos, D.; Gillman, L.M. Ultrasound Assessment of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter in Healthy Volunteers. J. Crit. Care 2016, 31, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ding, G.-S.; Zhao, Y.-C.; Yu, R.-G.; Zhou, J.-X. Ultrasound Measurement of Optic Nerve Diameter and Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter in Healthy Chinese Adults. BMC Neurol. 2015, 15, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.-B.; Tian, J.; Liu, X.-B.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Guo, J.-Y. Can Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Assessment Be Used as a Non-Invasive Tool to Dynamically Monitor Intracranial Pressure? J. Integr. Neurosci. 2022, 21, 054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messerer, M.; Berhouma, M.; Messerer, R.; Dubourg, J. Intérêt de l’échographie du diamètre de l’enveloppe du nerf optique pour la détection non invasive de l’hypertension intracrânienne. Neurochirurgie 2013, 59, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bäuerle, J.; Lochner, P.; Kaps, M.; Nedelmann, M. Intra- and Interobsever Reliability of Sonographic Assessment of the Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter in Healthy Adults. J. Neuroimaging 2012, 22, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, J.B.; Oliva, C.; Joyce, M.; Vitto, M.J.; Tozer, J.; Taylor, L.A.; Evans, D.P. Inter-Rater Reliability of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Measurement Using Real-Time Ultrasonography. Ultrasound J. 2022, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frumin, E.; Schlang, J.; Wiechmann, W.; Hata, S.; Rosen, S.; Anderson, C.; Pare, L.; Rosen, M.; Fox, J.C. Prospective Analysis of Single Operator Sonographic Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Measurement for Diagnosis of Elevated Intracranial Pressure. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 15, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thotakura, A.K.; Marabathina, N.R.; Danaboyina, A.R.; Mareddy, R.R. Role of Serial Ultrasonic Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Monitoring in Head Injury. Neurochirurgie 2017, 63, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangemi, M.; Cennamo, G.; Maiuri, F.; D’Andrea, F. Echographic Measurement of the Optic Nerve in Patients with Intracranial Hypertension. Min Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 1987, 30, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, W.D. Measurement of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter by Ultrasound: A Means of Detecting Acute Raised Intracranial Pressure in Hydrocephalus. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 86, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robba, C.; Santori, G.; Czosnyka, M.; Corradi, F.; Bragazzi, N.; Padayachy, L.; Taccone, F.S.; Citerio, G. Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Measured Sonographically as Non-Invasive Estimator of Intracranial Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2018, 44, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naldi, A.; Provero, P.; Vercelli, A.; Bergui, M.; Mazzeo, A.T.; Cantello, R.; Tondo, G.; Lochner, P. Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Asymmetry in Healthy Subjects and Patients with Intracranial Hypertension. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padayachy, L.C.; Padayachy, V.; Galal, U.; Gray, R.; Fieggen, A.G. The Relationship between Transorbital Ultrasound Measurement of the Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter (ONSD) and Invasively Measured ICP in Children: Part I: Repeatability, Observer Variability and General Analysis. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2016, 32, 1769–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padayachy, L.C.; Padayachy, V.; Galal, U.; Pollock, T.; Fieggen, A.G. The Relationship between Transorbital Ultrasound Measurement of the Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter (ONSD) and Invasively Measured ICP in Children: Part II: Age-Related ONSD Cut-off Values and Patency of the Anterior Fontanelle. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2016, 32, 1779–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cour-Andlauer, F.; Portefaix, A.; Wroblewski, I.; Rabilloud, M.; Bordet, F.; Cogniat, B.; Didier, C.; Pouyau, R.; Valla, F.V.; Kassai-Koupai, B.; et al. Predictive Value of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter for Diagnosis of Intracranial Hypertension in Children With Severe Brain Injury. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 894449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Brierley, J. Optic Nerve Sheath Measurement and Raised Intracranial Pressure in Paediatric Traumatic Brain Injury. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2012, 38, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajajee, V.; Vanaman, M.; Fletcher, J.J.; Jacobs, T.L. Optic Nerve Ultrasound for the Detection of Raised Intracranial Pressure. Neurocrit. Care 2011, 15, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Feng, L.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Feng, J.; Xing, Y. Optimal Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Threshold for the Identification of Elevated Opening Pressure on Lumbar Puncture in a Chinese Population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aspide, R.; Bertolini, G.; Belotti, L.M.B.; Albini Riccioli, L.; Toni, F.; Mazzatenta, D.; Palandri, G.; Vetrugno, L.; Biasucci, D.G. The CLOSED Protocol to Assess Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Using Color-Doppler: A Comparison Study in a Cohort of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Patients. Ultrasound J. 2022, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeraerts, T.; Merceron, S.; Benhamou, D.; Vigué, B.; Duranteau, J. Non-Invasive Assessment of Intracranial Pressure Using Ocular Sonography in Neurocritical Care Patients. Intensive Care Med. 2008, 34, 2062–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Panda, N.; Swain, A.; Mathew, P.; Singla, N.; Gupta, S.; Jangra, K.; Bhardwaj, A.; Bhagat, H. Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter: Correlation With Intra-Ventricular Intracranial Measurements in Predicting Dysfunctional Intracranial Compliance. Cureus 2021, 13, e13008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Chen, H.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Q.; Xing, Y. Reliability of Assessing Non-Severe Elevation of Intracranial Pressure Using Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter and Transcranial Doppler Parameters. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffiz, M.; Abdullah, J.M. Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Measurement: A Means of Detecting Raised ICP in Adult Traumatic and Non-Traumatic Neurosurgical Patients. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 35, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robba, C.; Cardim, D.; Tajsic, T.; Pietersen, J.; Bulman, M.; Rasulo, F.; Bertuetti, R.; Donnelly, J.; Xiuyun, L.; Czosnyka, Z.; et al. Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Assessment in Brain Injured Patients Using Ultrasound-Based Methods. In Intracranial Pressure & Neuromonitoring XVI; Heldt, T., Ed.; Acta Neurochirurgica Supplement; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 126, pp. 69–73. ISBN 978-3-319-65797-4. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.-J.; Chen, A.E.; Lin, E.E.; Hsia, S.-H.; Chiang, M.-C.; Lin, K.-L. Point-of-Care Ultrasound of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter to Detect Intracranial Pressure in Neurocritically Ill Children—A Narrative Review. Biomed. J. 2020, 43, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, J.R.; Liu, X.; Donnelly, J.; Cardim, D.; Czosnyka, M.; Robba, C. Clinical Application of Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Measurements. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 121, 500–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robba, C.; Bacigaluppi, S.; Cardim, D.; Donnelly, J.; Sekhon, M.S.; Aries, M.J.; Mancardi, G.; Booth, A.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Czosnyka, M.; et al. Intraoperative Non Invasive Intracranial Pressure Monitoring during Pneumoperitoneum: A Case Report and a Review of the Published Cases and Case Report Series. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2016, 30, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Bala, R.; Saini, S. Ultrasonographic Measurement of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter: A Point of Care Test Helps in Prognostication of Intensive Care Unit Patients. Indian J. Anaesth. 2017, 61, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Nam, S.; Ji, S.; Kim, E.; Lee, J.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, H.; Kim, J. Effect of End-tidal Carbon Dioxide Level on the Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Measured by Transorbital Ultrasonography in Anesthetized Pediatric Patients: A Randomized Trial. Pediatr. Anesth. 2022, 32, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Min, H.-G.; Ha, S.-I.; Jeong, H.-W.; Seo, H.; Kim, J.-U. Dynamic Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Responses to Short-Term Hyperventilation Measured with Sonography in Patients under General Anesthesia. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2014, 67, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weidner, N.; Kretschmann, J.; Bomberg, H.; Antes, S.; Leonhardt, S.; Tschan, C.; Oertel, J.; Volk, T.; Meiser, A.; Groesdonk, H.V. Real-Time Evaluation of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter (ONSD) in Awake, Spontaneously Breathing Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xing, Y. Ultrasonic Measurement of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter: A Non-Invasive Surrogate Approach for Dynamic, Real-Time Evaluation of Intracranial Pressure. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, S.-H.; Min, K.-T.; Park, E.-K.; Kim, M.-S.; Jung, J.-H.; Kim, H. Ultrasonography of the Optic Nerve Sheath to Assess Intracranial Pressure Changes after Ventriculo-Peritoneal Shunt Surgery in Children with Hydrocephalus: A Prospective Observational Study. Anaesthesia 2015, 70, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, A.; Das, P.K.; Parashar, S.; Misra, S.; Tripathi, M.; Malviya, D.; Singh, D. Clinical Relevance of Transorbital Ultrasonographic Measurement of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter (ONSD) for Estimation of Intracranial Pressure Following Cerebrospinal Fluid Diversion Surgery. Cureus 2022, 14, e25200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, B.C.P.; de Andrade, A.F.; Brasil, S.; Bor-Seng-Shu, E.; Belon, A.R.; Robertis, M.; de-Lima-Oliveira, M.; Rubiano, A.M.; Godoy, D.A.; Teixeira, M.J.; et al. Estimation of Intracranial Pressure by Ultrasound of the Optic Nerve Sheath in an Animal Model of Intracranial Hypertension. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 86, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dağdelen, K.; Ekici, M. Measuring Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Using Ultrasonography in Patients with Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2022, 80, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, K.; Pang, R.; Wang, N.; Qu, X.; Kang, J.; Wang, N.; Liu, H. Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Estimation Using Ultrasonographic Measurement of Area of Optic Nerve Subarachnoid Space. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.G.R.J.; Zeiler, F.A.; Unger, B.; Hansen, G.; Karakitsos, D.; Gillman, L.M. Estimating the Accuracy of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Measurement Using a Pocket-Sized, Handheld Ultrasound on a Simulation Model. Crit. Ultrasound J. 2016, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, G.G.R.J.; Jelic, T.; Derksen, A.; Unger, B.; Zeiler, F.A.; Ziesmann, M.T.; Gillman, L.M. Accuracy of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Measurements in Pocket-Sized Ultrasound Devices in a Simulation Model. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 831778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix, H.; Oliveira, E.S. Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Monitoring and Its Applicability in Spaceflight. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2022, 93, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Wu, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, H.; Ni, Z.; Wang, Y. Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Assessment Using Shear-Wave Elastography in Neuro-Critical Care Patients. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 99, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soroushmehr, R.; Rajajee, K.; Williamson, C.; Gryak, J.; Najarian, K.; Ward, K.; Tiba, M.H. Automated Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Measurement Using Super-Pixel Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 2793–2796. [Google Scholar]
- Tantiwongkosi, B.; Mafee, M.F. Imaging of Optic Neuropathy and Chiasmal Syndromes. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2015, 25, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashima, Y. High-Resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Intraorbital Optic Nerve and Subarachnoid Space in Patients With Papilledema and Optic Atrophy. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1996, 114, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passi, N.; Degnan, A.J.; Levy, L.M. MR Imaging of Papilledema and Visual Pathways: Effects of Increased Intracranial Pressure and Pathophysiologic Mechanisms. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haredy, M.; Zuccoli, G.; Tamber, M.; Davis, A.; Nischal, K.; Goldstein, J.A. Use of Neuroimaging Measurements of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter to Assess Intracranial Pressure in Craniosynostosis. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2018, 34, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Hao, D.; Tang, G.; Zhou, R.; Pang, J.; Dong, C. High-Resolution MRI Assessment of Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter in Adults: Optic Nerve Sheath Variation and a New Diagnostic Tool for Intracranial Hypertension. Acta Radiol. 2021, 62, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golshani, K.; Ebrahim Zadeh, M.; Farajzadegan, Z.; Khorvash, F. Diagnostic Accuracy of Optic Nerve Ultrasonography and Ophthalmoscopy in Prediction of Elevated Intracranial Pressure. Emerg. Tehran Iran 2015, 3, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, S.; Anand, D.; Dutta, T.K.; Roopesh Kumar, V.R.; Kar, S.S. Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Analysis in Cases of Papilledema Using Optical Coherence Tomography—A Case Control Study. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2015, 136, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Pass, A.; Urfy, M.Z.; Tang, R.; Cajavilca, C.; Calvillo, E.; Suarez, J.I.; Venkatasubba Rao, C.P.; Bershad, E.M. Optical Coherence Tomography of the Optic Nerve Head Detects Acute Changes in Intracranial Pressure. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 29, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesler, A.; Vakhapova, V.; Korczyn, A.D.; Drory, V.E. Visual Evoked Potentials in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.I.; Li, Y.; Minhui, X.; Yihua, Z. Realization of a Comprehensive Non-Invasive Detection of Intracranial Pressure Analyzer Based upon FVEP and TCD. In Intracranial Pressure and Brain Monitoring XIV; Schuhmann, M.U., Czosnyka, M., Eds.; Acta Neurochirurgica Supplementum; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2012; Volume 114, pp. 127–129. ISBN 978-3-7091-0955-7. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, L.; Sjölund, J.; Nilsson, J. Flash Visual Evoked Potentials Are Unreliable as Markers of ICP Due to High Variability in Normal Subjects. Acta Neurochir. (Wien) 2012, 154, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, M.D.; Behrends, M. Portable Infrared Pupillometry: A Review. Anesth. Analg. 2015, 120, 1242–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Gombart, Z.; Rogers, S.; Gardiner, S.; Cecil, S.; Bullock, R. Pupillary Reactivity as an Early Indicator of Increased Intracranial Pressure: The Introduction of the Neurological Pupil Index. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2011, 2, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jahns, F.-P.; Miroz, J.P.; Messerer, M.; Daniel, R.T.; Taccone, F.S.; Eckert, P.; Oddo, M. Quantitative Pupillometry for the Monitoring of Intracranial Hypertension in Patients with Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchbanks, R.J.; Reid, A.; Martin, A.M.; Brightwell, A.P.; Bateman, D. The Effect of Raised Intracranial Pressure on Intracochlear Fluid Pressure: Three Case Studies. Br. J. Audiol. 1987, 21, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, S.; Marchbanks, R.; Burge, D. Non-Invasive Assessment of Ventricular Shunt Function Using Tympanic Membrane Displacement Measurement Technique. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1990, 45, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, M.; Burge, D.; Marchbanks, R. Quantitative Assessment of Intracranial Pressure by the Tympanic Membrane Displacement Audiometric Technique in Children with Shunted Hydrocephalus. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1998, 8, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwer, S.; Sheward, V.; Birch, A.; Marchbanks, R.; Idro, R.; Newton, C.R.; Kirkham, F.J.; Lin, J.-P.; Lim, M. The Tympanic Membrane Displacement Analyser for Monitoring Intracranial Pressure in Children. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2013, 29, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharif, S.J.; Campbell-Bell, C.M.; Bulters, D.O.; Marchbanks, R.J.; Birch, A.A. Does the Variability of Evoked Tympanic Membrane Displacement Data (V m) Increase as the Magnitude of the Pulse Amplitude Increases? In Intracranial Pressure & Neuromonitoring XVI; Heldt, T., Ed.; Acta Neurochirurgica Supplement; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 126, pp. 103–106. ISBN 978-3-319-65797-4. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell-Bell, C.M.; Birch, A.A.; Vignali, D.; Bulters, D.; Marchbanks, R.J. Reference Intervals for the Evoked Tympanic Membrane Displacement Measurement: A Non-Invasive Measure of Intracranial Pressure. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, L.C.; Marchbanks, R.J.; Bulters, D.; Birch, A.A. Refining Non-Invasive Techniques to Measure Intracranial Pressure: Comparing Evoked and Spontaneous Tympanic Membrane Displacements. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 025007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büki, B.; Avan, P.; Lemaire, J.J.; Dordain, M.; Chazal, J.; Ribári, O. Otoacoustic Emissions: A New Tool for Monitoring Intracranial Pressure Changes through Stapes Displacements. Hear. Res. 1996, 94, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, A.M.; Alexiou, C.; Hulin, P.; Janssen, T.; Arnold, W.; Trappe, A.E. Non-Invasive Measurement of Intracranial Pressure Changes by Otoacoustic Emissions (OAEs)--a Report of Preliminary Data. Zentralbl. Neurochir. 2000, 61, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büki, B.; Chomicki, A.; Dordain, M.; Lemaire, J.-J.; Wit, H.P.; Chazal, J.; Avan, P. Middle-Ear Influence on Otoacoustic Emissions. II: Contributions of Posture and Intracranial Pressure. Hear. Res. 2000, 140, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straßen, U.G.P. Untersuchung der Veränderung der Distorsionsprodukte otoakustischer Emissionen (DPOAEs) bei Hirndruckanstieg mit Hinblick auf eine mögliche Anwendung für ein nicht-invasives Hirndruckmonitoring. Ph.D. Thesis, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Munich, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Büki, B.; de Kleine, E.; Wit, H.P.; Avan, P. Detection of Intracochlear and Intracranial Pressure Changes with Otoacoustic Emissions: A Gerbil Model. Hear. Res. 2002, 167, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yücel, E.; Ardıç, F.N.; Tümkaya, F.; Kara, C.O.; Topuz, B. Detecting intralabyrinthine pressure increase by postural manipulation with wideband tympanometry and distortion product otoacoustic emissions. Turk. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 58, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostick, N.; Manwaring, K.; Dhar, R.; Sandler, R.; Mansy, H. The “Brain Stethoscope”: A Non-Invasive Method for Detecting Elevated Intracranial Pressure. Cureus 2021, 13, e13865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakka, L.; Thalamy, A.; Giraudet, F.; Hassoun, T.; Avan, P.; Chazal, J. Electrophysiological Monitoring of Cochlear Function as a Non-Invasive Method to Assess Intracranial Pressure Variations. In Intracranial Pressure and Brain Monitoring XIV; Schuhmann, M.U., Czosnyka, M., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2012; Volume 114, pp. 131–134. ISBN 978-3-7091-0955-7. [Google Scholar]
- Giraudet, F.; Longeras, F.; Mulliez, A.; Thalamy, A.; Pereira, B.; Avan, P.; Sakka, L. Noninvasive Detection of Alarming Intracranial Pressure Changes by Auditory Monitoring in Early Management of Brain Injury: A Prospective Invasive versus Noninvasive Study. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Büki, B.; Giraudet, F.; Avan, P. Non-Invasive Measurements of Intralabyrinthine Pressure Changes by Electrocochleography and Otoacoustic Emissions. Hear. Res. 2009, 251, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evensen, K.B.; Paulat, K.; Prieur, F.; Holm, S.; Eide, P.K. Utility of the Tympanic Membrane Pressure Waveform for Non-Invasive Estimation of The Intracranial Pressure Waveform. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Huang, W.; Wu, X.-J.; Shi, X.-L.; Hu, R.-R.; Chen, W.; Zhang, T.-F.; Xu, X.-L.; Huang, C.-G.; Hou, L.-J. Invention of a Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure (ICP) Monitoring System—An Enlightenment from a Hydrocephalus Study. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 36, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levinsky, A.; Papyan, S.; Weinberg, G.; Stadheim, T.; Eide, P.K. Non-Invasive Estimation of Static and Pulsatile Intracranial Pressure from Transcranial Acoustic Signals. Med. Eng. Phys. 2016, 38, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganslandt, O.; Mourtzoukos, S.; Stadlbauer, A.; Sommer, B.; Rammensee, R. Evaluation of a Novel Noninvasive ICP Monitoring Device in Patients Undergoing Invasive ICP Monitoring: Preliminary Results. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 128, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herklots, M.W.; Moudrous, W.; Oldenbeuving, A.; Roks, G.; Mourtzoukos, S.; Schoonman, G.G.; Ganslandt, O. Prospective Evaluation of Noninvasive HeadSense Intracranial Pressure Monitor in Traumatic Brain Injury Patients Undergoing Invasive Intracranial Pressure Monitoring. World Neurosurg. 2017, 106, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Vascular Methods | Ophthalmic Methods | Otic Methods | Brain | Whole Head |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - middle cerebral artery (Doppler) | - central artery (waveform analysis, two-depth-Doppler) | - tympanic membrane (displacement, temperature) | - ventricle and subarachnoid spaces (CT and MRI) | - blood and CSF circulation (NIRS and dielectric properties) |
| - retina and papilla (optical coherence tomography and ophthalmoscopy) | - cochlear microphonic potential | - CSF dynamics (MRI) | - spontaneous electrical activity of the head and brain (EEG) | |
| - ONSD (sonography and MRI) | - ear-to-ear ultrasound | - whole head (micromotions) | ||
| - whole optic tract (VEP) | - fontanelle (pressure) | |||
| - retinal veins (DVA, photo-plethysmography) | ||||
| - pupil (pupillometry) |
| Category | No. of Studies | State of the Method
| Sensitivity for Detecting Increased ICP | Specificity for Detecting Increased ICP | Correlation with Invasive ICP Coefficient r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MR-ICP | 7 | 2 | 100% | 100% | r = 0.95–0.98 |
| TCD | 22 | 3 | 92% | 92% | r = 0.62–0.92 |
| ONSD | 68 | 3 | 83–96% | 74–96% | r = 0.53–0.82 |
| Ocular vessels | 19 | 2 | 87–94% | 50–92% | r = 0.74–0.99 |
| Tympanic membrane | 10 | 2 | 81–100% | 96–100% | r = 0.93 |
| Dielectric properties | 9 | 1–2 | 77–90% | 76–89% | r = 0.76–0.98 |
| Time | Name | Inventor | Idea |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 to present | ICM+ (and other software tools) | Cambridge Enterprise Ltd., University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK | Multimodal flow monitoring and analysis |
| 1988 to present | Transcranial Doppler | Several investigators | Flow pattern analysis |
| 1990 | headband electrode | Russegger and Ennemoser, Neurosurgery, Innsbruck, Austria | Dielectric properties |
| 2000 to present | MR-ICP | Alperin et al., University of Illinois at Chicago | CSF and blood flow calculations |
| 2005 to present | Two-depth Doppler | Health Telematics Science Institute at the Kaunas University of Technology, Kaunas, Lithuania | Two-depth Doppler measurement of the ophthalmic artery |
| 2005 to present | Dynamic vessel analyzer | (not primarily intended for ICP estimation) Imedos, Jena, Germany | Retinal vessel pulsations |
| 2013 to present | Non-invasive cerebrovascular autoregulation | Health Telematics Science Institute at the Kaunas University of Technology, Kaunas, Lithuania | Ultrasonic time of flight |
| 2017 to present | HS-1000 | HeadSense Medical Ltd., Netanya, Israel | Ear-to-ear ultrasound |
| 2019 to present | Braincare | Braincare, São Carlos, Brazil | Cranial expansion |
| 2021 to present | Micromotions pillow | Charles University in Prague and the Military University Hospital, Prague, Czech Republic | Micromotions |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Müller, S.J.; Henkes, E.; Gounis, M.J.; Felber, S.; Ganslandt, O.; Henkes, H. Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Monitoring. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062209
Müller SJ, Henkes E, Gounis MJ, Felber S, Ganslandt O, Henkes H. Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Monitoring. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(6):2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062209
Chicago/Turabian StyleMüller, Sebastian Johannes, Elina Henkes, Matthew J. Gounis, Stephan Felber, Oliver Ganslandt, and Hans Henkes. 2023. "Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Monitoring" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 6: 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062209
APA StyleMüller, S. J., Henkes, E., Gounis, M. J., Felber, S., Ganslandt, O., & Henkes, H. (2023). Non-Invasive Intracranial Pressure Monitoring. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(6), 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062209







