Comparison of Short- and Long-Term Effectiveness between Anti-TNF and Ustekinumab after Vedolizumab Failure as First-Line Therapy in Crohn’s Disease: A Multi-Center Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Outcome Definitions
2.2. Statistical Methods
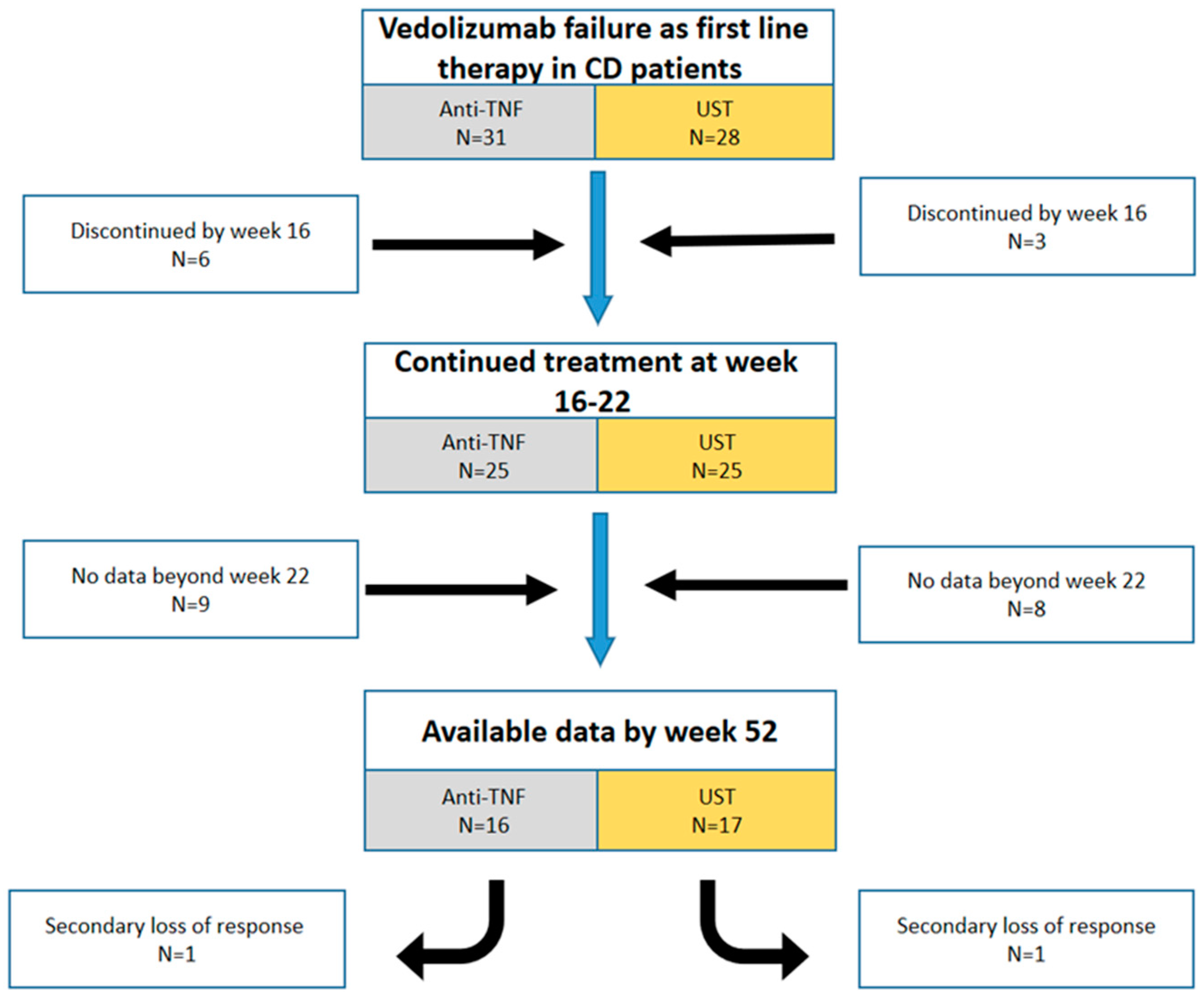
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Treatment Outcomes
3.2.1. Initial Response
3.2.2. Maintenance of Response
3.2.3. Changes in CRP and FCP
3.3. Discontinuation of Therapy
3.4. Safety
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dreesen, E.; Gils, A. Letter: Overcoming secondary loss of response to infliximab-it is not the drug, it is how you use it! Authors’ reply. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 1029–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopylov, U.; Seidman, E. Predicting durable response or resistance to antitumor necrosis factor therapy in inflammatory bowel disease. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2016, 9, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stidham, R.W.; Lee, T.C.H.; Higgins, P.D.R.; Deshpande, A.R.; Sussman, D.A.; Singal, A.G.; Elmunzer, B.J.; Saini, S.D.; Vijan, S.; Waljee, A.K. Systematic review with network meta-analysis: The efficacy of anti-TNF agents for the treatment of Crohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1349–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preda, C.; Fulger, L.E.; Gheorghe, L.; Gheorghe, C.; Goldis, A.; Trifan, A.; Tantau, M.; Tantau, A.; Negreanu, L.; Manuc, M.; et al. Infliximab and Adalimumab in Crohn’s disease: Real-life data from a national cohort study. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2016, 42, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stidham, R.W.; Lee, T.C.H.; Higgins, P.D.R.; Deshpande, A.R.; Sussman, D.A.; Singal, A.G.; Waljee, A.K. Effects of vedolizumab induction therapy for patients with Crohn’s disease in whom tumor necrosis factor antagonist treatment failed. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 618–627.e3. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeire, S.; Loftus, E.V., Jr.; Colombel, J.-F.; Feagan, B.G.; Sandborn, W.J.; Sands, B.E.; Danese, S.; D’Haens, G.R.; Kaser, A.; Panaccione, R.; et al. Long-term Efficacy of Vedolizumab for Crohn’s Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2017, 11, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sands, B.E.; Sandborn, W.J.; Van Assche, G.; Lukas, M.; Xu, J.; James, A.; Lasch, K. Vedolizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for crohn’s disease in patients naïve to or who have failed tumor necrosis factor antagonist therapy. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sands, B.E.; Sandborn, W.J.; Van Assche, G.; Lukas, M.; Xu, J.; James, A.; Lasch, K. Vedolizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for Crohn’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 711–721. [Google Scholar]
- Kopylov, U.; Avni-Biron, I.; Ron, Y.; Koslowsky, B.; Waterman, M.; Daher, S.; Ungar, B.; Schwartz, D.; Zittan, E.; Openhaim, M.; et al. Effectiveness and safety of vedolizumab for maintenance treatment in inflammatory bowel disease-The Israeli real world experience. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macaluso, F.S.; Fries, W.; Renna, S.; Viola, A.; Muscianisi, M.; Cappello, M.; Sicilian Network for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (SN-IBD). Effectiveness and safety of vedolizumab in biologically naïve patients: A real-world multi-centre study. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2020, 8, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubesch, A.; Rueter, L.; Farrag, K.; Krause, T.; Stienecker, K.; Hausmann, J.; Blumenstein, I. Short and Long-Term Effectiveness of Ustekinumab in Patients with Crohn’s Disease: Real-World Data from a German IBD Cohort. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liefferinckx, C.; Verstockt, B.; Gils, A.; Noman, M.; Van Kemseke, C.; Macken, E.; Belgian Inflammatory Bowel Disease Research and Development Group [BIRD Group]. Long-term Clinical Effectiveness of Ustekinumab in Patients with Crohn’s Disease Who Failed Biologic Therapies: A National Cohort Study. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feagan, B.G.; Sandborn, W.J.; Gasink, C.; Jacobstein, D.; Lang, Y.; Friedman, J.R.; Blank, M.A.; Johanns, J.; Gao, L.-L.; Miao, Y.; et al. Ustekinumab as induction and maintenance therapy for crohn’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1946–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreesen, E.; Van Stappen, T.; Ballet, V.; Peeters, M.; Compernolle, G.; Tops, S.; Van Steen, K.; Van Assche, G.; Ferrante, M.; Vermeire, S.; et al. Anti-infliximab antibody concentrations can guide treatment intensification in patients with Crohn’s disease who lose clinical response. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amiot, A.; Grimaud, J.-C.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Filippi, J.; Pariente, B.; Roblin, X.; Buisson, A.; Stefanescu, C.; Trang-Poisson, C.; Altwegg, R.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Vedolizumab Induction Therapy for Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 1593–1601.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shmidt, E.; Kochhar, G.; Hartke, J.; Chilukuri, P.; Meserve, J.; Chaudrey, K.; Koliani-Pace, J.L.; Hirten, R.; Faleck, D.; Barocas, M.; et al. Predictors and management of loss of response to vedolizumab in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 2461–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisbert, J.P.; Panés, J. Loss of response and requirement of infliximab dose intensification in Crohn’s disease: A review. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billioud, V.; Sandborn, W.J.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Loss of response and need for adalimumab dose intensification in Crohn’s disease: A systematic review. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, R.S.; Njie, C.; Marcus, J.; Gupta, S.; Allegretti, J.R. Predictors of ustekinumab failure in crohn’s disease after dose intensification. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2021, 27, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Danese, S.; Argollo, M.; Pouillon, L.; Peppas, S.; Gonzalez-Lorenzo, M.; Lytras, T.; Bonovas, S. Loss of Response to Vedolizumab and Ability of Dose Intensification to Restore Response in Patients with Crohn’s Disease or Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 838–846.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Attauabi, M.; Höglund, C.; Fassov, J.; Pedersen, K.B.; Hansen, H.B.; Wildt, S.; Burisch, J. Vedolizumab as first-line biological therapy in elderly patients and those with contraindications for anti-TNF therapy: A real-world, nationwide cohort of patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgart, D.C.; Bokemeyer, B.; Drabik, A.; Stallmach, A.; Schreiber, S. Vedolizumab Germany Consortium. Vedolizumab induction therapy for inflammatory bowel disease in clinical practice--a nationwide consecutive German cohort study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 1090–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopylov, U.; Verstockt, B.; Biedermann, L.; Sebastian, S.; Pugliese, D.; Sonnenberg, E.; Steinhagen, P.R.; Arebi, N.; Ron, Y.; Kucharzik, T.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Vedolizumab in Anti-TNF-Naïve Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease-A Multicenter Retrospective European Study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 2442–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazlewood, G.S.; Rezaie, A.; Borman, M.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Seow, C.H.; Kaplan, G.G. Comparative effectiveness of immunosuppressants and biologics for inducing and maintaining remission in Crohn’s disease: A network meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 344–354.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S. Network meta-analysis to inform positioning of biologics in patients with Crohn’s disease: Promise and perils. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 38–39, 101614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Fumery, M.; Sandborn, W.J.; Murad, M.H. Systematic review and network meta-analysis: First- and second-line biologic therapies for moderate-severe Crohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 394–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeire, S.; Schreiber, S.; Sandborn, W.J.; Dubois, C.; Rutgeerts, P. Correlation between the Crohn’s disease activity and Harvey-Bradshaw indices in assessing Crohn’s disease severity. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, C.; Marsal, J.; Bergemalm, D.; Vigren, L.; Björk, J.; Eberhardson, M.; Halfvarson, J. Long-term effectiveness of vedolizumab in inflammatory bowel disease: A national study based on the Swedish National Quality Registry for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (SWIBREG). Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, T.; Ungar, B.; Yung, D.E.; Ben-Horin, S.; Eliakim, R.; Kopylov, U. Vedolizumab in IBD-Lessons from Real-world Experience; A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis. J. Crohns Colitis 2018, 12, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allegretti, J.R.; Barnes, E.L.; Stevens, B.; Storm, M.; Ananthakrishnan, A.; Yajnik, V.; Korzenik, J. Predictors of Clinical Response and Remission at 1 Year Among a Multicenter Cohort of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treated with Vedolizumab. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 1590–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolinger, M.; Rolfes, P.; Phan, B.; Pan, S.; Dubinsky, M. P082 anti-tnf efficacy after primary vedolizumab failure in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2020, 26 (Suppl. S1), S71–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albshesh, A.; Taylor, J.; Savarino, E.V.; Truyens, M.; Armuzzi, A.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Kopylov, U. Effectiveness of Third-Class Biologic Treatment in Crohn’s Disease: A Multi-Center Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alric, H.; Amiot, A.; Kirchgesner, J.; Tréton, X.; Allez, M.; Bouhnik, Y.; Beaugerie, L.; Carbonnel, F.; Meyer, A. The effectiveness of either ustekinumab or vedolizumab in 239 patients with Crohn’s disease refractory to anti-tumour necrosis factor. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 948–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taxonera, C.; Rodríguez, C.; Bertoletti, F.; Menchén, L.; Arribas, J.; Sierra, M.; Arias, L.; Martínez-Montiel, P.; Juan, A.; Iglesias, E.; et al. Clinical Outcomes of Golimumab as First, Second or Third Anti-TNF Agent in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Ulcerative Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 1394–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iborra, M.; Beltrán, B.; Clotet, A.F.; Gutiérrez, A.; Antolín, B.; Huguet, J.; De Francisco, R.; Merino, O.; Carpio, D.; García-López, S.; et al. Real-world short-term effectiveness of ustekinumab in 305 patients with Crohn’s disease: Results from the ENEIDA registry. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussias, N.; Rizzello, F.; Calabrese, C.; Passino, A.S.; Melotti, L.; Scaioli, E.; Gionchetti, P. Effec-tiveness of ustekinumab after vedolizumab failure in patients with anti-TNF-refractory Crohn’s disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2021, 15, S528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, T.E.; Fourment, C.; Kuten, S.A.; Hardin, T.C.; Van Anglen, L.J. 728°Second-Line Biologic Therapy After Vedolizumab. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, S429–S430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, T.E.; Fourment, C.; Okoro, T.C.; Hardin, T.C.; Van Anglen, L.J. Failure of Vedolizumab as First-Line Biologic Does Not Decrease Response Rates of Second-Line Therapy: 681. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2018, 113, S382–S383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegbola, S.O.; Sahnan, K.; Warusavitarne, J.; Hart, A.; Tozer, P. Anti-TNF Therapy in Crohn’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engel, T.; Yung, D.E.; Ma, C.; Pariente, B.; Wils, P.; Eliakim, R.; Ungar, B.; Ben-Horin, S.; Kopylov, U. Effectiveness and safety of Ustekinumab for Crohn’s disease; systematic review and pooled analysis of real-world evidence. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Overall | UST | Anti-TNF | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient number, N (%) | 59 | 28 (47.5) | 31 (52.5) | 0.7 |
| Demographics | ||||
| Mean (SD) age, years | 52 (19) | 58 (17.5) | 46 (19) | 0.9 |
| Gender [male], n(%) | 25 (42.4) | 12 (42.8) | 13 (41.9) | 0.9 |
| Gender [female], n(%) | 34 (57.6) | 16 (57.1) | 18 (58) | 0.9 |
| Smoking status | ||||
| Current, n (%) | 9 (15.2) | 5 (17.8) | 4 (12.9) | 0.6 |
| Former, n (%) | 13 (22) | 8 (28.5) | 5 (16.1) | 0.3 |
| Never smoked, n (%) | 37 (62.8) | 15 (53.5) | 22 (70.9) | 0.5 |
| Clinical characteristics | ||||
| Disease duration, years (IQR) | 35 (23–56.5) | 43 (25–60) | 36 (21–48) | 0.4 |
| Disease location | ||||
| Ileal | 19 (32.4) | 11 (39.2) | 8 (25.8) | 0.4 |
| Colonic | 18 (30.5) | 9 (32.1) | 9 (29) | 0.8 |
| Ileocolonic | 21 (35.5) | 7 (25) | 14 (45.1) | 0.2 |
| Upper-GI | 1 (1.6) | 1 (3.5) | 0 (0) | 0.4 |
| Behavior | ||||
| Non-stricturing, non-penetrating | 39 (66.2) | 20 (71.4) | 19 (61.2) | 0.7 |
| Stricturing | 16 (27.1) | 7 (25) | 9 (29) | 0.7 |
| Penetrating | 4 (6.7) | 1 (3.5) | 3 (9.6) | 0.3 |
| Perianal disease | 5 (8.4) | 3 (10.7) | 2 (6.4) | 0.5 |
| History of surgery | 17 (28.8) | 8 (28.5) | 9 (29) | 0.9 |
| Mean vedolizumab therapy duration, months (IQR) | 12 (5–17) | 14.3 (6–18.7) | 10 (4–14) | 0.1 |
| Disease activity at treatment onset | ||||
| HBI median, (IQR) | 8 (6–9) | 9 (7–10.7) | 7 (6–9) | 0.6 |
| Elevated CRP, n (%) | 36 (66.6) | 16 (59.2) | 20 (74) | 0.7 |
| Elevated FCP, n (%) | 26 (68.4) | 12 (66.5) | 14 (70) | 0.9 |
| Concomitant corticosteroid | 23 (38.9) | 13 (46.4) | 10 (32.2) | 0.6 |
| Concomitant immunomodulators | 6 (10.1) | 1 (3.5) | 5 (16.1) | 0.1 |
| Patients Number | Drug | Adverse Events | Stopped Therapy | Required Hospitalization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient 1 | UST | Rash in the extremities and itchy | Yes | No |
| Patient 2 | Anti-TNF | Allergic reaction to anti TNF | No | No |
| Patient 3 | Anti-TNF | Fatigue, arthralgia, myalgia | No | No |
| Patient 4 | Anti-TNF | Worsening in ITP | Yes | Yes |
| Patient 5 | UST | Uneasiness, loss of strength | Yes | No |
| Patient 6 | Anti-TNF | Pancreatitis | No | Yes |
| Patient 7 | UST | Lung cancer | Yes | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albshesh, A.; Bannon, L.; Sharar Fischler, T.; Truyens, M.; Vavricka, S.R.; Tepes, K.; Pugliese, D.; Savarino, E.V.; Zittan, E.; Drobne, D.; et al. Comparison of Short- and Long-Term Effectiveness between Anti-TNF and Ustekinumab after Vedolizumab Failure as First-Line Therapy in Crohn’s Disease: A Multi-Center Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072503
Albshesh A, Bannon L, Sharar Fischler T, Truyens M, Vavricka SR, Tepes K, Pugliese D, Savarino EV, Zittan E, Drobne D, et al. Comparison of Short- and Long-Term Effectiveness between Anti-TNF and Ustekinumab after Vedolizumab Failure as First-Line Therapy in Crohn’s Disease: A Multi-Center Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(7):2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072503
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbshesh, Ahmad, Lian Bannon, Tali Sharar Fischler, Marie Truyens, Stephan R. Vavricka, Katja Tepes, Daniela Pugliese, Edoardo V. Savarino, Eran Zittan, David Drobne, and et al. 2023. "Comparison of Short- and Long-Term Effectiveness between Anti-TNF and Ustekinumab after Vedolizumab Failure as First-Line Therapy in Crohn’s Disease: A Multi-Center Retrospective Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 7: 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072503
APA StyleAlbshesh, A., Bannon, L., Sharar Fischler, T., Truyens, M., Vavricka, S. R., Tepes, K., Pugliese, D., Savarino, E. V., Zittan, E., Drobne, D., Roblin, X., Bar-Gil Shitrit, A., Armuzzi, A., Lobaton, T., Maharshak, N., Yanai, H., Ben-Horin, S., & Kopylov, U. (2023). Comparison of Short- and Long-Term Effectiveness between Anti-TNF and Ustekinumab after Vedolizumab Failure as First-Line Therapy in Crohn’s Disease: A Multi-Center Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(7), 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072503










