Quantitative and Qualitative Assessments of Retinal Structure with Variable A-Scan Rate Spectralis OCT: Insights into IPL Multilaminarity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Selection
2.2. Ophthalmic Evaluations
2.3. OCT Settings
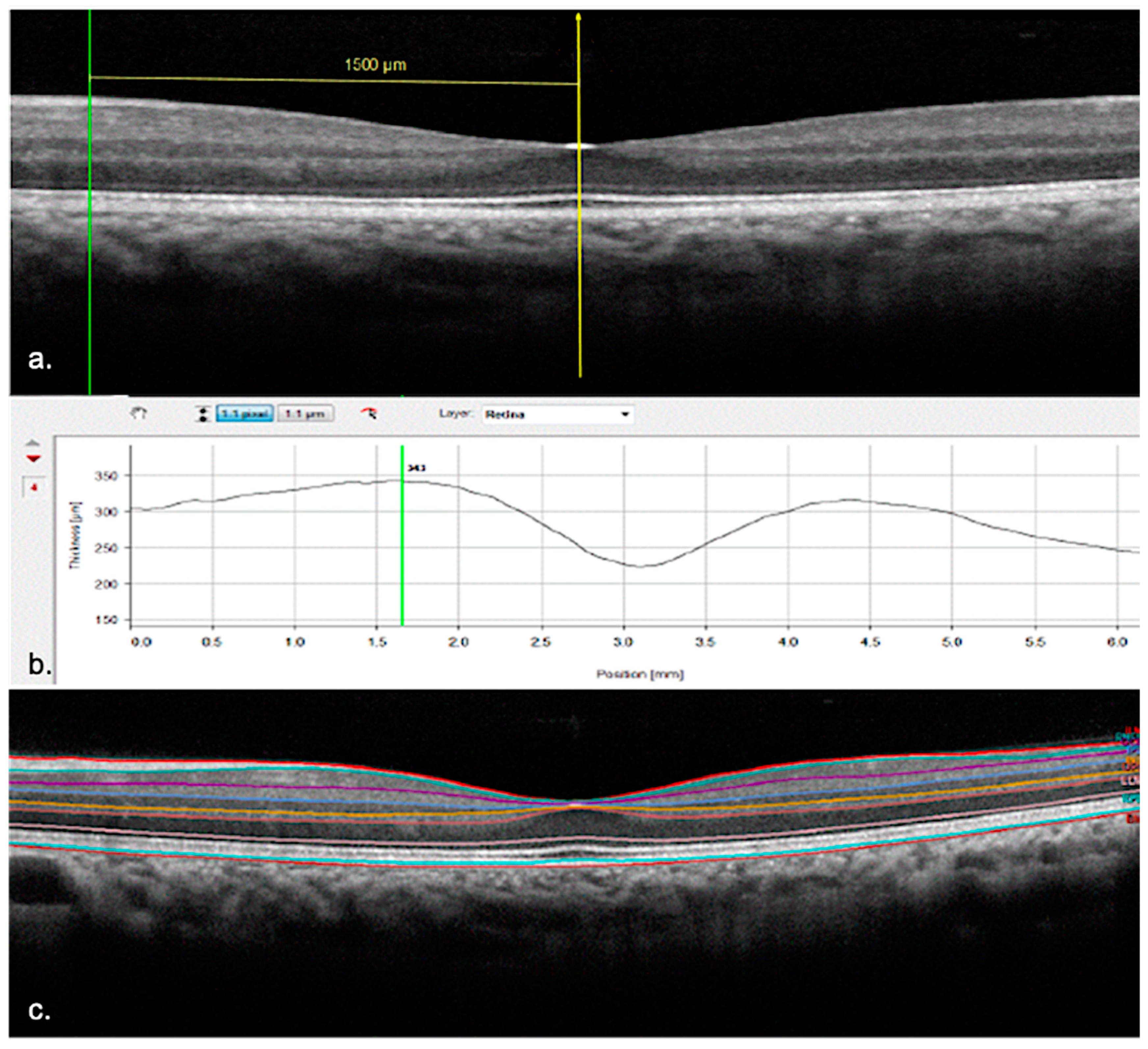
2.4. Quantitative Assessment
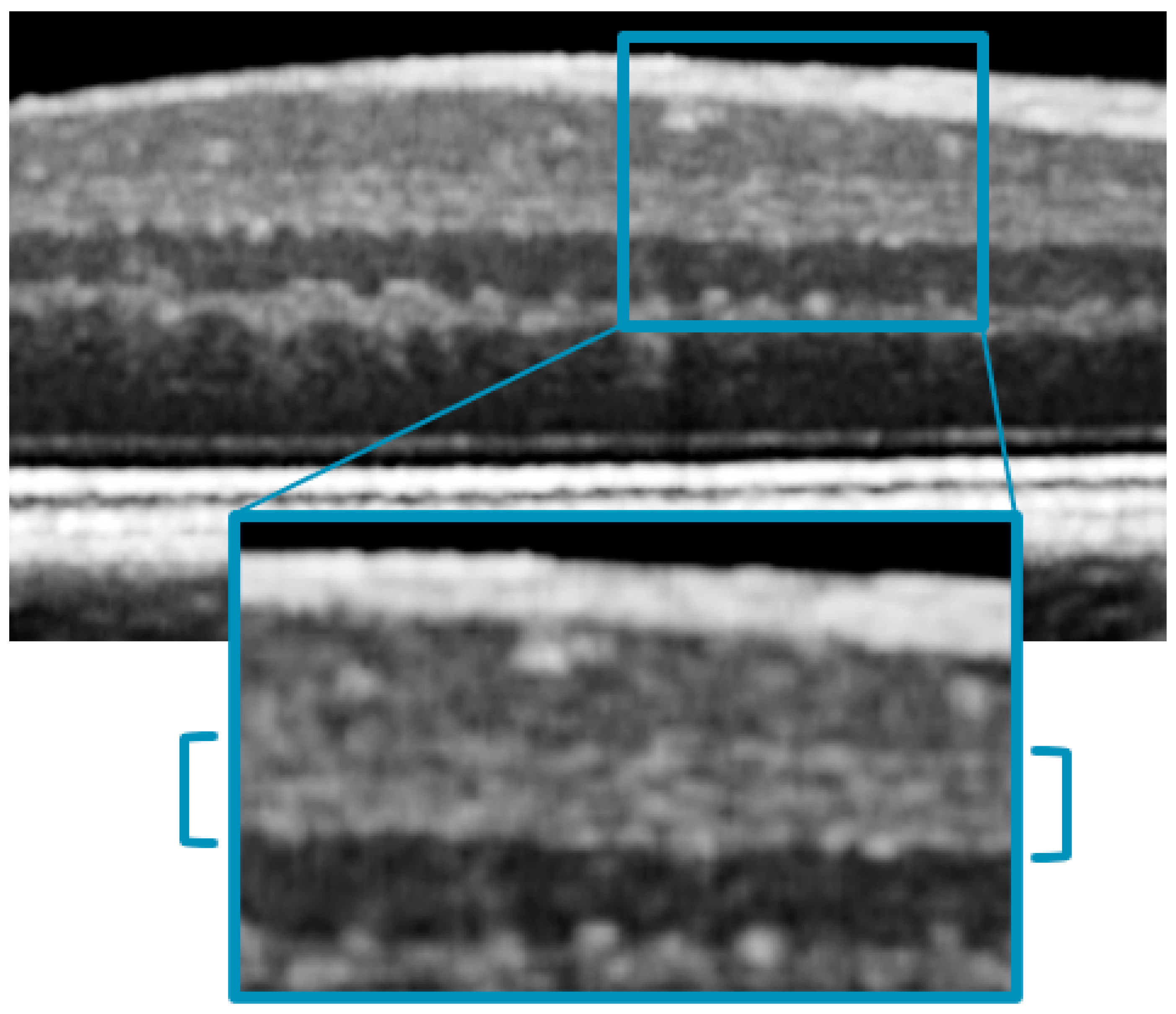
2.5. Qualitative Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
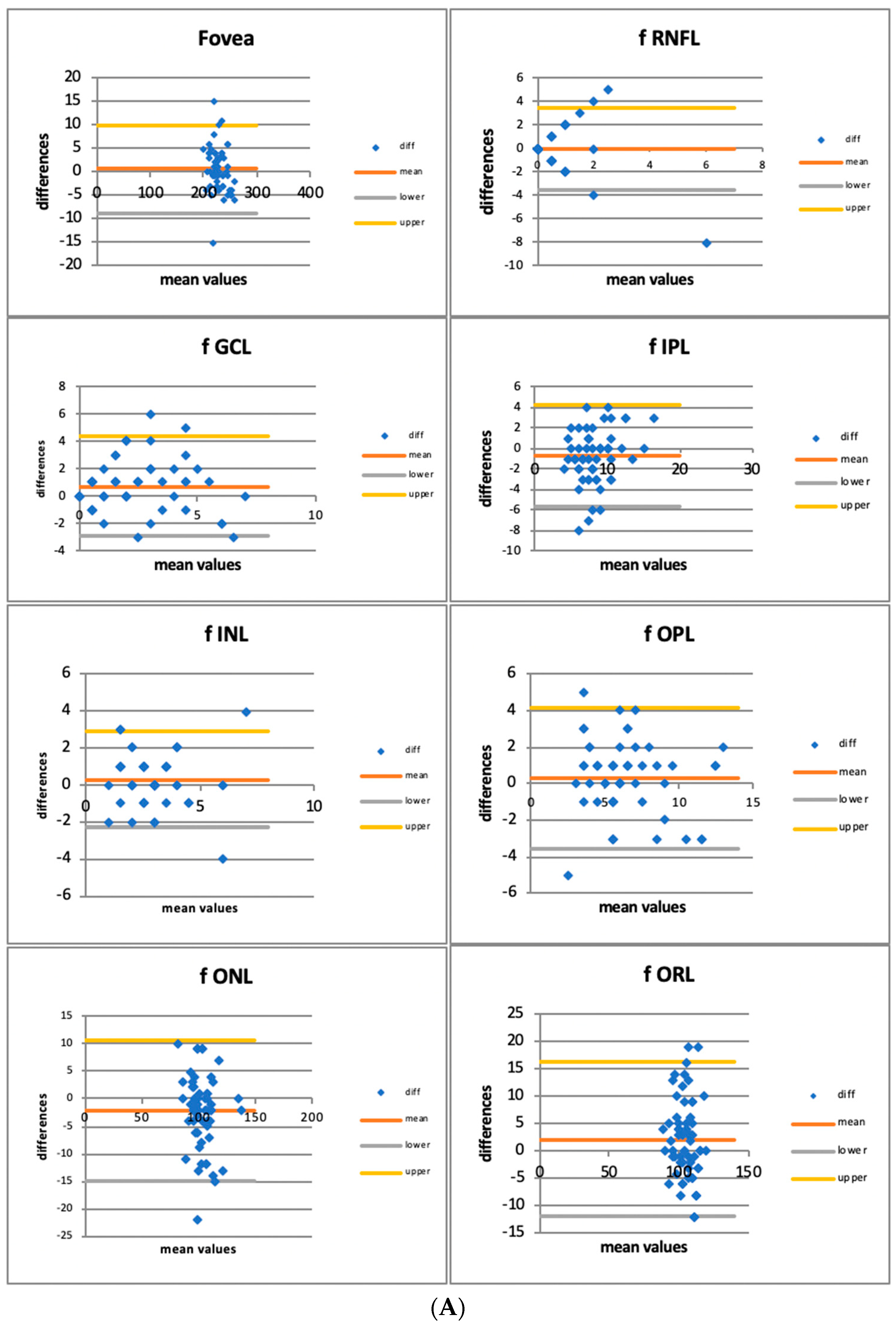
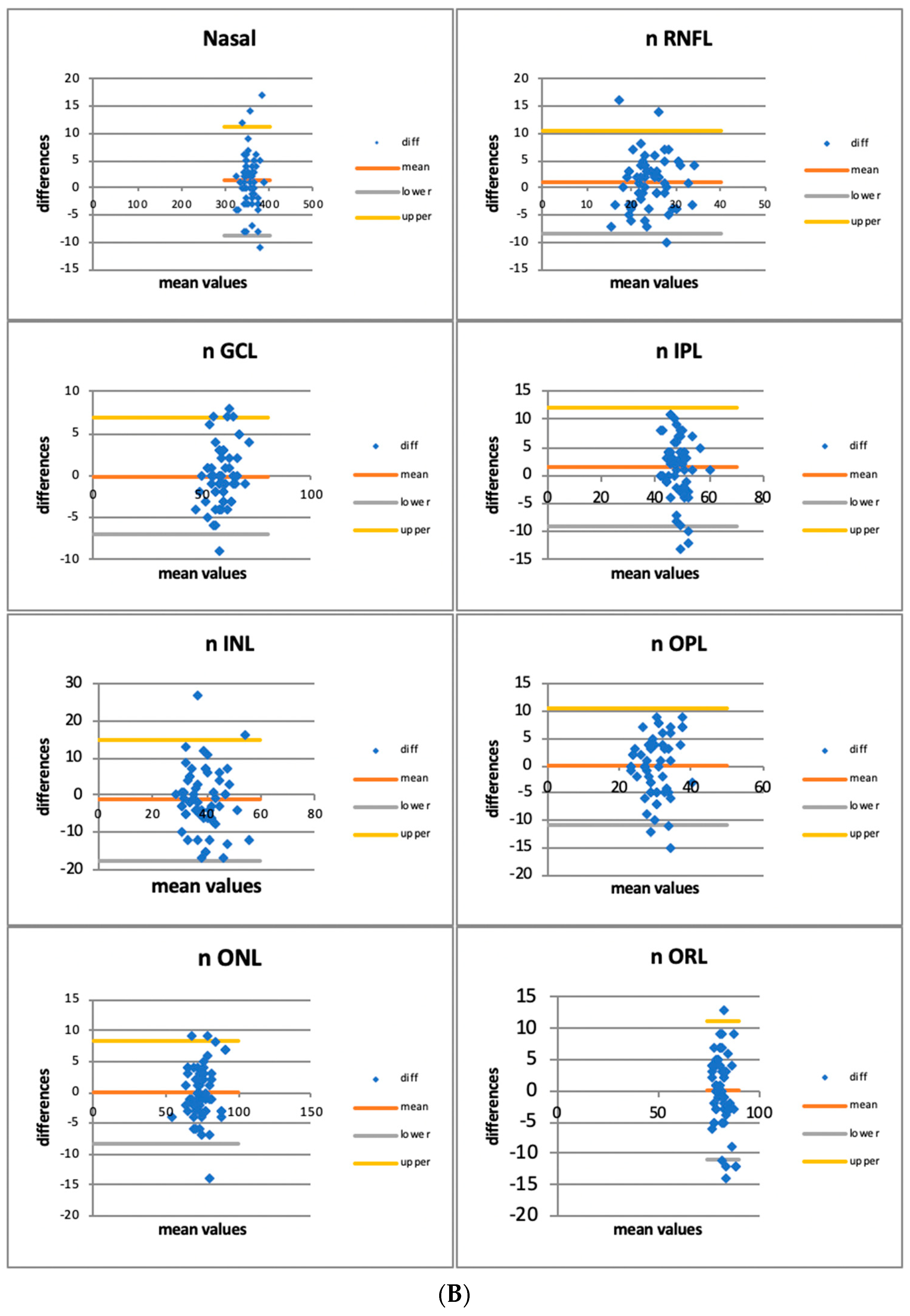
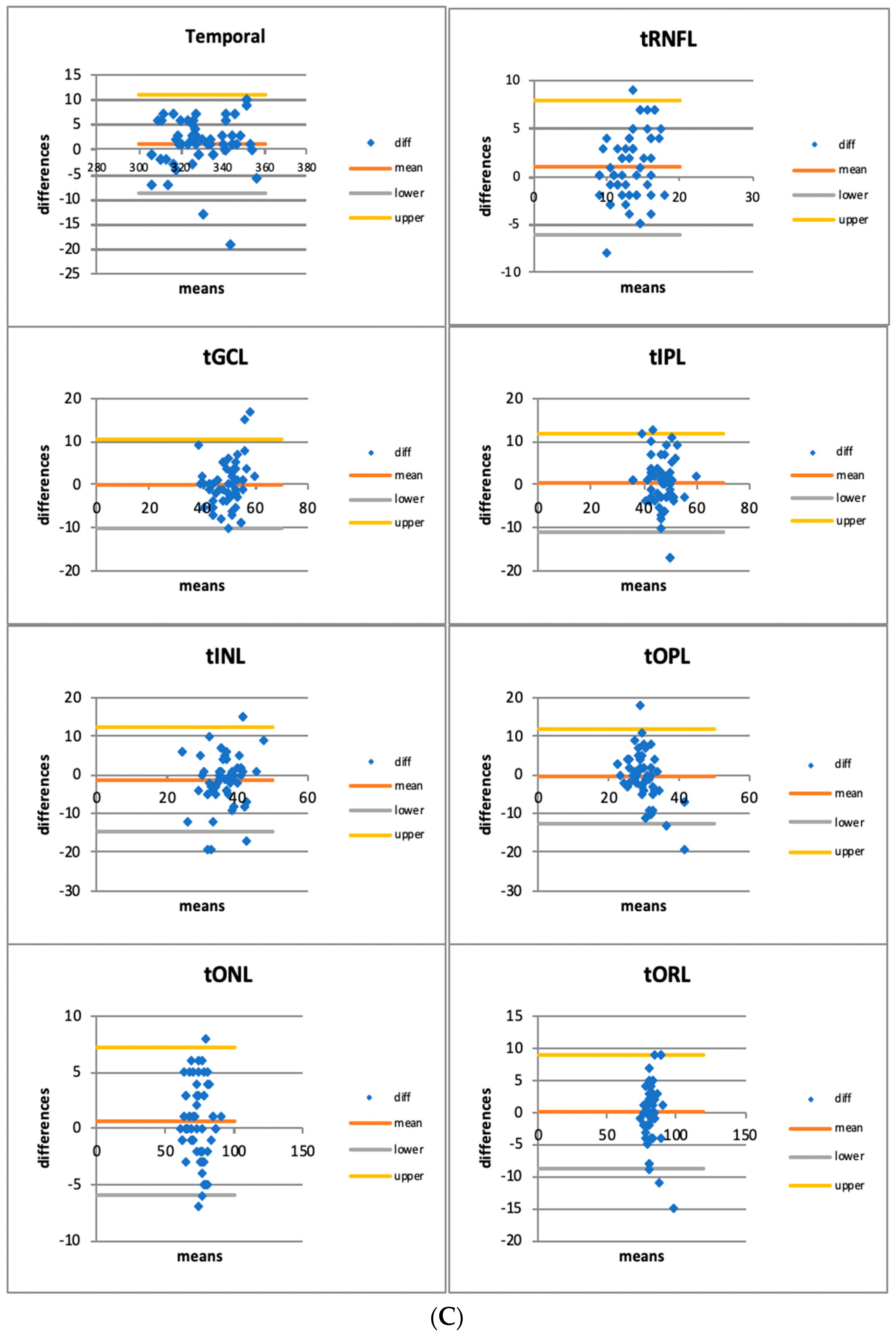
3.1. Quantitative Assessment
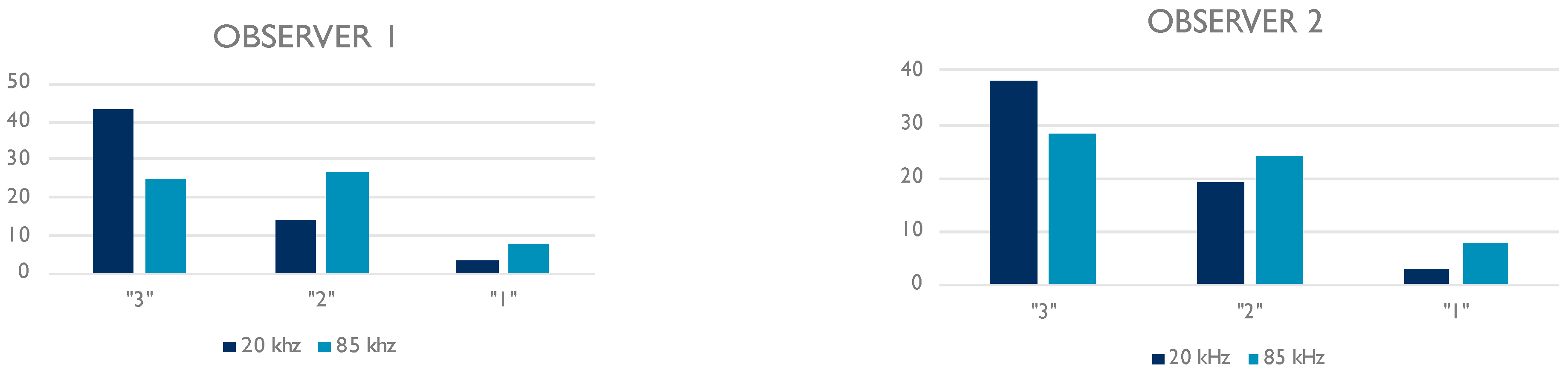
3.2. Qualitative Assessment
- 20 kHz Observer 1–Observer 2: R = 0.735 (p < 0.001)
- 85 kHz Observer 1–Observer 2: R = 0.777 (p < 0.001).
3.3. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, D.; Swanson, E.A.; Lin, C.P.; Schuman, J.S.; Stinson, W.G.; Chang, W.; Hee, M.R.; Flotte, T.; Gregory, K.; Puliafito, C.A. Optical coherence tomography. Science 1991, 254, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fercher, A.F.; Hitzenberger, C.K.; Kamp, G.; El-Zaiat, S.Y. Measurement of intraocular distances by backscattering spectral interferometry. Opt. Commun. 1995, 117, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidelberg Engineering sponsored You Set the Pace. The Ophthalmologist. Available online: https://theophthalmologist.com/subspecialties/you-set-the-pace (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Choi, W.; Moult, E.M.; Waheed, N.K.; Adhi, M.; Lee, B.; Lu, C.D.; de Carlo, T.E.; Jayaraman, V.; Rosenfeld, P.J.; Duker, J.S.; et al. Ultrahigh-Speed, Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography in Nonexudative Age-Related Macular Degeneration with Geographic Atrophy. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 2532–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploner, S.B.; Moult, E.M.; Choi, W.; Waheed, N.K.; Lee, B.; Novais, E.A.; Cole, E.D.; Potsaid, B.; Husvogt, L.; Schottenhamml, J.; et al. Toward quantitative optical coherence tomography angiography. Retina 2016, 36, S118–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltzien, F.; Percival, K.A.; Martin, P.R.; Grünert, U. Analysis of bipolar and amacrine populations in marmoset retina. J. Comp. Neurol. 2015, 523, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, R.; Gan, L. Development of Retinal Amacrine Cells and Their Dendritic Stratification. Curr. Ophthalmol. Rep. 2014, 2, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, E.V.J.; Kolb, H. Structural basis for ON-and OFF-center responses in retinal ganglion cells. Science 1976, 194, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.; Famiglietti, E.V.; Kolb, H. Intracellular staining reveals different levels of stratification for on- and off-center ganglion cells in cat retina. J. Neurophysiol. 1978, 41, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norcia, A.M.; Yakovleva, A.; Hung, B.; Goldberg, J.L. Dynamics of Contrast Decrement and Increment Responses in Human Visual Cortex. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanna, H.; Dubis, A.M.; Ayub, N.; Tait, D.M.; Rha, J.; Stepien, K.E.; Carroll, J. Retinal imaging using commercial broadband optical coherence tomography. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 94, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.T.; Kurokawa, K. Cellular-Scale Imaging of Transparent Retinal Structures and Processes Using Adaptive Optics Optical Coherence Tomography. Annu. Rev. Vis. Sci. 2020, 6, 115–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Kho, A.M.; Srinivasan, V.J. Improving visible light OCT of the human retina with rapid spectral shaping and axial tracking. Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Kho, A.M.; Srinivasan, V.J. In vivo Morphometry of Inner Plex Layer (IPL) Stratification in the Human Retina With Visible Light Optical Coherence Tomography. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 655096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, I.; Smretschnig, E.; Moussa, S.; Brannath, W.; Womastek, I.; Binder, S. Quality and reproducibility of retinal thickness measurements in two spectral-domain optical coherence tomography machines. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 6925–6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershoni, A.; Barayev, E.; Vainer, I.; Allon, R.; Yavnieli, R.; Shapira, Y.; Mimouni, M.; Geffen, N.; Nemet, A.Y.; Segal, O. Thickness measurements taken with the spectralis OCT increase with decreasing signal strength. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022, 22, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Vicent, A.; Brautaset, R.; Venkataraman, A.P. Repeatability of quantitative measurements of retinal layers with SD-OCT and agreement between vertical and horizontal scan protocols in healthy eyes. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szkulmowski, M.; Gorczynska, I.; Szlag, D.; Sylwestrzak, M.; Kowalczyk, A.; Wojtkowski, M. Efficient reduction of speckle noise in Optical Coherence Tomography. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teussink, M.M.; Donner, S.; Otto, T.; Williams, K.; Tafreshi, A. State-of-the-art commercial spectral-domain and swept-source OCT technologies and their clinical applications in ophthalmology. Heidelb. Eng. 2019, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- de Boer, J.F.; Leitgeb, R.; Wojtkowski, M. Twenty-five years of optical coherence tomography: The paradigm shift in sensitivity and speed provided by Fourier domain OCT [Invited]. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyak, S.L. The Retina: The Anatomy and the Histology of the Retina in Man, Ape, and Monkey, Including the Consideration of Visual Functions, the History of Physiological Optics, and the Histological Laboratory Technique; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Marc, R.E. Neurochemical stratification in the inner plexiform layer of the vertebrate retina. Vision Res. 1986, 26, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koontz, M.A.; Hendrickson, A.E. Stratified distribution of synapses in the inner plexiform layer of primate retina. J. Comp. Neurol. 1987, 263, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drexler, W.; Fujimoto, J.G. State-of-the-art retinal optical coherence tomography. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2008, 27, 45–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| 20 kHz | 85 kHz | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOVEAL | Mean (μm) | SD | Mean (μm) | SD | p | |
| TOTAL | 228.55 | 13.576 | 227.92 | 14.563 | 0.310 | |
| RNFL | 0.52 | 1.066 | 0.55 | 1.466 | 0.883 | |
| GCL | 2.58 | 2.102 | 2.61 | 2.051 | 0.521 | |
| IPL | 7.87 | 2.100 | 8.62 | 2.525 | 0.056 | |
| INL | 3.07 | 1.364 | 2.77 | 1.430 | 0.086 | |
| OPL | 6.56 | 2.380 | 6.19 | 2.757 | 0.130 | |
| ONL | 102.00 | 10.025 | 102.12 | 11.073 | 0.154 | |
| ORL | 105.87 | 7.386 | 102.58 | 12.730 | 0.053 | |
| NASAL | Mean (μm) | SD | Mean (μm) | SD | p | |
| TOTAL | 356.40 | 15.075 | 355.17 | 15.107 | 0.066 | |
| RNFL | 24.75 | 4.963 | 23.70 | 4.816 | 0.099 | |
| GCL | 58.78 | 5.693 | 58.85 | 4.772 | 0.884 | |
| IPL | 48.93 | 3.970 | 48.73 | 4.876 | 0.484 | |
| INL | 38.32 | 7.149 | 39.50 | 7.659 | 0.276 | |
| OPL | 29.95 | 4.931 | 30.05 | 4.597 | 0.889 | |
| ONL | 74.05 | 7.559 | 74.07 | 7.095 | 0.976 | |
| ORL | 81.50 | 3.606 | 81.40 | 4.851 | 0.892 | |
| TEMPORAL | Mean (μm) | SD | Mean (μm) | SD | p | |
| TOTAL | 330.08 | 14.377 | 328.88 | 13.748 | 0.072 | |
| RNFL | 13.60 | 3.396 | 13.32 | 2.451 | 0.346 | |
| GCL | 49.23 | 6.264 | 49.17 | 5.156 | 0.923 | |
| IPL | 46.90 | 4.874 | 46.40 | 5.493 | 0.511 | |
| INL | 35.63 | 6.175 | 36.93 | 5.713 | 0.150 | |
| OPL | 29.73 | 3.672 | 30.25 | 6.078 | 0.526 | |
| ONL | 73.55 | 7.210 | 72.58 | 7.777 | 0121 | |
| ORL | 81.57 | 4.327 | 81.55 | 4.659 | 0.977 | |
| COV 20 kHz | COV 85 kHz | COV 20 kHz | COV 85 kHz | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOVEAL | 5.9% | 6.4% | N INL | 18.7% | 19.4% |
| F RNFL | 206.2% | 266.6% | N OPL | 16.5% | 15.3% |
| F GPL | 81.4% | 108.9% | N ONL | 10.2% | 9.6% |
| F IPL | 29.3% | 39.4% | N ORL | 4.4% | 6.0% |
| F INL | 44.5% | 51.7% | TEMPORAL | 4.4% | 4.2% |
| F OPL | 36.3% | 44.4% | T RNFL | 25.0% | 19.5% |
| F ONL | 9.8% | 10.6% | TGPL | 12.7% | 10.5% |
| F ORL | 7.0% | 12.4% | T IPL | 10.4% | 11.8% |
| NASAL | 4.2% | 4.3% | T INL | 17.3% | 15.5% |
| N RNFL | 20.1% | 20.3% | T OPL | 12.4% | 20.1% |
| N GPL | 9.7% | 8.1% | T ONL | 9.8% | 10.7% |
| N IPL | 8.1% | 10.3% | T ORL | 5.3% | 5.7% |
| 20 kHz | ||
| Observer 1 | Observer 2 | |
| Grade “3” | 43 (71.7%) | 38 (63.3%) |
| Grade “2” | 14 (23.3%) | 19 (31.7%) |
| Grade “1” | 3 (5%) | 3 (5%) |
| 85 kHz | ||
| Observer 1 | Observer 2 | |
| Grade “3” | 25 (41.7%) | 28 (46.7%) |
| Grade “2” | 27 (45%) | 24 (40%) |
| Grade “1” | 8 (13.3%) | 8 (13.3%) |
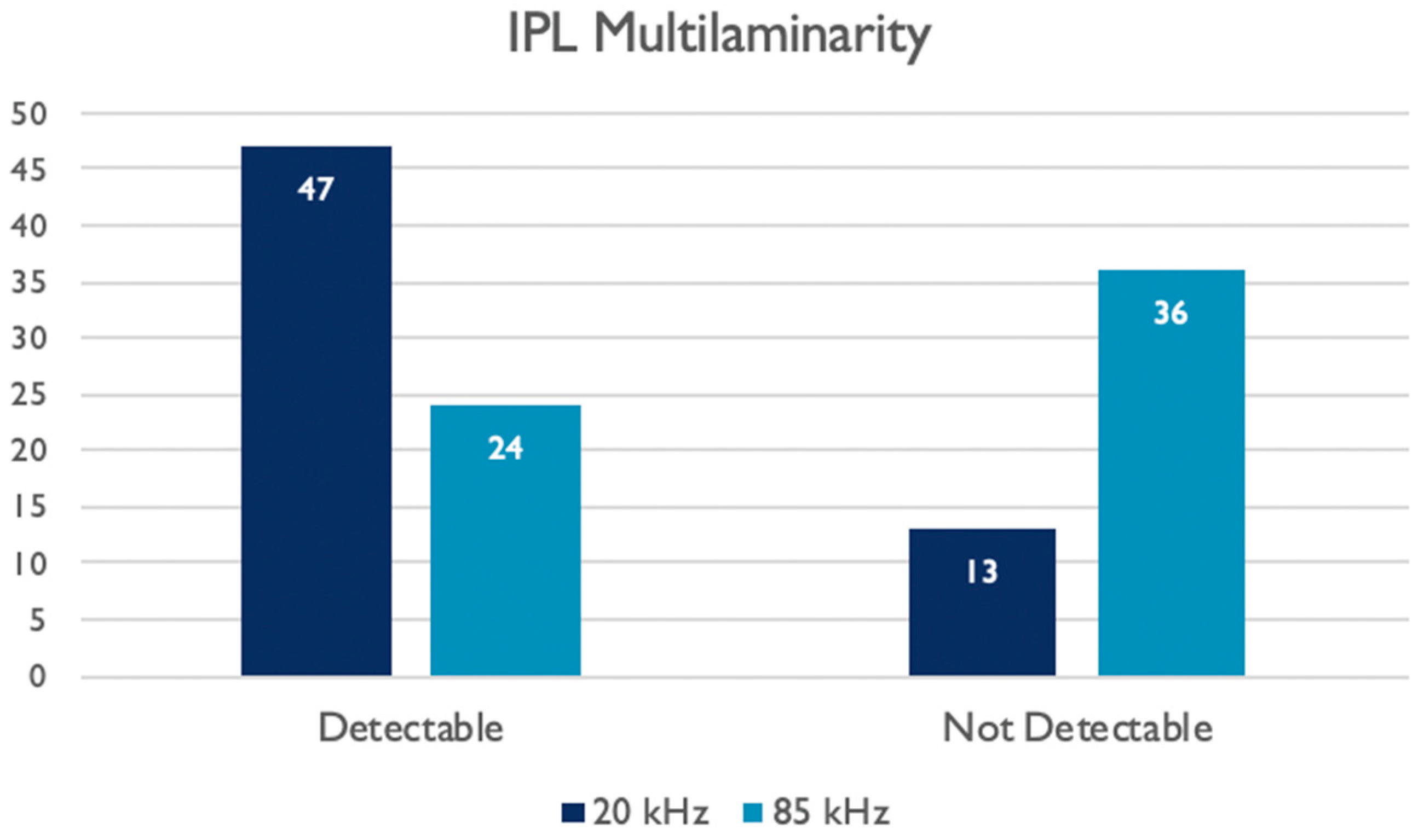
| IPL Multilaminarity Detection | 20 kHz Images | - | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not Detectable | Detectable | TOT | ||
| 85 kHz Images | Not Detectable | 4 | 32 | 36 (60, 0%) |
| Detectable | 9 | 15 | 24 (40, 0%) | |
| TOT | 13 (21, 7%) | 47 (78, 3%) | 60 (100%) | |
| FOVEAL | NASAL | TEMPORAL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOTAL THICKNESS 20 vs. 85 kHz | R | 0.938 | 0.935 | 0.946 |
| p | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | |
| RNFL 20 vs. 85 kHz | R | −0.132 | 0.551 | 0.317 |
| p | 0.315 | 0.001 | 0.014 | |
| GCL 20 vs. 85 kHz | R | 0.570 | 0.738 | 0.606 |
| p | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | |
| IPL 20 vs. 85 kHz | R | 0.516 | 0.224 | 0.313 |
| p | 0.001 | 0.085 | 0.015 | |
| INL 20 vs. 85 kHz | R | 0.547 | 0.378 | 0.324 |
| p | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.012 | |
| OPL 20 vs. 85 kHz | R | 0.609 | 0.329 | 0.154 |
| p | 0.001 | 0.010 | 0.240 | |
| ONL 20 vs. 85 kHz | R | 0.754 | 0.817 | 0.826 |
| p | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | |
| ORL 20 vs. 85 kHz | R | 0.509 | 0.163 | 0.477 |
| p | 0.001 | 0.214 | 0.001 |
| Multilaminarity Detection | ||
|---|---|---|
| Observer 1 20 kHz | R | 0.847 |
| p | <0.001 | |
| Observer 2 20 kHz | R | 0.720 |
| p | <0.001 | |
| Observer 1 85 kHz | R | 0.735 |
| p | <0.001 | |
| Observer 2 85 kHz | R | 0.771 |
| p | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lupidi, M.; Mangoni, L.; Centini, C.; Pompucci, G.; Lanzafame, L.; Danieli, L.; Fruttini, D.; Peiretti, E.; Chhablani, J.; Mariotti, C. Quantitative and Qualitative Assessments of Retinal Structure with Variable A-Scan Rate Spectralis OCT: Insights into IPL Multilaminarity. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2637. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072637
Lupidi M, Mangoni L, Centini C, Pompucci G, Lanzafame L, Danieli L, Fruttini D, Peiretti E, Chhablani J, Mariotti C. Quantitative and Qualitative Assessments of Retinal Structure with Variable A-Scan Rate Spectralis OCT: Insights into IPL Multilaminarity. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(7):2637. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072637
Chicago/Turabian StyleLupidi, Marco, Lorenzo Mangoni, Chiara Centini, Gregorio Pompucci, Luca Lanzafame, Luca Danieli, Daniela Fruttini, Enrico Peiretti, Jay Chhablani, and Cesare Mariotti. 2023. "Quantitative and Qualitative Assessments of Retinal Structure with Variable A-Scan Rate Spectralis OCT: Insights into IPL Multilaminarity" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 7: 2637. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072637
APA StyleLupidi, M., Mangoni, L., Centini, C., Pompucci, G., Lanzafame, L., Danieli, L., Fruttini, D., Peiretti, E., Chhablani, J., & Mariotti, C. (2023). Quantitative and Qualitative Assessments of Retinal Structure with Variable A-Scan Rate Spectralis OCT: Insights into IPL Multilaminarity. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(7), 2637. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072637








