Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Archival Human Vestibular Schwannoma Tissue from Patients with and without Tinnitus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
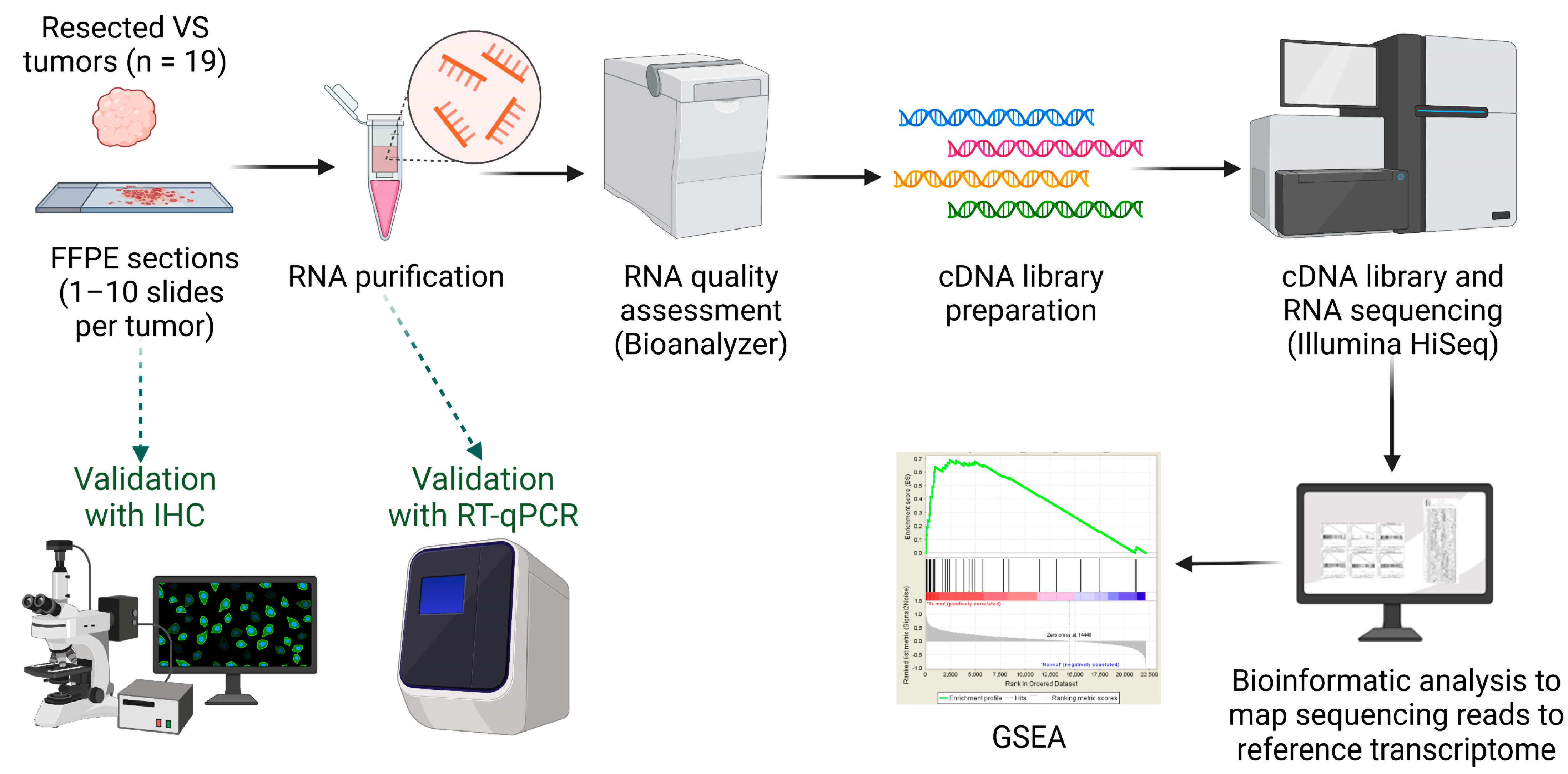
2.1. Study Population and Tissue Collection
2.2. RNA Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.3. Complementary DNA (cDNA) Library Preparation and RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq)
2.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.5. Gene Enrichment Analyses and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
2.6. Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.7. Immunohistochemistry
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
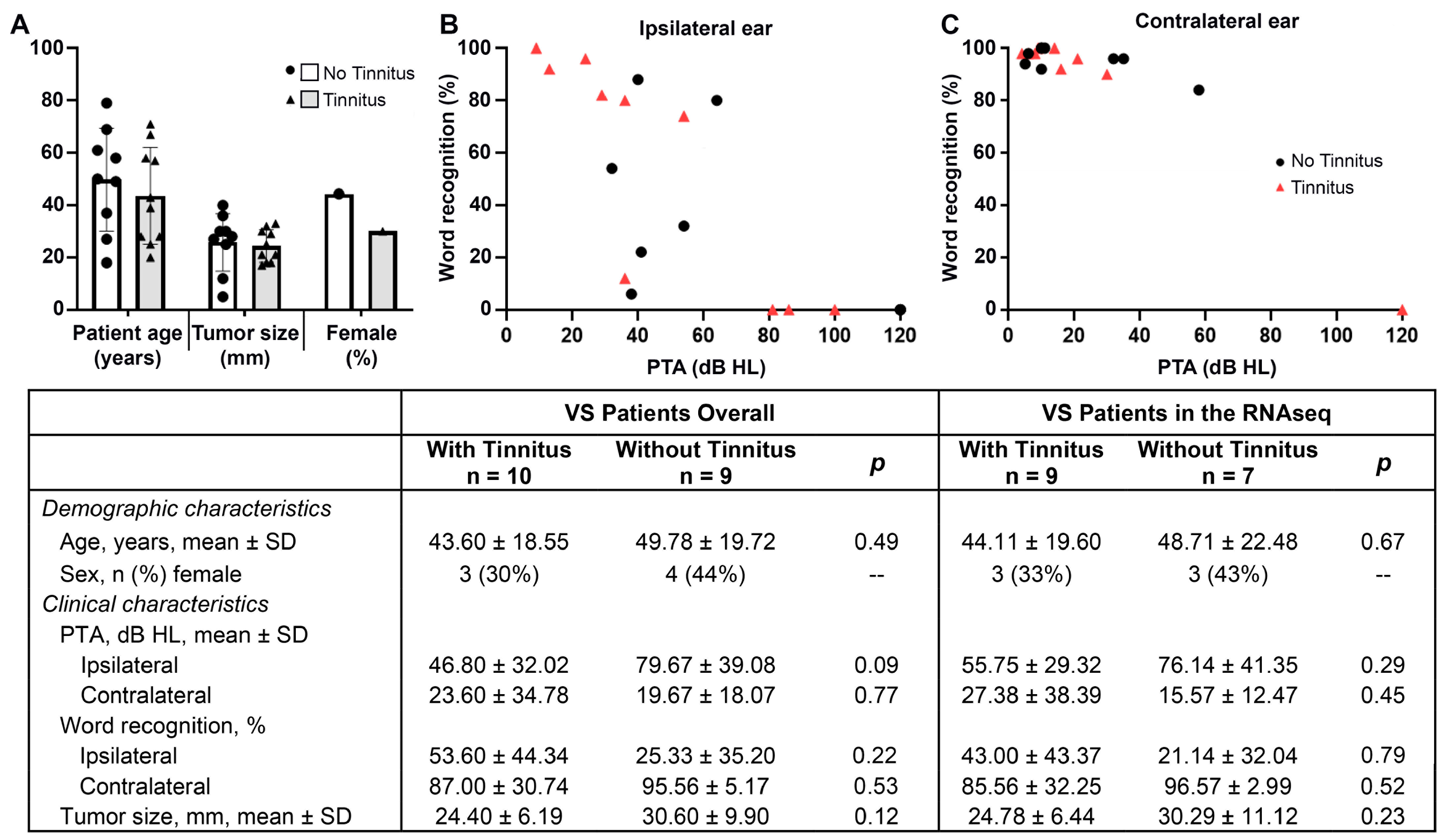
3.1. Characteristics of VS Sample Donors
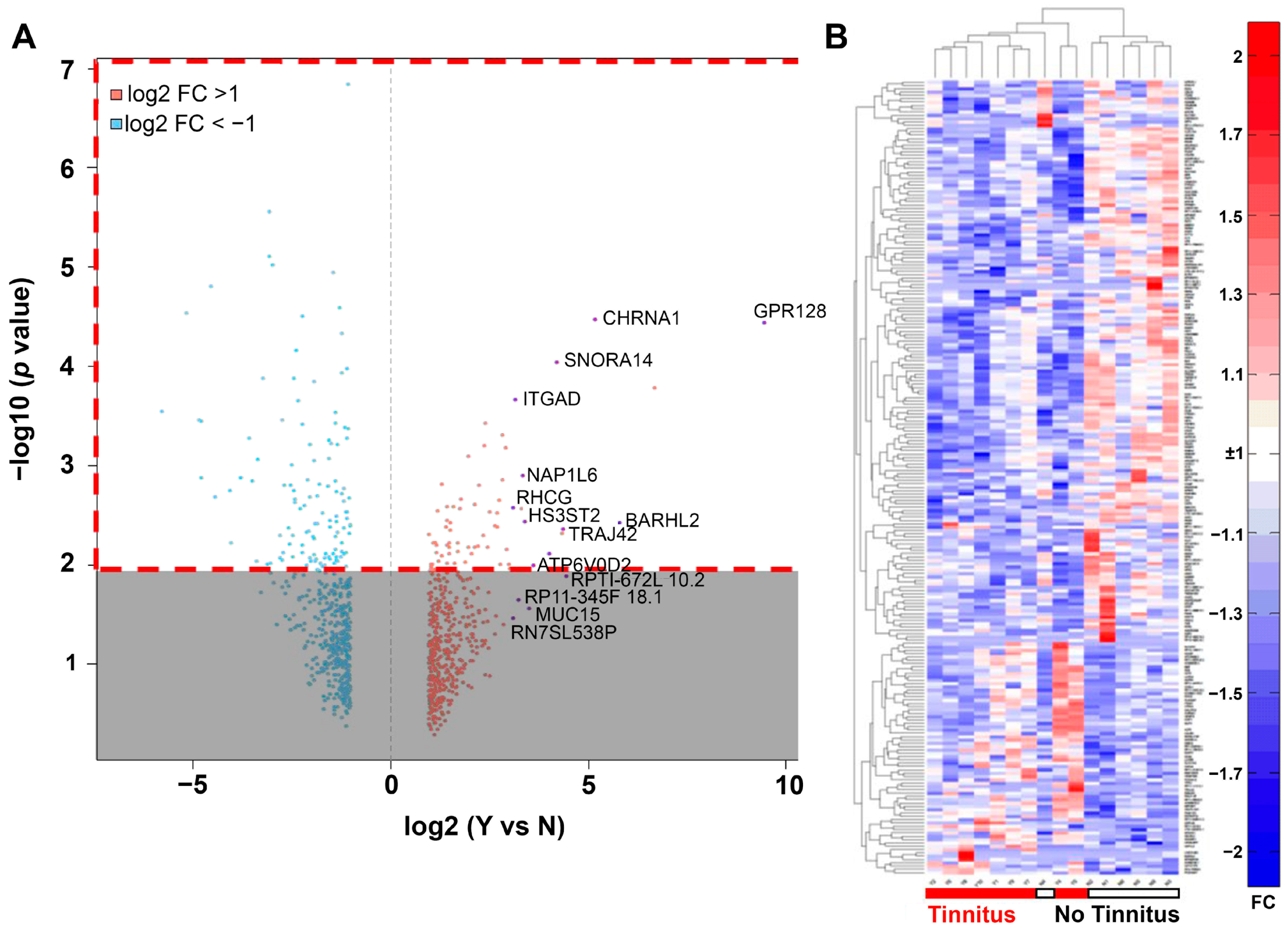
3.2. RNA-Seq Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes in VS with or without Associated Tinnitus
3.3. Functional Enrichment Analysis and GSEA
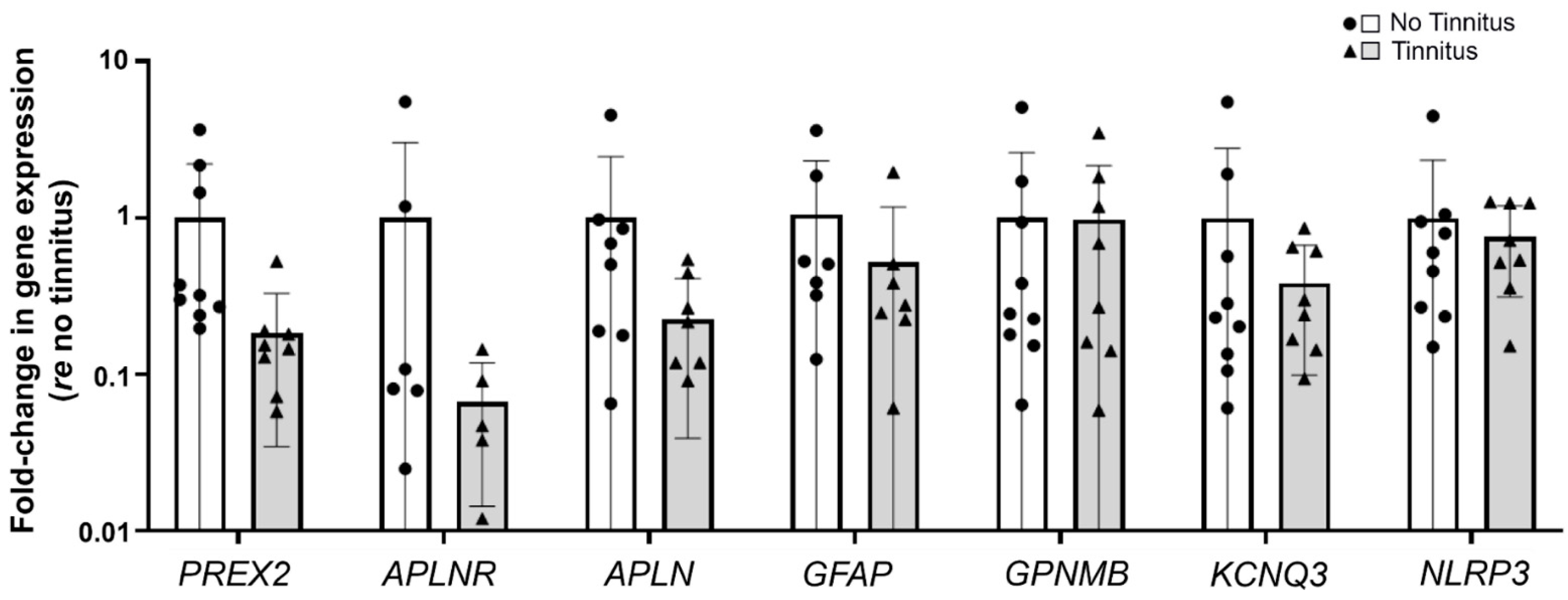
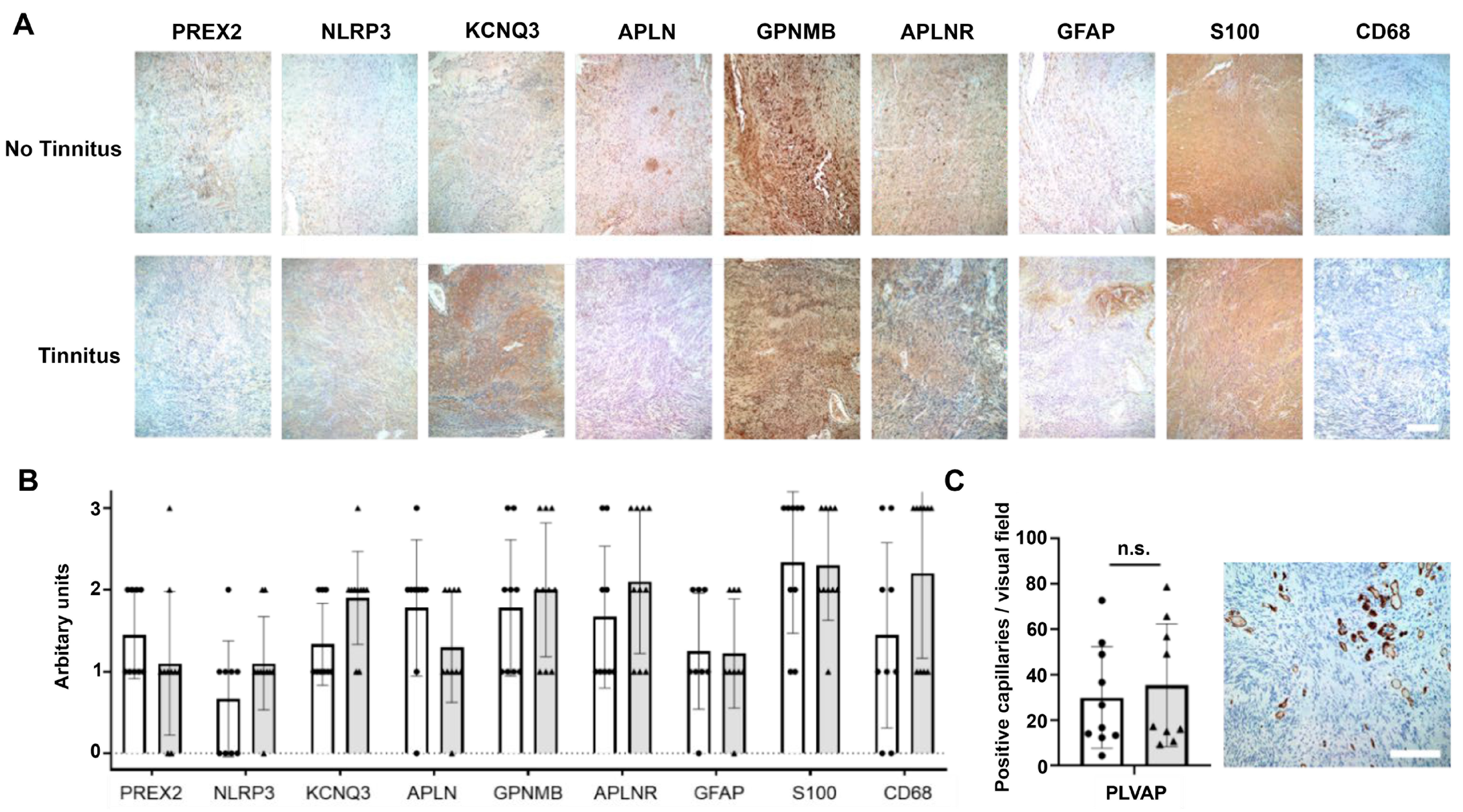
3.4. Validation of RNA-Seq Results with Real-Time RT-qPCR and Immunohistochemistry
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahaley, M.S., Jr.; Mettlin, C.; Natarajan, N.; Laws, E.R., Jr.; Peace, B.B. Analysis of patterns of care of brain tumor patients in the United States: A study of the Brain Tumor Section of the AANS and the CNS and the Commission on Cancer of the ACS. Clin. Neurosurg. 1990, 36, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carlson, M.L.; Link, M.J. Vestibular schwannomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1335–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinna, M.H.; Bento, R.F.; Neto, R.V. Vestibular schwannoma: 825 cases from a 25-year experience. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 16, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.G.R.; Lye, R.; Neary, W.; Black, G.; Strachan, T.; Wallace, A.; Ramsden, R.T. Probability of bilateral disease in people presenting with a unilateral vestibular schwannoma. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1999, 66, 764–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samii, M.; Matthies, C. Management of 1000 vestibular schwannomas (acoustic neuromas): Clinical presentation. Neurosurgery 1997, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, J.A.; Dennis, K.C.; Schechter, M.A. General review of tinnitus: Prevalence, mechanisms, effects, and management. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2005, 48, 1204–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Linge, A.; Borsboom, G.J.J.M.; Wieringa, M.H.; Goedegebure, A. Hearing loss progresses faster in patients with growing intracanalicular vestibular schwannomas. Otol. Neurotol. 2016, 37, 1442–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, M.M.; Jesus, O.D. Vestibular schwannoma. [Updated 26 November 2022]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562312/ (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- Harati, A.; Scheufler, K.M.; Schultheiss, R.; Tonkal, A.; Harati, K.; Oni, P.; Deitmer, T. Clinical features, microsurgical treatment, and outcome of vestibular schwannoma with brainstem compression. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2017, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Fung, K.; Lownie, S.P.; Parnes, L.S. Assessing impairment and disability of facial paralysis in patients with vestibular schwannoma. Arch. Otolaryngol. 2007, 133, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.P.; Crane, B.T. The management and imaging of vestibular schwannomas. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 2034–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo Clinic. Acoustic Neuroma. Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/acoustic-neuroma/care-at-mayo-clinic/mac-20356135 (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Ferri, G.G.; Pirodda, A.; Ceroni, A.R.; Fioravanti, A.; Calbucci, F.; Modugno, G.C. Management of growing vestibular schwannomas. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2013, 270, 2013–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, J.J.S.; Kaanders, J.H.; van Overbeeke, J.J.; Cremers, C.W.R.J. Radiation therapy for vestibular schwannomas. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. 2012, 20, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, J.M.; Lin, H.W.; Bhattacharyya, N. Prevalence, severity, exposures, and treatment patterns of tinnitus in the United States. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 142, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameda, K.; Shono, T.; Hashiguchi, K.; Yoshida, F.; Sasaki, T. Effect of tumor removal on tinnitus in patients with vestibular schwannoma: Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. 2010, 112, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Feng, Y.M.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.Q.; Shi, H.B.; Chen, Z.N.; Yin, S.K. Changes in tinnitus after vestibular schwannoma surgery. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baguley, D.M.; Humphriss, R.L.; Axon, P.R.; Moffat, D.A. The clinical characteristics of tinnitus in patients with vestibular schwannoma. Skull Base 2006, 16, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffat, D.A.; Baguley, D.M.; Beynon, G.J.; Da Cruz, M. Clinical acumen and vestibular schwannoma. Am. J. Otol. 1998, 19, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, M.L.; Tveiten, Ø.V.; Driscoll, C.L.; Goplen, F.K.; Neff, B.A.; Pollock, B.E.; Tombers, N.M.; Lund-Johansen, M.; Link, M.J. What drives quality of life in patients with sporadic vestibular schwannoma? Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris-Celda, M.; Graffeo, C.S.; Perry, A.; Kleinstern, G.; Kerezoudis, P.; Driscoll, C.L.W.; Carlson, M.L.; Link, M.J. Beyond the ABCs: Hearing loss and quality of life in vestibular schwannoma. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 2420–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naros, G.; Sandritter, J.; Liebsch, M.; Ofori, A.; Rizk, A.R.; Del Moro, G.; Ebner, F.; Tatagiba, M. Predictors of preoperative tinnitus in unilateral sporadic vestibular schwannoma. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipper, M.; Mazurek, B.; van Dijk, P.; Schulze, H. Too blind to see the elephant? Why neuroscientists ought to be interested in tinnitus. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2021, 22, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krauss, P.; Tziridis, K.; Metzner, C.; Schilling, A.; Hoppe, U.; Schulze, H. Stochastic resonance controlled upregulation of internal noise after hearing loss as a putative cause of tinnitus-related neuronal hyperactivity. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggermont, J.J.; Roberts, L.E. The neuroscience of tinnitus. Trends Neurosci. 2004, 27, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, P.J. Phantom auditory perception (tinnitus): Mechanisms of generation and perception. Neurosci. Res. 1990, 8, 221–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.; Early, S.; Vasilijic, S.; Stankovic, K.M. Sporadic vestibular schwannoma size and location do not correlate with the severity of hearing loss at initial presentation. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 836504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.R.; Anderson-Kim, S.J.; Low, C.; Leonetti, J.P. The persistence of tinnitus after acoustic neuroma surgery. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 155, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannan, C.J.; Lewis, D.; O’Leary, C.; Donofrio, C.A.; Evans, D.G.; Roncaroli, F.; Brough, D.; King, A.T.; Coope, D.; Pathmanaban, O.N. The inflammatory microenvironment in vestibular schwannoma. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2020, 2, vdaa023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennink, L.M.; Aalbers, M.W.; van Dijk, P.; van Dijk, J.M.C. The role of inflammation in tinnitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Early, S.; Rinnooy Kan, C.E.; Eggink, M.; Frijns, J.H.M.; Stankovic, K.M. Progression of contralateral hearing loss in patients with sporadic vestibular schwannoma. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukutla, P.; Ahmed, S.G.; DuBreuil, D.M.; Abdelnabi, A.; Cetinbas, M.; Fulci, G.; Aldikacti, B.; Stemmer-Rachamimov, A.; Plotkin, S.R.; Wainger, B.; et al. Transcriptomic signature of painful human neurofibromatosis type 2 schwannomas. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2021, 8, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.I.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, T.Y.; Lim, J.S.; Shin, K.S. Tinnitus: Characteristics, causes, mechanisms, and treatments. J. Clin. Neurol. 2009, 5, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Li, H.; Chen, L. Advances in understanding, diagnosis, and treatment of tinnitus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol 2019, 1130, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunkel, D.E.; Bauer, C.A.; Sun, G.H.; Rosenfeld, R.M.; Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Cunningham, E.R., Jr.; Archer, S.M.; Blakley, B.W.; Carter, J.M.; Granieri, E.C.; et al. Clinical practice guideline: Tinnitus. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2014, 151, S1–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Fu, J.; Cibulskis, C.; Jhaveri, A.; Gumbs, C.; Das, B.; Sanchez-Espiridion, B.; Janssens, S.; Taing, L.; Wang, J.; et al. Cross-site concordance evaluation of tumor DNA and RNA sequencing platforms for the CIMAC-CIDC Network. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 5049–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putri, G.H.; Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Pimanda, J.E.; Zanini, F. Analysing high-throughput sequencing data in Python with HTSeq 2.0. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 2943–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic. Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagers, J.E.; Sahin, M.I.; Moon, I.; Ahmed, S.G.; Stemmer-Rachamimov, A.; Brenner, G.J.; Stankovic, K.M. NLRP3 inflammasome activation in human vestibular schwannoma: Implications for tumor-induced hearing loss. Hear. Res. 2019, 381, 107770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankovic, K.M.; Corfas, G. Real-time quantitative RT-PCR for low-abundance transcripts in the inner ear: Analysis of neurotrophic factor expression. Hear. Res. 2003, 185, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papangeli, I.; Kim, J.; Maier, I.; Park, S.; Lee, A.; Kang, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Khan, O.F.; Ju, H.; Kojima, Y.; et al. MicroRNA 139-5p coordinates APLNR-CXCR4 crosstalk during vascular maturation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ensari, N.; Gür, E.Ö.; Gür, N.; Selçuk, T.Ö.; Renda, L.; Yılmaz, M.D.; Öztürk, M.T.; Çekin, Y. Can apelin play a role in the etiology of tinnitus? Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 49, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinos, L.; Kouvaros, S.; Bizup, B.; Hambach, B.; Wipf, P.; Tzounopoulos, T. Transient delivery of a KCNQ2/3-specific channel activator 1 week after noise trauma mitigates noise-induced tinnitus. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2021, 22, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Moine, A.; Goldman, M.; Abramowicz, D. Multiple pathways to allograft rejection. Transplantation 2002, 73, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, A.; Wang, W.; Luo, H.; Bao, S.; Searchfield, G.; Zhang, J. Neuroinflammation and tinnitus. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2021, 51, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepek, A.J.; Haupt, H.; Klapp, B.F.; Olze, H.; Mazurek, B. Biological correlates of tinnitus-related distress: An exploratory study. Hear. Res. 2014, 318, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, L.S.; Zinsmaier, A.K.; Patterson, G.; Leptich, E.J.; Shoemaker, S.L.; Yatskievych, T.A.; Gibboni, R.; Pace, E.; Luo, H.; et al. Neuroinflammation mediates noise-induced synaptic imbalance and tinnitus in rodent models. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Jeun, S.-S.; Rha, S.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Ko, Y.J.; Won, J.; Lee, K.-H.; Rha, H.K.; Wang, Y.-P. Inhibition of NF-κB activation by merlin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 296, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinero, L.L.; Alegre, M.L. Role of T cell-nuclear factor κB in transplantation. Transplant. Rev. 2012, 26, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiscott, J.; Marois, J.; Garoufalis, J.; D’Addario, M.; Roulston, A.; Kwan, I.; Pepin, N.; Lacoste, J.; Nguyen, H.; Bensi, G.; et al. Characterization of a functional NF-kappa B site in the human interleukin 1 beta promoter: Evidence for a positive autoregulatory loop. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 6231–6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Stankovic, K.M. The role of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) in hearing loss and vestibular schwannomas. Curr. Otorhinolaryngol. Rep. 2018, 6, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilwali, S.; Landegger, L.D.; Soares, V.Y.; Deschler, D.G.; Stankovic, K.M. Secreted factors from human vestibular schwannomas can cause cochlear damage. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilwali, S.; Briët, M.C.; Kao, S.Y.; Fujita, T.; Landegger, L.D.; Platt, M.P.; Stankovic, K.M. Preclinical validation of anti-nuclear factor-kappa B therapy to inhibit human vestibular schwannoma growth. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumi, S.; Sahin, M.I.; Lewis, R.M.; Iyer, J.S.; Landegger, L.D.; Stankovic, K.M. Intracochlear perfusion of tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces sensorineural hearing loss and synaptic degeneration in guinea pigs. Front. Neurol. 2020, 10, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, E.Q.; Yang, J.; Canis, M.; Reimann, K.; Ivanov, K.; Diehl, C.D.; Backx, P.H.; Wier, W.G.; Strieth, S.; Wangemann, P.; et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α enhances microvascular tone and reduces blood flow in the cochlea via enhanced sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling. Stroke 2010, 41, 2618–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangaj, D.; Bruand, M.; Grimm, A.J.; Ronet, C.; Barras, D.; Duttagupta, P.A.; Lanitis, E.; Duraiswamy, J.; Tanyi, J.L.; Benencia, F.; et al. Cooperation between constitutive and inducible chemokines enables t cell engraftment and immune attack in solid tumors. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 885–900.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, K.; Pillarisetty, V.G.; Kim, T.S. Key chemokines direct migration of immune cells in solid tumors. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, R.; Zhang, W.; Naseem, M.; Puccini, A.; Berger, M.D.; Soni, S.; McSkane, M.; Baba, H.; Lenz, H.J. CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11/CXCR3 axis for immune activation—A target for novel cancer therapy. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 63, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroi, M.; Ohmori, Y. The transcriptional coactivator CREB-binding protein cooperates with STAT1 and NF-κB for synergistic transcriptional activation of the CXC Ligand 9/monokine induced by Interferon-γ gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, S.; Dreyer, T.F.; Stange, C.; Steiger, K.; Bräuer, R.; Scheutz, L.; Multhoff, G.; Weichert, W.; Kiechle, M.; Magdolen, V.; et al. CXCL9 inhibits tumour growth and drives anti-PD-L1 therapy in ovarian cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 1470–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Lu, P.; Xia, Y.; Ding, S.; Fan, Y.; Li, X.; Han, P.; Liu, J.; Tian, D.; Liu, M. CXCL9: Evidence and contradictions for its role in tumor progression. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 3246–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mense, S.M.; Barrows, D.; Hodakoski, C.; Steinbach, N.; Schoenfeld, D.; Su, W.; Hopkins, B.D.; Su, T.; Fine, B.; Hibshoosh, H.; et al. PTEN inhibits PREX2-catalyzed activation of RAC1 to restrain tumor cell invasion. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, ra32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandiella, A.; Montero, J.C. Molecular pathways: P-Rex in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4564–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, B.; Hodakoski, C.; Koujak, S.; Su, T.; Saal, L.H.; Maurer, M.; Hopkins, B.; Keniry, M.; Sulis, M.L.; Mense, S.; et al. Activation of the PI3K pathway in cancer through inhibition of PTEN by exchange factor P-REX2a. Science 2009, 325, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.H.; Yen, C.H.; Chen, Y.F.; Fang, C.C.; Li, C.H.; Lee, K.J.; Lin, Y.H.; Weng, C.H.; Liu, T.T.; Huang, S.F.; et al. Somatic mutations of PREX2 gene in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Xiao, M. PREX2 mutation serves as a novel predictor of response to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 treatment in melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, e21504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.F.; Hodis, E.; Heffernan, T.P.; Deribe, Y.L.; Lawrence, M.S.; Protopopov, A.; Ivanova, E.; Watson, I.R.; Nickerson, E.; Ghosh, P.; et al. Melanoma genome sequencing reveals frequent PREX2 mutations. Nature 2012, 485, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, P. Reduced RAC1 activity inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in neurofibromatosis type 2(NF2)-associated schwannoma. Neurol. Res. 2017, 39, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Long, J.; Ren, J.; Huang, X.; Zhong, P.; Wang, B. Potential molecular biomarkers of vestibular schwannoma growth: Progress and prospects. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 731441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioffi, J.A.; Yue, W.Y.; Mendolia-Loffredo, S.; Hansen, K.R.; Wackym, P.A.; Hansen, M.R. MicroRNA-21 overexpression contributes to vestibular schwannoma cell proliferation and survival. Otol. Neurotol. 2010, 31, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawrin, C.; Kirches, E.; Boltze, C.; Dietzmann, K. PTEN is not altered in sporadic vestibular schwannomas. Histopathology 2002, 40, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshsirat, S.; Abbaszadeh, H.A.; Peyvandi, A.A.; Heidari, F.; Peyvandi, M.; Simani, L.; Niknazar, S. Apelin-13 prevents apoptosis in the cochlear tissue of noise-exposed rat via Sirt-1 regulation. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2021, 114, 101956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhang, H.; Kong, Y.; Wang, C.; Guo, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, L.; Yang, X.; Chen, J. Apelin protects auditory cells from cisplatin-induced toxicity in vitro by inhibiting ROS and apoptosis. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 728, 134948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Martin, M.; Lassaletta, L.; San-Roman-Montero, J.; De Campos, J.M.; Isla, A.; Gavilan, J.; Melendez, B.; Pinto, G.R.; Burbano, R.R.; Castresana, J.S.; et al. Microarray analysis of gene expression in vestibular schwannomas reveals SPP1/MET signaling pathway and androgen receptor deregulation. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, R.; Vijendren, A.; Phillips, J. Objective measures of tinnitus: A systematic review. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, N.; Bunne, M.; Sass, H.; Cayé-Thomasen, P. Cochlear implantation for patients with a vestibular schwannoma: Effect on tinnitus handicap. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2022, 18, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leao, M.T.; Machetanz, K.; Sandritter, J.; Liebsch, M.; Stengel, A.; Tatagiba, M.; Naros, G. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for tinnitus treatment in vestibular schwannoma: A pilot study. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 646014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, B.S.; Shipp, D.B.; Nedzelski, J.M. Subjective benefits reported by adult Nucleus 22-channel cochlear implant users. J. Otolaryngol. 1994, 23, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, B.; Harris, S.; Lindbaek, M. Tinnitus in cochlear implant patients--a comparison with other hearing-impaired patients. Int. J. Audiol. 2002, 41, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, E.J.; Deep, N.L.; Friedmann, D.R.; Jethanamest, D.; McMenomey, S.O.; Roland, J.T., Jr. Cochlear Implantation in Sporadic Vestibular Schwannoma and Other Retrocochlear Pathology: A Case Series. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, e425–e432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Neto, P.H.; Zamponi, J.O.; Hamerschmidt, R.; Wiemes, G.R.M.; Rassi, M.S.; Borba, L.A.B. Simultaneous cochlear implantation as a therapeutic option in vestibular schwannoma surgery: Case report. Neurosurg. Focus 2018, 44, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooth, M.A.; Dillon, M.T.; Brown, K.D. Prospective evaluation of patients undergoing translabyrinthine excision of vestibular schwannoma with concurrent cochlear implantation. Otol. Neurotol. 2017, 38, 1512–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassepass, F.; Arndt, S.; Aschendorff, A.; Laszig, R.; Wesarg, T. Cochlear implantation for hearing rehabilitation in single-sided deafness after translabyrinthine vestibular schwannoma surgery. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 2373–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nondahl, D.M.; Cruickshanks, K.J.; Dalton, D.S.; Klein, B.E.; Klein, R.; Schubert, C.R.; Tweed, T.S.; Wiley, T.L. The impact of tinnitus on quality of life in older adults. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2007, 18, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Härter, M.; Maurischat, C.; Weske, G.; Laszig, R.; Berger, M. Psychological stress and impaired quality of life in patients with tinnitus. HNO 2004, 52, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langguth, B. A review of tinnitus symptoms beyond ‘ringing in the ears’: A call to action. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2011, 27, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeman, F.; Koller, M.; Langguth, B.; Landgrebe, M.; Tinnitus Research Initiative database study, g. Which tinnitus-related aspects are relevant for quality of life and depression: Results from a large international multicentre sample. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2014, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, D.A.; Limb, C.J. Tinnitus. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 102, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
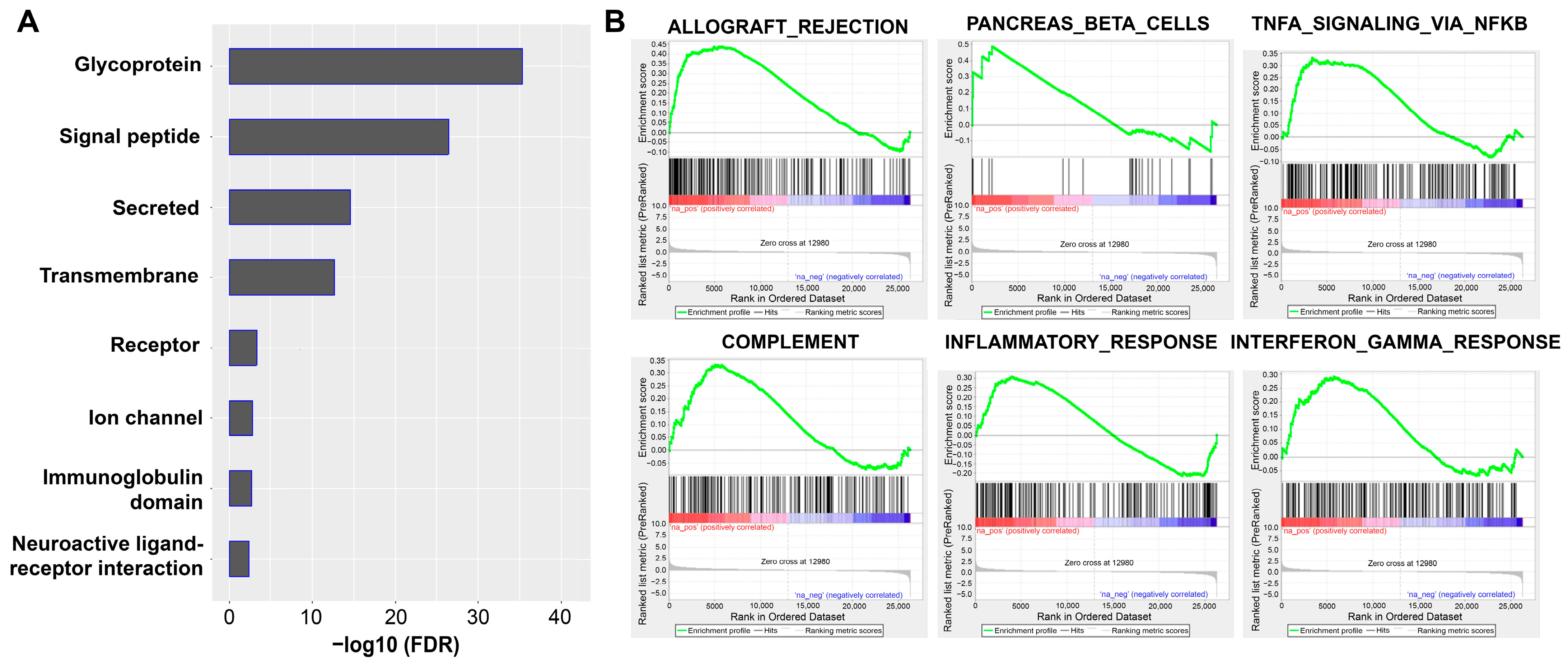
| p-Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathway | Description | Nominal a | FDR b | FWER |
| HALLMARK_ALLOGRAFT_REJECTION | Genes up-regulated during transplant rejection | 0 * | 0.022 * | 0.045 * |
| HALLMARK_PANCREAS_BETA_CELLS | Genes specifically up-regulated in pancreatic beta cells | 0.134 | 0.309 | 0.741 |
| HALLMARK_TNFA_SIGNALING_VIA_NFKB | Genes regulated by NF-kB in response to TNFα | 0.04 | 0.284 | 0.845 |
| HALLMARK_COMPLEMENT | Genes encoding components of the complement system, which is part of the innate immune system | 0.070 | 0.269 | 0.898 |
| HALLMARK_INFLAMMATORY_RESPONSE | Genes defining inflammatory response | 0.114 | 0.353 | 0.979 |
| HALLMARK_INTERFERON_GAMMA_RESPONSE | Genes up-regulated in response to IFNG | 0.222 | 0.491 | 0.998 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bommakanti, K.; Seist, R.; Kukutla, P.; Cetinbas, M.; Batts, S.; Sadreyev, R.I.; Stemmer-Rachamimov, A.; Brenner, G.J.; Stankovic, K.M. Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Archival Human Vestibular Schwannoma Tissue from Patients with and without Tinnitus. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2642. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072642
Bommakanti K, Seist R, Kukutla P, Cetinbas M, Batts S, Sadreyev RI, Stemmer-Rachamimov A, Brenner GJ, Stankovic KM. Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Archival Human Vestibular Schwannoma Tissue from Patients with and without Tinnitus. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(7):2642. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072642
Chicago/Turabian StyleBommakanti, Krishna, Richard Seist, Phanidhar Kukutla, Murat Cetinbas, Shelley Batts, Ruslan I. Sadreyev, Anat Stemmer-Rachamimov, Gary J. Brenner, and Konstantina M. Stankovic. 2023. "Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Archival Human Vestibular Schwannoma Tissue from Patients with and without Tinnitus" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 7: 2642. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072642
APA StyleBommakanti, K., Seist, R., Kukutla, P., Cetinbas, M., Batts, S., Sadreyev, R. I., Stemmer-Rachamimov, A., Brenner, G. J., & Stankovic, K. M. (2023). Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Archival Human Vestibular Schwannoma Tissue from Patients with and without Tinnitus. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(7), 2642. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072642







