Can Immunoexpression of Cancer Stem Cell Markers Prognosticate Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction
3. Results
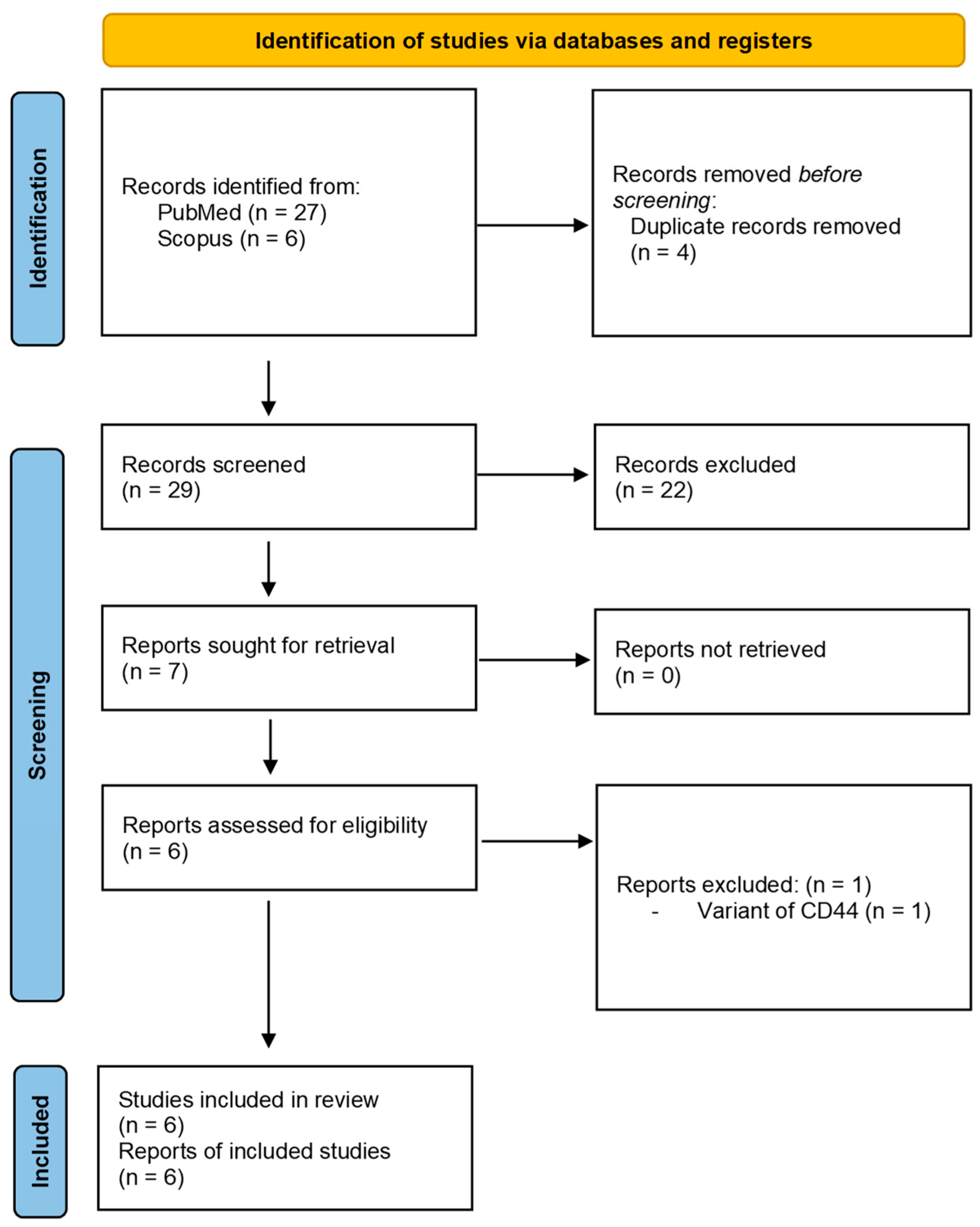
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Quality Assessment
3.4. Meta-Analysis
3.4.1. Association of CSC Markers with Tumor Stage
3.4.2. Association of CSC Markers with Histological Grading
3.4.3. Correlation of CSC Markers with Nodal Metastasis
3.4.4. Correlation of CSC Markers with Overall Survival
3.5. Heterogeneity Analysis
3.6. Sensitivity Analysis
3.7. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Canning, M.; Guo, G.; Yu, M.; Myint, C.; Groves, M.W.; Byrd, J.K.; Cui, Y. Heterogeneity of the Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Immune Landscape and Its Impact on Immunotherapy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clevers, H. The cancer stem cell: Premises, promises and challenges. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Routray, S.; Mohanty, N. Cancer Stem Cells Accountability in Progression of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: The Most Recent Trends! Mol. Biol. Int. 2014, 2014, 375325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lapidot, T.; Sirard, C.; Vormoor, J.; Murdoch, B.; Hoang, T.; Caceres-Cortes, J.; Minden, M.; Paterson, B.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Dick, J.E. A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after transplantation into SCID mice. Nature 1994, 367, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hajj, M.; Wicha, M.S.; Benito-Hernandez, A.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F. Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3983–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prince, M.E.; Sivanandan, R.; Kaczorowski, A.; Wolf, G.T.; Kaplan, M.J.; Dalerba, P.; Weissman, I.L.; Clarke, M.F.; Ailles, L.E. Identification of a subpopulation of cells with cancer stem cell properties in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.K.; Hawkins, C.; Clarke, I.D.; Squire, J.A.; Bayani, J.; Hide, T.; Henkelman, R.M.; Cusimano, M.D.; Dirks, P.B. Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature 2004, 432, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxberg, M.; Götz, C.; Haidari, S.; Dorfner, C.; Jesinghaus, M.; Drecoll, E.; Boskov, M.; Wolff, K.D.; Weichert, W.; Haller, B.; et al. Immunohistochemical expression of CD44 in oral squamous cell carcinoma in relation to histomorphological parameters and clinicopathological factors. Histopathology 2018, 73, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkel, J.; Vaittinen, S.; Koivunen, P.; Laranne, J.; Mäkinen, M.J.; Tommola, S.; Irjala, H. Tumoral Expression of CD44 and HIF1α Predict Stage I Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma Outcome. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2016, 1, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moraes, F.P.P.; Lourenço, S.V.; Ianez, R.C.F.; de Sousa, E.A.; Silva, M.M.D.C.; Damascena, A.S.; Kowalski, L.P.; Soares, F.A.; Coutinho-Camillo, C.M. Expression of stem cell markers in oral cavity and oropharynx squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2017, 123, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, M.; Gunduz, E.; Tamagawa, S.; Enomoto, K.; Hotomi, M. Cancer stem cells in oropharyngeal cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.-L.; Fan, S.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Chen, W.-X.; Li, Q.-X.; Pan, G.-K.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Wang, W.-W.; Weng, B.; Zhang, Z.; et al. SOX8 regulates cancer stem-like properties and cisplatin-induced EMT in tongue squamous cell carcinoma by acting on the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 1252–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bayo, P.; Jou, A.; Stenzinger, A.; Shao, C.; Gross, M.; Jensen, A.; Grabe, N.; Mende, C.H.; Rados, P.V.; Debus, J.; et al. Loss of SOX2 expression induces cell motility via vimentin up-regulation and is an unfavorable risk factor for survival of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1704–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayry, V.; Makinen, L.K.; Atula, T.S.; Sariola, H.; A Makitie, A.; Leivo, I.; Keskisantti, H.; Lundin, J.; Haglund, C.M.; Hagstrom, J. Bmi-1 expression predicts prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokko, L.-L.; Hurme, S.; Maula, S.-M.; Alanen, K.; Grénman, R.; Kinnunen, I.; Ventelä, S. Significance of site-specific prognosis of cancer stem cell marker CD44 in head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2011, 47, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, S.; Siddappa, G.; Valiyaveedan, S.G.; Ramanjanappa, R.D.T.; Das, D.; Pandian, R.; Khora, S.S.; Kuriakose, M.A.; Suresh, A. Cancer stem cell markers in patterning differentiation and in prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 101042831770365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiou, S.-H.; Yu, C.-C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Lin, S.-C.; Liu, C.-J.; Tsai, T.-H.; Chou, S.-H.; Chien, C.-S.; Ku, H.-H.; Lo, J.-F. Positive Correlations of Oct-4 and Nanog in Oral Cancer Stem-Like Cells and High-Grade Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 4085–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carinci, F.; Stabellini, G.; Calvitti, M.; Pelucchi, S.; Targa, L.; Farina, A.; Pezzetti, F.; Pastore, A. CD44 as Prognostic Factor in Oral and Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2002, 13, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosunen, A.; Pirinen, R.; Ropponen, K.; Pukkila, M.; Kellokoski, J.; Virtaniemi, J.; Sironen, R.; Juhola, M.; Kumpulainen, E.; Johansson, R.; et al. CD44 expression and its relationship with MMP-9, clinicopathological factors and survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2007, 43, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Moles, M.; Gil-Montoya, J.; Ruiz-Avila, I.; Esteban, F.; Delgado-Rodriguez, M.; Bascones-Martinez, A. Prognostic significance of p21WAF1/CIP1, p16INK4a and CD44s in tongue cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 18, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huber, G.F.; Albinger-Hegyi, A.; Soltermann, A.; Roessle, M.; Graf, N.; Haerle, S.K.; Holzmann, D.; Moch, H.; Hegyi, I. Expression patterns of Bmi-1 and p16 significantly correlate with overall, disease-specific, and recurrence-free survival in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 2011, 117, 4659–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, C.; Baretton, G.; Soost, F.; Terpe, H.-J.; Domide, P.; Löhrs, U. Prognostic importance of the expression of CD44 splice variants in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 1999, 35, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, M.C.; Pramana, J.; van der Wal, J.E.; Lacko, M.; Peutz-Kootstra, C.J.; de Jong, J.M.; Takes, R.P.; Kaanders, J.H.; van der Laan, B.F.; Wachters, J.; et al. CD44 Expression Predicts Local Recurrence after Radiotherapy in Larynx Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5329–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; PRISMA-P Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McShane, L.M.; Altman, D.G.; Sauerbrei, W.; Taube, S.E.; Gion, M.; Clark, G.M. Reporting Recommendations for Tumor Marker Prognostic Studies (REMARK). JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2005, 97, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almangush, A.; Heikkinen, I.; Mäkitie, A.A.; Coletta, R.D.; Läärä, E.; Leivo, I.; Salo, T. Prognostic biomarkers for oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gierisch, J.M.; Beadles, C.; Shapiro, A.; McDuffie, J.R.; Cunningham, N.; Bradford, D.; Strauss, J.; Callahan, M.; Chen, M.; Hemminger, A.; et al. Health Disparities in Quality Indicators of Healthcare Among Adults with Mental Illness [Internet]; APPENDIX B, NEWCASTLE-OTTAWA SCALE CODING MANUAL FOR COHORT STUDIES; Department of Veterans Affairs (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2014. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK299087/ (accessed on 4 April 2023).
- Sato, S.; Miyauchi, M.; Takekoshi, T.; Zhao, M.; Kudo, Y.; Ogawa, I.; Kitagawa, S.; Fujita, M.; Takata, T. Reduced expression of CD44 variant 9 is related to lymph node metastasis and poor survival in squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. Oral Oncol. 2000, 36, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.C.; Han, J.H.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, B.H.; Choi, E.C.; Kim, C.-H. Overexpression of c-Met promotes invasion and metastasis of small oral tongue carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-H.; Koh, Y.W.; Han, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, J.S.; Baek, S.J.; Hwang, H.S.; Choi, E.C. c-Met expression as an indicator of survival outcome in patients with oral tongue carcinoma. Head Neck 2010, 32, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Zheng, G.; Wang, S.; et al. Sox2 nuclear expression is closely associated with poor prognosis in patients with histologically node-negative oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2011, 47, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noi, M.; Mukaisho, K.; Murakami, S.; Koshinuma, S.; Machida, Y.; Yamori, M.; Nakayama, T.; Ogawa, T.; Nakata, Y.; Shimizu, T.; et al. Expressions of ezrin, ERK, STAT3, and AKT in tongue cancer and association with tumor characteristics and patient survival. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2020, 6, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Qiao, B.; Zhao, T.; Hu, F.; Lam, A.; Tao, Q. Sox2 promotes tumor aggressiveness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, M.F.; Xavier, F.; de Andrade, N.P.; Lopes, C.; Luiz, L.M.; Sedassari, B.T.; Ibarra, A.M.C.; López, R.V.M.; Schmerling, C.K.; Moyses, R.A.; et al. Prognostic implications of CD44, NANOG, OCT4, and BMI1 expression in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2018, 40, 1759–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Li, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Liang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, B.; Xia, J. Prognostic Value of Cancer Stem Cell Markers in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gopinath, D.; Menon, R.K. Unravelling the molecular signatures in HNSCC: Is the homogenous paradigm becoming obsolete? Oral Oncol. 2018, 82, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.-R.; Wang, W.-M.; Huang, C.-F.; Zhang, W.-F.; Sun, Z.-J. Anterior gradient protein 2 expression in high grade head and neck squamous cell carcinoma correlated with cancer stem cell and epithelial mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 8807–8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Li, Q. Cancer stem cells, lymphangiogenesis, and lymphatic metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2015, 357, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakamatsu, Y.; Sakamoto, N.; Oo, H.Z.; Naito, Y.; Uraoka, N.; Anami, K.; Sentani, K.; Oue, N.; Yasui, W. Expression of cancer stem cell markers ALDH1, CD44 and CD133 in primary tumor and lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer. Pathol. Int. 2012, 62, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Zhu, L.; Ma, L. The association of {SOX}2 with clinical features and prognosis in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-F.; Xu, X.-R.; Wu, T.-F.; Sun, Z.-J.; Zhang, W.-F. Correlation of ALDH1, CD44, OCT4 and SOX2 in tongue squamous cell carcinoma and their association with disease progression and prognosis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2014, 43, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freier, K.; Knoepfle, K.; Flechtenmacher, C.; Pungs, S.; Devens, F.; Toedt, G.; Hofele, C.; Joos, S.; Lichter, P.; Radlwimmer, B. Recurrent copy number gain of transcription factor SOX2 and corresponding high protein expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2010, 49, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, B.; Wang, R.; Huang, D.; Jin, W.; Yang, S. SOX2 as prognostic factor in head and neck cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Otolaryngol. 2014, 134, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javaeed, A.; Ghauri, S.K. Metastatic potential and prognostic significance of SOX2: A meta-analysis. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 10, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naini, F.B.; Shakib, P.A.; Abdollahi, A.; Hodjat, M.; Mohammadpour, H.; Khoozestani, N.K. Relative Expression of OCT4, SOX2 and NANOG in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Versus Adjacent Non- Tumor Tissue. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 20, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Vicente, J.C.; del Molino, P.D.-P.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Allonca, E.; Hermida-Prado, F.; Granda-Díaz, R.; Santamarta, T.R.; García-Pedrero, J.M. SOX2 Expression Is an Independent Predictor of Oral Cancer Progression. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brabletz, T.; Jung, A.; Spaderna, S.; Hlubek, F.; Kirchner, T. Migrating cancer stem cells an integrated concept of malignant tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author | IHC Marker | Population | N | Age | M:F | Follow Up (years) | Cut-Off Value | Compliance to REMARK Guidelines | NOS Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lim et al., 2012 [29] | c-MET | Korea | 71 | NM | 50:21 | 6.1 | >30% | Study design was incompletely described | 9 |
| Kim et al., 2010 [30] | c-MET | Korea | 61 | 22–79 | 41:20 | 11.6 | ≥30% | Study design was incompletely described | 9 |
| Rodrigues et al., 2018 [34] | OCT4 | Brazil | 60 | ≥40 | NM | 5 | 25–49% | fulfilled | 9 |
| Rodrigues et al., 2018 [34] | BMI1 | Brazil | 60 | ≥40 | NM | 15 | 25–49% | fulfilled | 9 |
| Rodrigues et al., 2018 [34] | NANOG | Brazil | 60 | ≥40 | NM | 5 | 25–49% | fulfilled | 9 |
| Noi et al., 2020 [32] | STAT3 | Japan | 63 | 33–86 | 34:29 | 8 | NM | Study design was incompletely described | 9 |
| Du et al., 2011 [31] | SOX2 | China | 82 | NM | 55:27 | 6 | 25% | fulfilled | 9 |
| Liu et al., 2018 [33] | SOX2 | China | 61 | 53.4 | 35:26 | 10 | NM | Study design was incompletely described | 9 |
| Rodrigues et al., 2018 [34] | CD44 | Brazil | 60 | ≥40 | NM | 5 | 25–49% | fulfilled | 9 |
| Author | IHC Marker | Immuno-Positive Cases | TNM Stage | Grading | Outcome in Immuno-Positive Cases | Immuno-Negative Cases | TNM Stage | Grading | Outcome in Immuno-Negative Cases | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t1 + t2 | t3 + t4 | Nodes (+) | Nodes (−) | Well | Moderate to Poor | LNM | Recurrence | DM | OS | t1 + t2 | t3 + t4 | nodes (+) | nodes (−) | Well | Moderate to Poor | LNM | Recurrence | DM | OS | ||||
| Lim et al., 2012 [29] | c-MET | 39 | 17 | 22 | 24 | 15 | 24 | 12 | 24 | NM | NM | NM | 32 | 15 | 17 | 7 | 25 | 22 | 13 | 7 | NM | NM | NM |
| Kim et al., 2010 [30] | c-MET | 33 | 26 | 7 | 24 | 9 | 22 | 11 | 24 | 13 | 2 | NM | 28 | 25 | 3 | 10 | 18 | 17 | 11 | 10 | 13 | 2 | NM |
| Rodrigues et al., 2018 [34] | OCT4 | 46 | 24 | 12 | 23 | 13 | NM | NM | 23 | NM | NM | 23 | 24 | 18 | 6 | 7 | 15 | NM | NM | 7 | NM | NM | 16 |
| Rodrigues et al., 2018 [34] | BMI 1 | 23 | 17 | 6 | 8 | 13 | NM | NM | 8 | NM | NM | 13 | 37 | 25 | 12 | 22 | 15 | NM | NM | 22 | NM | NM | 26 |
| Rodrigues et al., 2018 [34] | NANOG | 39 | 29 | 10 | 23 | 14 | NM | NM | 23 | NM | NM | 22 | 21 | 13 | 8 | 7 | 14 | NM | NM | 7 | NM | NM | 17 |
| Noi et al., 2020 [32] | STAT 3 | 40 | 27 | 13 | 13 | 27 | 30 | 10 | 13 | NM | NM | NM | 15 | 13 | 2 | 3 | 12 | 12 | 3 | 3 | NM | NM | NM |
| Du et al., 2011 [31] | SOX 2 | 51 | 31 | 20 | 0 | 51 | 25 | 26 | 0 | 20 | 12 | 26 | 31 | 26 | 5 | 0 | 31 | 18 | 13 | 0 | 20 | 12 | 26 |
| Liu et al., 2018 [33] | SOX 2 | 39 | 26 | 13 | 19 | 20 | 16 | 23 | 19 | NM | NM | NM | 22 | 20 | 2 | 4 | 18 | 15 | 7 | 4 | NM | NM | NM |
| Rodrigues et al., 2018 [34] | CD 44 | 51 | 36 | 15 | 27 | 23 | NM | NM | 27 | NM | NM | 30 | 9 | 6 | 3 | 6 | 2 | NM | NM | 6 | NM | NM | 9 |
| Clinicopathological Parameters | Coefficient | Estimate with 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor stage | Slope | −4.3754 (−8.1679, 0.5829) | 0.059 |
| Bias | 7.6302 (−0.0431, 15.2172) | 0.051 | |
| Grading | Slope | −0.2267 (−11.7652, 11.3117) | 0.954 |
| Bias | −0.0892 (−23.9120, 23.7335) | 0.991 | |
| Nodal status | Slope | −3.4001 (−7.2616, 0.4614) | 0.080 |
| Bias | 6.3674 (−0.2440, 12.4907) | 0.073 | |
| Overall survival | Slope | −3.2114 (−14.7502, 8.3273) | 0.354 |
| Bias | 6.1181 (−11.4157, 23.6519) | 0.272 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaudhury, S.; Panda, S.; Mohanty, N.; Panda, S.; Mohapatra, D.; Nagaraja, R.; Sahoo, A.; Gopinath, D.; Lewkowicz, N.; Lapinska, B. Can Immunoexpression of Cancer Stem Cell Markers Prognosticate Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082753
Chaudhury S, Panda S, Mohanty N, Panda S, Mohapatra D, Nagaraja R, Sahoo A, Gopinath D, Lewkowicz N, Lapinska B. Can Immunoexpression of Cancer Stem Cell Markers Prognosticate Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(8):2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082753
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaudhury, Sayantanee, Swagatika Panda, Neeta Mohanty, Saurav Panda, Diksha Mohapatra, Ravishankar Nagaraja, Alkananda Sahoo, Divya Gopinath, Natalia Lewkowicz, and Barbara Lapinska. 2023. "Can Immunoexpression of Cancer Stem Cell Markers Prognosticate Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 8: 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082753
APA StyleChaudhury, S., Panda, S., Mohanty, N., Panda, S., Mohapatra, D., Nagaraja, R., Sahoo, A., Gopinath, D., Lewkowicz, N., & Lapinska, B. (2023). Can Immunoexpression of Cancer Stem Cell Markers Prognosticate Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(8), 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082753