Cerebellar Tonsillar Descent Mimicking Chiari Malformation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
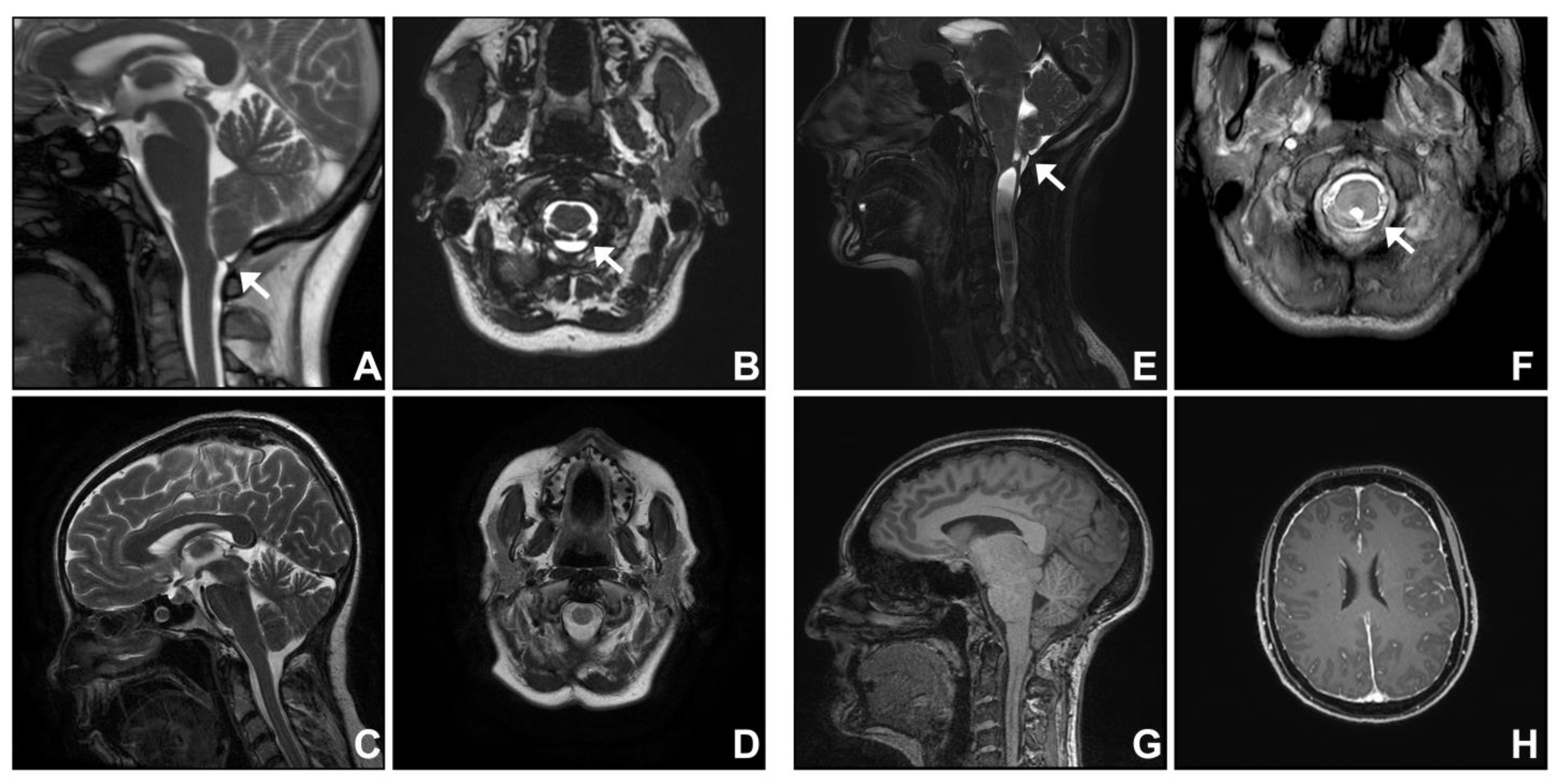
3.1. Group One. Post-Traumatic Cranio-Cervical Junction Arachnoiditis and Syringomyelia
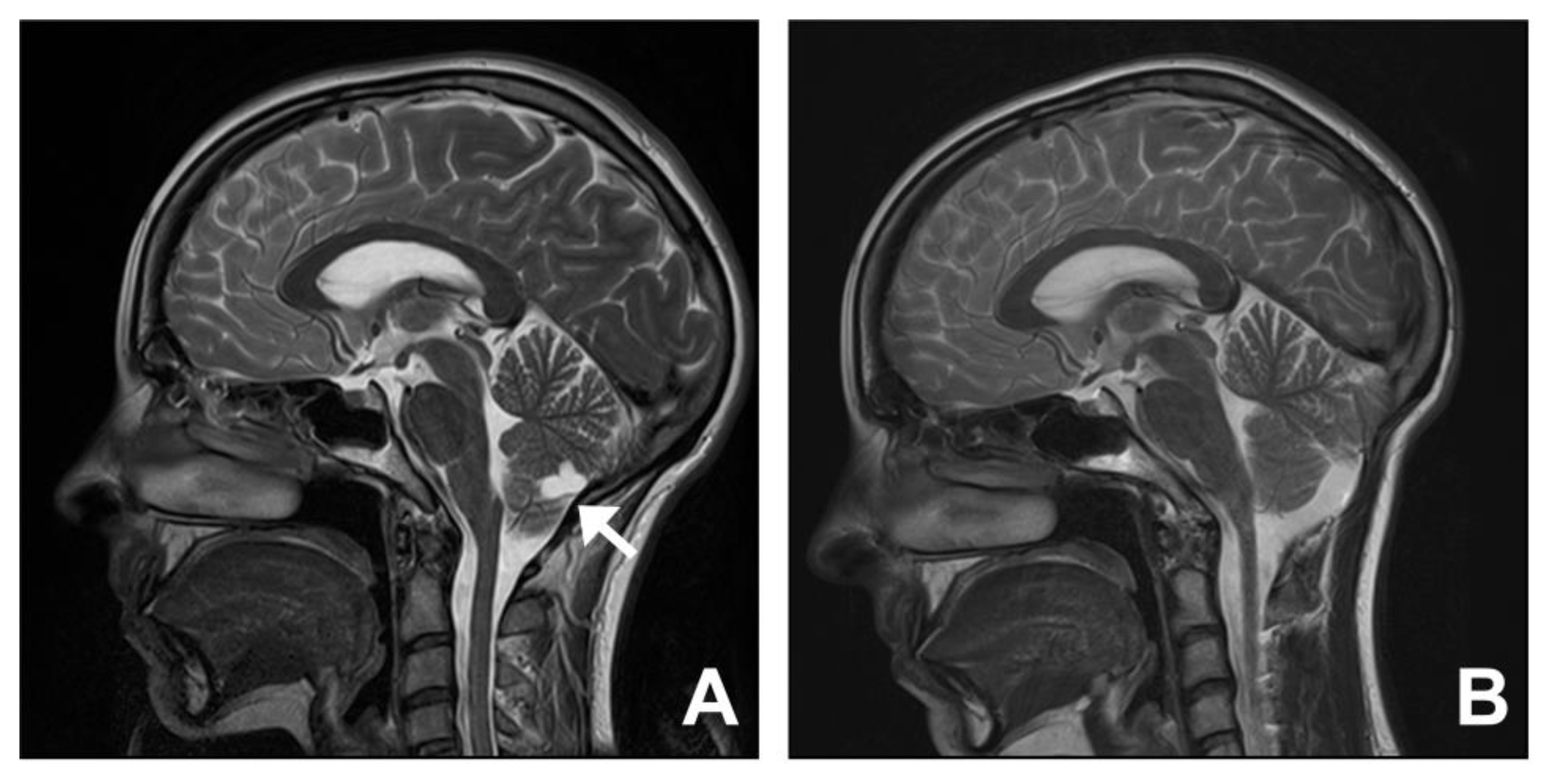
3.2. Group Two. Dural Band
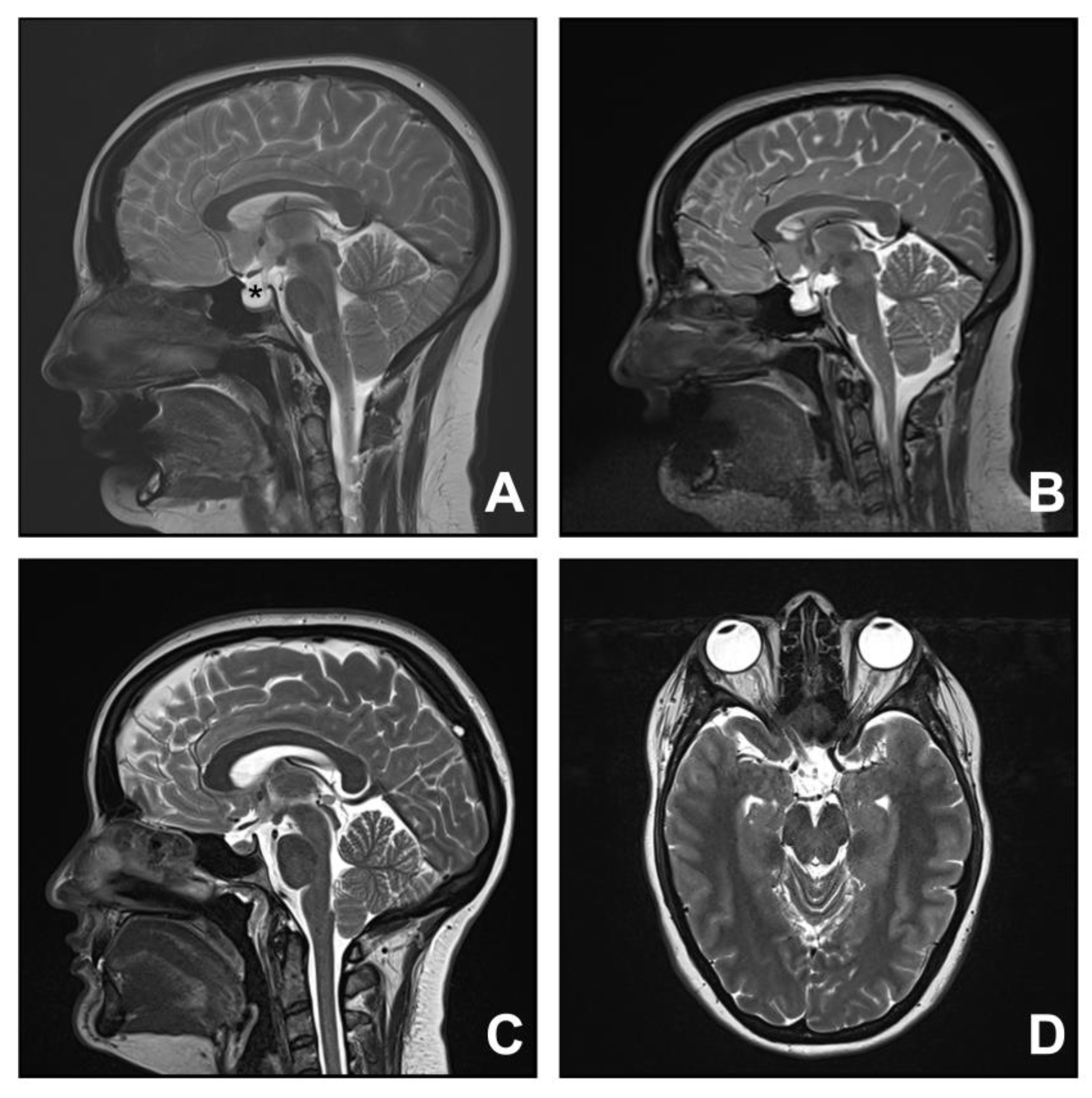
3.3. Group Three. Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
3.4. Group Four. Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
3.5. Group Five. Cysts: Arachnoid, Choroid Plexus, and Cerebellum
4. Discussion
4.1. Cranio-Cervical Junction Arachnoiditis
4.2. Dural Band
4.3. Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
4.4. Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
4.5. Cysts: Arachnoid, Choroid Plexus, Cerebellum
4.6. Syringomyelia
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marin-Padilla, M.; Marin-Padilla, T.M. Morphogenesis of experimentally induced Arnold—Chiari malformation. J. Neurol. Sci. 1981, 50, 29–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiari, H. Ueber Veränderungen des Kleinhirns infolge von Hydrocephalie des Grosshirns. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 1891, 17, 1172–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaramitaro, P.; Massimi, L.; Bertuccio, A.; Solari, A.; Farinotti, M.; Peretta, P.; Saletti, V.; Chiapparini, L.; Barbanera, A.; Garbossa, D.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of Chiari malformation and syringomyelia in adults: International consensus document. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 1327–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milhorat, T.H.; Chou, M.W.; Trinidad, E.M.; Kula, R.W.; Mandell, M.; Wolpert, C.; Speer, M.C. Chiari I malformation redefined: Clinical and radiographic findings for 364 symptomatic patients. Neurosurgery 1999, 44, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnemari, A.; Mansour, T.R.; Gregory, S.; Miller, W.K.; Buehler, M.; Gaudin, D. Chiari I malformation with underlying pseudotumor cerebri: Poor symptom relief following posterior decompression surgery. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2017, 38, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejjani, G.K. Association of the Adult Chiari Malformation and Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: More than a coincidence. Med. Hypotheses 2003, 60, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagan, L.H.; Ferguson, S.; Yassari, R.; Frim, D.M. The Chiari pseudotumor cerebri syndrome: Symptom recurrence after decompressive surgery for Chiari malformation type I. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2006, 42, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.L.H.; Vuong, K.; Chugh, T.; Carroll, I. Cerebellar tonsillar descent: A diagnostic dilemma between Chiari malformation type 1 and spinal cerebrospinal fluid leak. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puget, S.; Kondageski, C.; Wray, A.; Boddaert, N.; Roujeau, T.; Di Rocco, F.; Zerah, M.; Sainte-Rose, C. Chiari-like tonsillar herniation associated with intracranial hypotension in Marfan syndrome. Case report. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 106, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milhorat, T.H.; Nishikawa, M.; Kula, R.W.; Dlugacz, Y.D. Mechanisms of cerebellar tonsil herniation in patients with Chiari malformations as guide to clinical management. Acta Neurochir. 2010, 152, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, A.; Bradley, W.G.; Foster, J.B.; Hankinson, J.; Hudgson, P. Syringomyelia due to chronic arachnoiditis at the foramen magnum. J. Neurol. Sci. 1969, 8, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klekamp, J.; Iaconetta, G.; Batzdorf, U.; Samii, M. Syringomyelia associated with foramen magnum arachnoiditis. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 97, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dlouhy, B.J.; Dawson, J.D.; Menezes, A.H. Intradural pathology and pathophysiology associated with Chiari I malformation in children and adults with and without syringomyelia. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2017, 20, 526–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klekamp, J. Surgical treatment of Chiari I malformation--analysis of intraoperative findings, complications, and outcome for 371 foramen magnum decompressions. Neurosurgery 2012, 71, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubbs, R.S.; Smyth, M.D.; Wellons, J.C., 3rd; Oakes, W.J. Arachnoid veils and the Chiari I malformation. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 100, 465–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.A.; Guerrero, A.I.; Martinez, M.I.; Vazquez, M.E.; Fernandez, J.B.; Chesa i Octavio, E.; Labrado Jde, L.; Silva, M.E.; de Araoz, M.F.; Garcia-Ramos, R.; et al. Malformations of the craniocervical junction (Chiari type I and syringomyelia: Classification, diagnosis and treatment). BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2009, 10 (Suppl. S1), S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerji, N.K.; Millar, J.H. Chiari malformation presenting in adult life. Its relationship to syringomyelia. Brain 1974, 97, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, W.O.; Charney, E.B.; Bruce, D.A.; Sutton, L.N.; Schut, L. Symptomatic Arnold-Chiari malformation: Review of experience with 22 cases. J. Neurosurg. 1987, 66, 812–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, N.; Iwasaki, Y.; Hida, K.; Abe, H.; Fujioka, Y.; Nagashima, K. Dural band pathology in syringomyelia with Chiari type I malformation. Neuropathology 2000, 20, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schievink, W.I.; Meyer, F.B.; Atkinson, J.L.; Mokri, B. Spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks and intracranial hypotension. J. Neurosurg. 1996, 84, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schievink, W.I. Spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks and intracranial hypotension. JAMA 2006, 295, 2286–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkan, I.I.; Albayram, S.; Ozaras, R.; Yilmaz, M.H.; Ozbayrak, M.; Mete, B.; Yemisen, M.; Tabak, F. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome may mimic aseptic meningitis. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 44, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrocky, T.; Grunder, L.; Breiding, P.S.; Branca, M.; Limacher, A.; Mosimann, P.J.; Mordasini, P.; Zibold, F.; Haeni, L.; Jesse, C.M.; et al. Assessing Spinal Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension with a Scoring System Based on Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houk, J.L.; Amrhein, T.J.; Gray, L.; Malinzak, M.D.; Kranz, P.G. Differentiation of Chiari malformation type 1 and spontaneous intracranial hypotension using objective measurements of midbrain sagging. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 136, 1796–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schievink, W.I. Spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks: A review. Neurosurg. Focus 2000, 9, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schievink, W.I.; Maya, M.M.; Nuno, M. Chronic cerebellar hemorrhage in spontaneous intracranial hypotension: Association with ventral spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks: Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2011, 15, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranz, P.G.; Amrhein, T.J.; Choudhury, K.R.; Tanpitukpongse, T.P.; Gray, L. Time-Dependent Changes in Dural Enhancement Associated with Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2016, 207, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, I.; Hawke, S.; Halmagyi, M.; Teo, C. The pseudotumor syndrome. Disorders of cerebrospinal fluid circulation causing intracranial hypertension without ventriculomegaly. Arch. Neurol. 1991, 48, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farb, R.I.; Vanek, I.; Scott, J.N.; Mikulis, D.J.; Willinsky, R.A.; Tomlinson, G.; terBrugge, K.G. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: The prevalence and morphology of sinovenous stenosis. Neurology 2003, 60, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stienen, A.; Weinzierl, M.; Ludolph, A.; Tibussek, D.; Hausler, M. Obstruction of cerebral venous sinus secondary to idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Eur. J. Neurol. 2008, 15, 1416–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiken, A.H.; Hoots, J.A.; Saindane, A.M.; Hudgins, P.A. Incidence of cerebellar tonsillar ectopia in idiopathic intracranial hypertension: A mimic of the Chiari I malformation. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 1901–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, R.; Lin, D.; Miller, N.R. Prevalence of Chiari I malformation and cerebellar ectopia in patients with pseudotumor cerebri. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 247, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimzadeh, S.A.; Du, E.; Chang, Y.M.; Bouffard, M.; Loth, F.; Bhadelia, R.A. MRI findings differentiating tonsillar herniation caused by idiopathic intracranial hypertension from Chiari I malformation. Neuroradiology 2022, 64, 2307–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Takanashi, J.; Kobayashi, K.; Nagasawa, K.; Tashima, K.; Kohno, Y. MR imaging of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2001, 22, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bejjani, G.K.; Cockerham, K.P.; Rothfus, W.E.; Maroon, J.C.; Maddock, M. Treatment of failed Adult Chiari Malformation decompression with CSF drainage: Observations in six patients. Acta Neurochir. 2003, 145, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarza, M.; Lopez-Guerrero, A.L.; Martinez-Lage, J.F. Posterior fossa arachnoid cysts and cerebellar tonsillar descent: Short review. Neurosurg. Rev. 2010, 33, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Alotaibi, N.M.; Samuel, N.; Ibrahim, G.M.; Fallah, A.; Cusimano, M.D. Acquired Chiari Malformation and Syringomyelia Secondary to Space-Occupying Lesions: A Systematic Review. World Neurosurg. 2017, 98, 800–808.e802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, M.C.; Enterline, D.S.; Mehltretter, L.; Hammock, P.; Joseph, J.; Dickerson, M.; Ellenbogen, R.G.; Milhorat, T.H.; Hauser, M.A.; George, T.M. Review Article: Chiari Type I Malformation with or without Syringomyelia: Prevalence and Genetics. J. Genet. Couns. 2003, 12, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidoff, C.L.; Liu, S.; Wong, J.H.Y.; Koustais, S.; Rogers, J.M.; Stoodley, M.A. Treatment of Syringomyelia in Patients with Arachnoiditis at the Craniocervical Junction. World Neurosurg. 2017, 107, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, K.A.; Rogers, J.M.; Stoodley, M.A. Syrinx to Subarachnoid Shunting for Syringomyelia. World Neurosurg. 2018, 110, e53–e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middlebrooks, E.H.; Okromelidze, L.; Vilanilam, G.K.; Gopal, N.; Luetmer, P.H.; Gupta, V. Syrinx Secondary to Chiari-like Tonsillar Herniation in Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension. World Neurosurg. 2020, 143, e268–e274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.J.; Goodall, R.J. The surgical treatment of Arnold-Chiari malformation in adults; an explanation of its mechanism and importance of encephalography in diagnosis. J. Neurosurg. 1950, 7, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B. Simultaneous cerebral and spinal fluid pressure recordings. I. Technique, physiology, and normal results. Acta Neurochir. 1981, 58, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B. Simultaneous cerebral and spinal fluid pressure recordings. 2. Cerebrospinal dissociation with lesions at the foramen magnum. Acta Neurochir. 1981, 59, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Case | Age (Years) | Sex | Presentation | Duration (Years) | MRI (Additional Features to Tonsillar Descent) | Management | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post-traumatic cranio-cervical junction arachnoiditis | |||||||
| 1 | 62 | F | Balance and gait deterioration | 10 | Septa at cervico-medullary junction, syringomyelia | Posterior fossa decompression and insertion of fourth ventricle to spinal subarachnoid shunt | Stable |
| 2 | 26 | F | Cough-induced left upper limb sensory disturbance | 10 | Septa at cervico-medullary junction, holocord syringomyelia | Posterior fossa decompression and insertion of fourth ventricle to spinal subarachnoid shunt | Improved |
| Dural band | |||||||
| 3 | 41 | F | Occipital headache, neck and bilateral upper limb pain | 4 | Septation at cranio-cervical junction, inferior to cerebellar tonsil | Posterior fossa decompression | Improved |
| 4 | 49 | F | Left trunk and upper limb sensory disturbance | 9 | Septation at cranio-cervical junction (inferior to cerebellar tonsil), cervico-thoracic syringomyelia | Posterior fossa decompression | Stable; Lost to follow-up |
| Spontaneous intracranial hypotension | |||||||
| 5 | 49 | F | Headache | 8 | Pachymeningeal enhancement Brain sagging | Blood patch | Improved |
| 6 | 73 | F | Headache | 1 | Brain sagging | Blood patch | Improved |
| 7 | 47 | F | Headache | 5 | Brain sagging | Thoracic laminectomy for CSF leak | Improved |
| 8 | 52 | F | Headache | 2 | Pachymeningeal enhancement, pituitary gland engorgement | Blood patch Thoracic laminectomy for CSF leak | Improved |
| 9 | 51 | F | Headache | 8 | Pachymeningeal enhancement, venous sinus engorgement, brain sagging, syrinx | Multiple surgical decompressions Shunt insertion and revision for syrinx Thoracic laminectomy for CSF repair | Improved |
| 10 | 68 | F | Headache | 2 | Pachymeningeal enhancement, venous sinus engorgement, brain sagging, syrinx | Blood patch | Stable |
| Idiopathic intracranial hypertension | |||||||
| 11 | 26 | F | Occipital headache Visual disturbance | 5 | Empty sella, CSF around optic nerves | Surgical decompression Ventriculoperitoneal shunt insertion | Improved |
| 12 | 30 | F | Occipital headache | 8 | Tortuosity of optic nerve | Medical management | Not applicable |
| Cysts—arachnoid, choroid plexus, cerebellum | |||||||
| 13 | 57 | M | Headache Visual changes | 1 | Arachnoid cyst | Surgical decompression and fenestration of cyst | Improved |
| 14 | 23 | F | Headache | 5 | Extra-axial cyst | Surgical decompression and excision of cyst | Improved |
| 15 | 61 | F | Headache | 1 | Supra-cerebellar cyst | Expectant management | Improved |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, R.J.; Unnikrishnan, S.; Berliner, J.; Magnussen, J.; Liu, S.; Stoodley, M.A. Cerebellar Tonsillar Descent Mimicking Chiari Malformation. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082786
Park RJ, Unnikrishnan S, Berliner J, Magnussen J, Liu S, Stoodley MA. Cerebellar Tonsillar Descent Mimicking Chiari Malformation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(8):2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082786
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Rachel J., Sunil Unnikrishnan, Joel Berliner, John Magnussen, Shinuo Liu, and Marcus A. Stoodley. 2023. "Cerebellar Tonsillar Descent Mimicking Chiari Malformation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 8: 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082786
APA StylePark, R. J., Unnikrishnan, S., Berliner, J., Magnussen, J., Liu, S., & Stoodley, M. A. (2023). Cerebellar Tonsillar Descent Mimicking Chiari Malformation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(8), 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082786





