A Supplement with Ribes Nigrum, Boswellia Serrata, Bromelain and Vitamin D to Stop Local Inflammation in Chronic Sinusitis: A Case-Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Information and Randomization
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Clinical Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
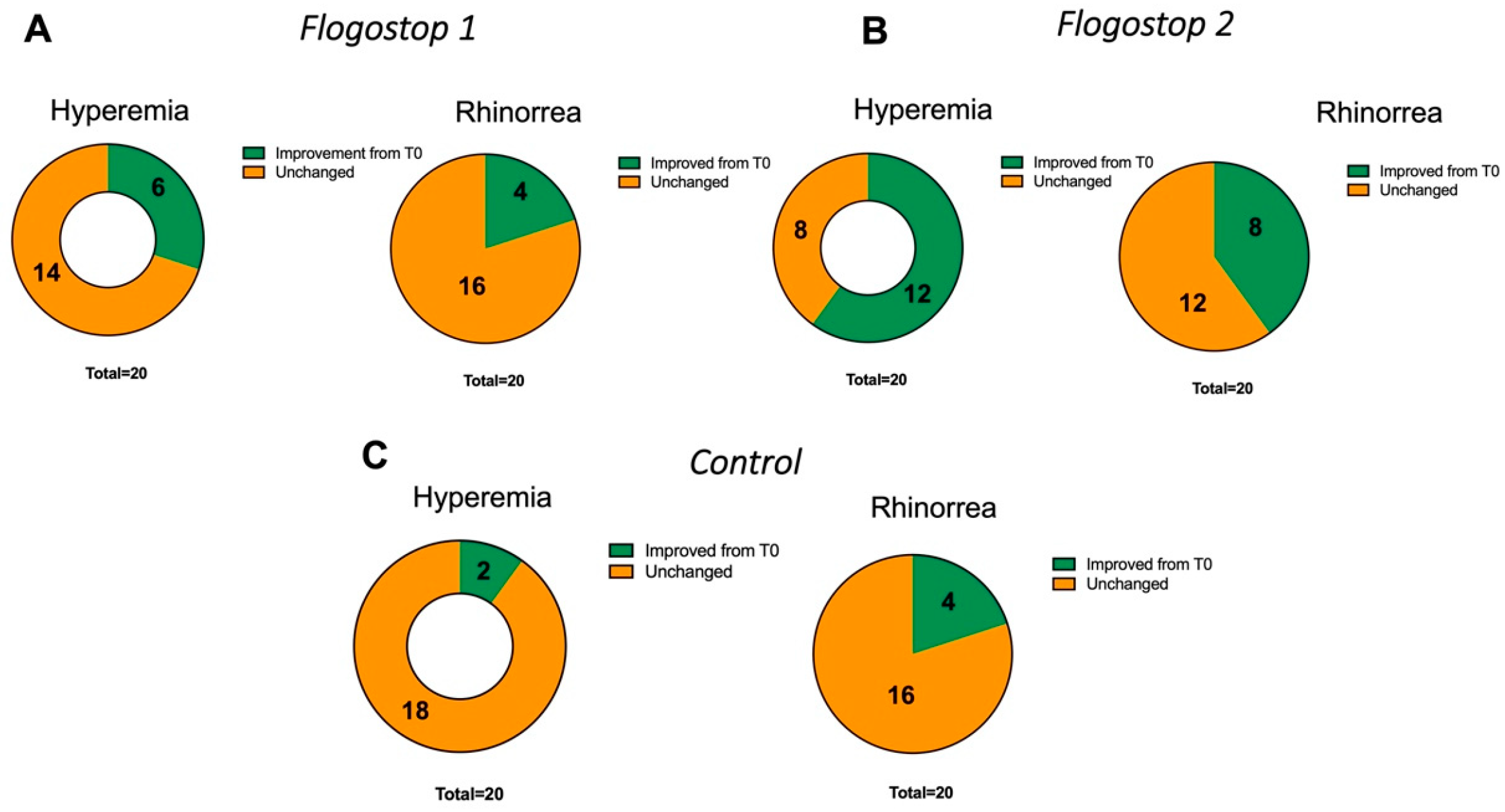
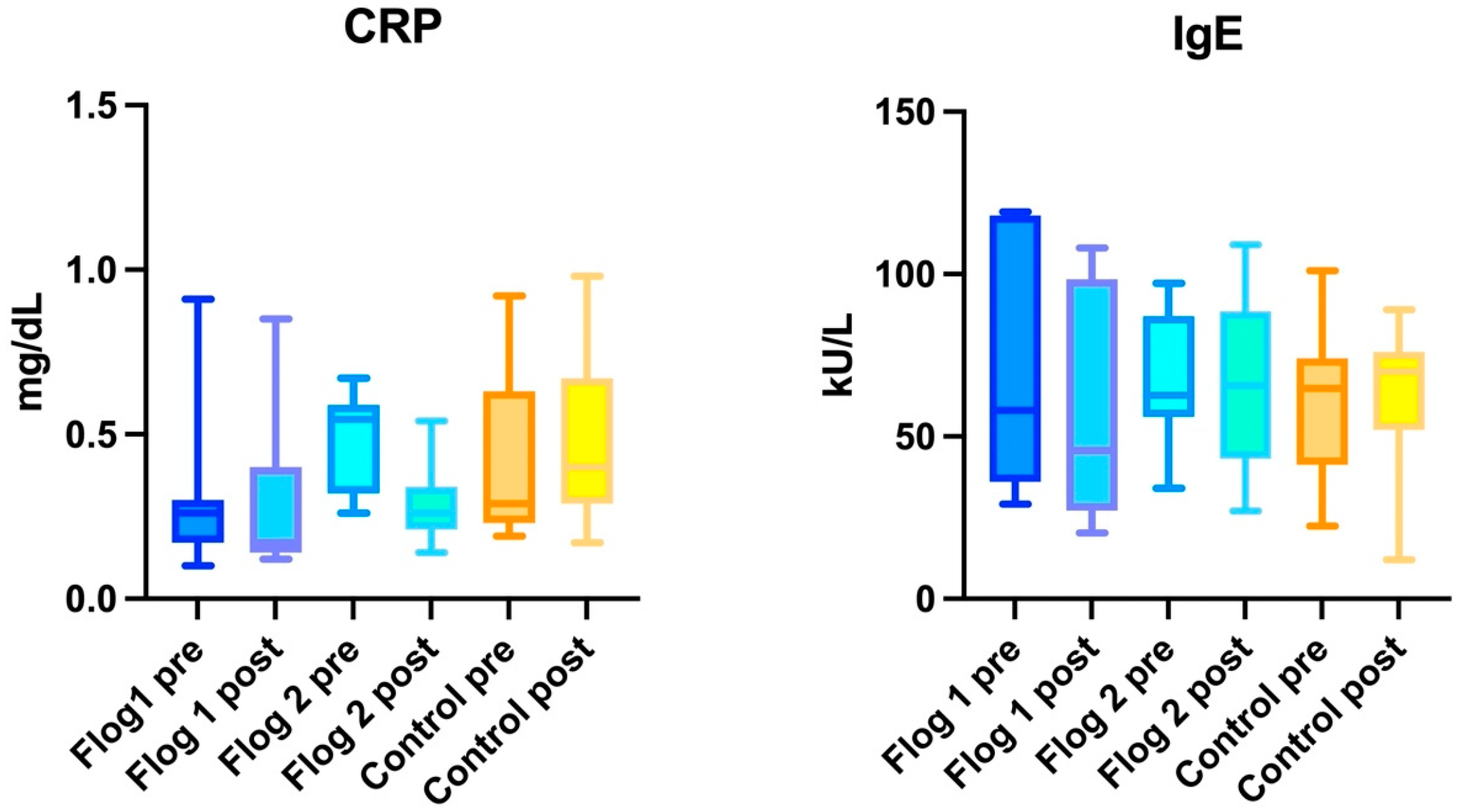
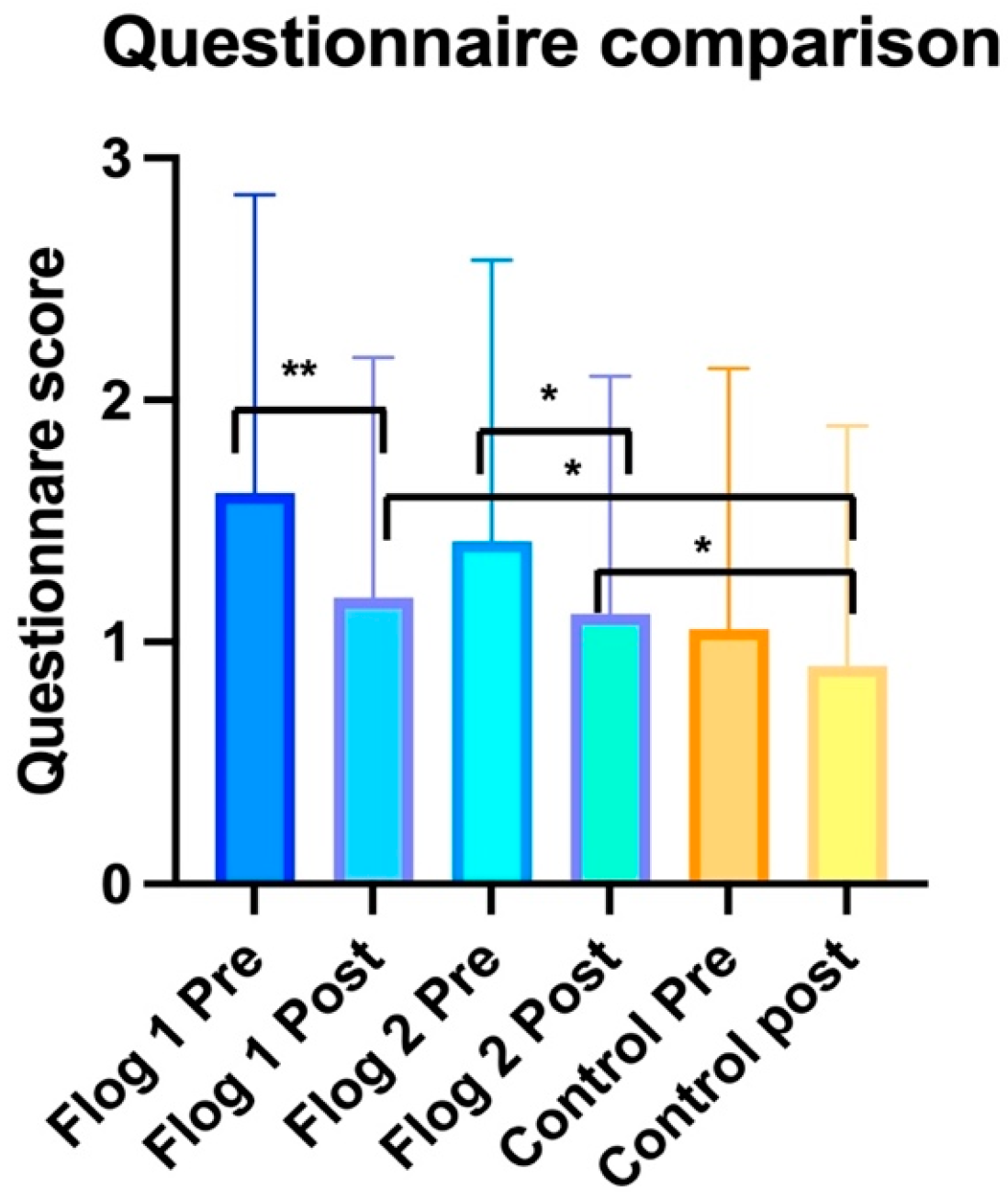
3.1. Within Group Analysis
3.1.1. Treatment Group 1
3.1.2. Treatment Group 2
3.1.3. Control Group
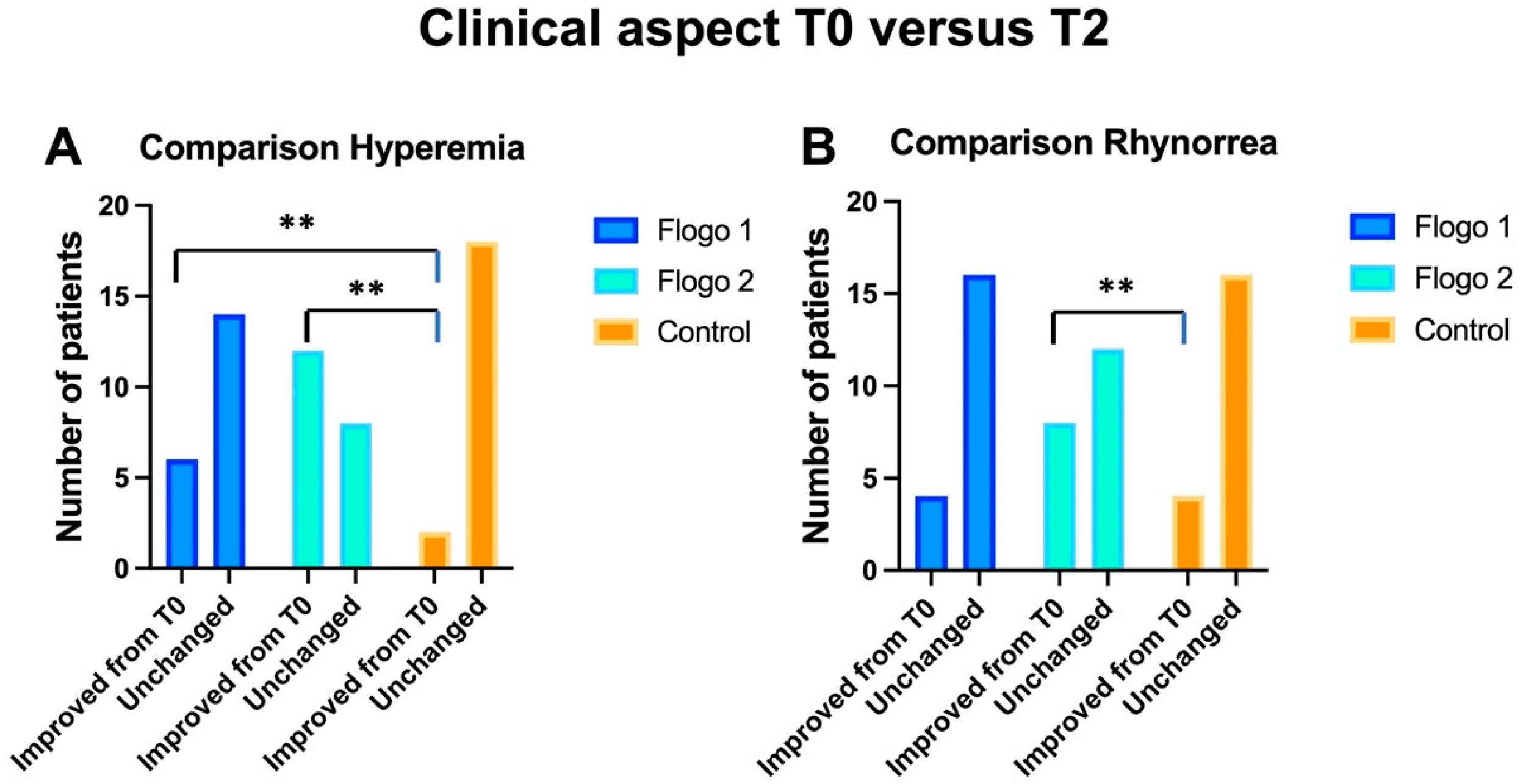
3.2. Between Groups Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klimek, L.; Koennecke, M.; Hagemann, J.; Wollenberg, B.; Becker, S. Immunology of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps as a basis for treatment with biologicals. HNO 2019, 67, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipolo, C.; Saibene, A.M.; Felisati, G. Prevalence of pain due to rhinosinusitis: A review. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 39 (Suppl. 1), 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonino, M.; Nicolò, M.; Jerome Renee, L.; Federico, M.; Chiara, V.; Stefano, S.; Maria, S.; Salvatore, C.; Antonio, B.; Calvo-Henriquez, C.; et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphism in chronic rhinosinusitis: A systematic review. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2022, 47, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioacchini, F.M.; Ferlito, S.; Ralli, M.; Scarpa, A.; La Mantia, I.; Re, M.; Romani, L.; Di Stadio, A. Nasal Microbiota and Neuroinflammation: Relationship between Nasal Flora and Multiple Sclerosis Onset/Progression. Life 2022, 12, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stryjewska-Makuch, G.; Janik, M.A.; Lisowska, G.; Kolebacz, B. Bacteriological analysis of isolated chronic sinusitis without polyps. Postep. Derm. Alergol. 2018, 35, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Kim, C.H. Oxygen matters: Hypoxia as a pathogenic mechanism in rhinosinusitis. BMB Rep. 2018, 51, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philpott, C.M.; Erskine, S.; Hopkins, C.; Kumar, N.; Anari, S.; Kara, N.; Sunkaraneni, S.; Ray, J.; Clark, A.; Wilson, A.; et al. Prevalence of asthma, aspirin sensitivity and allergy in chronic rhinosinusitis: Data from the UK National Chronic Rhinosinusitis Epidemiology Study. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, J.; Hartzell, L.; Putt, C.; Kennedy, J.L. Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Children: Pathophysiology, Evaluation, and Medical Management. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018, 18, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.H.; Seidel, D.U.; Bachert, C.; Dazert, S.; Kostev, K. Medication use in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis in Germany—A large retrospective patient-based study. Rhinology 2019, 57, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barac, A.; Ong, D.S.Y.; Jovancevic, L.; Peric, A.; Surda, P.; Tomic Spiric, V.; Rubino, S. Fungi-Induced Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Allergic Diseases: One Entity. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, L.Y.; Head, K.; Hopkins, C.; Philpott, C.; Schilder, A.G.; Burton, M.J. Intranasal steroids versus placebo or no intervention for chronic rhinosinusitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 4, CD011996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaser, M.J.; Melby, M.K.; Lock, M.; Nichter, M. Accounting for variation in and overuse of antibiotics among humans. Bioessays 2021, 43, e2000163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, P.G.; Karadag, A.S.; Selvi, Y.; Boysan, M.; Bilgili, S.G.; Aydin, A.; Onder, S. Assessment of the effects of antihistamine drugs on mood, sleep quality, sleepiness, and dream anxiety. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2014, 18, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stadio, A.; Ishai, R.; Gambacorta, V.; Korsch, F.; Ricci, G.; Della Volpe, A.; Bernitsas, E. Nutraceuticals as immune-stimulating therapy to fight COVID-19. Combination of elements to improve the efficacy. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 9182–9187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Di Stadio, A.; Costantini, C.; Renga, G.; Pariano, M.; Ricci, G.; Romani, L. The Microbiota/Host Immune System Interaction in the Nose to Protect from COVID-19. Life 2020, 10, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, S.; Sánchez, B.; Margolles, A.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Ruiz, L. Molecules Produced by Probiotics and Intestinal Microorganisms with Immunomodulatory Activity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Mantia, I.; Gelardi, M.; Drago, L.; Aragona, S.E.; Cupido, G.; Vicini, C.; Berardi, C.; Ciprandi, G.; Italian Study Group on Upper Respiratory Infections; Albanese, G.; et al. Probiotics in the add-on treatment of rhinosinusitis: A clinical experience. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents. 2020, 34 (Suppl. 1), 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, Z.A.; Ahmad, T. Therapeutic uses of pineapple-extracted bromelain in surgical care—A review. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2017, 67, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Tsuzuki, K.; Nishikawa, H.; Okazaki, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Sakagami, M. Nasal Symptom Questionnaire: Our Proposed Scoring System and Prognostic Factors in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2018, 80, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorland’s Pocket Medical Dictionary; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; p. 660. ISBN 978-81-312-3501-0.
- Eccles, R. The role of nasal congestion as a defence against respiratory viruses. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2021, 46, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikisz, P.; Bernasinska-Slomczewska, J. Beneficial Properties of Bromelain. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helms, S.; Miller, A.L. Natural treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis. Altern. Med. Rev. 2006, 11, 196–207. [Google Scholar]
- Di Stadio, A.; Della Volpe, A.; Korsch, F.M.; De Lucia, A.; Ralli, M.; Martines, F.; Ricci, G. Difensil Immuno Reduces Recurrence and Severity of Tonsillitis in Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Wang, M.; Zhou, L.; Wen, Q.; Zou, J. Association between serum vitamin D and chronic rhinosinusitis: A meta-analysis. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 87, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.Z. Boswellia serrata, a potential antiinflammatory agent: An overview. Indian J. Pharm Sci. 2011, 73, 255–261. [Google Scholar]
- Hüsch, J.; Bohnet, J.; Fricker, G.; Skarke, C.; Artaria, C.; Appendino, G.; Schubert-Zsilavecz, M.; Abdel-Tawab, M. Enhanced absorption of boswellic acids by a lecithin delivery form (Phytosome(®)) of Boswellia extract. Fitoterapia 2013, 84, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, R.E.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E. Blackcurrants (Ribes nigrum): A Review on Chemistry, Processing, and Health Benefits. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2387–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, J.Y. Blackcurrant (Ribes nigrum) Extract Exerts an Anti-Inflammatory Action by Modulating Macrophage Phenotypes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuta, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Kaneko, H.; Mori, S.; Ohashi, K.; Suzutani, T. Anti-viral and anti-bacterial activities of an extract of blackcurrants (Ribes nigrum L.). Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 56, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Volpe, A.; De Luca, P.; De Lucia, A.; Martines, F.; Piroli, P.; D’Ascanio, L.; Camaioni, A.; La Mantia, I.; Di Stadio, A. Single-Center-Single-Blinded Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy of a Nutraceutical Containing Boswellia Serrata, Bromelain, Zinc, Magnesium, Honey, Tyndallized Lactobacillus Acidophilus and Casei to Fight Upper Respiratory Tract Infection and Otitis Media. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Luca, P.; D’Ascanio, L.; Cingolani, C.; Latini, G.; Grigaliute, E.; Di Mauro, P.; Ralli, M.; La Mantia, I.; Di Stadio, A. A Supplement with Ribes Nigrum, Boswellia Serrata, Bromelain and Vitamin D to Stop Local Inflammation in Chronic Sinusitis: A Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2929. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082929
De Luca P, D’Ascanio L, Cingolani C, Latini G, Grigaliute E, Di Mauro P, Ralli M, La Mantia I, Di Stadio A. A Supplement with Ribes Nigrum, Boswellia Serrata, Bromelain and Vitamin D to Stop Local Inflammation in Chronic Sinusitis: A Case-Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(8):2929. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082929
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Luca, Pietro, Luca D’Ascanio, Cristina Cingolani, Gino Latini, Egle Grigaliute, Paola Di Mauro, Massimo Ralli, Ignazio La Mantia, and Arianna Di Stadio. 2023. "A Supplement with Ribes Nigrum, Boswellia Serrata, Bromelain and Vitamin D to Stop Local Inflammation in Chronic Sinusitis: A Case-Control Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 8: 2929. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082929
APA StyleDe Luca, P., D’Ascanio, L., Cingolani, C., Latini, G., Grigaliute, E., Di Mauro, P., Ralli, M., La Mantia, I., & Di Stadio, A. (2023). A Supplement with Ribes Nigrum, Boswellia Serrata, Bromelain and Vitamin D to Stop Local Inflammation in Chronic Sinusitis: A Case-Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(8), 2929. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082929








