High-Resolution Single-Shot Fast Spin-Echo MR Imaging with Deep Learning Reconstruction Algorithm Can Improve Repeatability and Reproducibility of Follicle Counting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
2.3. Qualitative Analysis
2.4. Assessment of Follicle Number Per Ovary (FNPO)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Participants
3.2. Qualitative Image Analysis
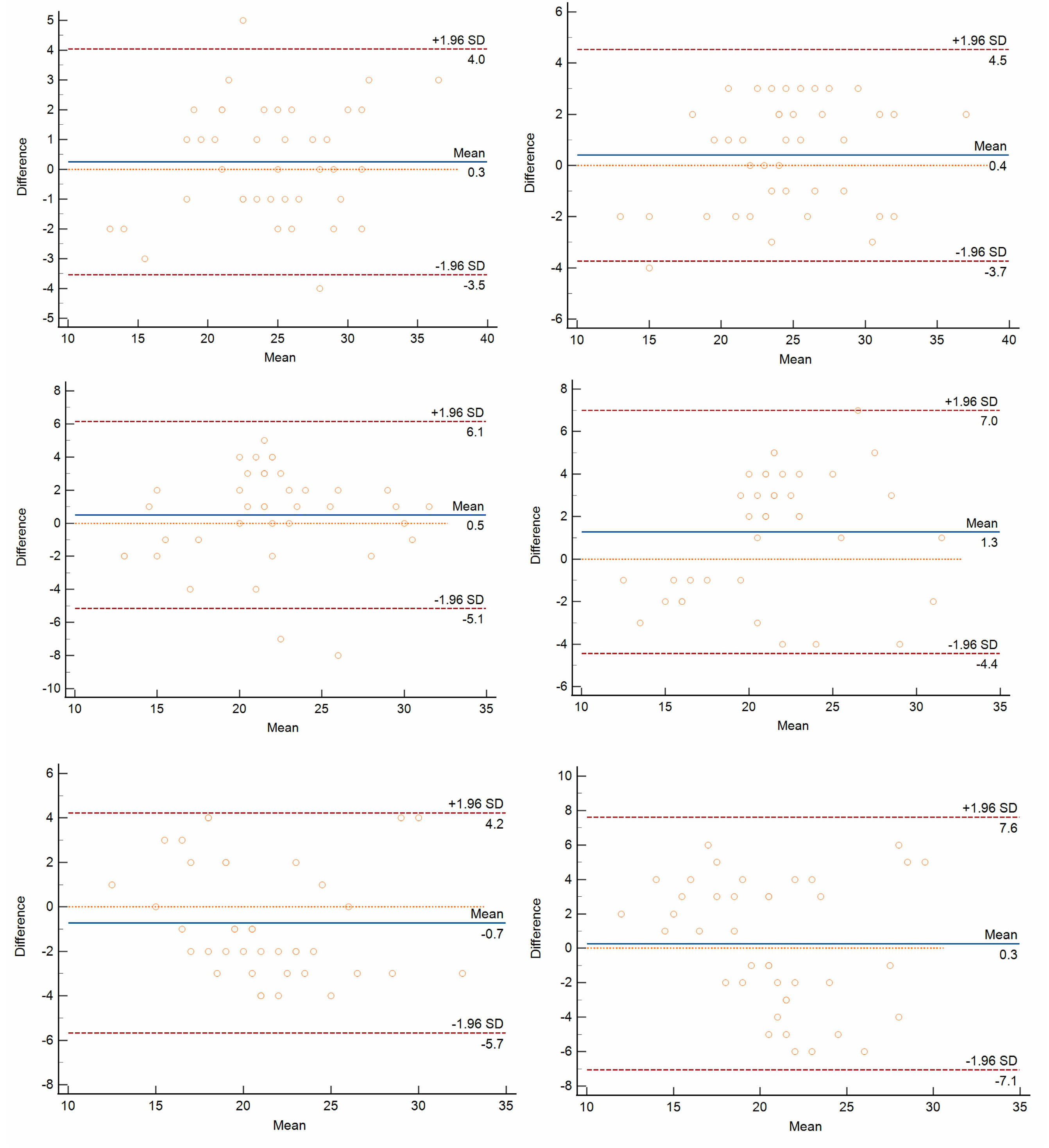
3.3. Repeatability and Reproducibility of FNPO Assessment
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fauser, B.C.; Tarlatzis, B.C.; Rebar, R.W.; Legro, R.S.; Balen, A.H.; Lobo, R.; Carmina, E.; Chang, J.; Yildiz, B.O.; Laven, J.S.; et al. Consensus on women’s health aspects of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): The Amsterdam ESHRE/ASRM-Sponsored 3rd PCOS Consensus Workshop Group. Fertil. Steril. 2012, 97, 28–38.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotterdam ESHRE/ASRM-Sponsored PCOS Consensus Workshop Group. Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic criteria and long-term health risks related to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Hum. Reprod. 2004, 19, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewailly, D.; Lujan, M.E.; Carmina, E.; Cedars, M.I.; Laven, J.; Norman, R.J.; Escobar-Morreale, H.F. Definition and significance of polycystic ovarian morphology: A task force report from the Androgen Excess and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Society. Hum. Reprod. Update 2014, 20, 334–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teede, H.J.; Misso, M.L.; Costello, M.F.; Dokras, A.; Laven, J.; Moran, L.; Piltonen, T.; Norman, R.J.; International PCOS Network. Recommendations from the international evidence-based guideline for the assessment and management of polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum. Reprod. 2018, 33, 1602–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenigsberg, L.E.; Agarwal, C.; Sin, S.; Shifteh, K.; Isasi, C.R.; Crespi, R.; Ivanova, J.; Coupey, S.M.; Heptulla, R.A.; Arens, R. Clinical utility of magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasonography for diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome in adolescent girls. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 104, 1302–1309.e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lujan, M.E.; Jarrett, B.Y.; Brooks, E.D.; Reines, J.K.; Peppin, A.K.; Muhn, N.; Haider, E.; Pierson, R.A.; Chizen, D.R. Updated ultrasound criteria for polycystic ovary syndrome: Reliable thresholds for elevated follicle population and ovarian volume. Hum. Reprod. 2013, 28, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayemba-Kay’s, S.; Pambou, A.; Heron, A.; Benosman, S.M. Polycystic ovary syndrome: Pelvic MRI as alternative to pelvic ultrasound for the diagnosis in overweight and obese adolescent girls. Int. J. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2017, 4, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, T.M.; Alvey, C.; Greenslade, T.; Gooding, M.; Barber, D.; Smith, R.; Marland, A.; Wass, J.A.; Child, T.; McCarthy, M.I.; et al. Patterns of ovarian morphology in polycystic ovary syndrome: A study utilising magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2010, 20, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonhardt, H.; Gull, B.; Stener-Victorin, E.; Hellström, M. Ovarian volume and antral follicle count assessed by MRI and transvaginal ultrasonography: A methodological study. Acta Radiol. 2014, 55, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Zhang, M.M.; Duan, N.; Hu, X.Y.; Ren, S.; Cao, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.P.; Wang, Z.Q. Using transvaginal ultrasonography and MRI to evaluate ovarian volume and follicle count of infertile women: A comparative study. Clin. Radiol. 2022, 77, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fondin, M.; Rachas, A.; Huynh, V.; Franchi-Abella, S.; Teglas, J.P.; Duranteau, L.; Adamsbaum, C. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Adolescents: Which MR Imaging-based Diagnostic Criteria? Radiology 2017, 285, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.; Park, A.S.; Shayya, R.F.; Wolfson, T.; Su, H.I.; Chang, R.J. Ovarian imaging by magnetic resonance in adolescent girls with polycystic ovary syndrome and age-matched controls. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 38, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, Y.; Tang, Y.; Abe, Y.; Mitsuzaki, K.; Takahashi, M. Comparison of ultrafast half-Fourier single-shot turbo spin-echo sequence with turbo spin-echo sequences for T2-weighted imaging of the female pelvis. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1998, 8, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboyama, T.; Takei, O.; Okada, A.; Honda, T.; Kuriyama, K. Comparison of HASTE with multiple signal averaging versus conventional turbo spin echo sequence: A new option for T2-weighted MRI of the female pelvis. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 3245–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidoh, M.; Shinoda, K.; Kitajima, M.; Isogawa, K.; Nambu, M.; Uetani, H.; Morita, K.; Nakaura, T.; Tateishi, M.; Yamashita, Y.; et al. Deep Learning Based Noise Reduction for Brain MR Imaging: Tests on Phantoms and Healthy Volunteers. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2020, 19, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, A.S.; Fang, Z.; Kogan, F.; Wood, J.; Stevens, K.J.; Gibbons, E.K.; Lee, J.H.; Gold, G.E.; Hargreaves, B.A. Super-resolution musculoskeletal MRI using deep learning. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 2139–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Weighted kappa: Nominal scale agreement with provision for scaled disagreement or partial credit. Psychol. Bull. 1968, 70, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Applying the right statistics: Analyses of measurement studies. Ultrasound. Obstet. Gynecol. 2003, 22, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S. Ultrasound Evaluation in Female Infertility: Part 1, the Ovary and the Follicle. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 46, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylander, M.; Frøssing, S.; Bjerre, A.H.; Chabanova, E.; Clausen, H.V.; Faber, J.; Skouby, S.O. Ovarian morphology in polycystic ovary syndrome: Estimates from 2D and 3D ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging and their correlation to anti-Müllerian hormone. Acta Radiol. 2017, 58, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassenmaier, S.; Herrmann, J.; Nickel, D.; Kannengiesser, S.; Afat, S.; Seith, F.; Hoffmann, R.; Othman, A.E. Image Quality Improvement of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Gradient Echo Magnetic Resonance Imaging by Iterative Denoising and Edge Enhancement. Investig. Radiol. 2021, 56, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebel, R.M. Performance characterization of a novel deep learning-based MR image reconstruction pipeline. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.06559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Velde, N.; Hassing, H.C.; Bakker, B.J.; Wielopolski, P.A.; Lebel, R.M.; Janich, M.A.; Kardys, I.; Budde, R.P.J.; Hirsch, A. Improvement of late gadolinium enhancement image quality using a deep learning-based reconstruction algorithm and its influence on myocardial scar quantification. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 3846–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanbhogue, K.; Tong, A.; Smereka, P.; Nickel, D.; Arberet, S.; Anthopolos, R.; Chandarana, H. Accelerated single-shot T2-weighted fat-suppressed (FS) MRI of the liver with deep learning-based image reconstruction: Qualitative and quantitative comparison of image quality with conventional T2-weighted FS sequence. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 8447–8457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, J.; Gassenmaier, S.; Nickel, D.; Arberet, S.; Afat, S.; Lingg, A.; Kündel, M.; Othman, A.E. Diagnostic confidence and feasibility of a deep learning accelerated HASTE sequence of the abdomen in a single breath-hold. Investig. Radiol. 2021, 56, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, N.F.; Cobin, R.H.; Futterweit, W.; Glueck, J.S.; Legro, R.S.; Carmina, E. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, American College of Endocrinology, and Androgen Excess and PCOS Society disease state clinical review: Guide to the best practices in the evaluation and treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome—Part 1. Endocr. Pract. 2015, 21, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azziz, R.; Carmina, E.; Dewailly, D.; Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Escobar-Morreale, H.F.; Futterweit, W.; Janssen, O.E.; Legro, R.S.; Norman, R.J.; Taylor, A.E.; et al. Androgen Excess Society. Positions statement: Criteria for defining polycystic ovary syndrome as a predominantly hyperandrogenic syndrome: An Androgen Excess Society guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 4237–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.J.; Zhao, M.J.; Li, C.; Su, X. The comparison of evaluative effectiveness between antral follicle count/age ratio and ovarian response prediction index for the ovarian reserve and response functions in infertile women. Medicine 2020, 99, e21979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Eshraghi, C.F.; Tao, R.; Chiuzan, C.C.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, W.; Lerner, J.P.; Oberfield, S.E.; Sopher, A.B. Ovarian follicle count by magnetic resonance imaging is greater in adolescents and young adults with polycystic ovary syndrome than in controls. F. S. Rep. 2022, 3, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
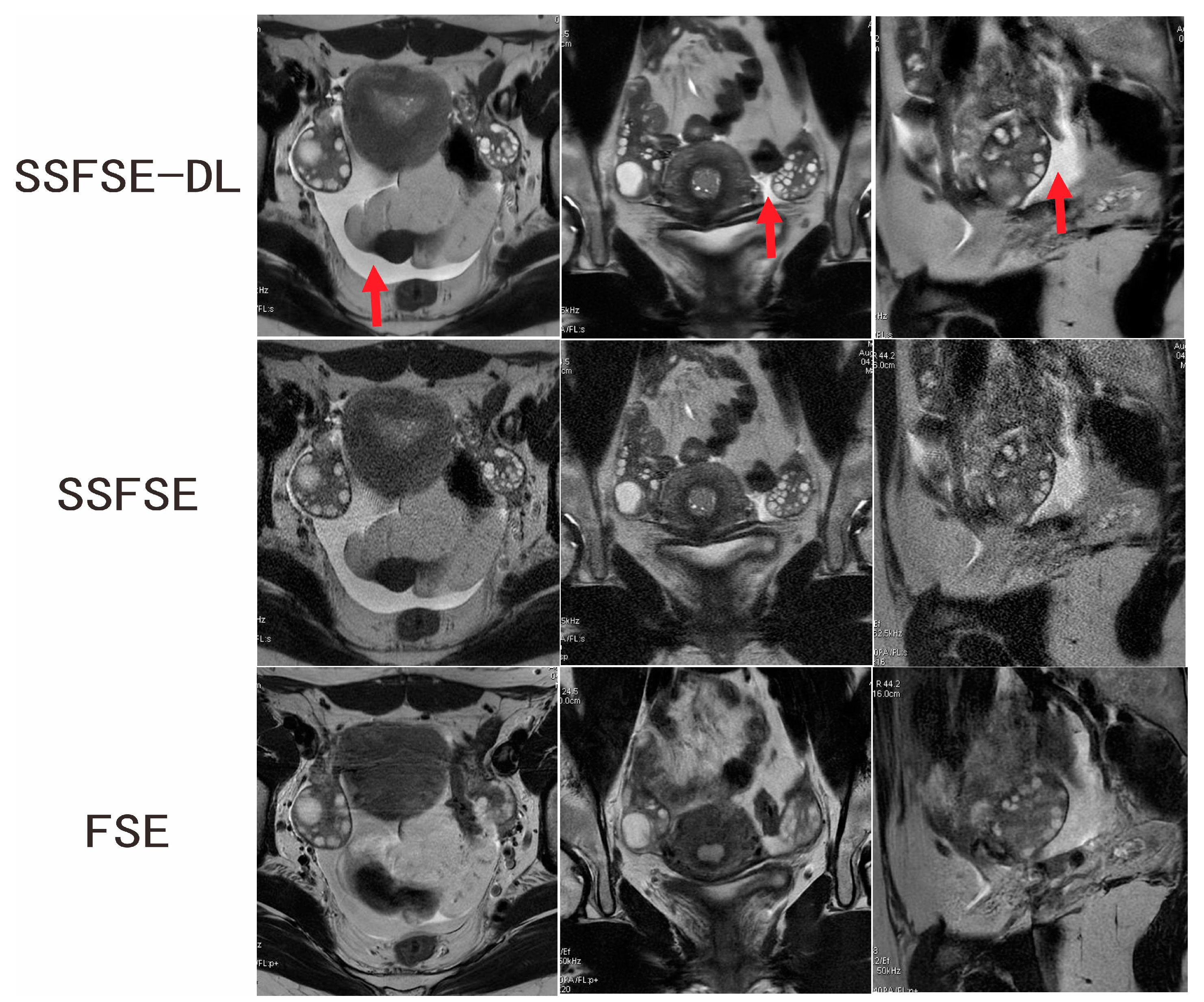
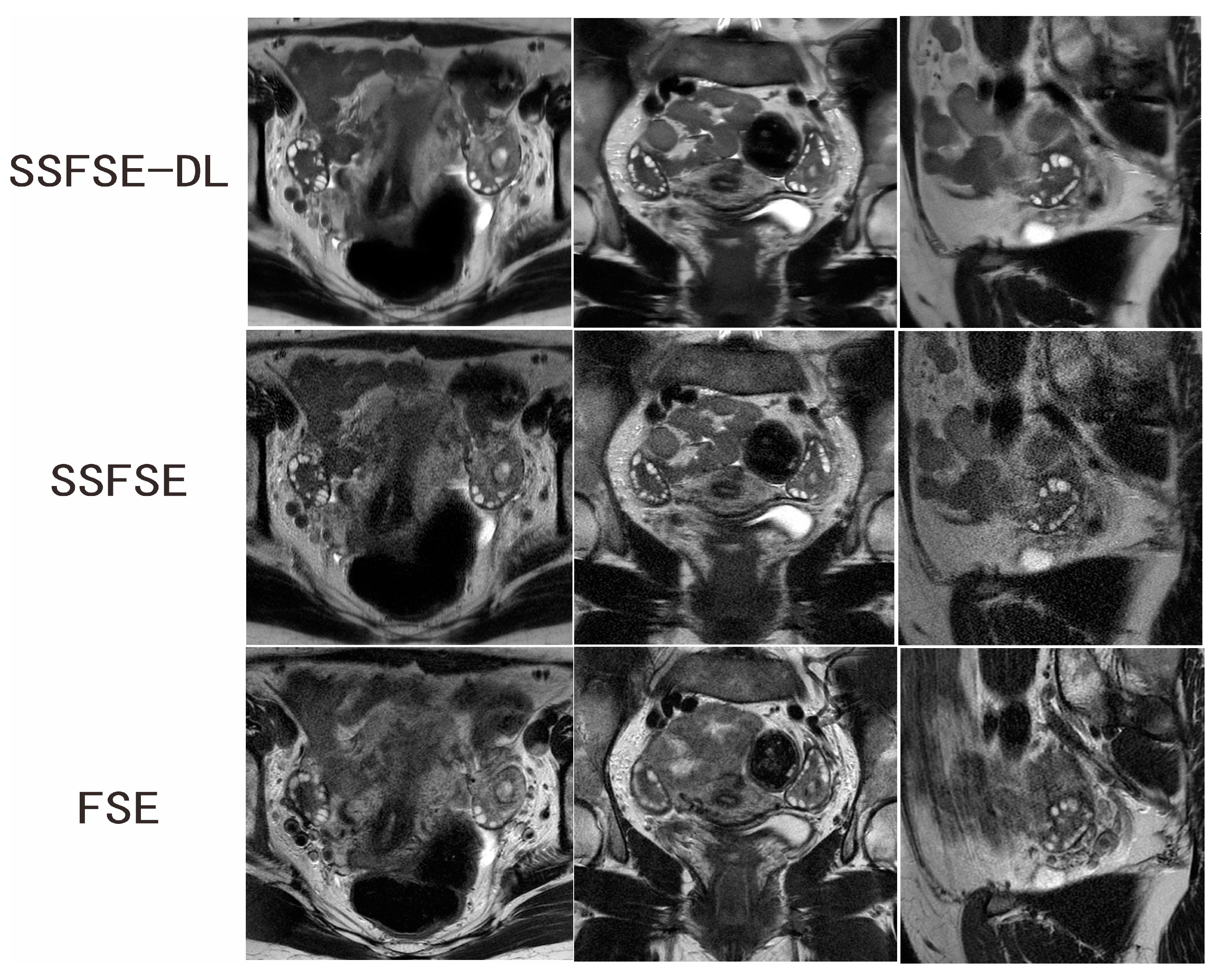
| Rated Feature | Observer | SSFSE-DL | SSFSE | FSE | SSFSE-DL vs. SSFSE | SSFSE-DL vs. FSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blurring artifacts | 1 | 2.600 ± 0.598 | 2.200 ± 0.834 | 1.950 ± 0.826 | p = 0.0117 | p = 0.0015 |
| 2 | 2.550 ± 0.510 | 2.050 ± 0.759 | 1.900 ± 0.788 | p = 0.0051 | p = 0.0022 | |
| Inter-observer agreement | 0.720 (0.463–0.976) | 0.591 (0.338–0.843) | 0.474 (0.165–0.783) | |||
| Subjective noise | 1 | 2.750 ± 0.550 | 1.500 ± 0.513 | 2.450 ± 0.605 | p = 0.0001 | p = 0.0277 |
| 2 | 2.650 ± 0.587 | 1.700 ± 0.571 | 2.250 ± 0.550 | p = 0.0001 | p = 0.0051 | |
| Inter-observer agreement | 0.789 (0.498–1.000) | 0.636 (0.352–0.921) | 0.664 (0.366–0.961) | |||
| Clarity of the follicles | 1 | 4.150 ± 0.745 | 3.700 ± 0.657 | 3.150 ± 0.875 | p = 0.0164 | p = 0.0003 |
| 2 | 4.400 ± 0.681 | 3.800 ± 0.696 | 3.200 ± 1.005 | p = 0.0051 | p = 0.0007 | |
| Inter-observer agreement | 0.671 (0.423–0.919) | 0.565 (0.245–0.885) | 0.536 (0.260–0.812) |
| Sequence | Observer | Session | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSFSE-DL | 1 | 1 | 12 | 38 | 24.7 | 5.4 |
| 2 | 2 | 14 | 35 | 24.4 | 5.0 | |
| 1 | 3 | 14 | 36 | 24.3 | 4.8 | |
| SSFSE | 1 | 1 | 12 | 32 | 22.1 | 5.0 |
| 2 | 2 | 14 | 31 | 21.6 | 4.8 | |
| 1 | 3 | 13 | 32 | 20.9 | 4.2 | |
| FSE | 1 | 1 | 13 | 32 | 20.8 | 4.1 |
| 2 | 2 | 12 | 34 | 21.6 | 4.7 | |
| 1 | 3 | 11 | 30 | 20.6 | 5.0 |
| Sequence | Intra-Observer ICC (95% CI) | Inter-Observer ICC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| SSFSE-DL | 0.930 (0.878–0.962) | 0.914 (0.843–0.953) |
| SSFSE | 0.825 (0.693–0.903) | 0.798 (0.650–0.888) |
| FSE | 0.839 (0.716–0.912) | 0.669 (0.454–0.810) |
| Parameter | SSFSE-DL | SSFSE | FSE | SSFSE-DL vs. SSFSE | SSFSE-DL vs. FSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-observer difference | 1.475 ± 1.062 | 2.300 ± 1.772 | 2.325 ± 1.163 | p = 0.0185 | p = 0.0001 |
| Inter-observer difference | 1.900 ± 0.955 NS | 2.825 ± 1.412 NS | 3.325 ± 1.655 * | p = 0.0004 | p < 0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, R.; Zou, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Wen, Z.; Li, L.; Sun, C.; Hu, M.; Zha, Y. High-Resolution Single-Shot Fast Spin-Echo MR Imaging with Deep Learning Reconstruction Algorithm Can Improve Repeatability and Reproducibility of Follicle Counting. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093234
Yang R, Zou Y, Liu W, Liu C, Wen Z, Li L, Sun C, Hu M, Zha Y. High-Resolution Single-Shot Fast Spin-Echo MR Imaging with Deep Learning Reconstruction Algorithm Can Improve Repeatability and Reproducibility of Follicle Counting. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(9):3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093234
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Renjie, Yujie Zou, Weiyin (Vivian) Liu, Changsheng Liu, Zhi Wen, Liang Li, Chenyu Sun, Min Hu, and Yunfei Zha. 2023. "High-Resolution Single-Shot Fast Spin-Echo MR Imaging with Deep Learning Reconstruction Algorithm Can Improve Repeatability and Reproducibility of Follicle Counting" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 9: 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093234
APA StyleYang, R., Zou, Y., Liu, W., Liu, C., Wen, Z., Li, L., Sun, C., Hu, M., & Zha, Y. (2023). High-Resolution Single-Shot Fast Spin-Echo MR Imaging with Deep Learning Reconstruction Algorithm Can Improve Repeatability and Reproducibility of Follicle Counting. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(9), 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093234





