Utility of MRI in Quantifying Tissue Injury in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
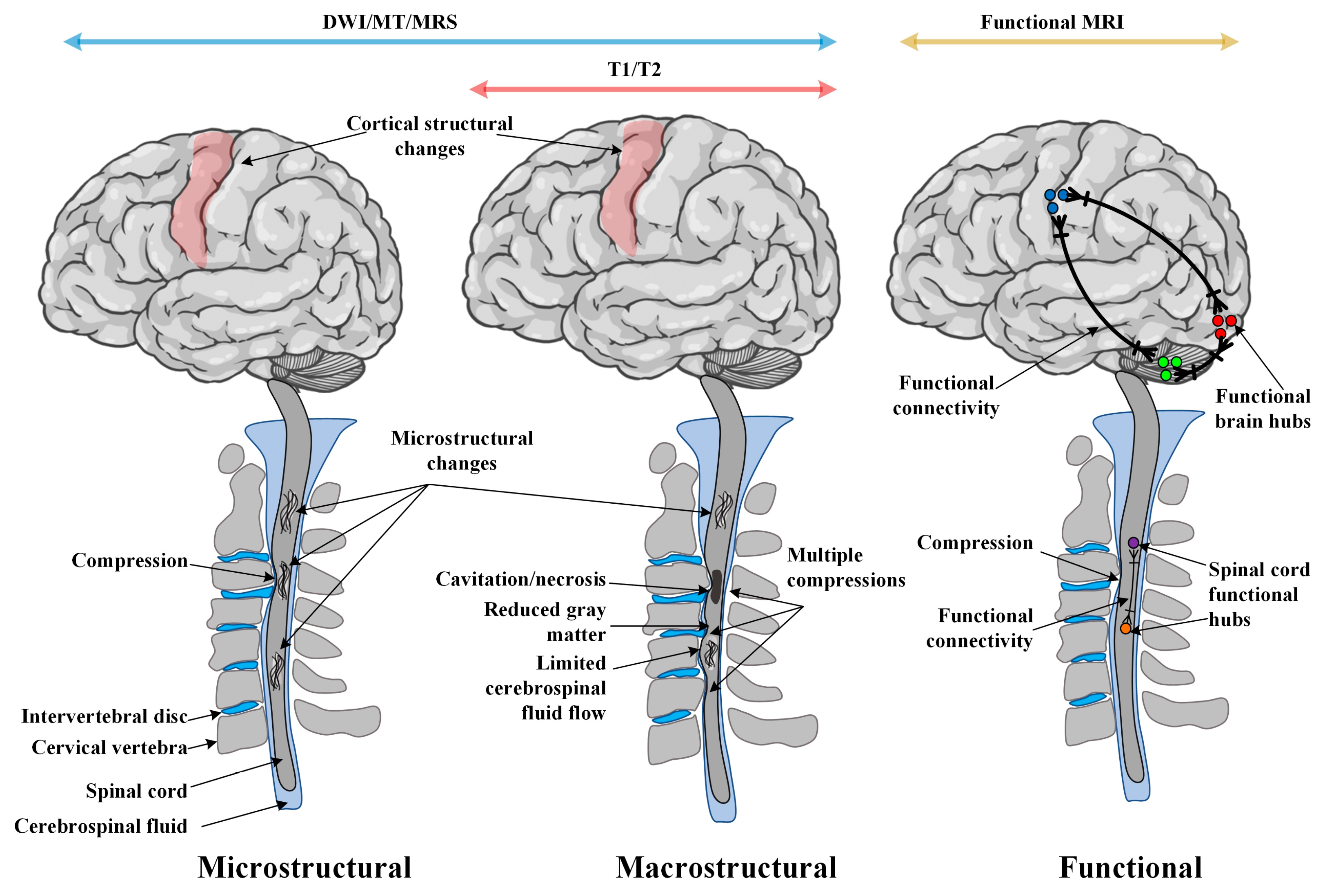
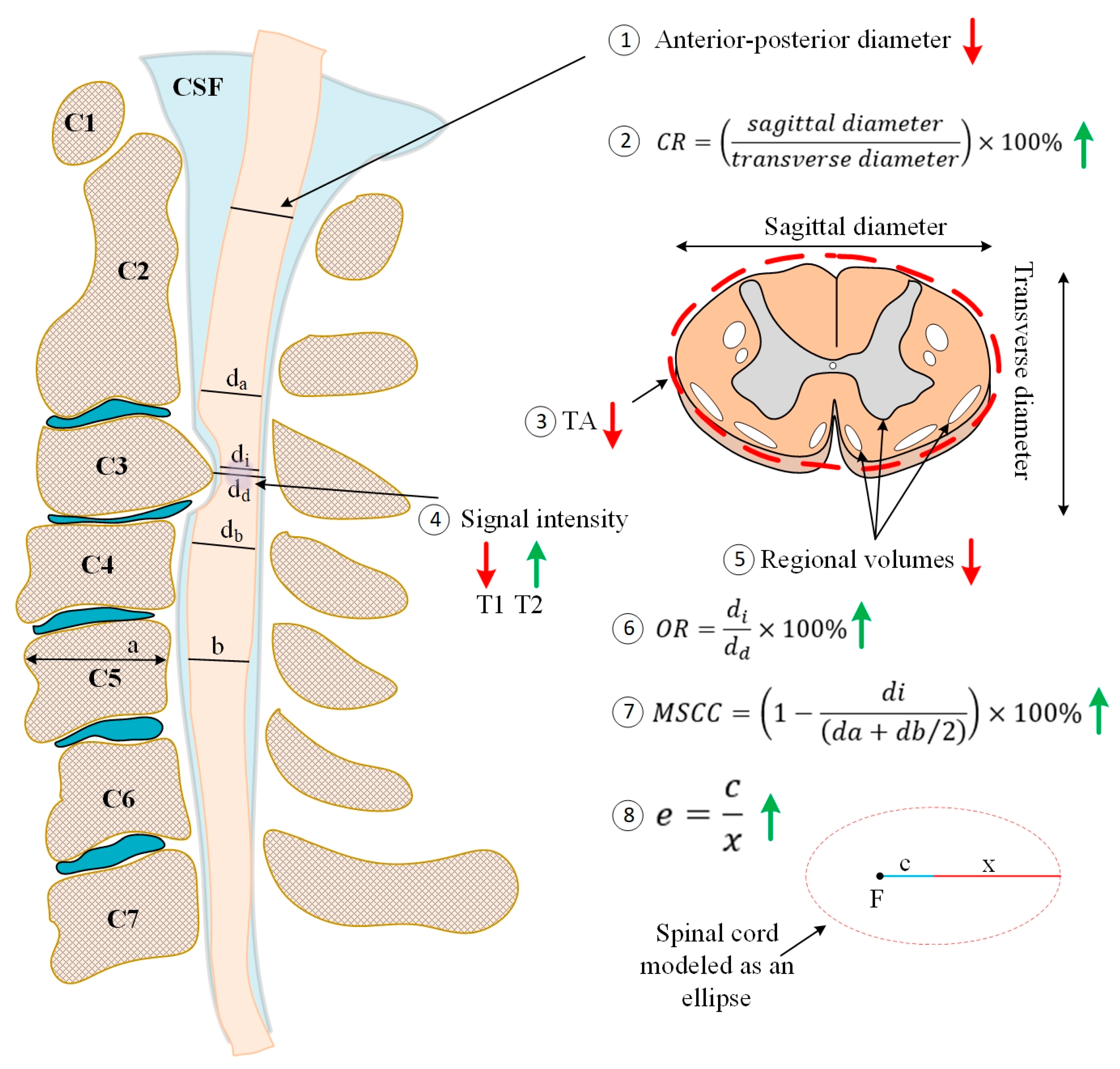
2. The Heterogeneity of CSM Poses a Diagnostic and Treatment Challenge
3. Macrostructural Tissue Injury
3.1. Compression of the Cervical Spinal Cord

3.2. Atrophy of the Spinal Cord and Brain
4. Microstructural Tissue Injury
4.1. Exploiting Water Movement to Assess White Matter Tissue Injury

4.2. Reduced Myelin Content Is Associated with Tissue Injury

4.3. Exploiting Metabolite Concentrations to Study Tissue Injury
5. Using Functional Changes as a Proxy to Study Tissue Injury

6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fehlings, M.G.; Tetreault, L.; Nater, A.; Choma, T.; Harrop, J.; Mroz, T.; Santaguida, C.; Smith, J.S. The Aging of the Global Population: The Changing Epidemiology of Disease and Spinal Disorders. Neurosurgery 2015, 77, S1–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, T.; Lafage, R.; Lafage, V.; Protopsaltis, T.; Challier, V.; Shaffrey, C.; Kim, H.J.; Arnold, P.; Chapman, J.; Schwab, F.; et al. Comparing Quality of Life in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy with Other Chronic Debilitating Diseases Using the Short Form Survey 36-Health Survey. World Neurosurg. 2017, 106, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogino, H.; Tada, K.; Okada, K.; Yonenobu, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Ono, K.; Namiki, H. Canal diameter, anteroposterior compression ratio, and spondylotic myelopathy of the cervical spine. Spine 1983, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; MacMillian, E.L.; Jutzeler, C.R.; Ljungberg, E.; MacKay, A.L.; Kolind, S.H.; Madler, B.; Li, D.K.B.; Dvorak, M.F.; Curt, A.; et al. Assessing structure and function of myelin in cervical spondylotic myelopathy: Evidence of demyelination. Neurology 2017, 89, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Z.A.; Weber, K.A., 2nd; Paliwal, M.; Hopkins, B.S.; Barry, A.J.; Cantrell, D.; Ganju, A.; Koski, T.R.; Parrish, T.B.; Dhaher, Y. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Atlas-Based Volumetric Mapping of the Cervical Cord Gray Matter in Cervical Canal Stenosis. World Neurosurg. 2020, 134, e497–e504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sanvito, F.; Oughourlian, T.C.; Islam, S.; Salamon, N.; Holly, L.T.; Ellingson, B.M. Structural Relationship between Cerebral Gray and White Matter Alterations in Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy. Tomography 2023, 9, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ellingson, B.M.; Oughourlian, T.C.; Salamon, N.; Holly, L.T. Evolution of brain functional plasticity associated with increasing symptom severity in degenerative cervical myelopathy. eBioMedicine 2022, 84, 104255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehlings, M.G.; Wilson, J.R.; Yoon, S.T.; Rhee, J.M.; Shamji, M.F.; Lawrence, B.D. Symptomatic progression of cervical myelopathy and the role of nonsurgical management: A consensus statement. Spine 2013, 38, S19–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhiwala, J.H.; Ahuja, C.S.; Akbar, M.A.; Witiw, C.D.; Nassiri, F.; Furlan, J.C.; Curt, A.; Wilson, J.R.; Fehlings, M.G. Degenerative cervical myelopathy—Update and future directions. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laule, C.; Moore, G.R.W. Myelin water imaging to detect demyelination and remyelination and its validation in pathology. Brain Pathol. 2018, 28, 750–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, F.J.; Blamire, A.M.; Manners, D.N.; Styles, P.; Rajagopalan, B. Quantitative proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the cervical spinal cord. Magn. Reson. Med. 2004, 51, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horak, T.; Horakova, M.; Svatkova, A.; Kadanka, Z.; Kudlicka, P.; Valosek, J.; Rohan, T.; Kerkovsky, M.; Vlckova, E.; Kadanka, Z.; et al. In vivo Molecular Signatures of Cervical Spinal Cord Pathology in Degenerative Compression. J. Neurotrauma 2021, 38, 2999–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellingson, B.M.; Salamon, N.; Grinstead, J.W.; Holly, L.T. Diffusion tensor imaging predicts functional impairment in mild-to-moderate cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine J. 2014, 14, 2589–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.R.; De Leener, B.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Cadotte, D.W.; Kalsi-Ryan, S.; Lange, S.F.; Tetreault, L.; Nouri, A.; Crawley, A.; Mikulis, D.J.; et al. Clinically Feasible Microstructural MRI to Quantify Cervical Spinal Cord Tissue Injury Using DTI, MT, and T2*-Weighted Imaging: Assessment of Normative Data and Reliability. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Q.; Yu, C.; Li, F.; Liang, M.; Zong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xiong, W.; Su, Z.; et al. Functional Connectivity Changes of the Visual Cortex in the Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Patients: A Resting-State fMRI Study. Spine 2020, 45, E272–E279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroman, P.W.; Tomanek, B.; Krause, V.; Frankenstein, U.N.; Malisza, K.L. Mapping of neuronal function in the healthy and injured human spinal cord with spinal fMRI. Neuroimage 2002, 17, 1854–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zileli, M.; Maheshwari, S.; Kale, S.S.; Garg, K.; Menon, S.K.; Parthiban, J. Outcome Measures and Variables Affecting Prognosis of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: WFNS Spine Committee Recommendations. Neurospine 2019, 16, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurick, S. The natural history and the results of surgical treatment of the spinal cord disorder associated with cervical spondylosis. Brain 1972, 95, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetreault, L.; Kopjar, B.; Nouri, A.; Arnold, P.; Barbagallo, G.; Bartels, R.; Qiang, Z.; Singh, A.; Zileli, M.; Vaccaro, A. The modified Japanese Orthopaedic Association scale: Establishing criteria for mild, moderate and severe impairment in patients with degenerative cervical myelopathy. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 26, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, A.; Arun, R.; Davis, A.M.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Mikulis, D.J.; Sooyong, C.; Rabin, D.; Craciunas, S.; Smith, S.R.; Hansen, M.A.; et al. Reliability of quantitative magnetic resonance imaging methods in the assessment of spinal canal stenosis and cord compression in cervical myelopathy. Spine 2013, 38, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houten, J.K.; Cooper, P.R. Laminectomy and posterior cervical plating for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: Effects on cervical alignment, spinal cord compression, and neurological outcome. Neurosurgery 2003, 52, 1081–1087, discussion 1087–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Crockard, H.A.; Platts, A.; Stevens, J. Clinical and radiological correlates of severity and surgery-related outcome in cervical spondylosis. J. Neurosurg. 2001, 94, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yone, K.; Sakou, T.; Yanase, M.; Ijiri, K. Preoperative and postoperative magnetic resonance image evaluations of the spinal cord in cervical myelopathy. Spine 1992, 17, S388–S392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, E.; Ohmura, M.; Yonenobu, K. Intramedullary changes of the spinal cord in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine 1995, 20, 2226–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilton, B.; Tempest-Mitchell, J.; Davies, B.M.; Francis, J.; Mannion, R.J.; Trivedi, R.; Timofeev, I.; Crawford, J.R.; Hay, D.; Laing, R.J. Cord compression defined by MRI is the driving factor behind the decision to operate in degenerative cervical myelopathy despite poor correlation with disease severity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, B.S.; Weber, K.A., 2nd; Cloney, M.B.; Paliwal, M.; Parrish, T.B.; Smith, Z.A. Tract-Specific Volume Loss on 3T MRI in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Spine 2018, 43, E1204–E1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehlings, M.G.; Rao, S.C.; Tator, C.H.; Skaf, G.; Arnold, P.; Benzel, E.; Dickman, C.; Cuddy, B.; Green, B.; Hitchon, P.; et al. The optimal radiologic method for assessing spinal canal compromise and cord compression in patients with cervical spinal cord injury. Part II: Results of a multicenter study. Spine 1999, 24, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, Y.; Seichi, A.; Takeshita, K.; Chikuda, H.; Ono, T.; Baba, S.; Morii, J.; Oka, H.; Kawaguchi, H.; Nakamura, K.; et al. Natural course and prognostic factors in patients with mild cervical spondylotic myelopathy with increased signal intensity on T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Spine 2012, 37, 1909–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, F.; Yukawa, Y.; Suda, K.; Yamagata, M.; Ueta, T. Normal morphology, age-related changes and abnormal findings of the cervical spine. Part II: Magnetic resonance imaging of over 1200 asymptomatic subjects. Eur. Spine J. 2012, 21, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, K.; Yoshimura, N.; Hashizume, H.; Muraki, S.; Ishimoto, Y.; Yamada, H.; Takiguchi, N.; Nakagawa, Y.; Minamide, A.; Oka, H. The prevalence of cervical myelopathy among subjects with narrow cervical spinal canal in a population-based magnetic resonance imaging study: The Wakayama Spine Study. Spine J. 2014, 14, 2811–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y.; Ikata, T.; Katoh, S.; Yamada, H. Morphologic analysis of the cervical spinal cord, dural tube, and spinal canal by magnetic resonance imaging in normal adults and patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine 1994, 19, 2331–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.-D.; Lu, Q.; Sun, J.-J.; Yuan, Q.; Luo, Z.-P.; Yang, H.-L. Effect and prognostic factors of laminoplasty for cervical myelopathy with an occupying ratio greater than 50%. Spine 2016, 41, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, Y.; Ikata, T.; Yamada, H.; Sakamoto, R.; Katoh, S. Magnetic resonance imaging study on the results of surgery for cervical compression myelopathy. Spine 1993, 18, 2024–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvin, B.; Kalsi-Ryan, S.; Karpova, A.; Mercier, D.; Furlan, J.C.; Massicotte, E.M.; Fehlings, M.G. Postoperative magnetic resonance imaging can predict neurological recovery after surgery for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: A prospective study with blinded assessments. Neurosurgery 2011, 69, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, A.; Tetreault, L.; Zamorano, J.J.; Dalzell, K.; Davis, A.M.; Mikulis, D.; Yee, A.; Fehlings, M.G. Role of magnetic resonance imaging in predicting surgical outcome in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine 2015, 40, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabher, P.; Mohammadi, S.; Trachsler, A.; Friedl, S.; David, G.; Sutter, R.; Weiskopf, N.; Thompson, A.J.; Curt, A.; Freund, P. Voxel-based analysis of grey and white matter degeneration in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jutzeler, C.R.; Ulrich, A.; Huber, B.; Rosner, J.; Kramer, J.L.K.; Curt, A. Improved Diagnosis of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy with Contact Heat Evoked Potentials. J. Neurotrauma 2017, 34, 2045–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Lu, S.B.; Sun, X.Y.; Kong, C.; Guo, M.C.; Sun, S.Y.; Ding, J.Z.; Yang, Y.M. Clinical and magnetic resonance imaging predictors of the surgical outcomes of patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 174, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, A.; Craciunas, S.; Chua, S.Y.; Rabin, D.; Smith, S.; Fehlings, M.G. Accuracy and reliability of MRI quantitative measurements to assess spinal cord compression in cervical spondylotic myelopathy: A prospective study. Evid. Based Spine Care J. 2010, 1, 56–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchiku, T.; Taguchi, T.; Kaneko, K.; Fuchigami, Y.; Yonemura, H.; Kawai, S. A correlation between magnetic resonance imaging and electrophysiological findings in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine 2001, 26, e294–e299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.-S.; Lee, J.-K.; Kim, B.-K. Prognostic factors that affect the surgical outcome of the laminoplasty in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2010, 2, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Yamashita, Y.; Sakamoto, Y.; Kojima, R. Chronic cervical cord compression: Clinical significance of increased signal intensity on MR images. Radiology 1989, 173, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouri, A.; Martin, A.R.; Kato, S.; Kermani, H.R.; Riehm, L.; Fehlings, M.G. The Relationship Between MRI Signal Intensity Changes, Clinical Presentation and Surgical Outcome in Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy: Analysis of a Global Cohort. Spine J. 2017, 17, S133–S134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, A.; Martin, A.R.; Mikulis, D.; Fehlings, M.G. Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of degenerative cervical myelopathy: A review of structural changes and measurement techniques. Neurosurg. Focus 2016, 40, E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloney, M.B.; Smith, Z.A.; Weber, K.A., 2nd; Parrish, T.B. Quantitative Magnetization Transfer MRI Measurements of the Anterior Spinal Cord Region are Associated with Clinical Outcomes in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Spine 2018, 43, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jütten, K.; Mainz, V.; Schubert, G.A.; Gohmann, R.F.; Schmidt, T.; Ridwan, H.; Clusmann, H.; Mueller, C.A.; Blume, C. Cortical volume reductions as a sign of secondary cerebral and cerebellar impairment in patients with degenerative cervical myelopathy. NeuroImage Clin. 2021, 30, 102624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oughourlian, T.C.; Wang, C.; Salamon, N.; Holly, L.T.; Ellingson, B.M. Sex-Dependent Cortical Volume Changes in Patients with Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabeu-Sanz, A.; Molla-Torro, J.V.; Lopez-Celada, S.; Moreno Lopez, P.; Fernandez-Jover, E. MRI evidence of brain atrophy, white matter damage, and functional adaptive changes in patients with cervical spondylosis and prolonged spinal cord compression. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, B.; Li, Q.; Qi, F.; Guo, Q. Sensorimotor cortex atrophy in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Neuroreport 2018, 29, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basser, P.J.; Mattiello, J.; LeBihan, D. MR diffusion tensor spectroscopy and imaging. Biophys. J. 1994, 66, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.L.; Li, X.; Chan, T.Y.; Mak, K.C.; Luk, K.D.; Hu, Y. Quantitative assessment of column-specific degeneration in cervical spondylotic myelopathy based on diffusion tensor tractography. Eur. Spine J. 2015, 24, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiangshui, M.; Xiangjun, C.; Xiaoming, Z.; Qingshi, Z.; Yi, C.; Chuanqiang, Q.; Xiangxing, M.; Chuanfu, L.; Jinwen, H. 3 T magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging and fibre tracking in cervical myelopathy. Clin. Radiol. 2010, 65, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, S.; Yerramshetty, J.S.; Chittode, V.S.; Kanna, R.M.; Balamurali, G.; Shetty, A.P. The assessment of neuronal status in normal and cervical spondylotic myelopathy using diffusion tensor imaging. Spine 2014, 39, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Loy, D.N.; Liang, H.F.; Trinkaus, K.; Schmidt, R.E.; Song, S.K. Noninvasive diffusion tensor imaging of evolving white matter pathology in a mouse model of acute spinal cord injury. Magn. Reason. Med. 2007, 58, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.K.; Sun, S.W.; Ju, W.K.; Lin, S.J.; Cross, A.H.; Neufeld, A.H. Diffusion tensor imaging detects and differentiates axon and myelin degeneration in mouse optic nerve after retinal ischemia. Neuroimage 2003, 20, 1714–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, P.G.; Feydy, A.; Sanchez, K.; Rannou, F.; Maier, M.A. Measures of spinal canal stenosis and relationship to spinal cord structure in patients with cervical spondylosis. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 39, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, C.; Allen, P.S. Determinants of anisotropic water diffusion in nerves. Magn. Reason. Med. 1994, 31, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, A.; Ries, M.; Moonen, C.T.; Vital, J.M.; Dehais, J.; Arne, P.; Caille, J.M.; Dousset, V. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with apparent diffusion coefficient and apparent diffusion tensor maps in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Radiology 2003, 229, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkovský, M.; Bednarík, J.; Dušek, L.; Šprláková-Puková, A.; Urbánek, I.; Mechl, M.; Válek, V.; Kadanka, Z. Magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging in patients with cervical spondylotic spinal cord compression: Correlations between clinical and electrophysiological findings. Spine 2012, 37, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamata, H.; Jolesz, F.A.; Maier, S.E. Apparent diffusion coefficient and fractional anisotropy in spinal cord: Age and cervical spondylosis-related changes. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2005, 22, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budzik, J.F.; Balbi, V.; Le Thuc, V.; Duhamel, A.; Assaker, R.; Cotten, A. Diffusion tensor imaging and fibre tracking in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 21, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T.; Chen, W.J.; Yang, B.; Zhao, H.P.; Huang, J.W.; Cai, M.J.; Dong, T.F.; Li, T.S. Diffusion tensor imaging in the cervical spinal cord. Eur. Spine. J. 2011, 20, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uda, T.; Takami, T.; Tsuyuguchi, N.; Sakamoto, S.; Yamagata, T.; Ikeda, H.; Nagata, T.; Ohata, K. Assessment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy using diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging parameter at 3.0 tesla. Spine 2013, 38, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banaszek, A.; Bladowska, J.; Szewczyk, P.; Podgorski, P.; Sasiadek, M. Usefulness of diffusion tensor MR imaging in the assessment of intramedullary changes of the cervical spinal cord in different stages of degenerative spine disease. Eur. Spine J. 2014, 23, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Wu, Y.; Song, P.; Qian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Yin, M.; Zhang, R.; Tao, H.; Ge, P.; et al. A preliminary study of 3.0-T magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Eur. Spine. J. 2018, 27, 1839–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabher, P.; Mohammadi, S.; David, G.; Freund, P. Neurodegeneration in the Spinal Ventral Horn Prior to Motor Impairment in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. J. Neurotrauma 2017, 34, 2329–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renoux, J.; Facon, D.; Fillard, P.; Huynh, I.; Lasjaunias, P.; Ducreux, D. MR diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tracking in inflammatory diseases of the spinal cord. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 1947–1951. [Google Scholar]
- Vedantam, A.; Jirjis, M.B.; Schmit, B.D.; Wang, M.C.; Ulmer, J.L.; Kurpad, S.N. Diffusion tensor imaging of the spinal cord: Insights from animal and human studies. Neurosurgery 2014, 74, 1–8, discussion 8; quiz 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inano, S.; Takao, H.; Hayashi, N.; Abe, O.; Ohtomo, K. Effects of age and gender on white matter integrity. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 2103–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, M.; Fukunaga, I.; Masutani, Y.; Nakanishi, A.; Shimoji, K.; Kamagata, K.; Asahi, K.; Hamasaki, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Aoki, S. New diffusion metrics for spondylotic myelopathy at an early clinical stage. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 1797–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.W.; Jensen, J.H.; Hu, C.C.; Tabesh, A.; Falangola, M.F.; Helpern, J.A. Effect of cerebral spinal fluid suppression for diffusional kurtosis imaging. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2013, 37, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.H.; Helpern, J.A.; Ramani, A.; Lu, H.; Kaczynski, K. Diffusional kurtosis imaging: The quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reason. Med. 2005, 53, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, J.A.; Zhang, J.; Jones, M.V.; Deboy, C.A.; Hoffman, P.N.; Landman, B.A.; Smith, S.A.; Reich, D.S.; Calabresi, P.A.; van Zijl, P.C. q-space and conventional diffusion imaging of axon and myelin damage in the rat spinal cord after axotomy. Magn. Reason. Med. 2010, 63, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masutani, Y.; Aoki, S. Fast and robust estimation of diffusional kurtosis imaging (DKI) parameters by general closed-form expressions and their extensions. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2014, 13, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, E.S.; Cheung, M.M.; Qi, L.; Wu, E.X. Towards better MR characterization of neural tissues using directional diffusion kurtosis analysis. Neuroimage 2008, 42, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helpern, J.A.; Adisetiyo, V.; Falangola, M.F.; Hu, C.; Di Martino, A.; Williams, K.; Castellanos, F.X.; Jensen, J.H. Preliminary evidence of altered gray and white matter microstructural development in the frontal lobe of adolescents with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A diffusional kurtosis imaging study. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2011, 33, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, J.A.; Smith, S.A.; Gordon-Lipkin, E.M.; Reich, D.S.; Calabresi, P.A.; van Zijl, P.C. High b-value q-space diffusion-weighted MRI of the human cervical spinal cord in vivo: Feasibility and application to multiple sclerosis. Magn. Reason. Med. 2008, 59, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, Y.; Pasternak, O. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)-based white matter mapping in brain research: A review. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2008, 34, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurnher, M.M.; Law, M. Diffusion-weighted imaging, diffusion-tensor imaging, and fiber tractography of the spinal cord. Magn. Reason. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2009, 17, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasekera, D.; Zhang, J.K.; Blum, J.; Jakes, R.; Sun, P.; Javeed, S.; Greenberg, J.K.; Song, S.K.; Ray, W.Z. Analysis of combined clinical and diffusion basis spectrum imaging metrics to predict the outcome of chronic cervical spondylotic myelopathy following cervical decompression surgery. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2022, 1, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, M.; Hagiwara, A.; Fukunaga, I.; Ueda, R.; Kamiya, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Liu, W.; Murata, K.; Takamura, T.; Hamasaki, N.; et al. Application of Quantitative Microstructural MR Imaging with Atlas-based Analysis for the Spinal Cord in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.K.; Sun, P.; Han, R.H.; Griffin, K.J.; Wagner, J.; Yarbrough, C.K.; Wright, N.M.; Dorward, I.G.; Riew, K.D.; Kelly, M.P.; et al. Fractional anisotropy to quantify cervical spondylotic myelopathy severity. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2018, 62, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.K.; Jayasekera, D.; Song, C.; Greenberg, J.K.; Javeed, S.; Dibble, C.F.; Blum, J.; Sun, P.; Song, S.-K.; Ray, W.Z. Diffusion Basis Spectrum Imaging Provides Insights into Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Pathology. Neurosurgery 2023, 92, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Han, X.; Jiang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, X.; Chen, H.; Guo, H.; et al. A Follow-up Study of Postoperative DCM Patients Using Diffusion MRI with DTI and NODDI. Spine 2018, 43, E898–E904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okita, G.; Ohba, T.; Takamura, T.; Ebata, S.; Ueda, R.; Onishi, H.; Haro, H.; Hori, M. Application of neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging or diffusion tensor imaging to quantify the severity of cervical spondylotic myelopathy and to assess postoperative neurologic recovery. Spine J. 2018, 18, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.K.; Dortch, R.D.; Dethrage, L.M.; Smith, S.A. Rapid, high-resolution quantitative magnetization transfer MRI of the human spinal cord. Neuroimage 2014, 95, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkelman, R.M.; Stanisz, G.J.; Graham, S.J. Magnetization transfer in MRI: A review. NMR Biomed. 2001, 14, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmierer, K.; Scaravilli, F.; Altmann, D.R.; Barker, G.J.; Miller, D.H. Magnetization transfer ratio and myelin in postmortem multiple sclerosis brain. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 56, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, N.C.; Barker, G.J.; Losseff, N.A.; Gawne-Cain, M.L.; MacManus, D.G.; Thompson, A.J.; Miller, D.H. Magnetisation transfer ratio measurement in the cervical spinal cord: A preliminary study in multiple sclerosis. Neuroradiology 1997, 39, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.A.; Golay, X.; Fatemi, A.; Mahmood, A.; Raymond, G.V.; Moser, H.W.; van Zijl, P.C.; Stanisz, G.J. Quantitative magnetization transfer characteristics of the human cervical spinal cord in vivo: Application to adrenomyeloneuropathy. Magn. Reason. Med. 2009, 61, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Adad, J.; El Mendili, M.M.; Lehericy, S.; Pradat, P.F.; Blancho, S.; Rossignol, S.; Benali, H. Demyelination and degeneration in the injured human spinal cord detected with diffusion and magnetization transfer MRI. Neuroimage 2011, 55, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, M.; Bozzali, M.; Horsfield, M.A.; Rocca, M.A.; Sormani, M.P.; Iannucci, G.; Colombo, B.; Comi, G. A conventional and magnetization transfer MRI study of the cervical cord in patients with MS. Neurology 2000, 54, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.; Saidha, S.; Chen, M.; Smith, S.A.; Prince, J.; Jones, C.; Diener-West, M.; Van Zijl, P.C.; Reich, D.S.; Calabresi, P.A. Spinal cord quantitative MRI discriminates between disability levels in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2013, 80, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, M.; Weber, K.A., 2nd; Hopkins, B.S.; Cantrell, D.R.; Hoggarth, M.A.; Elliott, J.M.; Dahdaleh, N.S.; Mackey, S.; Parrish, T.D.; Dhaher, Y.; et al. Magnetization Transfer Ratio and Morphometrics of the Spinal Cord Associates with Surgical Recovery in Patients with Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy. World Neurosurg. 2020, 144, e939–e947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, L.I.; Weber, K.A., 2nd; Rosenthal, B.D.; Bhatt, S.A.; Savage, J.W.; Hsu, W.K.; Patel, A.A.; Parrish, T.B. High-resolution magnetization transfer MRI in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 51, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.E.; Kim, W.T.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.W.; Yoo, W.K. Utility of Diffusion and Magnetization Transfer MRI in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Alexander, A.L.; Fleming, J.O.; Duncan, I.D.; Field, A.S. Myelin water fraction in human cervical spinal cord in vivo. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2006, 30, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Adad, J.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C. Quantitative MRI of the Spinal Cord; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Laule, C.; Vavasour, I.M.; Zhao, Y.; Traboulsee, A.L.; Oger, J.; Vavasour, J.D.; Mackay, A.L.; Li, D.K. Two-year study of cervical cord volume and myelin water in primary progressive multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2010, 16, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMillan, E.L.; Mädler, B.; Fichtner, N.; Dvorak, M.F.; Li, D.K.; Curt, A.; MacKay, A.L. Myelin water and T2 relaxation measurements in the healthy cervical spinal cord at 3.0 T: Repeatability and changes with age. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, W.R. MR spectroscopy in neurodegenerative disease. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2007, 9, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S. In vivo proton spectroscopy. Experimental aspects and potential. In In-Vivo Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy III: In-Vivo MR Spectroscopy: Potential and Limitations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.F.T.; Badawy, A.E. Feasibility of 1H-MR Spectroscopy in evaluation of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2013, 44, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiehuis, A.; van der Meer, F.; Mali, W.; Pleizier, M.; Biessels, G.J.; Kappelle, J.; Luijten, P. MR spectroscopy of cerebral white matter in type 2 diabetes; no association with clinical variables and cognitive performance. Neuroradiology 2010, 52, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simone, I.L.; Tortorella, C.; Federico, F.; Liguori, M.; Lucivero, V.; Giannini, P.; Carrara, D.; Bellacosa, A.; Livrea, P. Axonal damage in multiple sclerosis plaques: A combined magnetic resonance imaging and 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2001, 182, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Aziz, K.; Schneider, T.; Solanky, B.S.; Yiannakas, M.C.; Altmann, D.R.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.; Peters, A.L.; Day, B.L.; Thompson, A.J.; Ciccarelli, O. Evidence for early neurodegeneration in the cervical cord of patients with primary progressive multiple sclerosis. Brain 2015, 138, 1568–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Aziz, K.; Solanky, B.S.; Yiannakas, M.C.; Altmann, D.R.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.; Thompson, A.J.; Ciccarelli, O. Age related changes in metabolite concentrations in the normal spinal cord. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marliani, A.F.; Clementi, V.; Albini-Riccioli, L.; Agati, R.; Leonardi, M. Quantitative proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the human cervical spinal cord at 3 Tesla. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 57, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, D.P.; Law, M. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain: Review of metabolites and clinical applications. Clin. Radiol. 2009, 64, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Anson, B.; MacManus, D.G.; Parker, G.J.; Davie, C.A.; Barker, G.J.; Moseley, I.F.; McDonald, W.I.; Miller, D.H. In vivo 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the spinal cord in humans. Neuroradiology 2000, 42, 515–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holly, L.T.; Ellingson, B.M.; Salamon, N. Metabolic imaging using proton magnetic spectroscopy as a predictor of outcome following surgery for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Clin. Spine Surg. 2017, 30, E615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingson, B.M.; Salamon, N.; Hardy, A.J.; Holly, L.T. Prediction of Neurological Impairment in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy using a Combination of Diffusion MRI and Proton MR Spectroscopy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, N.; Ellingson, B.M.; Nagarajan, R.; Gebara, N.; Thomas, A.; Holly, L.T. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of human cervical spondylosis at 3T. Spinal Cord 2013, 51, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, S.; Tank, D.W.; Menon, R.; Ellermann, J.M.; Kim, S.G.; Merkle, H.; Ugurbil, K. Intrinsic signal changes accompanying sensory stimulation: Functional brain mapping with magnetic resonance imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 5951–5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshizawa, T.; Nose, T.; Moore, G.J.; Sillerud, L.O. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of motor activation in the human cervical spinal cord. Neuroimage 1996, 4, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroman, P.W.; Nance, P.W.; Ryner, L.N. BOLD MRI of the human cervical spinal cord at 3 tesla. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 42, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinany, N.; Pirondini, E.; Martuzzi, R.; Mattera, L.; Micera, S.; Van de Ville, D. Functional imaging of rostrocaudal spinal activity during upper limb motor tasks. Neuroimage 2019, 200, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.A., 2nd; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Kahnt, T.; Parrish, T.B. Lateralization of cervical spinal cord activity during an isometric upper extremity motor task with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage 2016, 125, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornelsen, J.; Smith, S.D.; McIver, T.A. A neural correlate of visceral emotional responses: Evidence from fMRI of the thoracic spinal cord. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2015, 10, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosma, R.L.; Stroman, P.W. Spinal cord response to stepwise and block presentation of thermal stimuli: A functional MRI study. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2015, 41, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosta, F.; Valsasina, P.; Caputo, D.; Rocca, M.A.; Filippi, M. Tactile-associated fMRI recruitment of the cervical cord in healthy subjects. Hum. Brain. Mapp. 2009, 30, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qian, W.; Jin, R.; Li, X.; Luk, K.D.; Wu, E.X.; Hu, Y. Amplitude of Low Frequency Fluctuation (ALFF) in the Cervical Spinal Cord with Stenosis: A Resting State fMRI Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Eippert, F.; Beckmann, C.F.; Andersson, J.; Finsterbusch, J.; Buchel, C.; Tracey, I.; Brooks, J.C. Intrinsically organized resting state networks in the human spinal cord. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18067–18072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, R.L.; Smith, S.A.; Dula, A.N.; Gore, J.C. Resting state functional connectivity in the human spinal cord. eLife 2014, 3, e02812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadotte, D.W.; Bosma, R.; Mikulis, D.; Nugaeva, N.; Smith, K.; Pokrupa, R.; Islam, O.; Stroman, P.W.; Fehlings, M.G. Plasticity of the injured human spinal cord: Insights revealed by spinal cord functional MRI. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrabalek, L.; Hok, P.; Hlustik, P.; Cechakova, E.; Wanek, T.; Otruba, P.; Vaverka, M.; Kanovsky, P. Longitudinal brain activation changes related to electrophysiological findings in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy before and after spinal cord decompression: An fMRI study. Acta Neurochir. 2018, 160, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhan, Y.; He, L. The Correlation between Functional Connectivity of the Primary Somatosensory Cortex and Cervical Spinal Cord Microstructural Injury in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 2623179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liang, M.; Zhao, R.; Zhu, J.; Xiong, W.; Su, Z.; Yu, C.; Xue, Y. Visual cortex neural activity alteration in cervical spondylotic myelopathy patients: A resting-state fMRI study. Neuroradiology 2018, 60, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, K.; Goncalves, S.; Bartha, R.; Duggal, N. Motor network recovery in patients with chronic spinal cord compression: A longitudinal study following decompression surgery. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2018, 28, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Su, Q.; Sun, H.; Liang, M.; Xue, Y. Functional MRI evidence for primary motor cortex plasticity contributes to the disease's severity and prognosis of cervical spondylotic myelopathy patients. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 3693–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroman, P.W.; Kornelsen, J.; Bergman, A.; Krause, V.; Ethans, K.; Malisza, K.L.; Tomanek, B. Noninvasive assessment of the injured human spinal cord by means of functional magnetic resonance imaging. Spinal Cord 2004, 42, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornelsen, J.; Stroman, P.W. Detection of the neuronal activity occurring caudal to the site of spinal cord injury that is elicited during lower limb movement tasks. Spinal Cord 2007, 45, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroman, P.W.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.; Bacon, M.; Schwab, J.M.; Bosma, R.; Brooks, J.; Cadotte, D.; Carlstedt, T.; Ciccarelli, O.; Cohen-Adad, J.; et al. The current state-of-the-art of spinal cord imaging: Methods. Neuroimage 2014, 84, 1070–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroman, P.W.; Ryner, L.N. Functional MRI of motor and sensory activation in the human spinal cord. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2001, 19, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winklhofer, S.; Schoth, F.; Stolzmann, P.; Krings, T.; Mull, M.; Wiesmann, M.; Stracke, C. Spinal Cord Motion: Influence of Respiration and Cardiac Cycle. In RöFo-Fortschritte auf dem Gebiet der Röntgenstrahlen und der Bildgebenden Verfahren; Thieme Gruppe: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Figley, C.R.; Stroman, P.W. Investigation of human cervical and upper thoracic spinal cord motion: Implications for imaging spinal cord structure and function. Magn. Reason. Med. 2007, 58, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Z.; Ou-Yang, H.Q.; Liu, J.F.; Jin, D.; Wang, C.J.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, X.G.; Liu, Z.J.; Lang, N.; et al. Utility of Advanced DWI in the Detection of Spinal Cord Microstructural Alterations and Assessment of Neurologic Function in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Patients. J. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2022, 55, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leener, B.; Levy, S.; Dupont, S.M.; Fonov, V.S.; Stikov, N.; Louis Collins, D.; Callot, V.; Cohen-Adad, J. SCT: Spinal Cord Toolbox, an open-source software for processing spinal cord MRI data. Neuroimage 2017, 145, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallotton, K.; David, G.; Hupp, M.; Pfender, N.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Fehlings, M.G.; Samson, R.S.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.; Curt, A.; Freund, P.; et al. Tracking White and Gray Matter Degeneration along the Spinal Cord Axis in Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy. J. Neurotrauma 2021, 38, 2978–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Adad, J.; Alonso-Ortiz, E.; Abramovic, M.; Arneitz, C.; Atcheson, N.; Barlow, L.; Barry, R.L.; Barth, M.; Battiston, M.; Buchel, C.; et al. Generic acquisition protocol for quantitative MRI of the spinal cord. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 4611–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakuzu, A.; Biswas, L.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Stikov, N. Vendor-neutral sequences and fully transparent workflows improve inter-vendor reproducibility of quantitative MRI. Magn. Reason. Med. 2022, 88, 1212–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.M.; Wright, G.A.; Pauly, J.M. Flexible real-time magnetic resonance imaging framework. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–5 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, G.; Gaspar, A.S.; Qian, E.; Ravi, K.S.; Vaughan, J.T., Jr.; Nunes, R.G.; Geethanath, S. A framework for validating open-source pulse sequences. Magn. Reason. Imaging 2022, 87, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Langkammer, C.; Pichler, A.; Pinter, D.; Gattringer, T.; Bachmaier, G.; Ropele, S.; Fuchs, S.; Enzinger, C.; Fazekas, F. Dynamics of brain iron levels in multiple sclerosis: A longitudinal 3T MRI study. Neurology 2015, 84, 2396–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hametner, S.; Wimmer, I.; Haider, L.; Pfeifenbring, S.; Bruck, W.; Lassmann, H. Iron and neurodegeneration in the multiple sclerosis brain. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 74, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halefoglu, A.M.; Yousem, D.M. Susceptibility weighted imaging: Clinical applications and future directions. World J. Radiol. 2018, 10, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, M.E.; Schumacher, A.-M.; Mahler, C.F.; Bewersdorf, J.P.; Lehmitz, J.; Scheiter, A.; Sánchez, P.; Williams, P.R.; Griesbeck, O.; Naumann, R. Calcium influx through plasma-membrane nanoruptures drives axon degeneration in a model of multiple sclerosis. Neuron 2019, 101, 615–624.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaBan, M.M.; Green, M.L. Concurrent (tandem) cervical and lumbar spinal stenosis: A 10-yr review of 54 hospitalized patients. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 83, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, H.; Uchida, K.; Maezawa, Y.; Furusawa, N.; Wada, M.; Imura, S. Three-dimensional computed tomography for evaluation of cervical spinal canal enlargement after en bloc open-door laminoplasty. Spinal Cord 1997, 35, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.R.; Tetreault, L.; Nouri, A.; Curt, A.; Freund, P.; Rahimi-Movaghar, V.; Wilson, J.R.; Fehlings, M.G.; Kwon, B.K.; Harrop, J.S.; et al. Imaging and Electrophysiology for Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy [AO Spine RECODE-DCM Research Priority Number 9]. Global Spine J. 2022, 12, 130S–146S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.Y.; Cui, J.L.; Mak, K.C.; Luk, K.D.; Hu, Y. Diffusion tensor imaging of somatosensory tract in cervical spondylotic myelopathy and its link with electrophysiological evaluation. Spine J. 2014, 14, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarík, J.; Kadanka, Z.; Vohánka, S.; Stejskal, L.; Vlach, O.; Schröder, R. The value of somatosensory-and motor-evoked potentials in predicting and monitoring the effect of therapy in spondylotic cervical myelopathy: Prospective randomized study. Spine 1999, 24, 1593–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quraishi, N.A.; Lewis, S.J.; Kelleher, M.O.; Sarjeant, R.; Rampersaud, Y.R.; Fehlings, M.G. Intraoperative multimodality monitoring in adult spinal deformity: Analysis of a prospective series of one hundred two cases with independent evaluation. Spine 2009, 34, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotra, A.; King, N.K.K.; Catley, M.; Mendoza, N.; McGregor, A.H.; Strutton, P.H. Evaluation of corticospinal excitability in cervical myelopathy, before and after surgery, with transcranial magnetic stimulation: A pilot study. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.J.; Combs, K.; Kay, R.D.; Bryman, J.; Tye, E.Y.; Rolfe, K. Combined Motor and Sensory Intraoperative Neuromonitoring for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Surgery Causes Confusion: A Level-1 Diagnostic Study. Spine 2021, 46, E1185–E1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, A.F.; Haynes, G.; Mohammadi, E.; Muhammad, F.; Hameed, S.; Smith, Z.A. Utility of MRI in Quantifying Tissue Injury in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3337. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093337
Khan AF, Haynes G, Mohammadi E, Muhammad F, Hameed S, Smith ZA. Utility of MRI in Quantifying Tissue Injury in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(9):3337. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093337
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Ali Fahim, Grace Haynes, Esmaeil Mohammadi, Fauziyya Muhammad, Sanaa Hameed, and Zachary A. Smith. 2023. "Utility of MRI in Quantifying Tissue Injury in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 9: 3337. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093337
APA StyleKhan, A. F., Haynes, G., Mohammadi, E., Muhammad, F., Hameed, S., & Smith, Z. A. (2023). Utility of MRI in Quantifying Tissue Injury in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(9), 3337. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12093337





