The Symptomatic Calcification and Ossification of the Ligamentum Flavum in the Spine: Our Experience and Review of the Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Clinical Features: Ex, Age, Prevalence, Location, Associated Diseases, Neurological Symptoms and Signs, and Neuroradiological Examination (Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4)
| CLF | OLF | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex: Male/Female | 4/11 | 15/5 |
| Age: years old (mean ± 1SD) | 71~91 (79.7 ± 5.2) | 34.4~82.7 (60.1 ± 15.2) |
| 30~39 | 0 | 2 |
| 40~49 | 0 | 5 |
| 50~59 | 0 | 2 |
| 60~69 | 0 | 2 |
| 70~79 | 8 | 7 |
| 80~89 | 6 | 2 |
| 90~99 | 1 | 0 |
| Prevalence/spondylotic change | ||
| Followed by surgery (%) | 15/1800 (0.8) | 20/1800 (1.1) |
| Location | ||
| Cervical spine | 12 | 0 |
| Cervico-thoracic spine | 3 | 5 |
| Thoracic spine | 0 | 12 |
| Upper | 0 | 4 |
| Lower | 0 | 8 |
| Thoraco-lumbar spine | 0 | 3 |
| Lumbar spine | 0 | 0 |
| Associatated disease | ||
| HTN | 15 | 18 |
| Dyslipidemia | 14 | 17 |
| DM | 12 | 15 |
| Obesity | 12 | 14 |
| Hypothyroidism | 7 | 3 |
| COPD | 4 | 2 |
| Uric acidemia | 2 | 2 |
| CKD | 2 | 1 |
| CHF | 2 | 1 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 2 | 1 |
| CLF | OLF | |
|---|---|---|
| Neurological symptoms | ||
| Gradually progresive gait disturbance | 15 | 20 |
| Motor weakness of the expremities | 15 | 20 |
| Impairment of fine movement of fingers | 15 | 5 |
| Focal numbness and/or dysthesia at the extremities | 15 | 15 |
| Radicular pain at the lesion levels | 0 | 7 |
| Neurological signs | ||
| Transverse myelopathy at the cord level | 10 | 6 |
| Tetraparesis | 7 | 3 |
| Paraparesis | 3 | 3 |
| Sensory disturbance | 10 | 6 |
| Brown-Sequard type myelopathy at the cord level | 5 | 3 |
| Conus medullaris syndrome | 0 | 7 |
| Roots signs at lumbar levels | 0 | 4 |
| JOA score (average ± SD) (Pre-Op.) | ||
| Cervical, cervico-thoracic spine (full: 17 points) | 5~10 (7.6 ± 2.1) | 4~7 (3.3 ± 2.2) |
| Thoracic, thoraco-lumbar spine (full: 11 points) | N.A. | 3~5 (3.8 ± 1.3) |
| Lumbar spine (full: 9 points) | N.A. | 3~5 (3.3 ± 1.0) |
| CLF | OLF | |
|---|---|---|
| Radiological associated condition | ||
| Spndylotic change | 15 | 17 |
| DNSC | 5 | 7 |
| Disc hernia | 4 | 7 |
| OPLL | 3 | 4 |
| DISH | 0 | 4 |
| ASH | 0 | 3 |
| 2D-CT scan images | egg shape high density | semilunar & laminar high density |
| salt and pepper like high density | involed inter vertebaral foramen | |
| diffuse and speck like high density | large round high density | |
| MR images | various size | semilunar & laminar low intensity |
| round low intensity mass | involed inter vertebaral foramen | |
| large round low intensity | ||
| and its attached to the dura matter | ||
| high intensity spots in low intensity |
| CLF | OLF | |
|---|---|---|
| Surgery | ||
| Laminectomy | 2 | 12 |
| Laminoplasty | 8 | 5 |
| Laminectomy with PLF | 5 | 3 |
| Outcome | ||
| Improvement of neurological symptoms (improvement rate (%)) | ||
| Gradually progresive gait disturbance | 15/15 (100) | 17/20 (85) |
| Motor weakness of the expremities | 15/15 (100) | 17/20 (85) |
| Impairment of fine movement of fingers | 13/15 (87) | 4/5 (80) |
| Focal numbness and/or dysthesia at the extremities | 11/15 (73) | 8/15 (53) |
| Radicular pain at the lesioin levels | 0 | 6/7 (86) |
| Improvement of neurological signs (improvement rate (%)) | ||
| Transverse myelopathy at the cord level | 10/10 (100) | 15/15 (100) |
| Tetra-paresis | 7/7 (100) | 3/3 (100) |
| Para-paresis | 3/3 (100) | 3/3 (100) |
| Sensory disturbance | 7/10(70) | 4/6 (67) |
| Brown sequred type myelopathy at the cord level | 11/15 (73) | 5/6 (83) |
| Conus medullaris syndrome | 0 | 7/11 (64) |
| Roots signs | 0 | 8/10 (80) |
| Post-Op. JOA score (average ± SD) | ||
| Recovery rate R.R. (%) (average ± SD) | ||
| Cervical, cervico-thjoracic spine (full: 17 points) | 14~17 (15.8 ± 1.5) | 13~17 (15.4 ± 2.5) |
| R.R. (%) (average ± SD) | 67.7–85.7 (72.0 ± 5.4) | 66.7–87.5 (71.3 ± 11.5) |
| Thoracic, thoraco-lumbar spine (full: 11 points) | N.A. | 8~11 (9.8 ± 2.6) |
| R.R. (%) (average ± SD) | N.A. | 58.7–78.7 (68.3 ± 10.1) |
| Lumbar spine (full: 9 points) | N.A. | 7~9 (8.8 ± 1.4) |
| R.R. (%) (average ± SD) | N.A. | 58.3–79.5 (69.3 ± 10.7) |
2.2.2. Surgical Indication and Procedure (Figure 1 and Figure 2, Table 4)


2.2.3. Histopathological Examination (Table 5)
| CLF | OLF |
|---|---|
| HA and/or CPPD deposition | laminar ossification |
| Island of calcification | hyaline cartilage |
| calcification not closing the dura mater | adjacent chondrocytes |
| the surface of the dura mater: intact | osteoblasts and bone marrow |
| chondrocytes and osteoblasts closing ossification of dura mater | |
| ossification invades into dura mater |
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Features: Sex, Prevalence, Location, and Associated Diseases (Table 1)
3.2. Neurological Symptoms, Signs, and JOA Score (Table 2)
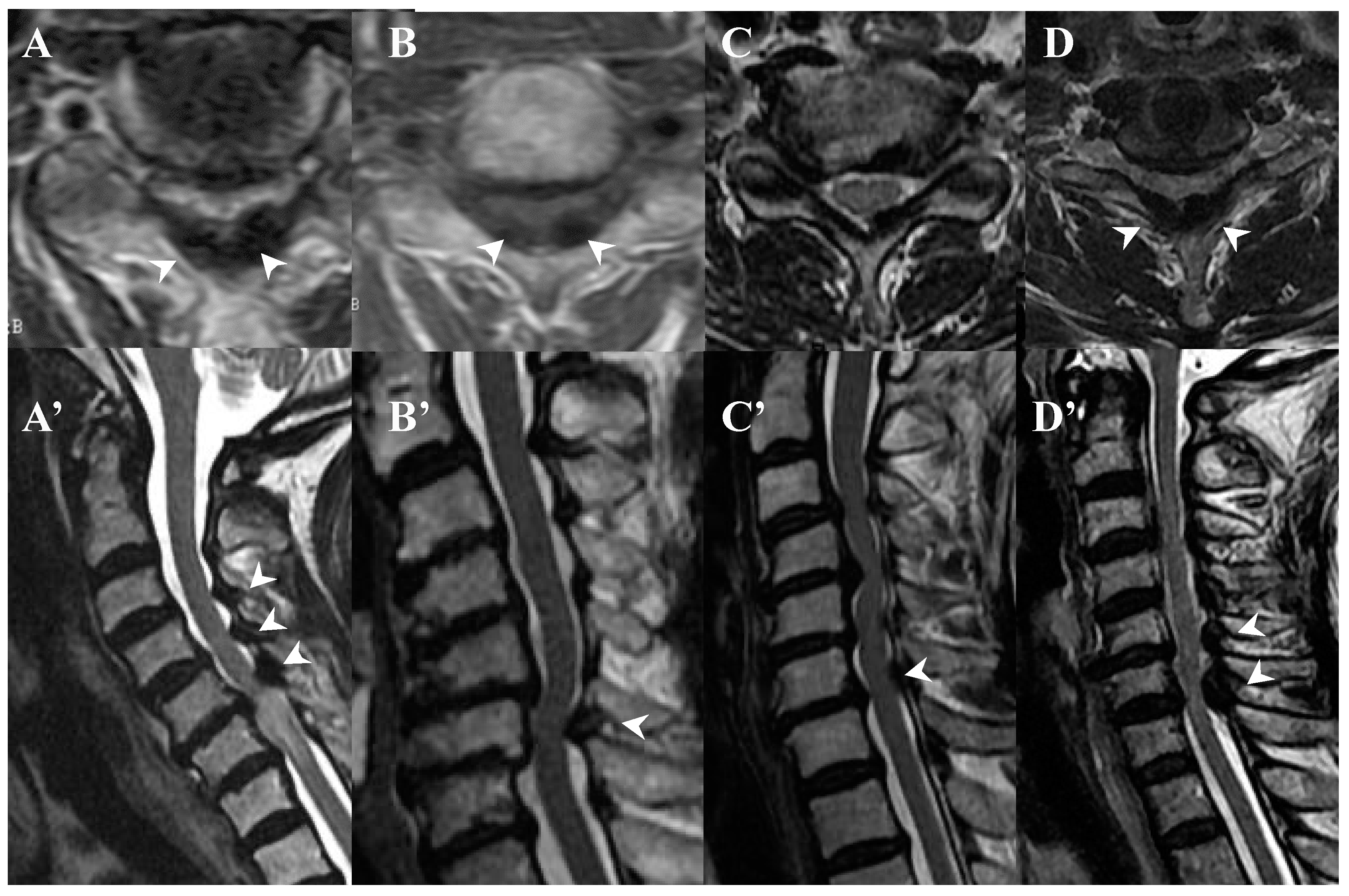
3.3. Neuroradiological Findings (Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6; Table 3)



3.4. Surgeries and Outcomes (Table 4)
3.5. Histopathological Findings (Figure 7 and Figure 8; Table 5)


4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Clinical Features between CLF and OLF (Table 1 and Table 2)
4.2. Comparison of Neuroradiological Findings between CLF and OLF (Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6; Table 3)
4.3. Surgical Treatments and Outcomes in CLF and OLF (Figure 1 and Figure 2; Table 4)
4.4. Pathogenesis of CLF and OLF Based on Histopathological Findings (Figure 7 and Figure 8; Table 5)
4.5. Study Limitations
4.5.1. Prevalence
4.5.2. Chronological Evidence
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawano, N.; Yoshida, S.; Ohwada, T.; Yada, K.; Sasaki, T.; Matsuno, T. Cervical radiculomtyelopathy casused by deposition of calcium pyrophoaphate dihydrate crystals in the ligamentum flava. Case report. J. Neurosurg. 1980, 52, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, M.; Baba, I.; Sumida, T. Myelopathy due to ossification of the ligementum of the cervical spine: A report of two cases. Spine 1981, 6, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, Y.; Akino, N.; Abe, H.; Tsuru, M.; Tashiro, K.; Miyasaka, K.; Kaneda, K.; Isu, T.; Ito, T. Calcification of the ligamentum flavum of the cervical spine. Report of four cases. J. Neurosurg. 1983, 59, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, N.; Matsuno, T.; Miyazawa, S.; Iida, H.; Yada, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Iwasaki, Y. Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease in the cervical ligamentum flavum. J. Neurosurg. 1988, 68, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, H.; Chou, A.M. Myeloradiculopathy secondary to pseudogout in the cervical ligamentum flavum: Case repaort. Neurosurgery 1989, 25, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Okada, K.; Onoda, K.; Horikoshi, S. Ossification of the cervical ligamentum flavum. Surg. Neurol. 1991, 35, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, S.; Hukuda, S. Cervical radiculomyeopathy due to deposition of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal in the ligamentum flavum: Historical and histological evaluation of attendant inflammation. J. Spinal Disord. 1994, 7, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fye, K.H.; Weinstein, P.R.; Donald, F. Compressive cervical myelopathy due to calcium pyrophospahte dihydrate deposition disease: Report of a case and review of the lierature. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Isu, N.; Kobayasshi, S.; Nomura, R.; Kobayashi, S.; Teramoto, A. Cervical ligamentum flavum ossification: Two case reports. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2008, 48, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, Y.; Takahata, M.; Abumi, K.; Ito, M.; Sudo, H.; Minami, A. Cervical myelopathy resulting from combined ossification of the ligamentum flavum and posterior longitudinal ligament: Report of two cases and literature review. Spine 2013, 13, e1–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Miyakoshi, N.; Abe, T.; Abe, E.; Kikuchi, K.; Noguchi, H.; Konno, N.; Shimada, Y. Acute neck pain caused by pseudogout attack of calcified cervical yellow ligament: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2016, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyasaka, K.; Kaneda, K.; Sato, S.; Iwasaki, Y.; Abe, S.; Takei, H.; Tsuru, M.; Tashiro, K.; Abe, H.; Fujioka, Y. Myelopathy due to ossipification or calcification of the ligamentum flavum: Radiologic and histologic evaluations. AJNR 1983, 4, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, C.; Takahama, M.; Shibata, T.; Nakamura, H.; Okada, K.; Morita, H.; Kubo, H. Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition in the cervical ligamenta flava causing myeloradiculopathy. J. Neurosurg. 1984, 60, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthulumar, N.; Karuppaswamy, U.; Sankarasubbu, B. Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease causing thoracic cord compression: Case report. Neurosurgery 2000, 46, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagami, T.; Kawano, N.; Nakano, H. Calcification of the cervical ligamentum flavum. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2000, 40, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthukumar, N.; Karuppaswarmy, U. Tumoral calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease of the ligamentum flavum. Neurosurgery 2003, 53, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnick, D. Calcification and ossification of the posterior spine ligament and tissues. In Diagnosis of Bone and Joint Disorders, 2nd ed.; Resnick, D., Niwayama, G., Eds.; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1988; pp. 1603–1615. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, K.; Oka, S.; Tohge, K.; Ono, K.; Hosoya, T. Thoracic myelopathy caused by ossification of the ligamentum flavum: Clinicopathological study and surgical treatment. Spine 1991, 16, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maigne, J.Y.; Ayral, X.; Guerin-Surville, H. Frequency and size of ossifications in the caudal attachments of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine. Role of rotatory starins in their development. An anatomic study of 121 spines. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 1992, 14, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Takaoka, K.; Yonenobu, K. Ossification of the ligamentum flavum induced by bone morphogenic protein. An experimental study in mice. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1992, 74, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Yonenobu, K.; Ono, K. Elevated plasma fibronection concentration in patients with ossification of the ligamentum flavum. Spine 1993, 18, 2267–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Ishidou, Y.; Yonenobu, K. Expression and localization of bone morphogenic proteins (BMPs) and BMP receptors in ossification of the ligamentum flavum. Bone 1997, 21, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshi, K.; Amizuka, N.; Sakou, T. Fibroblasts of spinal ligaments pathologically differentiate into chondrocytes induced by reconbinant human bone morphogenic protein-2: Morphological examinations for ossification of spinal ligaments. Bone 1997, 21, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimatsu, K.; Kishi, S.; Hashizume, Y. Experimental chronic compression on the spinal cord of the rabbit by ectopic bone formation in the ligamentum flavum with bone morphogenic protein. Spinal Cord 1997, 35, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostenbrugge, R.J.; Herper, M.J.; Jruijk, J.R. Spine cord compression caused by unusual location and extension of ossified ligamenta flava Caucasian male. Spine 1999, 24, 486–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, P.; Behari, S.; Beneji, P.D.; Jain, V.K.; Chbabra, D.K. Thoracic myelopathy secondary to ossified ligamentum flavum. Acta Neurochir. 2001, 143, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamouda, K.B.; Jemei, H.; Haouwet, S.; Khaidi, M. Thoracic myelopathy caused by ossification of the ligamentum flavum: A case report of 18 cases. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 99, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascal-moussellard, H.; Cabre, P.; Smadja, D.; Catonne, Y. Symptomatic ossfication of the ligamentum flavum: A clinical series from the French Antilles. Spine 2005, 30, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.C.; Min, W.K.; Oh, C.W.; Jeon, I.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kyung, H.S.; Oh, S.H. Surgical outcome of thoracic myelopathy secondary to ossification of ligamentum flavum. Jt. Bone Spine 2007, 74, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayama, T.; Uchida, K.; Kobayashi, S. Thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum: Histological and immunohistochemical findings around ossified lesions. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2007, 67, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukmar, N. Dural Ossipification in ossification of the ligamentum flavum. Spine 2009, 24, 2654–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.J.; Luk, K.D.K.; Karppinen, J.; Yang, H.; Cheung, K.M.C. Prevalence, distribution amd morphology of ossification of the ligamentum flavum. Spine 2009, 35, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohindra, S.; Gupta, R.; Chhabrar, S.; Gupta, S.K. Compressive myeliopathy due to ossified yellow ligament among South Asia: Analysis of surgical outcome. Acta Neurochir. 2011, 153, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, V.; Giannachi, L.; Irace, C.; Corona, C. Thoracic spinal stenosis and myelopathy: Report of two rare cases and review of the literature. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2012, 56, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, D.M.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, G.C.; Jang, S.J.; Ju, C.I. Symptomatic myelopathy caused by ocssification of the yellow ligament. Korean J. Spine 2012, 9, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Kasahara, T.; Mimura, T.; Nishizawa, K.; Murakami, Y.; Matsusue, Y.; Imai, S. Prevalence, distrubution and morphology of thoracic ossification of the ligament in Japanese: Results of CT-based cross sectional study. Spine 2013, 38, E1216–E1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahh, D.K.; Lee, S.; Moon, S.H.; Boo, K.H.; Chang, B.K.; Lee, J.I. Ossification of the ligamentum flavum. Asian Spine J. 2014, 8, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, K.; Yayama, T.; Cai, H.X.; Nakajima, H.; Suhita, D.; Querrero, A.R.; Shigeru, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Chen, Y.K.B.; Baba, H. Ossification process involving the human thoracic ligamentum flavum: Role of transcription factors. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, B.J.; Kuh, S.U.; Kim, S.; Kim, K.S.; Cho, Y.E.; Chin, D.K. Prevalence, distribution, and significance of incidental thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum in Korean patients witn back or leg pain: MR-based cross sectional study. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2015, 58, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, S.; Fukukawa, K.; Ono, A.; Asari, T.; Harada, Y.; Wada, K.; Tanaka, T.; Inaba, W.; Mizukami, H.; Motomura, S.; et al. Immunohistochemical localization of mesenchymal stem cells in ossifiedn human spinal ligaments. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 12, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.X.; Yayama, T.; Uchida, K.; Nakajima, H.; Sugita, D.; Querrero, A.R.; Yoshida, A.; Baba, H. Cyclic tensile strain facilitates the ossification of ligamentum flavum through beta-catein signaling poathway: In vitro analysis. Spine 2012, 15, E639–E646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Chen, Z.; Fan, H.; Sun, C.; Zang, Y. MiR-132-3p regulates the osteogenic differemtiation of thoracic ligamentum flavum cells by inhibiting multiple osteogenesis-related genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 20, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigorita, V.J.; Ghekman, B.; Mintz, D. Skeletal and extraskeletal calcifiction and ossification syndrome. In Orthopaedic Pathogy, 3rd ed.; Wlsters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 55–73. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, S.; Chen, Z.; Fan, D.; Sun, C.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, Y.; Li, W.; Qu, X.; Ma, Y.; Yu, H. Genetic differences in osteogenic differentiation potency in the thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum under cyclic mechanical stress. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirabayashi, K. Japanese orthopaedic association (JOA) score in cervical spondylotic myelpathy. Nippon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zassi 1994, 68, 490–503. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Goto, T.; Ohata, K.; Takami, T.; Nishikawa, M.; Tsuyuguchi, N.; Morino, M.; Matsusaka, Y.; Nishio, A.; Inoue, Y.; Hara, M. Hydroxyapatite laminar spacers and titanium miniplates in cervical laminoplasty. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 97 (Suppl. S3), 323–329. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tani, S.; Suetsuna, F.; Mizuno, J.; Uchiokado, H.; Nagashima, H.; Akiyama, M.; Isoshima, H.; Ohashi, H.; Hirano, Y.; Abe, T. New titanium spacer for cervical laminoplasty: Initial clinical experience. Technical note. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2010, 50, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, M.; Oshige, H.; Masamura, S.; Inoue, K.; Kidosaki, Y.; Nakanishi, Y.; Ohata, Y.; Nagahama, A.; Uda, H.; Ikuno, H. Calcification of the ligamentum in the cervical spine. Our experiences and a review of the literatures. Spinal Surg. 2018, 32, 46–55. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, M.; Oshige, H.; Masamura, S.; Nakanishi, Y.; Ohata, Y.; Nagahama, A.; Uda, H.; Ikuno, H. One staged posterior decompression and fixation for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spinal Surg. 2015, 29, 315–322. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Feng, S. Surgical strategies for ossified ligamnentum flavum associated with dural ossification in thoracic spinal stenosis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 2102–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, M.; Inoue, K.; Goto, H.; Kidosaki, Y.; Oshige, H.; Nakanishi, Y.; Ohata, Y.; Nagahama, A.; Uda, H.; Ikuno, H. Thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum. Neuroradiologic and pathologic findings based on our experience and a literature review. Spinal Surg. 2018, 32, 167–174. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quo, Q.; Ni, B.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, J. Simultaneous ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and ossification of the ligamentum flavum causing upper thoracic myelopathy in DISH: Case report and literature review. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wei, F.; Long, H.; Han, G.; Sribastav, S.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, R.; Liang, C. Surgical outcome of thoracic myelopathy caused by ossification of ligamentum flavum. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 45, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, K.; Nakashima, H.; Machino, M.; Ito, S.; Segi, N.; Tomita, H.; Koshimizu, H.; Imagame, S. Postoperative progression of ligamentum flavum ossification after posterior instrumented surgery for thoracic posterior longitudinal ligament ossification: Longpterm outcomes a minimum 10-year follow up. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2021, 24, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Shindo, S.; Yoshii, T.; Ushio, S.; Kusano, K.; Iyake, N.; Arai, Y.; Otani, K.; Okawa, A.; Nakai, O. Surgical outocomes of the thoracic ossification of ligamentum flavum: A retrospective analysis of 61 cases. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, T.; Sun, C.; Chen, G.; Li, W.; Chen, Z. Clinical progression of ossification of the ligamentum flavum in thoracic spine: A 10- to 11-year follow-up study. Eur. Spine 2023, 32, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, H.; Wang, D.; Zhou, C.; Zhu, K.; Tu, C.; Kong, M.; Zhao, C.; Ma, X. Predictive risk factors of poor preliminary postoperative outcome for thoracic ossificatio of the ligamentum flavum. Orthop. Surg. 2021, 13, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.H.; Lin, H.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Chou, P.H.; Wang, S.T.; Liu, C.L.; Chang, M.C. Multilevels calcium pyrophosphate deposition inb cervical ligamentum flavum: Clinical characteristics and imaging features. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Hanakita, J.; Minami, M. Pathophysiology of calcification and ossificastion of the ligamnetum flavum in the cervical spine. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 29, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, F.; Mai, P.; Peng, Y.; Shu, X.; Nie, R. Mechanism analysis of vascular calcification based on fluid dynamics. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nishikawa, M.; Yoshimura, M.; Naito, K.; Yamagata, T.; Goto, H.; Hara, M.; Ikuno, H.; Goto, T. The Symptomatic Calcification and Ossification of the Ligamentum Flavum in the Spine: Our Experience and Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010105
Nishikawa M, Yoshimura M, Naito K, Yamagata T, Goto H, Hara M, Ikuno H, Goto T. The Symptomatic Calcification and Ossification of the Ligamentum Flavum in the Spine: Our Experience and Review of the Literature. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(1):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010105
Chicago/Turabian StyleNishikawa, Misao, Masaki Yoshimura, Kentaro Naito, Toru Yamagata, Hiroyuki Goto, Mitsuhiro Hara, Hiromichi Ikuno, and Takeo Goto. 2024. "The Symptomatic Calcification and Ossification of the Ligamentum Flavum in the Spine: Our Experience and Review of the Literature" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 1: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010105
APA StyleNishikawa, M., Yoshimura, M., Naito, K., Yamagata, T., Goto, H., Hara, M., Ikuno, H., & Goto, T. (2024). The Symptomatic Calcification and Ossification of the Ligamentum Flavum in the Spine: Our Experience and Review of the Literature. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(1), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010105






