Haemodynamic Parameters Underlying the Relationship between Sarcopenia and Blood Pressure Recovery on Standing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
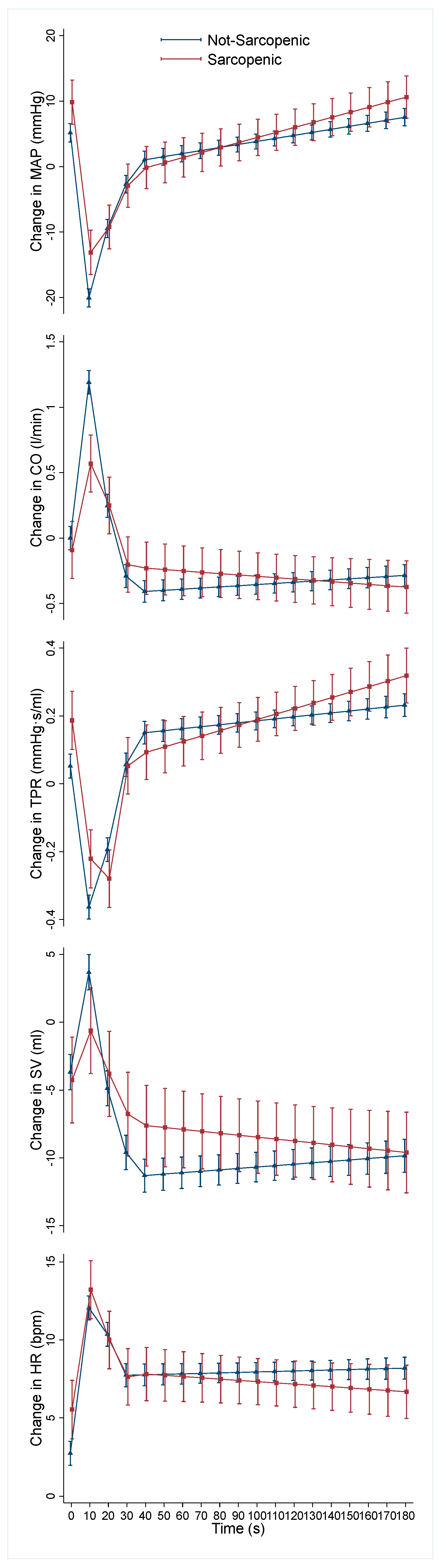
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dall, P.M.; Kerr, A. Frequency of the Sit to Stand Task: An Observational Study of Free-Living Adults. Appl. Ergon. 2010, 41, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomqvist, C.; Stone, H. Cadiovascular Adjustments to Gravitational Stress. In Handbook of Physiology: The Cardiovascular System: Peripheral Circulation and Organ Blood Flow; Shepherd, J., Abboud, F., Geiger, S., Eds.; American Physiological Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1983; Volume 3, pp. 1025–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.J.; Porth, C.M.; Erickson, M. Hemodynamic Response to the Upright Posture. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1994, 34, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, P.A.; Benarroch, E.E. Clinical Autonomic Disorders, 3rd ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-7817-7381-2. [Google Scholar]
- Borst, C.; Van Brederode, J.F.M.; Wieling, W.; Van Montfrans, G.A.; Dunning, A.J. Mechanisms of Initial Blood Pressure Response to Postural Change. Clin. Sci. 1984, 67, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprangers, R.L.; Wesseling, K.H.; Imholz, A.L.; Imholz, B.P.; Wieling, W. Initial Blood Pressure Fall on Stand up and Exercise Explained by Changes in Total Peripheral Resistance. J. Appl. Physiol. 1991, 70, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowell, L.B. Human Cardiovascular Control; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; ISBN 978-0-19-507362-1. [Google Scholar]
- Dani, M.; Dirksen, A.; Taraborrelli, P.; Panagopolous, D.; Torocastro, M.; Sutton, R.; Lim, P.B. Orthostatic Hypotension in Older People: Considerations, Diagnosis and Management. Clin. Med. 2021, 21, e275–e282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, R. Neurogenic Orthostatic Hypotension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorowski, A.; Ricci, F.; Hamrefors, V.; Sandau, K.E.; Hwan Chung, T.; Muldowney, J.A.S.; Gopinathannair, R.; Olshansky, B. Orthostatic Hypotension: Management of a Complex, But Common, Medical Problem. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2022, 15, e010573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Prado, C.M. Sarcopenia ≠ Low Muscle Mass. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2023, 14, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petermann-Rocha, F.; Balntzi, V.; Gray, S.R.; Lara, J.; Ho, F.K.; Pell, J.P.; Celis-Morales, C. Global Prevalence of Sarcopenia and Severe Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudart, C.; Zaaria, M.; Pasleau, F.; Reginster, J.-Y.; Bruyère, O. Health Outcomes of Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soysal, P.; Kocyigit, S.E.; Dokuzlar, O.; Bulut, E.A.; Smith, L.; Isik, A.T. Relationship between Sarcopenia and Orthostatic Hypotension. Age Ageing 2020, 49, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskin, K.; Çiftçi, S.; Öncö, J.; Dogan, G.M.; Çetinkal, G.; Yildiz, S.S.; Sigirci, S.; Kiliçkesmez, K.O. Orthostatic Hypotension and Age-Related Sarcopenia. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 67, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duggan, E.; Murphy, C.H.; Knight, S.P.; Davis, J.R.C.; O’Halloran, A.M.; Kenny, R.A.; Romero-Ortuno, R. Differential Associations Between Two Markers of Probable Sarcopenia and Continuous Orthostatic Hemodynamics in The Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2022, 78, glac243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duggan, E.; Knight, S.P.; Romero-Ortuno, R. Relationship between Sarcopenia and Orthostatic Blood Pressure Recovery in Older Falls Clinic Attendees. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2023, 14, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herring, N.; Paterson, D.J.; Levick, J.R. Levick’s Introduction to Cardiovascular Physiology, 6th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-0-8153-6361-3. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donoghue, P.J.; Claffey, P.; Rice, C.; Byrne, L.; Cunningham, C.; Kenny, R.A.; Romero-Ortuno, R. Association between Gait Speed and the SHARE Frailty Instrument in a Falls and Syncope Clinic. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2021, 12, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergi, G.; De Rui, M.; Veronese, N.; Bolzetta, F.; Berton, L.; Carraro, S.; Bano, G.; Coin, A.; Manzato, E.; Perissinotto, E. Assessing Appendicular Skeletal Muscle Mass with Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Free-Living Caucasian Older Adults. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finucane, C.; van Wijnen, V.K.; Fan, C.W.; Soraghan, C.; Byrne, L.; Westerhof, B.E.; Freeman, R.; Fedorowski, A.; Harms, M.P.M.; Wieling, W.; et al. A Practical Guide to Active Stand Testing and Analysis Using Continuous Beat-to-Beat Non-Invasive Blood Pressure Monitoring. Clin. Auton. Res. 2019, 29, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesseling, K.H.; Jansen, J.R.; Settels, J.J.; Schreuder, J.J. Computation of Aortic Flow from Pressure in Humans Using a Nonlinear, Three-Element Model. J. Appl. Physiol. 1993, 74, 2566–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, M.P.M.; Wesseling, K.H.; Pott, F.; Jenstrup, M.; Van Goudoever, J.; Secher, N.H.; Van Lieshout, J.J. Continuous Stroke Volume Monitoring by Modelling Flow from Non-Invasive Measurement of Arterial Pressure in Humans under Orthostatic Stress. Clin. Sci. 1999, 97, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soraghan, C.J.; Fan, C.W.; Hayakawa, T.; Cronin, H.; Foran, T.; Boyle, G.; Kenny, R.-A.; Finucane, C. TILDA Signal Processing Framework (SPF) for the Analysis of BP Responses to Standing in Epidemiological and Clinical Studies. In Proceedings of the IEEE-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI), Valencia, Spain, 1–4 June 2014; pp. 793–796. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, L.; O’Connor, J.D.; Romero-Ortuno, R.; Reilly, R.B.; Kenny, R.A. Supine Hypertension Is Associated With an Impaired Cerebral Oxygenation Response to Orthostasis: Finding From The Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing. Hypertension 2021, 78, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, J.D.; O’Connell, M.D.L.; Knight, S.P.; Newman, L.; Donoghue, O.A.; Kenny, R.A. Impaired Stabilisation of Orthostatic Cerebral Oxygenation Is Associated with Slower Gait Speed: Evidence from The Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2022, 77, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mol, A.; Slangen, L.R.N.; van Wezel, R.J.A.; Maier, A.B.; Meskers, C.G.M. Orthostatic Blood Pressure Recovery Associates with Physical Performance, Frailty and Number of Falls in Geriatric Outpatients. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bruïne, E.S.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Trappenburg, M.C.; Pasma, J.H.; de Vries, O.J.; Meskers, C.G.M.; Maier, A.B. Diminished Dynamic Physical Performance Is Associated With Orthostatic Hypotension in Geriatric Outpatients. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2019, 42, E28–E34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Sjöberg, B.J.; Thulesius, O. Cardiac Output and Blood Pressure during Active and Passive Standing. Clin. Physiol. 1996, 16, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Marshall, R.J.; Shepherd, J.T. The Effect of Changes in Posture and of Graded Exercise on Stroke Volume in Man. J. Clin. Investig. 1960, 39, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieling, W.; Veerman, D.P.; Dambrink, J.H.A.; Imholz, B.P.M. Disparities in Circulatory Adjustment to Standing between Young and Elderly Subjects Explained by Pulse Contour Analysis. Clin. Sci. 1992, 83, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wijnen, V.K.; Hove, D.T.; Finucane, C.; Wieling, W.; van Roon, A.M.; Ter Maaten, J.C.; Harms, M.P.M. Hemodynamic Mechanisms Underlying Initial Orthostatic Hypotension, Delayed Recovery and Orthostatic Hypotension. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2018, 19, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Twist, D.J.L.; Harms, M.P.M.; van Wijnen, V.K.; Claydon, V.E.; Freeman, R.; Cheshire, W.P.; Wieling, W. Diagnostic Criteria for Initial Orthostatic Hypotension: A Narrative Review. Clin. Auton. Res. 2021, 31, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilsted, J.; Parving, H.H.; Christensen, N.J.; Benn, J.; Galbo, H. Hemodynamics in Diabetic Orthostatic Hypotension. J. Clin. Investig. 1981, 68, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Denia, L.; Claffey, P.; Byrne, L.; Rice, C.; Kenny, R.A.; Finucane, C. Increased Multimorbidity Is Associated with Impaired Cerebral and Peripheral Hemodynamic Stabilization during Active Standing. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2022, 70, 1973–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronese, N.; Smith, L.; Cereda, E.; Maggi, S.; Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J.; Koyanagi, A. Multimorbidity Increases the Risk for Sarcopenia Onset: Longitudinal Analyses from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 156, 111624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesinovic, J.; Zengin, A.; De Courten, B.; Ebeling, P.R.; Scott, D. Sarcopenia and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Bidirectional Relationship. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 1057–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugge-Asperheim, B.; Kiil, F. Preload, Contractility, and Afterload as Determinants of Stroke Volume during Elevation of Aortic Blood Pressure in Dogs. Cardiovasc. Res. 1973, 7, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, J.M. Toward Consistent Definitions for Preload and Afterload. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2001, 25, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solaro, R.J. Regulation of Cardiac Contractility; Integrated Systems Physiology: From Molecule to Function to Disease; Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2011; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, D.R.; Tan, R.-S.; Lim, W.S.; Koh, A.S. Cardio-Sarcopenia: A Syndrome of Concern in Aging. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1027466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keng, B.M.H.; Gao, F.; Teo, L.L.Y.; Lim, W.S.; Tan, R.S.; Ruan, W.; Ewe, S.H.; Koh, W.; Koh, A.S. Associations between Skeletal Muscle and Myocardium in Aging: A Syndrome of “Cardio-Sarcopenia”? J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2019, 67, 2568–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelà, G.; Tagliaferri, S.; Perrino, F.; Bussolati, G.; Longobucco, Y.; Zerbinati, L.; Adorni, E.; Calvani, R.; Cesari, M.; Cherubini, A.; et al. Interaction of Skeletal and Left Ventricular Mass in Older Adults with Low Muscle Performance. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2021, 69, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seals, D.R. Influence of Muscle Mass on Sympathetic Neural Activation during Isometric Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1989, 67, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, M.; Landi, F.; Vellas, B.; Bernabei, R.; Marzetti, E. Sarcopenia and Physical Frailty: Two Sides of the Same Coin. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.H.; Kaufman, M.P.; Iwamoto, G.A. The Exercise Pressor Reflex: Its Cardiovascular Effects, Afferent Mechanisms, and Central Pathways. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1983, 45, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergi, G.; De Rui, M.; Stubbs, B.; Veronese, N.; Manzato, E. Measurement of Lean Body Mass Using Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis: A Consideration of the Pros and Cons. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 29, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remmen, J.J.; Aengevaeren, W.R.M.; Verheugt, F.W.A.; Van Der Werf, T.; Luijten, H.E.; Bos, A.; Jansen, R.W.M.M. Finapres Arterial Pulse Wave Analysis with Modelflow® Is Not a Reliable Non-Invasive Method for Assessment of Cardiac Output. Clin. Sci. 2002, 103, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhanji, S.; Dawson, J.; Pearse, R.M. Cardiac Output Monitoring: Basic Science and Clinical Application. Anaesthesia 2008, 63, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukawa, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Nakamoto, T.; Murata, J.; Komine, H.; Noso, M. Noninvasive Evaluation of Cardiac Output during Postural Change and Exercise in Humans: Comparison between the Modelflow and Pulse Dye-Densitometry. Jpn. J. Physiol. 2004, 54, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, J.; Tanabe, T.; Miyachi, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Takahashi, K.; Iemitsu, M.; Otsuki, T.; Homma, S.; Maeda, S.; Ajisaka, R.; et al. Non-invasive Assessment of Cardiac Output during Exercise in Healthy Young Humans: Comparison between Modelflow Method and Doppler Echocardiography Method. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2003, 179, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, R.; Carey, D.; Kennelly, S.P.; Kenny, R.A. Longitudinal Association Between Orthostatic Hypotension at 30 Seconds Post-Standing and Late-Life Depression. Hypertension 2018, 71, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finucane, C.; O’Connell, M.D.L.; Fan, C.W.; Savva, G.M.; Soraghan, C.J.; Nolan, H.; Cronin, H.; Kenny, R.A. Age-Related Normative Changes in Phasic Orthostatic Blood Pressure in a Large Population Study: Findings From The Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing (TILDA). Circulation 2014, 130, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, K.; Lavan, A.; Kenny, R.-A.; Briggs, R. Delayed Blood Pressure Recovery after Standing Independently Predicts Fracture in Community-Dwelling Older People. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2021, 22, 1235–1241.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finucane, C.; O’Connell, M.D.L.; Donoghue, O.; Richardson, K.; Savva, G.M.; Kenny, R.A. Impaired Orthostatic Blood Pressure Recovery Is Associated with Unexplained and Injurious Falls. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2017, 65, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagro, J.; Schoon, Y.; Heerts, I.; Meel-van den Abeelen, A.S.S.; Schalk, B.; Wieling, W.; Olde Rikkert, M.G.M.; Claassen, J.A.H.R. Impaired Systolic Blood Pressure Recovery Directly After Standing Predicts Mortality in Older Falls Clinic Patients. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernabei, R.; Landi, F.; Calvani, R.; Cesari, M.; Del Signore, S.; Anker, S.D.; Bejuit, R.; Bordes, P.; Cherubini, A.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; et al. Multicomponent Intervention to Prevent Mobility Disability in Frail Older Adults: Randomised Controlled Trial (SPRINTT Project). BMJ 2022, 377, e068788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, S.S.Y.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Pham, V.K.; Trappenburg, M.C.; Lim, W.K.; Meskers, C.G.M.; Maier, A.B. Sarcopenia and Its Association with Falls and Fractures in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brignole, M.; Moya, A.; de Lange, F.J.; Deharo, J.-C.; Elliott, P.M.; Fanciulli, A.; Fedorowski, A.; Furlan, R.; Kenny, R.A.; Martín, A.; et al. 2018 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Syncope. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 1883–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieling, W.; Kaufmann, H.; Claydon, V.E.; van Wijnen, V.K.; Harms, M.P.M.; Juraschek, S.P.; Thijs, R.D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Orthostatic Hypotension. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, E.L.; Khan, F.M.; Claydon, V.E. Counter Pressure Maneuvers for Syncope Prevention: A Semi-Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1016420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, C.H.; Schmidt, P.; Biaggioni, I.; Frazier-Mills, C.; Freeman, R.; Isaacson, S.; Karabin, B.; Kuritzky, L.; Lew, M.; Low, P.; et al. The Recommendations of a Consensus Panel for the Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Neurogenic Orthostatic Hypotension and Associated Supine Hypertension. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 1567–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No Sarcopenia (91/85%) | Sarcopenia (16/15%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age Group (n/%) | 0.143 † | ||
| 50–64 years | 30 (90.9) | 3 (9.1) | |
| 65–74 years | 34 (89.5) | 4 (10.5) | |
| 75+ years | 27 (75.0) | 9 (25.0) | |
| Women (n/%) | 52 (57.1) | 9 (56.3) | 0.947 * |
| Hypertension (n/%) | 42 (46.2) | 9 (56.3) | 0.456 * |
| Diabetes (n/%) | 15 (16.5) | 1 (6.3) | 0.457 † |
| Cardiovascular Meds (n/%) | 44 (48.4) | 10 (62.5) | 0.297 * |
| Psychotropic Meds (n/%) | 27 (29.7) | 7 (43.8) | 0.265 * |
| 0–10 s β (95% CI) | 10–20 s β (95% CI) | 20–30 s β (95% CI) | 30–40 s β (95% CI) | 40–180 s β (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAP | 0.23 (−0.13, 0.59) | −0.67 (−1.03, −0.31) *** | −0.05 (−0.41, 0.31) | −0.10 (−0.45, 0.31) | 0.03 (−0.02, 0.08) |
| CO | −0.05 (−0.08, −0.03) *** | 0.06 (0.03, 0.09) *** | 0.01 (−0.02, 0.04) | 0.01 (−0.02, 0.04) | <−0.01 (<−0.01, <0.01) |
| TPR | <0.01 (−0.01, 0.01) | −0.02 (−0.03, −0.01) *** | 0.01 (<−0.01, 0.02) | −0.01 (−0.02, <0.01) | <0.01 (<−0.01, <0.01) |
| SV | −0.37 (−0.72, −0.02) | 0.54 (0.19, 0.88) *** | 0.18 (−0.17, 0.52) | 0.09 (−0.25, 0.43) | −0.02 (−0.06, 0.02) |
| HR | −0.16 (−0.40, 0.08) | −0.15 (−0.39, 0.09) | 0.03 (−0.21, 0.26) | 0.02 (−0.22, 0.25) | −0.01 (−0.04, 0.01) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duggan, E.; Knight, S.P.; Xue, F.; Romero-Ortuno, R. Haemodynamic Parameters Underlying the Relationship between Sarcopenia and Blood Pressure Recovery on Standing. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010018
Duggan E, Knight SP, Xue F, Romero-Ortuno R. Haemodynamic Parameters Underlying the Relationship between Sarcopenia and Blood Pressure Recovery on Standing. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuggan, Eoin, Silvin P. Knight, Feng Xue, and Roman Romero-Ortuno. 2024. "Haemodynamic Parameters Underlying the Relationship between Sarcopenia and Blood Pressure Recovery on Standing" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010018
APA StyleDuggan, E., Knight, S. P., Xue, F., & Romero-Ortuno, R. (2024). Haemodynamic Parameters Underlying the Relationship between Sarcopenia and Blood Pressure Recovery on Standing. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010018







