Evaluating a Periapical Lesion Detection CNN on a Clinically Representative CBCT Dataset—A Validation Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Sample Size Calculation
2.3. Dataset
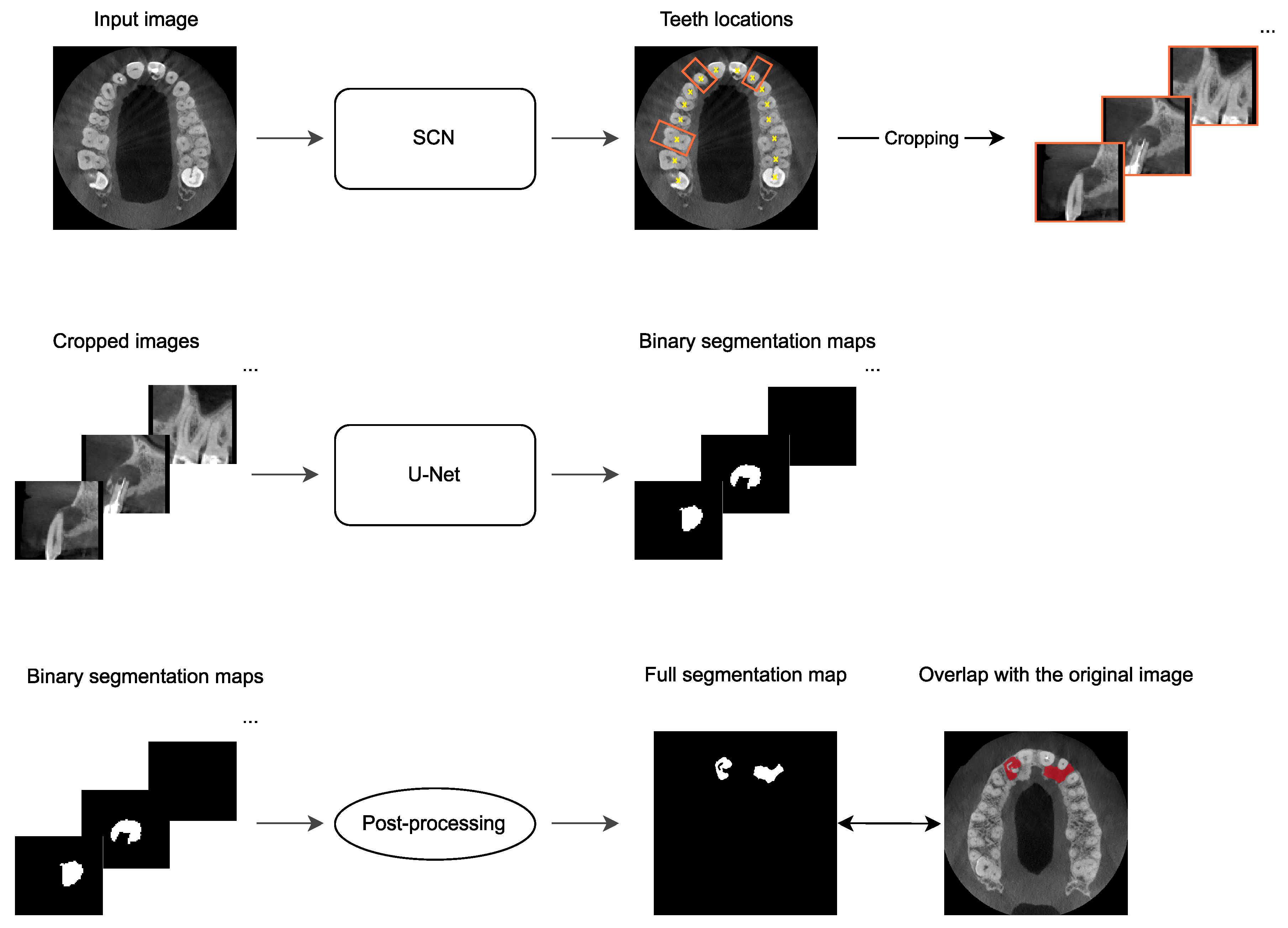
2.4. Automatic PAL Detection
2.5. Expert Assessment of Software PAL Detections
2.6. Statistical Analysis
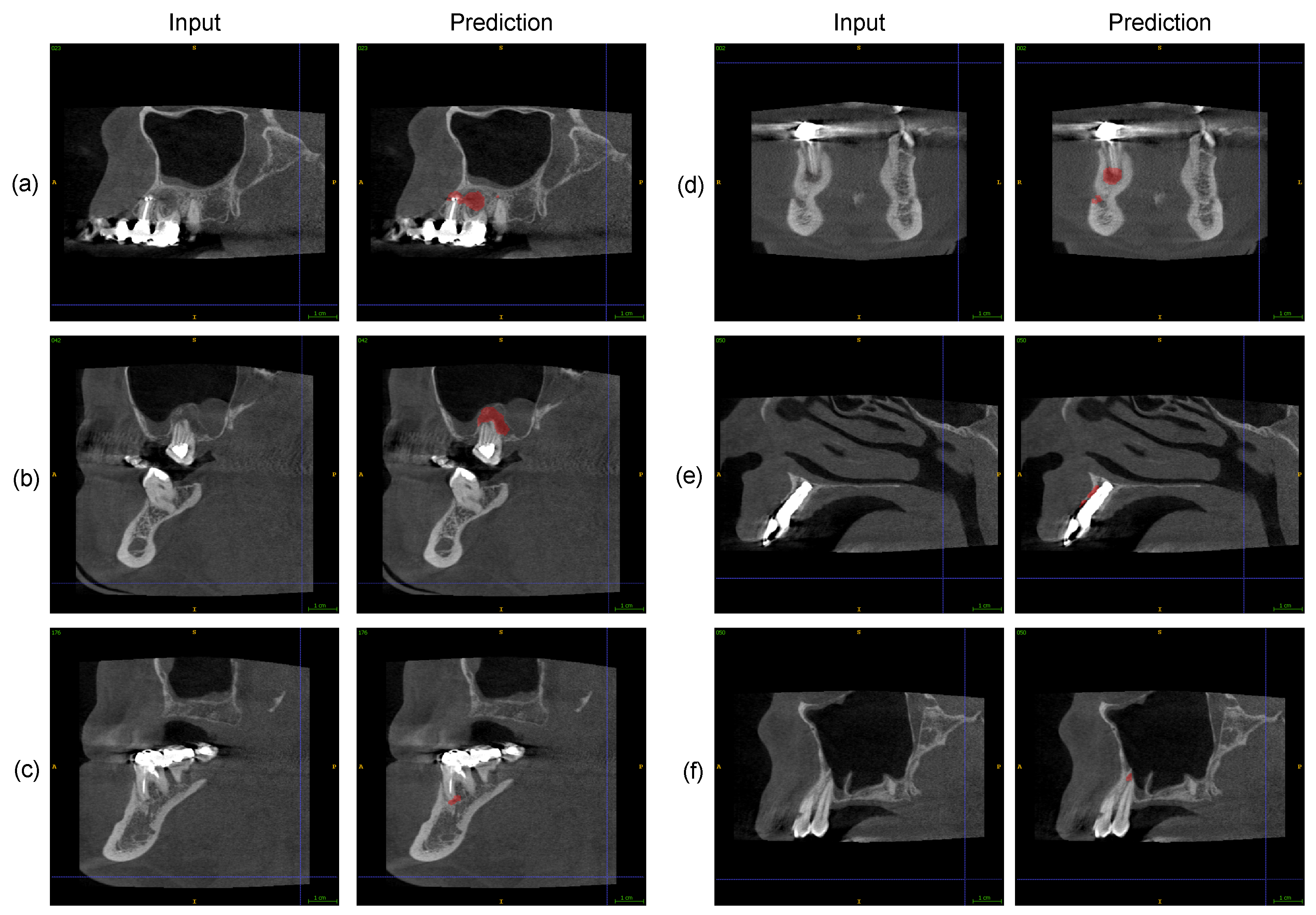
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CBCT | Cone-beam computed tomography |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| 3D | Three-dimensional |
| PAL | Periapical lesion |
| GDPR | General Data Protection Regulation |
| SCN | SpatialConfiguration-Net |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| TP | True positive |
| FN | False negative |
| FP | False positive |
References
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Yang, W.; Peng, S.; Zhou, J. A Survey of convolutional neural networks: Analysis, applications, and prospects. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 6999–7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; van der Laak, J.A.W.M.; van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Yang, L.T.; Zhang, Q.; Armstrong, D.; Deen, M.J. Convolutional neural networks for medical image analysis: State-of-the-art, comparisons, improvement and perspectives. Neurocomputing 2021, 444, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteva, A.; Kuprel, B.; Novoa, R.A.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Blau, H.M.; Thrun, S. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 2017, 542, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Fauw, J.; Ledsam, J.R.; Romera-Paredes, B.; Nikolov, S.; Tomasev, N.; Blackwell, S.; Askham, H.; Glorot, X.; O’Donoghue, B.; Visentin, D.; et al. Clinically applicable deep learning for diagnosis and referral in retinal disease. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinney, S.M.; Sieniek, M.; Godbole, V.; Godwin, J.; Antropova, N.; Ashrafian, H.; Back, T.; Chesus, M.; Corrado, G.S.; Darzi, A.; et al. International evaluation of an AI system for breast cancer screening. Nature 2020, 577, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwendicke, F.; Samek, W.; Krois, J. Artificial intelligence in dentistry: Chances and challenges. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.; Chug, A.; Afrashtehfar, K.I. Role of cone beam computed tomography in diagnosis and treatment planning in dentistry: An update. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2017, 7, S125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanagar, S.B.; Alfadley, A.; Alfouzan, K.; Awawdeh, M.; Alaqla, A.; Jamleh, A. Developments and performance of artificial intelligence models designed for application in endodontics: A systematic review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, J.; Jaber, M.; Rifai, I.; Mozdziak, P.; Kempisty, B.; Dyszkiewicz-Konwińska, M. Diagnostic Test Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence in Detecting Periapical Periodontitis on Two-Dimensional Radiographs: A Retrospective Study and Literature Review. Medicina 2023, 59, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, K.F.; Ai, Q.Y.H.; Wong, L.M.; Yeung, A.W.K.; Li, D.T.S.; Leung, Y.Y. Current applications of deep learning and radiomics on CT and CBCT for maxillofacial diseases. Diagnostics 2022, 13, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sin, C.; Akkaya, N.; Aksoy, S.; Orhan, K.; Öz, U. A deep learning algorithm proposal to automatic pharyngeal airway detection and segmentation on CBCT images. Orthod. Craniofacial Res. 2021, 24 (Suppl. S2), 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajami, M.; Tripathi, P.; Ling, H.; Mahdian, M. Automated detection of cervical carotid artery calcifications in cone beam computed tomographic images using deep convolutional neural networks. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, Z.K.; Mao, L.; Chen, H.; Sun, T.G.; Shen, X.M.; Liu, J.; Sun, Z.J. Improved diagnostic accuracy of ameloblastoma and odontogenic keratocyst on cone-beam CT by artificial intelligence. Front. Oncol. 2022, 11, 793417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, S.N. Diagnosis of cystic lesions using panoramic and cone beam computed tomographic images based on deep learning neural network. Oral Dis. 2020, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albitar, L.; Zhao, T.; Huang, C.; Mahdian, M. Artificial intelligence (AI) for detection and localization of unobturated second mesial buccal (MB2) canals in cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Guo, X.; Mu, C.; Qi, S.; Li, G. Detection of vertical root fractures by cone-beam computed tomography based on deep learning. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2023, 52, 20220345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier, K.M. Lesions of the Jaw. Semin. Ultrasound CT MR 2015, 36, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrela, C.; Bueno, M.R.; Azevedo, B.C.; Azevedo, J.R.; Pécora, J.D. A new periapical index based on cone beam computed tomography. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 1325–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becconsall-Ryan, K.; Tong, D.; Love, R.M. Radiolucent inflammatory jaw lesions: A twenty-year analysis. Int. Endod. J. 2010, 43, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthana, G.; Singh, N.; Yadav, R.; Duhan, J.; Tewari, S.; Gupta, A.; Sangwan, P.; Mittal, S. Comparative analysis of the accuracy of periapical radiography and cone-beam computed tomography for diagnosing complex endodontic pathoses using a gold standard reference—A prospective clinical study. Int. Endod. J. 2021, 54, 1448–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrela, C.; Bueno, M.R.; Leles, C.R.; Azevedo, B.; Azevedo, J.R. Accuracy of cone beam computed tomography and panoramic and periapical radiography for detection of apical periodontitis. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi Dutra, K.; Haas, L.; Porporatti, A.L.; Flores-Mir, C.; Nascimento Santos, J.; Mezzomo, L.A.; Corrêa, M.; De Luca Canto, G. Diagnostic Accuracy of Cone-beam Computed Tomography and Conventional Radiography on Apical Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, D.P.; Thomas, T.; Nivedhitha, M.S. Two-dimensional Periapical, Panoramic Radiography Versus Three-dimensional Cone-beam Computed Tomography in the Detection of Periapical Lesion After Endodontic Treatment: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2020, 12, e7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekert, T.; Krois, J.; Meinhold, L.; Elhennawy, K.; Emara, R.; Golla, T.; Schwendicke, F. Deep Learning for the Radiographic Detection of Apical Lesions. J. Endod. 2019, 45, 917–922.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setzer, F.C.; Shi, K.J.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, H.; Yoon, H.; Mupparapu, M.; Li, J. Artificial intelligence for the computer-aided detection of periapical lesions in cone-beam computed tomographic images. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Yan, H.; Setzer, F.C.; Shi, K.J.; Mupparapu, M.; Li, J. Anatomically constrained deep learning for automating dental CBCT segmentation and lesion detection. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, K.; Bayrakdar, I.; Ezhov, M.; Kravtsov, A.; Özyürek, T. Evaluation of artificial intelligence for detecting periapical pathosis on cone-beam computed tomography scans. Int. Endod. J. 2020, 53, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezhov, M.; Gusarev, M.; Golitsyna, M.; Yates, J.M.; Kushnerev, E.; Tamimi, D.; Aksoy, S.; Shumilov, E.; Sanders, A.; Orhan, K. Clinically applicable artificial intelligence system for dental diagnosis with CBCT. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, A.E.; Gültekin, S.; Simsar, E.; Özdemir, Ş.D.; Gündoğar, M.; Tokgöz, S.B.; Hamamcı, İ.E. Dental enumeration and multiple treatment detection on panoramic X-rays using deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirnbauer, B.; Hadzic, A.; Jakse, N.; Bischof, H.; Štern, D. Automatic detection of periapical osteolytic lesions on cone-beam computed tomography using deep convolutional neuronal networks. J. Endod. 2022, 48, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdan, M.H.; Tuzova, L.; Mol, A.; Tawil, P.Z.; Tuzoff, D.; Tyndall, D.A. The effect of a deep-learning tool on dentists’ performances in detecting apical radiolucencies on periapical radiographs. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2022, 51, 20220122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calazans, M.A.A.; Ferreira, F.A.B.S.; Alcoforado, M.d.L.M.G.; Santos, A.d.; Pontual, A.d.A.; Madeiro, F. Automatic classification system for periapical lesions in cone-beam computed tomography. Sensors 2022, 22, 6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varoquaux, G.; Cheplygina, V. Machine learning for medical imaging: Methodological failures and recommendations for the future. npj Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broers, D.L.; Dubois, L.; de Lange, J.; Su, N.; de Jongh, A. Reasons for tooth removal in adults: A systematic review. Int. Dent. J. 2022, 72, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payer, C.; Štern, D.; Bischof, H.; Urschler, M. Integrating spatial configuration into heatmap regression based CNNs for landmark localization. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 54, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadzic, A.; Kirnbauer, B.; Štern, D.; Urschler, M. Teeth Localization and Lesion Segmentation in CBCT Images using SpatialConfiguration-Net and U-Net. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.12189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.; Torabinejad, M.; Rice, D.; Azevedo, B. Accuracy of cone-beam computed tomography and periapical radiography in detecting small periapical lesions. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovljevic, A.; Nikolic, N.; Jacimovic, J.; Pavlovic, O.; Milicic, B.; Beljic-Ivanovic, K.; Miletic, M.; Andric, M.; Milasin, J. Prevalence of apical periodontitis and conventional nonsurgical root canal treatment in general adult population: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies published between 2012 and 2020. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 1371–1386.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.Q.; Srivastava, S.; Alotaibi, B.B.R.; Bhatti, U.A.; Abulhamael, A.M.; Habib, S.R. A Cone Beam Computed Tomography-Based Investigation of the Frequency and Pattern of Radix Entomolaris in the Saudi Arabian Population. Medicina 2023, 59, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Criterion | Kirnbauer et al. [32] | This Study |
|---|---|---|
| Field of view with a representation of the entire dental arch (upper jaw, lower jaw, or both) | Included | Included |
| Device and assessment parameters: Field of view of 10.0 × 5.9 cm or 10.0 × 9.3 cm, covering at least one completely visible dental arch, with a 200-µm voxel size (96 kV, 5.6–9.0 mA, 12 s), which is labeled as “normal” mode by the manufacturer | Included | Included |
| An acceptable degree of scatter and/or artifacts (exclusion of clinically insufficient interpretable datasets, i.e., severe metal artifacts inhibiting individual crown visualization, and ghost effects/double images due to long-motion artifacts) | Included | Included |
| Completed root development | Included | Included |
| No edentulism | Included | Included |
| Additional: | Additional: | |
| as few missing teeth as possible | up to 11 missing teeth per jaw | |
| Tooth gaps | Excluded | Included |
| Partially and totally impacted teeth | Excluded | Included |
| Dental implants | Excluded | Included |
| Augmentations | Excluded | Included |
| Number | Additional Information | |
|---|---|---|
| Images | 195 | One jaw: 164 |
| Both jaws: 31 | ||
| Jaws | 226 | Upper: 125 |
| Lower: 101 | ||
| Teeth present | 2947 | With lesion: 300 (10.2%) |
| Without lesion: 2647 (89.8%) | ||
| Lesion classification 1 | Score 1: 28 ( 9.3%) | Diameter > 0.5–1 mm |
| Score 2: 59 (19.7%) | Diameter > 1–2 mm | |
| Score 3: 67 (22.3%) | Diameter > 2–4 mm | |
| Score 4: 85 (28.3%) | Diameter > 4–8 mm | |
| Score 5: 61 (20.3%) | Diameter > 8 mm |
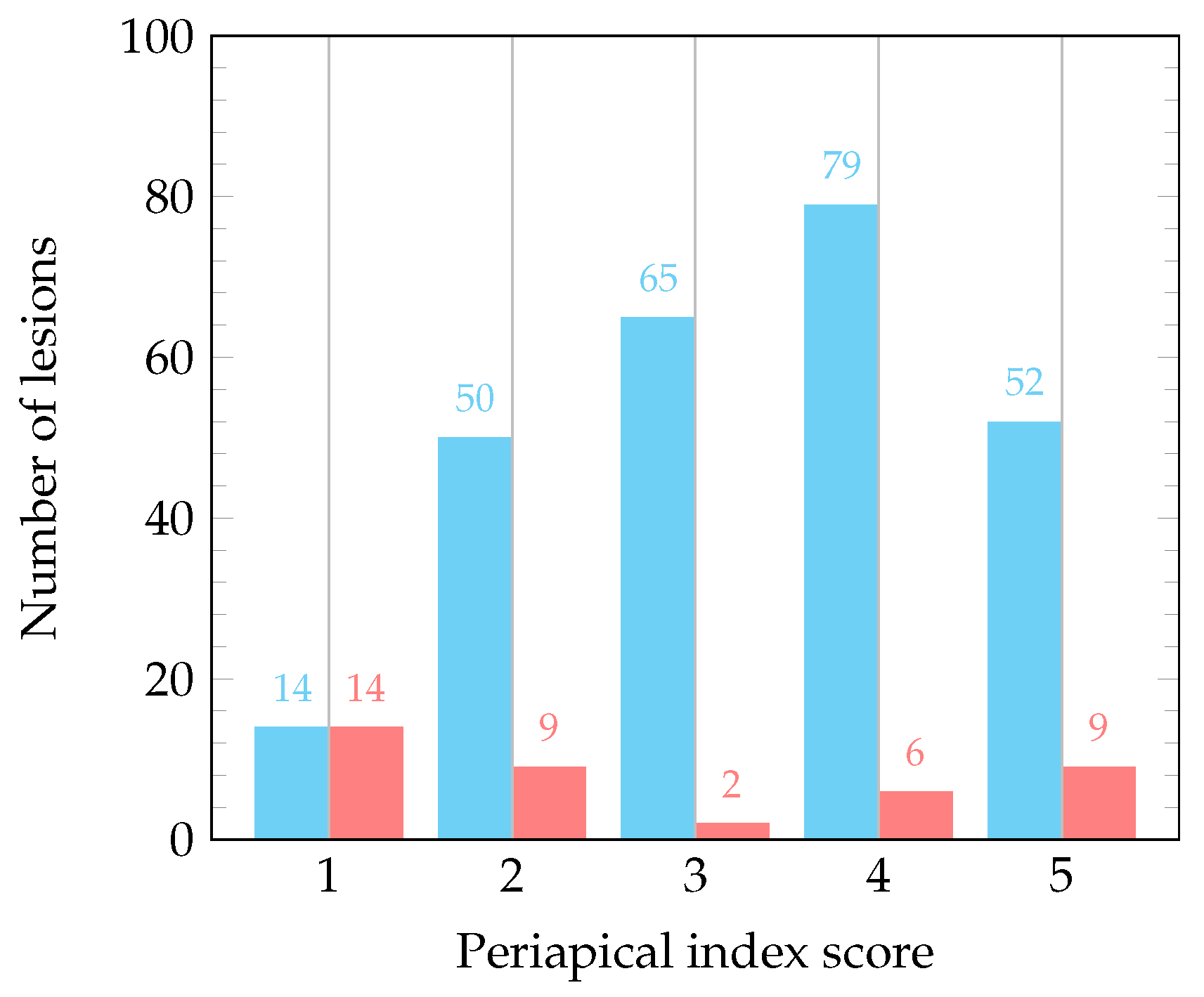
| Periapical Index Score | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Third molars | 3 (27.3%) | 4 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 11 |
| Second molars | 4 ( 6.0%) | 12 | 9 | 20 | 22 | 67 |
| First molars | 3 ( 3.5%) | 17 | 19 | 25 | 21 | 85 |
| Second premolars | 6 (14.0%) | 9 | 10 | 14 | 4 | 43 |
| First premolars | 2 ( 5.7%) | 9 | 11 | 8 | 5 | 35 |
| Canines | 1 ( 7.7%) | 3 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 13 |
| Lateral incisors | 3 (21.4%) | 1 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 14 |
| Central incisors | 6 (18.8%) | 4 | 10 | 10 | 2 | 32 |
| Total | 28 (9.3%) | 59 | 67 | 85 | 61 | 300 |
| Category | Lesion count | Sensitivity (%) | 95% CI Exact | Specificity (%) | 95% CI Exact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | 300 | 86.67 | 82.29–90.30% | 84.25 | 82.80–85.61% |
| Upper jaw | 196 | 87.76 | 82.33–91.99% | 82.31 | 80.21–84.27% |
| Lower jaw | 104 | 84.62 | 76.22–90.94% | 86.43 | 84.40–88.28% |
| Third molars | 11 | 63.64 | 30.79–89.07% | 81.61 | 75.04–87.07% |
| Second molars | 67 | 91.04 | 81.52–96.64% | 70.59 | 64.97–75.78% |
| First molars | 85 | 91.76 | 83.77–96.62% | 70.51 | 64.22–76.28% |
| Second premolars | 43 | 88.37 | 74.92–96.11% | 81.63 | 77.03–85.64% |
| First premolars | 35 | 82.86 | 66.35–93.44% | 87.37 | 83.60–90.54% |
| Canines | 13 | 69.23 | 38.57–90.91% | 89.70 | 86.41–92.41% |
| Lateral incisors | 14 | 64.29 | 35.14–87.24% | 92.68 | 89.72–95.01% |
| Central incisors | 32 | 90.63 | 74.98–98.02% | 88.03 | 84.44–91.04% |
| Predicted condition | ||||
| Lesion | Non-lesion | Total | ||
| Actual condition | Lesion | 260 | 40 | 300 |
| Non-lesion | 417 | 2230 | 2647 | |
| Total | 677 | 2270 | 2947 | |
| Predicted condition | ||||
| Lesion | Non-lesion | Total | ||
| Actual condition | Lesion | 260 | 40 | 300 |
| Non-lesion | 459 | 2857 | 3316 | |
| Total | 719 | 2897 | 3616 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hadzic, A.; Urschler, M.; Press, J.-N.A.; Riedl, R.; Rugani, P.; Štern, D.; Kirnbauer, B. Evaluating a Periapical Lesion Detection CNN on a Clinically Representative CBCT Dataset—A Validation Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010197
Hadzic A, Urschler M, Press J-NA, Riedl R, Rugani P, Štern D, Kirnbauer B. Evaluating a Periapical Lesion Detection CNN on a Clinically Representative CBCT Dataset—A Validation Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(1):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010197
Chicago/Turabian StyleHadzic, Arnela, Martin Urschler, Jan-Niclas Aaron Press, Regina Riedl, Petra Rugani, Darko Štern, and Barbara Kirnbauer. 2024. "Evaluating a Periapical Lesion Detection CNN on a Clinically Representative CBCT Dataset—A Validation Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 1: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010197
APA StyleHadzic, A., Urschler, M., Press, J.-N. A., Riedl, R., Rugani, P., Štern, D., & Kirnbauer, B. (2024). Evaluating a Periapical Lesion Detection CNN on a Clinically Representative CBCT Dataset—A Validation Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(1), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010197







