Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Special Patient Populations
Abstract
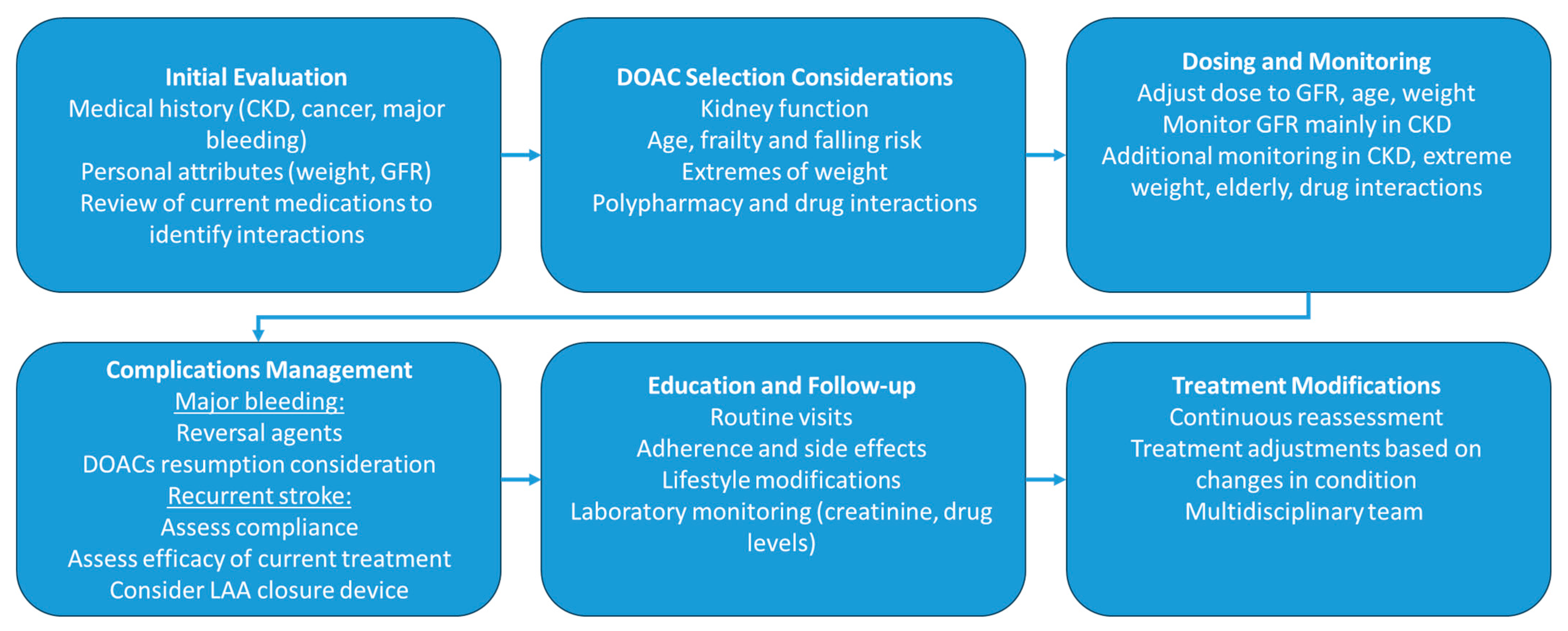
:1. Introduction
2. DOACs in Chronic Kidney Disease
3. DOACs in Advanced Age
4. Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Significant Drug–Drug Interactions (DDIs)
5. Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Extremes of Weight
6. DOACs in Recurrent Stroke
7. DOACs after Major Hemorrhage
8. DOACs in Patients with Cancer
9. Summary
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Benjamin, E.J.; Muntner, P.; Alonso, A.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Das, S.R.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2019 update: A report from the American heart association. Circulation 2019, 139, e56–e528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Zhang, Q.; Abu Much, A.; Maor, E.; Segev, A.; Beinart, R.; Adawi, S.; Lu, Y.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Wu, J. Global, regional, and national prevalence, incidence, mortality, and risk factors for atrial fibrillation, 1990–2017: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Eur. Hear. J.-Qual. Care Clin. Outcomes 2020, 7, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, S.I.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abate, K.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Ciobanu, L.G.; GBD 2016 DALYs and HALE Collaborators. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 333 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1260–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, J.-A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, P.A.; Abbott, R.D.; Kannel, W.B. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: The Framingham Study. Stroke 1991, 22, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kawaz, M.; Omran, S.S.; Parikh, N.S.; Elkind, M.S.; Soliman, E.Z.; Kamel, H. Comparative Risks of Ischemic Stroke in Atrial Flutter versus Atrial Fibrillation. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleindorfer, D.O.; Towfighi, A.; Chaturvedi, S.; Cockroft, K.M.; Gutierrez, J.; Lombardi-Hill, D.; Kamel, H.; Kernan, W.N.; Kittner, S.J.; Leira, E.C.; et al. 2021 Guideline for the Prevention of Stroke in Patients with Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack: A Guideline From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2021, 52, E364–E467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- January, C.T.; Wann, L.S.; Calkins, H.; Chen, L.Y.; Cigarroa, J.E.; Cleveland, J.C., Jr.; Ellinor, P.T., Jr.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Field, M.E.; Furie, K.L.; et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS Focused Update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society in Collaboration with the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Circulation 2019, 140, e125–e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.H. The ABC pathway: An integrated approach to improve AF management. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 627–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Lim, E.; Covic, A.; Verhamme, P.; Gale, C.P.; Camm, A.J.; Goldsmith, D. Anticoagulation in Concomitant Chronic Kidney Disease and Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 2204–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Stecker, E.; Warden, B.A. Direct Oral Anticoagulant Use: A Practical Guide to Common Clinical Challenges. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2020, 9, e017559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffel, J.; Collins, R.; Antz, M.; Cornu, P.; Desteghe, L.; Haeusler, K.G.; Oldgren, J.; Reinecke, H.; Roldan-Schilling, V.; Rowell, N.; et al. 2021 European Heart Rhythm Association Practical Guide on the Use of Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. EP Europace 2021, 23, 1612–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.R.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Garg, J.; Pan, G.; Singer, D.E.; Hacke, W.; Breithardt, G.; Halperin, J.L.; Hankey, G.J.; Piccini, J.P.; et al. Rivaroxaban versus Warfarin in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giugliano, R.P.; Ruff, C.T.; Braunwald, E.; Murphy, S.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Halperin, J.L.; Waldo, A.L.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Weitz, J.I.; Špinar, J.; et al. Edoxaban versus Warfarin in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, S.J.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Yusuf, S.; Eikelboom, J.; Oldgren, J.; Parekh, A.; Pogue, J.; Reilly, P.A.; Themeles, E.; Varrone, J.; et al. Dabigatran versus Warfarin in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granger, C.B.; Alexander, J.H.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lopes, R.D.; Hylek, E.M.; Hanna, M.; Al-Khalidi, H.R.; Ansell, J.; Atar, D.; Ave-zum, A.; et al. Apixaban versus Warfarin in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonde, A.N.; Lip, G.Y.; Kamper, A.-L.; Hansen, P.R.; Lamberts, M.; Hommel, K.; Hansen, M.L.; Gislason, G.H.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Olesen, J.B. Net Clinical Benefit of Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 2471–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, C.A.; Asinger, R.W.; Berger, A.K.; Charytan, D.M.; Díez, J.; Hart, R.G.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Kasiske, B.L.; McCullough, P.A.; Passman, R.S.; et al. Cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease. A clinical update from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 572–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Inselman, J.W.; Ross, J.S.; Izem, R.; Graham, D.J.; Martin, D.B.; Thompson, A.M.; Southworth, M.R.; Siontis, K.C.; Ngufor, C.G.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Oral Anticoagulants Across Kidney Function in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2020, 13, e006515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorney, S.D.; Chertow, G.M.; Al-Khalidi, H.R.; Gallup, D.; Dignacco, P.; Mussina, K.; Bansal, N.; Gadegbeku, C.A.; Garcia, D.A.; Garonzik, S.; et al. Apixaban for Patients with Atrial Fibrillation on Hemodialysis: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Circulation 2022, 146, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinecke, H.; Engelbertz, C.; Bauersachs, R.; Breithardt, G.; Echterhoff, H.-H.; Gerß, J.; Haeusler, K.G.; Hewing, B.; Hoyer, J.; Juergensmeyer, S.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Apixaban with the Vitamin K Antagonist Phenprocoumon in Patients on Chronic Hemodialysis: The AXADIA-AFNET 8 Study. Circulation 2023, 147, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Strategies for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation in patiEnts Receiving Dialysis (SAFE-D). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03987711 (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Kuno, T.; Takagi, H.; Ando, T.; Sugiyama, T.; Miyashita, S.; Valentin, N.; Shimada, Y.J.; Kodaira, M.; Numasawa, Y.; Briasoulis, A.; et al. Oral Anticoagulation for Patients with Atrial Fibrillation on Long-Term Dialysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siontis, K.C.; Zhang, X.; Eckard, A.; Bhave, N.; Schaubel, D.E.; He, K.; Tilea, A.; Stack, A.G.; Balkrishnan, R.; Yao, X.; et al. Outcomes Associated with Apixaban Use in Patients with End-Stage Kidney Disease and Atrial Fibrillation in the United States. Circulation 2018, 138, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joglar, J.A.; Chung, M.K.; Armbruster, A.L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Chyou, J.Y.; Cronin, E.M.; Deswal, A.; Eckhardt, L.L.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Gopinathannair, R.; et al. 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagerty, T.; Rich, M.W. Fall risk and anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation in the elderly: A delicate balance. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2017, 84, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, M.R.; Badri, M.; Prince, C.T.; Seltzer, J.; Kowey, P.R. Underrepresentation of Women, Elderly Patients, and Racial Minorities in the Randomized Trials Used for Cardiovascular Guidelines. JAMA Intern. Med. 2014, 174, 1868–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekerstad, N.; Karlsson, T.; Söderqvist, S.; Karlson, B.W. Hospitalized frail elderly patients—Atrial fibrillation, anticoagulation and 12 months’ outcomes. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man-Son-Hing, M.; Nichol, G.; Lau, A.; Laupacis, A. Choosing Antithrombotic Therapy for Elderly Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Who Are at Risk for Falls. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvorsen, S.; Atar, D.; Yang, H.; De Caterina, R.; Erol, C.; Garcia, D.; Granger, C.B.; Hanna, M.; Held, C.; Husted, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of apixaban compared with warfarin according to age for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: Observations from the ARISTOTLE trial. Eur. Hear. J. 2014, 35, 1864–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.H.; Shestakovska, O.; Connolly, S.J.; Eikelboom, J.W.; Avezum, A.; Diaz, R.; Lanas, F.; Yusuf, S.; Hart, R.G. Efficacy and safety of apixaban compared with aspirin in the elderly: A subgroup analysis from the AVERROES trial. Age Ageing 2015, 45, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halperin, J.L.; Hankey, G.J.; Wojdyla, D.M.; Piccini, J.P.; Lokhnygina, Y.; Patel, M.R.; Breithardt, G.; Singer, D.E.; Becker, R.C.; Hacke, W.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Rivaroxaban Compared with Warfarin among Elderly Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation in the Rivaroxaban Once Daily, Oral, Direct Factor Xa Inhibition Compared with Vitamin K Antagonism for Prevention of Stroke and Embolism Trial in Atrial Fibrillation (ROCKET AF). Circulation 2014, 130, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, E.T.; Giugliano, R.P.; Ruff, C.T.; Koretsune, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Kiss, R.G.; Nordio, F.; Murphy, S.A.; Kimura, T.; Jin, J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Edoxaban in Elderly Patients with Atrial Fibrillation in the ENGAGE AF–TIMI 48 Trial. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2016, 5, e003432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scala, I.; Bellavia, S.; Rizzo, P.A.; Di Giovanni, J.; Monforte, M.; Morosetti, R.; Della Marca, G.; Pilato, F.; Broccolini, A.; Profice, P.; et al. Prolonged Secondary Stroke Prevention with Edoxaban: A Long-Term Follow-Up of the SATES Study. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eikelboom, J.W.; Wallentin, L.; Connolly, S.J.; Ezekowitz, M.; Healey, J.S.; Oldgren, J.; Yang, S.; Alings, M.; Kaatz, S.; Hohnloser, S.H.; et al. Risk of Bleeding with 2 Doses of Dabigatran Compared with Warfarin in Older and Younger Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: An analysis of the randomized evaluation of long-term anticoagulant therapy (RE-LY) trial. Circulation 2011, 123, 2363–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deitelzweig, S.; Keshishian, A.; Li, X.; Kang, A.; Dhamane, A.D.; Luo, X.; Balachander, N.; Rosenblatt, L.; Mardekian, J.; Pan, X.; et al. Comparisons between Oral Anticoagulants among Older Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation Patients. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2019, 67, 1662–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, K.; Akao, M.; Yoshida, T.; Kawata, M.; Okazaki, O.; Akashi, S.; Eshima, K.; Tanizawa, K.; Fukuzawa, M.; Hayashi, T.; et al. Low-Dose Edoxaban in Very Elderly Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, T.-F.; Liu, C.-J.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chang, S.-L.; Lo, L.-W.; Hu, Y.-F.; Tuan, T.-C.; Liao, J.-N.; Chung, F.-P.; Chen, T.-J.; et al. Oral Anticoagulation in Very Elderly Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Circulation 2018, 138, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposeiras-Roubín, S.; Rodríguez, D.A.; Freire, S.J.C.; Abu-Assi, E.; Cobas-Paz, R.; Pascual, C.R.; Comesaña, J.G.; López, A.G.-C.; Fernández, N.C.; Ríos, L.-M.; et al. Vitamin K Antagonists and Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Nonagenarian Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Med Dir. Assoc. 2019, 21, 367–373.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, E.; White, C.M.; Patel, M.R.; Fields, L.E.; Peacock, W.F.; Crivera, C.; Coleman, C.I. Doses of apixaban and rivaroxaban prescribed in real-world United States cardiology practices compared to registration trials. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2016, 32, 1277–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissan, R.; Spectre, G.; Hershkovitz, A.; Green, H.; Shimony, S.; Cooper, L.; Nakav, S.; Shochat, T.; Grossman, A.; Fuchs, S. Apixaban Levels in Octogenarian Patients with Non-valvular Atrial Fibrillation. Drugs Aging 2018, 36, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proietti, M.; Romiti, G.F.; Raparelli, V.; Diemberger, I.; Boriani, G.; Vecchia, L.A.D.; Bellelli, G.; Marzetti, E.; Lip, G.Y.; Cesari, M. Frailty prevalence and impact on outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 1,187,000 patients. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 79, 101652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, C.; Wu, J.; Clegg, A.; Nadarajah, R.; Rockwood, K.; Todd, O.; Gale, C.P. Impact of oral anticoagulation on the association between frailty and clinical outcomes in people with atrial fibrillation: Nationwide primary care records on treatment analysis. EP Europace 2022, 24, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Søgaard, M.; Ording, A.G.; Skjøth, F.; Larsen, T.B.; Nielsen, P.B. Effectiveness and safety of direct oral anticoagulation versus warfarin in frail patients with atrial fibrillation. Eur. Hear. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Focks, J.J.; Brouwer, M.A.; Wojdyla, D.M.; Thomas, L.; Lopes, R.D.; Washam, J.B.; Lanas, F.; Xavier, D.; Husted, S.; Wallentin, L.; et al. Polypharmacy and effects of apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: Post hoc analysis of the ARISTOTLE trial. BMJ 2016, 353, i2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccini, J.P.; Hellkamp, A.S.; Washam, J.B.; Becker, R.C.; Breithardt, G.; Berkowitz, S.D.; Halperin, J.L.; Hankey, G.J.; Hacke, W.; Mahaffey, K.W.; et al. Polypharmacy and the Efficacy and Safety of Rivaroxaban versus Warfarin in the Prevention of Stroke in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2016, 133, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.-H.; Chou, I.-J.; Yeh, Y.-H.; Chiou, M.-J.; Wen, M.-S.; Kuo, C.-T.; See, L.-C.; Kuo, C.-F. Association Between Use of Non–Vitamin K Oral Anticoagulants with and without Concurrent Medications and Risk of Major Bleeding in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA 2017, 318, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grymonprez, M.; Petrovic, M.; De Backer, T.L.; Steurbaut, S.; Lahousse, L. The Impact of Polypharmacy on the Effectiveness and Safety of Non-vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronich, N.; Stein, N.; Muszkat, M. Association between Use of Pharmacokinetic-Interacting Drugs and Effectiveness and Safety of Direct Acting Oral Anticoagulants: Nested Case-Control Study. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 110, 1526–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rein, N.; Heide-Jørgensen, U.; Lijfering, W.M.; Dekkers, O.M.; Sørensen, H.T.; Cannegieter, S.C. Major Bleeding Rates in Atrial Fibrillation Patients on Single, Dual, or Triple Antithrombotic Therapy. Circulation 2019, 139, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DrugBank. Cytochrome P-450 CYP3A4 Inducers. Available online: https://go.drugbank.com/categories/DBCAT003896 (accessed on 2 October 2023).
- Goldstein, R.; Jacobs, A.R.; Zighan, L.; Gronich, N.; Bialer, M.; Muszkat, M. Interactions Between Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs) and Antiseizure Medications: Potential Implications on DOAC Treatment. CNS Drugs 2023, 37, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Minno, M.N.D.; Russolillo, A.; Di Minno, A.; Camera, M.; Parolari, A.; Tremoli, E. Direct anticoagulant drugs to overcome limitations of vitamin K antagonists. A critical appraisal of data in atrial fibrillation patients. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2013, 18, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Fact Sheet N311: Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 13 August 2023).
- Ogden, C.L.; Carroll, M.D.; Kit, B.K.; Flegal, K.M. Prevalence of Childhood and Adult Obesity in the United States, 2011-2012. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2014, 311, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubitza, D.; Becka, M.; Zuehlsdorf, M.; Mueck, W. Body Weight Has Limited Influence on the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, or Pharmacodynamics of Rivaroxaban (BAY 59-7939) in Healthy Subjects. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 47, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upreti, V.V.; Wang, J.; Barrett, Y.C.; Byon, W.; Boyd, R.A.; Pursley, J.; LaCreta, F.P.; Frost, C.E. Effect of extremes of body weight on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety and tolerability of apixaban in healthy subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 76, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsam, S.J.; Patel, J.P.; Roberts, L.N.; Kavarthapu, V.; Patel, R.K.; Green, B.; Arya, R. The impact of body weight on rivaroxaban pharmacokinetics. Res. Pr. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 1, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liesenfeld, K.; Lehr, T.; Dansirikul, C.; Reilly, P.A.; Connolly, S.J.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Yusuf, S.; Wallentin, L.; Haertter, S.; Staab, A. Population pharmacokinetic analysis of the oral thrombin inhibitor dabigatran etexilate in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation from the RE-LY trial. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 2168–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Koretsune, Y.; Yasaka, M.; Inoue, H.; Kawai, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Uchiyama, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Ogawa, S. Randomized, Multicenter, Warfarin-Controlled Phase II Study of Edoxaban in Japanese Patients with Non-Valvular Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. J. 2012, 76, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyawat, K.; Caron, F.; Li, A.; Chai-Adisaksopha, C.; Lim, W.; Iorio, A.; Lopes, R.D.; Garcia, D.; Crowther, M.A. Association of body weight with efficacy and safety outcomes in phase III randomized controlled trials of direct oral anticoagulants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohnloser, S.H.; Fudim, M.; Alexander, J.H.; Wojdyla, D.M.; Ezekowitz, J.A.; Hanna, M.; Atar, D.; Hijazi, Z.; Bahit, M.C.; Al-Khatib, S.M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Apixaban versus Warfarin in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Extremes in Body Weight. Circulation 2019, 139, 2292–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushnir, M.; Choi, Y.; Eisenberg, R.; Rao, D.; Tolu, S.; Gao, J.; Mowrey, W.; Billett, H.H. Efficacy and safety of direct oral factor Xa inhibitors compared with warfarin in patients with morbid obesity: A single-centre, retrospective analysis of chart data. Lancet Haematol. 2019, 6, e359–e365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-R.; Choi, E.-K.; Park, C.S.; Han, K.-D.; Jung, J.-H.; Oh, S.; Lip, G.Y. Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation and Low Body Weight. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce, J.; Nguyen, N.T.; Hutter, M.; Sudan, R.; Morton, J.M. American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery estimation of bariatric surgery procedures in the United States, 2011-2014. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2015, 11, 1199–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yska, J.P.; van der Linde, S.; Tapper, V.V.; Apers, J.A.; Emous, M.; Totté, E.R.; Wilffert, B.; van Roon, E.N. Influence of Bariatric Surgery on the Use and Pharmacokinetics of Some Major Drug Classes. Obes. Surg. 2013, 23, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, K.A.; Beyer-Westendorf, J.; Davidson, B.L.; Huisman, M.V.; Sandset, P.M.; Moll, S. Use of direct oral anticoagulants in patients with obesity for treatment and prevention of venous thromboembolism: Updated communication from the ISTH SSC Subcommittee on Control of Anticoagulation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 1874–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottenstreich, A.; Barkai, A.; Arad, A.; Raccah, B.H.; Kalish, Y. The effect of bariatric surgery on direct-acting oral anticoagulant drug levels. Thromb. Res. 2018, 163, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakeam, H.A.; Al-Sanea, N. Effect of major gastrointestinal tract surgery on the absorption and efficacy of direct acting oral anticoagulants (DOACs). J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2017, 43, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, A.S.; Reynolds, K.; Yang, J.; Gupta, N.; Lenane, J.; Sung, S.H.; Harrison, T.N.; Liu, T.I.; Solomon, M.D. Association of Burden of Atrial Fibrillation with Risk of Ischemic Stroke in Adults with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klijn, C.J.; Paciaroni, M.; Berge, E.; Korompoki, E.; Kõrv, J.; Lal, A.; Putaala, J.; Werring, D.J. Antithrombotic treatment for secondary prevention of stroke and other thromboembolic events in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack and non-valvular atrial fibrillation: A European Stroke Organisation guideline. Eur. Stroke J. 2019, 4, 198–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciaroni, M.; Agnelli, G.; Caso, V.; Silvestrelli, G.; Seiffge, D.J.; Engelter, S.; De Marchis, G.M.; Polymeris, A.; Zedde, M.L.; Yaghi, S.; et al. Causes and Risk Factors of Cerebral Ischemic Events in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Treated with Non–Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants for Stroke Prevention. Stroke 2019, 50, 2168–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polymeris, A.A.; Meinel, T.R.; Oehler, H.; Hölscher, K.; Zietz, A.; Scheitz, J.F.; Nolte, C.H.; Stretz, C.; Yaghi, S.; Stoll, S.; et al. Aetiology, secondary prevention strategies and outcomes of ischaemic stroke despite oral anticoagulant therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 93, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinel, T.R.; Branca, M.; De Marchis, G.M.; Nedeltchev, K.; Kahles, T.; Bonati, L.; Arnold, M.; Heldner, M.R.; Jung, S.; Carrera, E.; et al. Prior Anticoagulation in Patients with Ischemic Stroke and Atrial Fibrillation. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 89, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inohara, T.; Xian, Y.; Liang, L.; Matsouaka, R.A.; Saver, J.L.; Smith, E.E.; Schwamm, L.H.; Reeves, M.J.; Hernandez, A.F.; Bhatt, D.L.; et al. Association of Intracerebral Hemorrhage among Patients Taking Non–Vitamin K Antagonist vs. Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants with In-Hospital Mortality. JAMA 2018, 319, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurogi, R.; Nishimura, K.; Nakai, M.; Kada, A.; Kamitani, S.; Nakagawara, J.; Toyoda, K.; Ogasawara, K.; Ono, J.; Shiokawa, Y.; et al. Comparing intracerebral hemorrhages associated with direct oral anticoagulants or warfarin. Neurology 2018, 90, e1143–e1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiffge, D.J.; De Marchis, G.M.; Koga, M.; Paciaroni, M.; Wilson, D.; Cappellari, M.; Macha, K.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Ambler, G.; Arihiro, S.; et al. Ischemic Stroke despite Oral Anticoagulant Therapy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 87, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ip, Y.M.B.; Lau, K.K.; Ko, H.; Lau, L.; Yao, A.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Yip, T.C.-F.; Leng, X.; Chan, H.; Chan, H.; et al. Association of Alternative Anticoagulation Strategies and Outcomes in Patients with Ischemic Stroke While Taking a Direct Oral Anticoagulant. Neurology 2023, 101, E358–E369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arba, F.; Piccardi, B.; Palumbo, V.; Biagini, S.; Galmozzi, F.; Iovene, V.; Giannini, A.; Testa, G.D.; Sodero, A.; Nesi, M.; et al. Blood–brain barrier leakage and hemorrhagic transformation: The Reperfusion Injury in Ischemic StroKe (RISK) study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 3147–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, U.; Koga, M.; Strbian, D.; Branca, M.; Abend, S.; Trelle, S.; Paciaroni, M.; Thomalla, G.; Michel, P.; Nedeltchev, K.; et al. Early versus Later Anticoagulation for Stroke with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 2411–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharobeam, A.; Lin, L.; Lam, C.; Garcia-Esperon, C.; Gawarikar, Y.; Patel, R.; Lee-Archer, M.; Wong, A.; Roizman, M.; Gilligan, A.; et al. Early anticoagulation in patients with stroke and atrial fibrillation is associated with fewer ischaemic lesions at 1 month: The ATTUNE study. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisullo, G.; Profice, P.; Brunetti, V.; Scala, I.; Bellavia, S.; Broccolini, A.; Caliandro, P.; Di Iorio, R.; Morosetti, R.; Pilato, F.; et al. Prospective Observational Study of Safety of Early Treatment with Edoxaban in Patients with Ischemic Stroke and Atrial Fibrillation (SATES Study). Brain Sci. 2020, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Steiner, T.; Caso, V.; Wahlgren, N.; Participants, F.T.E.-K.S. Recommendations from the ESO-Karolinska Stroke Update Conference, Stockholm 13–15 November 2016. Eur. Stroke J. 2017, 2, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, D.R., Jr.; Alkhouli, M.; Reddy, V. Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion for The Unmet Clinical Needs of Stroke Prevention in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, V.Y.; Doshi, S.K.; Kar, S.; Gibson, D.N.; Price, M.J.; Huber, K.; Horton, R.P.; Buchbinder, M.; Neuzil, P.; Gordon, N.T.; et al. 5-Year Outcomes After Left Atrial Appendage Closure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 2964–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmancik, P.; Herman, D.; Neuzil, P.; Hala, P.; Taborsky, M.; Kala, P.; Poloczek, M.; Stasek, J.; Haman, L.; Branny, M.; et al. Left Atrial Appendage Closure versus Direct Oral Anticoagulants in High-Risk Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 3122–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruff, C.T.; Giugliano, R.P.; Braunwald, E.; Hoffman, E.B.; Deenadayalu, N.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Camm, A.J.; Weitz, J.I.; Lewis, B.S.; Parkhomenko, A.; et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet 2014, 383, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xian, Y.; Zhang, S.; Inohara, T.; Grau-Sepulveda, M.; Matsouaka, R.A.; Peterson, E.D.; Piccini, J.P.; Smith, E.E.; Sheth, K.N.; Bhatt, D.L.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes Associated with Oral Anticoagulant Use among Patients Hospitalized with Intracerebral Hemorrhage. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2037438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollack, C.V.J.; Reilly, P.A.; Eikelboom, J.; Glund, S.; Verhamme, P.; Bernstein, R.A.; Dubiel, R.; Huisman, M.V.; Hylek, E.M.; Kamphuisen, P.W.; et al. Idarucizumab for Dabigatran Reversal. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demchuk, A.M.; Yue, P.; Zotova, E.; Nakamya, J.; Xu, L.; Jr, T.J.M.; Ohara, T.; Goldstein, J.N.; Middeldorp, S.; Verhamme, P.; et al. Hemostatic Efficacy and Anti-FXa (Factor Xa) Reversal with Andexanet Alfa in Intracranial Hemorrhage: ANNEXA-4 Substudy. Stroke 2021, 52, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-G.; Lip, G.Y.H. Anticoagulation Resumption after Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2018, 20, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennlert, J.; Overholser, R.; Asplund, K.; Carlberg, B.; Van Rompaye, B.; Wiklund, P.-G.; Eriksson, M. Optimal Timing of Anticoagulant Treatment after Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Stroke 2017, 48, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreuder, F.H.B.M.; van Nieuwenhuizen, K.M.; Hofmeijer, J.; Vermeer, S.E.; Kerkhoff, H.; Zock, E.; Luijckx, G.-J.; Messchendorp, G.P.; van Tuijl, J.; Bienfait, H.P.; et al. Apixaban versus no anticoagulation after anticoagulation-associated intracerebral haemorrhage in patients with atrial fibrillation in the Netherlands (APACHE-AF): A randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, D.A.; Fisher, D.A.; Mulder, H.; Wruck, L.; De Caterina, R.; Halvorsen, S.; Granger, C.B.; Held, C.; Wallentin, L.; Alexander, J.H.; et al. Gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with atrial fibrillation treated with Apixaban or warfarin: Insights from the Apixaban for Reduction in Stroke and Other Thromboembolic Events in Atrial Fibrillation (ARISTOTLE) trial. Am. Hear. J. 2019, 221, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.; Lee, S.-R.; Choi, E.-K.; Lee, E.; Jung, J.-H.; Han, K.-D.; Cha, M.-J.; Oh, S.; Lip, G.Y. Non–Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Prior Gastrointestinal Bleeding. Stroke 2021, 52, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.-Q.; Chen, X.-H.; Tian, X.-Y.; Li, L. Differences In Gastrointestinal Safety Profiles among Novel Oral Anticoagulants: Evidence from A Network Meta-Analysis. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 11, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, W.C.; Torre, C.O.; Man, K.K.; Stewart, H.M.; Seager, S.; Van Zandt, M.; Reich, C.; Li, J.; Brewster, J.; Lip, G.Y.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness and Safety between Apixaban, Dabigatran, Edoxaban, and Rivaroxaban among Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2022, 175, 1515–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapaskar, N.; Pang, A.; Werner, D.A.; Sengupta, N. Resuming Anticoagulation following Hospitalization for Gastrointestinal Bleeding Is Associated with Reduced Thromboembolic Events and Improved Mortality: Results from a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 66, 554–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witt, D.M. What to do after the bleed: Resuming anticoagulation after major bleeding. Hematology 2016, 2016, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, A.R.; Lyon, A.R.; López-Fernández, T.; López-Fernández, T.; Couch, L.S.; Couch, L.S.; Asteggiano, R.; Asteggiano, R.; Aznar, M.C.; Aznar, M.C.; et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines on cardio-oncology developed in collaboration with the European Hematology Association (EHA), the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ESTRO) and the International Cardio-Oncology Society (IC-OS). Eur. Hear. J. 2022, 43, 4229–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmakis, D.; Parissis, J.; Filippatos, G. Insights Into Onco-Cardiology. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnelli, G.; Becattini, C.; Meyer, G.; Muñoz, A.; Huisman, M.V.; Connors, J.M.; Cohen, A.; Bauersachs, R.; Brenner, B.; Torbicki, A.; et al. Apixaban for the Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism Associated with Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBane, R.D.; Wysokinski, W.E.; Le-Rademacher, J.G.; Zemla, T.; Ashrani, A.; Tafur, A.; Perepu, U.; Anderson, D.; Gundabolu, K.; Kuzma, C.; et al. Apixaban and dalteparin in active malignancy-associated venous thromboembolism: The ADAM VTE trial. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 18, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A.M.; Marshall, A.; Thirlwall, J.; Chapman, O.; Lokare, A.; Hill, C.; Hale, D.; Dunn, J.A.; Lyman, G.H.; Hutchinson, C.; et al. Comparison of an Oral Factor Xa Inhibitor with Low Molecular Weight Heparin in Patients with Cancer with Venous Thromboembolism: Results of a Randomized Trial (SELECT-D). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raskob, G.E.; van Es, N.; Verhamme, P.; Carrier, M.; Di Nisio, M.; Garcia, D.; Grosso, M.A.; Kakkar, A.K.; Kovacs, M.J.; Mercuri, M.F.; et al. Edoxaban for the Treatment of Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, M.V.; Magnocavallo, M.; Straito, M.; Piro, A.; Severino, P.; Iannucci, G.; Chimenti, C.; Mancone, M.; Della Rocca, D.G.; Forleo, G.B.; et al. Direct oral anticoagulants versus vitamin K antagonists in patients with atrial fibrillation and cancer a meta-analysis. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2020, 51, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Apixaban | Dabigatran | Edoxaban | Rivaroxaban | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Criteria | Dose | CrCl (mL/min) | Dose | CrCl (mL/min) | Dose | CrCl (mL/min) | Dose |
| Regular | 5 mg BID | >30 | 150 mg BID | >95 | NA | >50 | 20 mg QD |
| >30 (high bleeding risk) | 110 mg BID | ||||||
| 2/3:Age >80Cr > 1.5 mg/dL weight < 60 kg | 2.5 mg BID | 15–30 | 75 mg BID | 50–95 | 60 mg QD | 15–50 | 15 mg QD |
| Hemodialysisand: Age < 80 or weight > 60 kg | 5 mg BID | <15 | NA | 15–50 | 30 mg QD | <15 | NA |
| Study | Participants | Study Type | DOAC | Comparator | Inclusion Criteria | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yao X (2020) [20] | 34,569 patients divided by eGFR | Retrospective | apixaban, dabigatran, rivaroxaban | warfarin | eGFR ≥ 15 mL/min/1.73 m2 | DOACs were associated with comparative or better outcomes across all ranges of kidney function |
| Pokorney SD (2022) [21] | 154 hemodialysis patients | RCT | apixaban | warfarin | Hemodialysis | Inadequate power to draw conclusion |
| Reinecke H (2023) [22] | 97 hemodialysis patients | RCT | apixaban | phenprocoumon | Hemodialysis | No difference in safety or efficacy |
| Kuno T (2020) [24] | 71,877 hemodialysis patients | Meta-analysis | apixaban, dabigatran, rivaroxaban | warfarin | Hemodialysis | No difference in efficacy, apixaban had lower bleeding risk |
| Siontis KC (2018) [25] | 25,523 hemodialysis patients | Retrospective | apixaban | warfarin | Hemodialysis | No difference in stroke/thromboembolic events, apixaban had lower bleeding risk. Apixaban 5 mg bid showed lower rates of stroke/thromboembolic events/death with no difference in bleeding |
| Study | Participants | Study Type | DOAC | Comparator | Inclusion Criteria | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ng KH (2016) [32] [AVERROES] | 1898 patients age > 75 366 patients age > 85 | RCT | apixaban | aspirin | Age > 75 and unsuitable for VKA treatment | Apixaban treatment resulted in lower stroke rates without difference in major hemorrhage rates compared to aspirin |
| Halperin JL (2014) [33] [ROCKET AF] | 6229 patients age > 75 | RCT | rivaroxaban | warfarin | Age > 75 | Elderly patients had higher rates of stroke and major hemorrhage with no difference between rivaroxaban and warfarin |
| Kato ET el al. (2016) [34] [ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48] | 8474 patients age > 75 | RCT | edoxaban | warfarin | Age > 75 | Same rates of stroke/systemic embolism with lower bleeding rate in the edoxaban group |
| Eikelboom JW et al. (2011) [36] [RE-LY] | 7248 patients age > 75 | RCT | dabigatran (150 mg, 110 mg) | warfarin | Age > 75 | Both doses of dabigatran were associated with lower ICHand higher extra-cranial hemorrhage compared to warfarin |
| Okumura K et al. (2020) [38] | 984 patients age > 80 | RCT | low-dose edoxaban | placebo | Age > 80 and unsuitable for OAC in standard dose | Low-dose edoxaban was superior to placebo in preventing stroke or systemic embolism without a significant elevation in major bleeding |
| Study | Participants | DOAC | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barsam J et al. (2017) [59] | 101 patients | rivaroxaban | Weight had no effect on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics |
| Kubitza D et al. (2007) [57] | 48 healthy subjects divided to groups by weight: <50 kg, 70–80 kg, >120 kg | rivaroxaban | Cmax of rivaroxaban was unaffected in subjects > 120 kg but was increased by 24% in subjects < 50 kg resulting in 15% increase in PT. AUC was unaffected by weight |
| Liesenfeld KH (2011) [60] | 9522 patients | dabigatran | Weight influenced the apparent volume of distribution with no effect on the AUC |
| Upreti VV et al. (2013) [58] | 54 healthy subjects divided to groups by weight:<50 kg, 65–85 kg, >120 kg | apixaban | Low body-weight group had 27% higher Cmax and 20% higher AUC (0, ∞). High body-weight group had 31% lower Cmax and 23% lower AUC (0, ∞). |
| Yamashita et al. (2012) [61] | 536 patients | edoxaban | Cmin was higher in patients < 60 kg |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kessler, A.; Kolben, Y.; Puris, G.; Ellis, M.; Alperin, M.; Simovich, V.; Lerman Shivek, H.; Muszkat, M.; Maaravi, Y.; Biton, Y. Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Special Patient Populations. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010216
Kessler A, Kolben Y, Puris G, Ellis M, Alperin M, Simovich V, Lerman Shivek H, Muszkat M, Maaravi Y, Biton Y. Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Special Patient Populations. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(1):216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010216
Chicago/Turabian StyleKessler, Asa, Yotam Kolben, Gal Puris, Martin Ellis, Mordechai Alperin, Vered Simovich, Hila Lerman Shivek, Mordechai Muszkat, Yoram Maaravi, and Yitschak Biton. 2024. "Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Special Patient Populations" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 1: 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010216
APA StyleKessler, A., Kolben, Y., Puris, G., Ellis, M., Alperin, M., Simovich, V., Lerman Shivek, H., Muszkat, M., Maaravi, Y., & Biton, Y. (2024). Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Special Patient Populations. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(1), 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010216








