Pathogenic Variant Frequencies in Hereditary Haemorrhagic Telangiectasia Support Clinical Evidence of Protection from Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
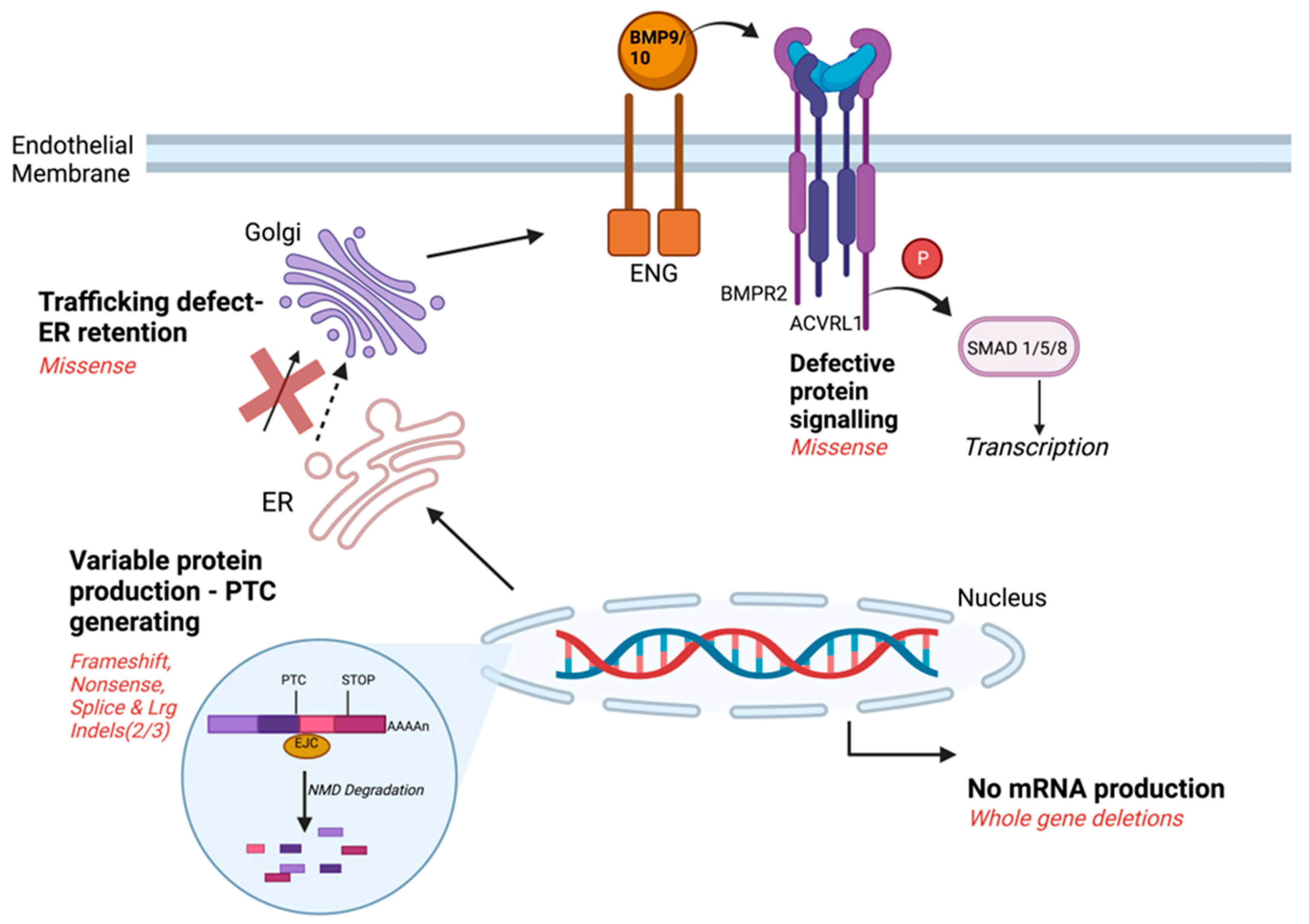
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Populations
2.1.1. Series 1: Hammersmith Hospital (Imperial) 2021–2023 Series
2.1.2. Series 2: Non-Overlapping Hammersmith Hospital (Imperial) 1992–1020 Series
2.1.3. Series 3: International HHT Mutation Database
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HHT Variant Distribution Patterns
3.1.1. Series 1
3.1.2. Series 2
3.1.3. HHT Mutation Database
3.1.4. Combined Analyses
3.2. HHT Variant Classification Patterns
3.3. Non-Biological Considerations
3.4. Mutational Hot Spot Examinations
3.5. Selective Pressure Considerations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Legg, W. A case of Haemophilia complicated with Multiple Naevi. Lancet 1876, 2, 856–857. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, H.G. Epistaxis as an indication of impaired nutrition, and of degeneration of the vascular system. Med. Mirror 1864, 1, 769–781. [Google Scholar]
- Babington, B.G. Hereditary epistaxis. Lancet 1865, 86, 362–363. [Google Scholar]
- Rendu, H. Épistaxis répetées chez un sujet porteur de petits angiomes cutanés et muquez. Gaz. Des. Hop. 1896, 135, 1322–1323. [Google Scholar]
- Osler, W. On a family form of recurring epistaxis, associated with multiple telangiectases of the skin and mucous membranes. Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1901, 12, 333–337. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, F. Multiple hereditary developmental angiomata (telangiectases) of the skin and mucous membranes associated with recurring haemorrhages. Lancet 1907, 2, 160–162. [Google Scholar]
- Renshaw, J.F. Multiple hemorrhagic telangiectasis with special reference to gastroscopic appearance. Clevel. Clin. Quart. 1936, 6, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, W. Cavernous haemangioma of the lung. Thorax 1947, 2, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundles, R.W. Hemorrhagic telangiectasia with pulmonary artery aneurysm: Case report. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1945, 210, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranniger, K.; Ödman, P. Angiographischer Nachweis, multipler arteriovenöser Anastemosen in der Leber bei einem Patienten mit familiärer Telangiektasie. Fortschritte Auf Dem Geb. Der Röntgenstrahlen Und Der Neuen Bildgeb. Verfahr. 1963, 93, 768. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.L.; Lineback, M.I. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, Nine cases in one negro family with special reference to hepatic lesions. Am. J. Med. 1954, 17, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, C.R.; Lovrien, E.W.; Reiss, J. Central nervous system arteriovenous malformations in multiple generations of a family with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Clin. Genet. 1977, 12, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Román, G.; Fisher, M.; Perl, D.P.; Poser, C.M. Neurological manifestations of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber Disease): Report of 2 cases and review of the literature. Ann. Neurol. 1978, 4, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobel, D.; Norman, D. CNS manifestations of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Am. J. Neuoradiol. 1984, 5, 569–573. [Google Scholar]
- Shovlin, C.L.; Guttmacher, A.E.; Buscarini, E.; Faughnan, M.E.; Hyland, R.H.; Westermann, C.J.; Kjeldsen, A.D.; Plauchu, H. Diagnostic criteria for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome). Am. J. Med. Genet. 2000, 91, 66–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttmacher, A.E.; Marchuk, D.A.; White, R.I., Jr. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plauchu, H.; de Chadarévian, J.-P.; Bideau, A.; Robert, J.-M. Age-related profile of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia in an epidemiologically recruited population. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1989, 32, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shovlin, C.L. Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia: Pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Blood Rev. 2010, 24, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VASCERN HHT Working Group. Orphanet Definition of Hereditary Haemorrhagic Telangiectasia. 2019. Available online: https://www.orpha.net/consor/www/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?lng=EN&Expert=774 (accessed on 19 December 2023).
- Shovlin, C.L.; Condliffe, R.; Donaldson, J.W.; Kiely, D.G.; Wort, S.J.; British Thoracic Society. British Thoracic Society Clinical Statement on Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations. Thorax 2017, 72, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shovlin, C.L.; Buscarini, E.; Sabbà, C.; Mager, H.J.; Kjeldsen, A.D.; Pagella, F.; Sure, U.; Ugolini, S.; Torring, P.M.; Suppressa, P.; et al. The European Rare Disease Network for HHT Frameworks for management of hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia in general and speciality care. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2022, 65, 104370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faughnan, M.E.; Mager, J.J.; Hetts, S.W.; Palda, V.A.; Lang-Robertson, K.; Buscarini, E.; Deslandres, E.; Kasthuri, R.S.; Lausman, A.; Poetker, D.; et al. Second International Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topiwala, K.K.; Patel, S.D.; Saver, J.L.; Streib, C.D.; Shovlin, C.L. Ischemic Stroke and Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review. Neurology 2022, 98, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Vascular diseases of the liver. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 179–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Hülsbeck, S.; Marques, L.; Maleux, G.; Osuga, K.; Pelage, J.P.; Wohlgemuth, W.A.; Andersen, P.E. CIRSE Standards of Practice on Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 43, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAllister, K.A.; Grogg, K.M.; Johnson, D.W.; Gallione, C.J.; Baldwin, M.A.; Jackson, C.E.; Helmbold, E.A.; Markel, D.S.; McKinnon, W.C.; Murrel, J.; et al. Endoglin, a TGF-β binding protein of endothelial cells, is the gene for hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia type 1. Nat. Genet. 1994, 8, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.W.; Berg, J.N.; Baldwin MAGallione, C.J.; Marondel, I.; Yoon, S.-J.; Stenzel, T.T.; Speer, M.; Pericak-Vance, M.A.; Diamond, A.; Guttmacher, A.E.; et al. Mutations in the activin receptor–like kinase 1 gene in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2. Nat. Genet. 1996, 13, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrana, J.L.; Attisano, L.; Wieser, R.; Ventura, F.; Massague, J. Mechanism of activation of the TGF-β receptor. Nature 1994, 370, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, C.; Das, P.; Finelli, A.L.; Townsend, S.R.; Sun, C.Y.; Baird, S.E.; Padgett, R.W. Caenorhabditis elegans genes sma-2, sma-3, and sma-4 define a conserved family of transforming growth factor beta pathway components. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekelsky, J.J.; Newfeld, S.J.; Raftery, L.A.; Chartoff, E.H.; Gelbart, W.M. Genetic characterization and cloning of mothers against dpp, a gene required for decapentaplegic function in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1995, 139, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derynck, R.; Gelbart, W.M.; Harland, R.M.; Heldin, C.H.; Kern, S.E.; Massagué, J.; Melton, D.A.; Mlodzik, M.; Padgett, R.W.; Roberts, A.B.; et al. Nomenclature: Vertebrate mediators of TGFbeta family signals. Cell 1996, 87, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallione, C.J.; Repetto, G.M.; Legius, E.; Rustgi, A.K.; Schelley, S.L.; Tejpar, S.; Mitchell, G.; Drouin, E.; Westermann, C.J.; Marchuk, D.A. A combined syndrome of juvenile polyposis and hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia associated with mutations in MADH4 (SMAD4). Lancet 2004, 363, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, L.; Mallet, C.; Mazerbourg, S.; Feige, J.J.; Bailly, S. Identification of BMP9 and BMP10 as functional activators of the orphan activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1) in endothelial cells. Blood 2007, 109, 1953–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townson, S.A.; Martinez-Hackert, E.; Greppi, C.; Lowden, P.; Sako, D.; Liu, J.; Ucran, J.A.; Liharska, K.; Underwood, K.W.; Seehra, J.; et al. Specificity and structure of a high affinity activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1) signaling complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 27313–27325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Bokhove, M.; Croci, R.; Zamora-Caballero, S.; Han, L.; Letarte, M.; de Sanctis, D.; Jovine, L. Structural Basis of the Human Endoglin-BMP9 Interaction: Insights into BMP Signaling and HHT1. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1917–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooderchak-Donahue, W.L.; McDonald, J.; O’Fallon, B.; Upton, P.D.; Li, W.; Roman, B.L.; Young, S.; Plant, P.; Fülöp, G.T.; Langa, C.; et al. BMP9 mutations cause a vascular-anomaly syndrome with phenotypic overlap with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandar, S.; Graves, T.J.; Shimonty, A.; Kerr, K.; Kilner, J.; Xiao, S.; Slade, R.; Sroya, M.; Alikian, M.; Curetean, E.; et al. Identification and validation of a novel pathogenic variant in GDF2 (BMP9) responsible for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia and pulmonary arteriovenous malformations. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2022, 188, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysal, M.; Demir, S.; Ümit, E.G.; Gürkan, H.; Baş, V.; Karaman Gülsaran, S.; Demirci, U.; Kırkızlar, H.O.; Demir, A.M. Genetic Diagnosis of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: Four Novel Pathogenic Variations in Turkish Patients. Balk. Med. J. 2019, 37, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Variant analysis in Chinese families with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenighofer, M.; Parzefall, T.; Frohne, A.; Allen, M.; Unterberger, U.; Laccone, F.; Schoefer, C.; Frei, K.; Lucas, T. Spectrum of Novel Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia Variants in an Austrian Patient Cohort. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 12, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutize, T.T.; Seedat, R.Y.; Ploos van Amstel, J.K.; Mager, J.J.; Brown, S.C.; Gebremariam, F.; Coetzee, M.J. The clinical and genetic features of hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) in central South Africa-three novel pathogenic variants. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 9967–9972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, R.; Añón, S.; Salazar-Mendiguchía, J.; Riera-Mestre, A.; RiHHTa Investigators of the Rare Diseases Working Group from the Spanish Society of Internal Medicine. Current HHT genetic overview in Spain and its phenotypic correlation: Data from RiHHTa registry. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 138. [Google Scholar]
- Kitayama, K.; Ishiguro, T.; Komiyama, M.; Morisaki, T.; Morisaki, H.; Minase, G.; Hamanaka, K.; Miyatake, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Kato, M.; et al. Mutational and clinical spectrum of Japanese patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. BMC Med. Genom. 2021, 14, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Major, T.; Bereczky, Z.; Gindele, R.; Balogh, G.; Rácz, B.; Bora, L.; Kézsmárki, Z.; Brúgós, B.; Pfliegler, G. Current Status of Clinical and Genetic Screening of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia Families in Hungary. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.G.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, M.J.; Moon, E.H.; Oh, J.H.; Park, J.W.; Cha, H.E.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Chung, J.W.; et al. Genetic Variants and Clinical Phenotypes in Korean Patients with Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 14, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shovlin, C.L.; Almaghlouth, F.I.; Alsafi, A.; Coote, N.; Rennie, C.; Wallace, G.M.; Govani, F.S.; Genomics England Research Consortium. Updates on diagnostic criteria for hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia in the light of whole genome sequencing of ‘gene-negative’ individuals recruited to the 100 000 Genomes Project. J. Med. Genet. 2023; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shovlin, C.L.; Patel, D.; Bielowka, A.; Ledermann, J.A.; Modarresi, A.; Genomics England Research Consortium; Bernabeu-Herrero, M.E.; Aldred, M.A.; Alsafi, A. MEK 1 inhibition and bleeding in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Br. J. Haematol. 2023; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.; Sharma, L.; Alsafi, A.; Shovlin, C.L. Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations may be the only clinical criterion present in genetically confirmed hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Thorax 2022, 77, 628–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buscarini, E.; Leandro, G.; Conte, D.; Danesino, C.; Daina, E.; Manfredi, G.; Lupinacci, G.; Brambilla, G.; Menozzi, F.; De Grazia, F.; et al. Natural history and outcome of hepatic vascular malformations in a large cohort of patients with hereditary hemorrhagic teleangiectasia. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 2166–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldsen, A.D.; Vase, P.; Green, A. Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia: A population-based study of prevalence and mortality in Danish patients. J. Intern. Med. 1999, 245, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldsen, A.D.; Kjeldsen, J. Gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livesey, J.A.; Manning, R.A.; Meek, J.H.; Jackson, J.E.; Kulinskaya, E.; Laffan, M.A.; Shovlin, C.L. Low serum iron levels are associated with elevated plasma levels of coagulation factor VIII and pulmonary emboli/deep venous thromboses in replicate cohorts of patients with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Thorax 2012, 67, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shovlin, C.L.; Chamali, B.; Santhirapala, V.; Livesey, J.A.; Angus, G.; Manning, R.; Laffan, M.A.; Meek, J.; Tighe, H.C.; Jackson, J.E. Ischaemic strokes in patients with pulmonary arteriovenous malformations and hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Associations with iron deficiency and platelets. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shovlin, C.L.; Gilson, C.; Busbridge, M.; Patel, D.; Shi, C.; Dina, R.; Abdulla, F.N.; Awan, I. Can Iron Treatments Aggravate Epistaxis in Some Patients with Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia? Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 2468–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shovlin, C.L.; Patel, T.; Jackson, J.E. Embolisation of PAVMs reported to improve nosebleeds by a subgroup of patients with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. ERJ Open Res. 2016, 2, 00035-2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boother, E.J.; Brownlow, S.; Tighe, H.C.; Bamford, K.B.; Jackson, J.E.; Shovlin, C.L. Cerebral Abscess Associated with Odontogenic Bacteremias, Hypoxemia, and Iron Loading in Immunocompetent Patients with Right-to-Left Shunting through Pulmonary Arteriovenous Malformations. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhtar, G.; Shovlin, C.L. Unsupervised machine learning algorithms identify expected haemorrhage relationships but define unexplained coagulation profiles mapping to thrombotic phenotypes in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. EJHaem 2023, 4, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjeldsen, A.; Aagaard, K.S.; Tørring, P.M.; Möller, S.; Green, A. 20-year follow-up study of Danish HHT patients-survival and causes of death. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2016, 11, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Gussem, E.M.; Kroon, S.; Hosman, A.E.; Kelder, J.C.; Post, M.C.; Snijder, R.J.; Mager, J.J. Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT) and Survival: The Importance of Systematic Screening and Treatment in HHT Centers of Excellence. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbà, C.; Pasculli, G.; Suppressa, P.; D’Ovidio, F.; Lenato, G.M.; Resta, F.; Assennato, G.; Guanti, G. Life expectancy in patients with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. J. Assoc. Physicians 2006, 99, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosman, A.E.; Devlin, H.L.; Silva, B.M.; Shovlin, C.L. Specific cancer rates may differ in patients with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia compared to controls. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2013, 8, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.W.; Murray, K.; Lucas, F.L.; Fairfield, K.; Miller, H.; Brooks, P.; Vary, C.P. Improved survival outcomes in cancer patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shovlin, C.L.; Awan, I.; Cahilog, Z.; Abdulla, F.N.; Guttmacher, A.E. Reported cardiac phenotypes in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia emphasize burdens from arrhythmias, anemia and its treatments, but suggest reduced rates of myocardial infarction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 215, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letteboer, T.G.; Mager, J.J.; Snijder, R.J.; Koeleman, B.P.; Lindhout, D.; Ploos van Amstel, J.K.; Westermann, C.J. Genotype-phenotype relationship in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. J. Med. Genet. 2006, 43, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayrak-Toydemir, P.; McDonald, J.; Markewitz, B.; Lewin, S.; Miller, F.; Chou, L.S.; Gedge, F.; Tang, W.; Coon, H.; Mao, R. Genotype-phenotype correlation in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Mutations and manifestations. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2006, 140, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesca, G.; Olivieri, C.; Burnichon, N.; Pagella, F.; Carette, M.F.; Gilbert-Dussardier, B.; Goizet, C.; Roume, J.; Rabilloud, M.; Saurin, J.C.; et al. Genotype-phenotype correlations in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Data from the French-Italian HHT network. Genet. Med. 2007, 9, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbà, C.; Pasculli, G.; Lenato, G.M.; Suppressa, P.; Lastella, P.; Memeo, M.; Dicuonzo, F.; Guant, G. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Clinical features in ENG and ALK1 mutation carriers. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letteboer, T.G.; Mager, H.J.; Snijder, R.J.; Lindhout, D.; Ploos van Amstel, H.K.; Zanen, P.; Westermann, K.J. Genotype-phenotype relationship for localization and age distribution of telangiectases in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2008, 146, 2733–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzinou, M.; Clermont, F.F.; Letteboer, T.G.; Kim, J.H.; Espejel, S.; Harradine, K.A.; Arbelaez, J.; Luu, M.T.; Roy, R.; Quigley, D.; et al. Mouse and human strategies identify PTPN14 as a modifier of angiogenesis and hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, K.; Freimuth, J.; Meyer, D.S.; Lee, M.M.; Tochimoto-Okamoto, A.; Benzinou, M.; Clermont, F.F.; Wu, G.; Roy, R.; Letteboer, T.G.; et al. Genetic variants of Adam17 differentially regulate TGFβ signaling to modify vascular pathology in mice and humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7723–7728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shovlin, C.L.; Simeoni, I.; Downes, K.; Frazer, Z.C.; Megy, K.; Bernabeu-Herrero, M.E.; Shurr, A.; Brimley, J.; Patel, D.; Kell, L.; et al. Mutational and phenotypic characterization of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Blood 2020, 136, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, K.E.; Onabanjo, E.; Brownlow, S.; Nur, F.; Olupona, K.; Fakayode, K.; Sroya, M.; Thomas, G.A.; Ferguson, T.; Redhead, J.; et al. Whole genome sequences discriminate hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia phenotypes by non-HHT deleterious DNA variation. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 3956–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabeu, C.; Bayrak-Toydemir, P.; McDonald, J.; Letarte, M. Potential Second-Hits in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snellings, D.A.; Gallione, C.J.; Clark, D.S.; Vozoris, N.T.; Faughnan, M.E.; Marchuk, D.A. Somatic Mutations in Vascular Malformations of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia Result in Bi-allelic Loss of ENG or ACVRL1. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 105, 894–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernabeu-Herrero, M.E.; Patel, D.; Bielowka, A.; Chaves Guerrero, P.; Maciniak, S.J.; Noseda, M.; Aldred, M.A.; Shovlin, C.L. Heterozygous transcriptional signatures unmask variable premature termination codon (PTC) burden alongside pathway-specific adaptations in blood outgrowth endothelial cells from patients with nonsense DNA variants causing hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. BioRxiv 2023. Available online: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.12.05.471269v2 (accessed on 19 December 2023).
- Xiao, S.; Kai, Z.; Murphy, D.; Li, D.; Patel, D.; Bielowka, A.M.; Bernabeu-Herrero, M.E.; Abdulmogith, A.; Mumford, A.D.; Westbury, S.K.; et al. Functional filter for whole-genome sequencing data identifies HHT and stress-associated non-coding SMAD4 polyadenylation site variants >5 kb from coding DNA. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2023, 110, 1903–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarley, S.C.; Murphy, D.A.; Thompson, J.; Shovlin, C.L. Pharmacogenomic considerations for anticoagulant prescription in patients with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govani, F.S.; Giess, A.; Mollet, I.G.; Begbie, M.E.; Jones, M.D.; Game, L.; Shovlin, C.L. Directional next-generation RNA sequencing and examination of premature termination codon mutations in endoglin/hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Mol. Syndromol. 2013, 4, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricard, N.; Bidart, M.; Mallet, C.; Lesca, G.; Giraud, S.; Prudent, R.; Feige, J.J.; Bailly, S. Functional analysis of the BMP9 response of ALK1 mutants from HHT2 patients: A diagnostic tool for novel ACVRL1 mutations. Blood 2010, 116, 1604–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hume, A.N.; John, A.; Akawi, N.A.; Al-Awadhi, A.M.; Al-Suwaidi, S.S.; Al-Gazali, L.; Ali, B.R. Retention in the endoplasmic reticulum is the underlying mechanism of some hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2 ALK1 missense mutations. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 373, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaa El Din, F.; Patri, S.; Thoreau, V.; Rodriguez-Ballesteros, M.; Hamade, E.; Bailly, S.; Gilbert-Dussardier, B.; Abou Merhi, R.; Kitzis, A. Functional and splicing defect analysis of 23 ACVRL1 mutations in a cohort of patients affected by Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilbeck, K.; Lewis, S.E.; Mungall, C.J.; Yandell, M.; Stein, L.; Durbin, R.; Ashburner, M. The Sequence Ontology: A tool for the unification of genome annotations. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, R44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NHS England. National Genomic Test Directory. 20 September 2023. Available online: https://www.england.nhs.uk/publication/national-genomic-test-directories/ (accessed on 19 December 2023).
- Sharma, L.; Almaghlouth, F.; Mckernan, H.; Springett, J.; Tighe, H.C.; Genomics England Research Consortium; Shovlin, C.L. Iron deficiency responses and integrated compensations in patients according to hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia ACVRL1, ENG and SMAD4 genotypes. Haematologica, 2023; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telangiectasia Self Help Group 2010 Fact Sheet. Available online: http://www.telangiectasia.co.uk/Telangiectasia%202010%20Fact%20Sheet%20Part%201%20of%202.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2010).
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Benson, M.; Brown, G.R.; Chao, C.; Chitipiralla, S.; Gu, B.; Hart, J.; Hoffman, D.; Jang, W.; et al. ClinVar: Improving access to variant interpretations and supporting evidence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1062–D1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Centre for Biotechnology Information. Homo Sapiens Activin A Receptor like Type 1 (ACVRL1), Transcript Variant 1. NCBI Reference Sequence: NM_000020.3. 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/NM_000020.3 (accessed on 19 December 2023).
- Abdalla, S.A.; Geisthoff, U.W.; Bonneau, D.; Plauchu, H.; McDonald, J.; Kennedy, S.; Faughnan, M.E.; Letarte, M. Visceral manifestations in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalla, S.A.; Gallione, C.J.; Barst, R.J.; Horn, E.M.; Knowles, J.A.; Marchuk, D.A.; Letarte, M.; Morse, J.H. Primary pulmonary hypertension in families with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 23, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalla, S.A.; Cymerman, U.; Rushlow, D.; Chen, N.; Stoeber, G.P.; Lemire, E.G.; Letarte, M. Novel mutations and polymorphisms in genes causing hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Hum. Mutat. 2005, 25, 320–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayrak-Toydemir, P.; Mao, R.; Lewin, S.; McDonald, J. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: An overview of diagnosis and management in the molecular era for clinicians. Genet. Med. 2004, 6, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.N.; Gallione, C.J.; Stenzel, T.T.; Johnson, D.W.; Allen, W.P.; Schwartz, C.E.; Jackson, C.E.; Porteous, M.E.; Marchuk, D.A. The activin receptor-like kinase 1 gene: Genomic structure and mutations in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 2. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1997, 61, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusgaard, K.; Kjeldsen, A.D.; Poulsen, L.; Moss, H.; Vase, P.; Rasmussen, K.; Kruse, T.A.; Hørder, M. Mutations in endoglin and in activin receptor-like kinase 1 among Danish patients with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. Clin. Genet. 2004, 66, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canzonieri, C.; Centenara, L.; Ornati, F.; Pagella, F.; Matti, E.; Alvisi, C.; Danesino, C.; Perego, M.; Olivieri, C. Endoscopic evaluation of gastrointestinal tract in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia and correlation with their genotypes. Genet. Med. 2014, 16, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-L, A.; Sanz-Rodriguez, F.; Zarrabeitia, R.; Pérez-Molino, A.; Hebbel, R.P.; Nguyen, J.; Bernabéu, C.; Botella, L.M. Blood outgrowth endothelial cells from Hereditary Haemorrhagic Telangiectasia patients reveal abnormalities compatible with vascular lesions. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 68, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-L, A.; Sanz-Rodriguez, F.; Zarrabeitia, R.; Perez-Molino, A.; Morales, C.; Restrepo, C.M.; Ramirez, J.R.; Coto, E.; Lenato, G.M.; Bernabeu, C.; et al. Mutation study of Spanish patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia and expression analysis of Endoglin and ALK1. Hum. Mutat. 2006, 27, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontalba, A.; Fernandez-L, A.; García-Alegria, E.; Albiñana, V.; Garrido-Martin, E.M.; Blanco, F.J.; Zarrabeitia, R.; Perez-Molino, A.; Bernabeu-Herrero, M.E.; Ojeda, M.L.; et al. Mutation study of Spanish patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. BMC Med. Genet. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Gedge, F.; McDonald, J.; Phansalkar, A.; Chou, L.S.; Calderon, F.; Mao, R.; Lyon, E.; Bayrak-Toydemir, P. Clinical and analytical sensitivities in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia testing and a report of de novo mutations. J. Mol. Diagn. 2007, 9, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.E.; Flanagan, J.A.; Sankelo, M.; Abdalla, S.A.; Rowell, J.; Machado, R.D.; Elliott, C.G.; Robbins, I.M.; Olschewski, H.; McLaughlin, V.; et al. Molecular and functional analysis identifies ALK-1 as the predominant cause of pulmonary hypertension related to hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjeldsen, A.D.; Brusgaard, K.; Poulsen, L.; Kruse, T.; Rasmussen, K.; Green, A.; Vase, P. Mutations in the ALK-1 gene and the phenotype of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia in two large Danish families. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2001, 98, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehl, H.K.; Caselitz, M.; Hasenkamp, S.; Wagner, S.; El-Harith, E.H.A.; Manns, M.P.; Stuhrmann, M. Hepatic manifestation is associated with ALK1 in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Identification of five novel ALK1 and one novel ENG mutations. Hum. Mutat. 2005, 25, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenato, G.M.; Lastella, P.; Di Giacomo, M.C.; Resta, N.; Suppressa, P.; Pasculli, G.; Sabbà, C.; Guanti, G. DHPLC-based mutation analysis of ENG and ALK-1 genes in HHT Italian population. Hum. Mutat. 2006, 27, 213–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesca, G.; Plauchu, H.; Coulet, F.; Lefebvre, S.; Plessis, G.; Odent, S.; Rivière, S.; Leheup, B.; Goizet, C.; Carette, M.F.; et al. French Rendu-Osler Network. Molecular screening of ALK1/ACVRL1 and ENG genes in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia in France. Hum. Mutat. 2004, 23, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesca, G.; Burnichon, N.; Raux, G.; Tosi, M.; Pinson, S.; Marion, M.J.; Babin, E.; Gilbert-Dussardier, B.; Rivière, S.; Goizet, C.; et al. French Rendu-Osler Network. Distribution of ENG and ACVRL1 (ALK1) mutations in French HHT patients. Hum. Mutat. 2006, 27, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.D.; Wu, J.Y.; Hsu, H.B.; Tsai, F.J.; Lee, C.C.; Tsai, C.H. Mutation analysis of a family with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia associated with hepatic arteriovenous malformation. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2001, 100, 817–819. [Google Scholar]
- Letteboer, T.G.; Zewald, R.A.; Kamping, E.J.; de Haas, G.; Mager, J.J.; Snijder, R.J.; Lindhout, D.; Hennekam, F.A.; Westermann, C.J.; Ploos van Amstel, J.K. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: ENG and ALK-1 mutations in Dutch patients. Hum. Genet. 2005, 116, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.; Damjanovich, K.; Millson, A.; Wooderchak, W.; Chibuk, J.M.; Stevenson, D.A.; Gedge, F.; Bayrak-Toydemir, P. Molecular diagnosis in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Findings in a series tested simultaneously by sequencing and deletion/duplication analysis. Clin. Genet. 2011, 79, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, T.; Faughnan, M.E.; Krings, T.; Chakinala, M.; Gossage, J.R.; Young, W.L.; Kim, H.; Pourmohamad, T.; Henderson, K.J.; Schrum, S.D.; et al. Brain arteriovenous malformations associated with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Gene-phenotype correlations. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2012, 158A, 2829–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, C.; Lanzarini, L.; Pagella, F.; Semino, L.; Corno, S.; Valacca, C.; Plauchu, H.; Lesca, G.; Barthelet, M.; Buscarini, E.; et al. Echocardiographic screening discloses increased values of pulmonary artery systolic pressure in 9 of 68 unselected patients affected with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Genet. Med. 2006, 8, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, C.; Pagella, F.; Semino, L.; Lanzarini, L.; Valacca, C.; Pilotto, A.; Corno, S.; Scappaticci, S.; Manfredi, G.; Buscarini, E.; et al. Analysis of ENG and ACVRL1 genes in 137 HHT Italian families identifies 76 different mutations (24 novel). Comparison with other European studies. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 52, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankelo, M.; Halme, M.; Laitinen, T.; Mattila, P.S. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia type 1 and 2 mutations in Finland. Acta Otolaryngol. 2008, 11, 1238–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Rodriguez, F.; Fernandez-L, A.; Zarrabeitia, R.; Perez-Molino, A.; Ramírez, J.R.; Coto, E.; Bernabeu, C.; Botella, L.M. Mutation analysis in Spanish patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: Deficient endoglin up-regulation in activated monocytes. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 2003–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, C.; Geisthoff, U.; Lux, A.; Kupka, S.; Zenner, H.P.; Blin, N.; Pfister, M. High frequency of ENG and ALK1/ACVRL1 mutations in German HHT patients. Hum. Mutat. 2005, 25, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trembath, R.C.; Thomson, J.R.; Machado, R.D.; Morgan, N.V.; Atkinson, C.; Winship, I.; Simonneau, G.; Galie, N.; Loyd, J.E.; Humbert, M.; et al. Clinical and molecular genetic features of pulmonary hypertension in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, L.E.; Folz, B.J.; Argyriou, L.; Twelkemeyer, S.; Teske, U.; Geisthoff, U.W.; Werner, J.A.; Engel, W.; Nayernia, K. Mutation analysis in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia in Germany reveals 11 novel ENG and 12 novel ACVRL1/ALK1 mutations. Clin. Genet. 2006, 69, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.S.; Yi, Y.; Peng, H.L.; Shen, J.K.; Xie, D.H.; He, X.B. Clinical phenotypes, ALK1 gene mutation and level of related plasma proteins in Chinese hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Chin. Med. J. 2004, 117, 808–812. [Google Scholar]
- Nassar, L.R.; Barber, G.P.; Benet-Pagès, A.; Casper, J.; Clawson, H.; Diekhans, M.; Fischer, C.; Gonzalez, J.N.; Hinrichs, A.S.; Lee, B.T.; et al. The UCSC Genome Browser database: 2023 update. Nucl. Acid Res. 2023, 51, D1188–D1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FANTOM Consortium and the RIKEN PMI and CLST (DGT); Forrest, A.R.; Kawaji, H.; Rehli, M.; Baillie, J.K.; de Hoon, M.J.; Haberle, V.; Lassmann, T.; Kulakovskiy, I.V.; Lizio, M.; et al. A promoter-level mammalian expression atlas. Nature 2014, 507, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lek, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Minikel, E.V.; Samocha, K.E.; Banks, E.; Fennell, T.; O’Donnell-Luria, A.H.; Ware, J.S.; Hill, A.J.; Cummings, B.B.; et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60706 humans. Nature 2016, 536, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piel, F.B.; Patil, A.P.; Howes, R.E.; Nyangiri, O.A.; Gething, P.W.; Williams, T.N.; Weatherall, D.J.; Hay, S.I. Global distribution of the sickle cell gene and geographical confirmation of the malaria hypothesis. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, M.; Libert, F.; Doranz, B.J.; Rucker, J.; Liesnard, C.; Farber, C.M.; Saragosti, S.; Lapoumeroulie, C.; Cognaux, J.; Forceille, C.; et al. Resistance to HIV-1 infection in caucasian individuals bearing mutant alleles of the CCR-5 chemokine receptor gene. Nature 1996, 382, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotimi, C.N.; Bentley, A.R.; Doumatey, A.P.; Chen, G.; Shriner, D.; Adeyemo, A. The genomic landscape of African populations in health and disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, R225–R236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Schleer, H.; Park, H.; Jang, E.; Boyer, M.; Tao, B.; Gamez-Mendez, A.; Singh, A.; Folta-Stogniew, E.; Zhang, X.; et al. Genetic or therapeutic neutralization of ALK1 reduces LDL transcytosis and atherosclerosis in mice. Nat. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 2, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, B.; Kraehling, J.R.; Ghaffari, S.; Ramirez, C.M.; Lee, S.; Fowler, J.W.; Lee, W.L.; Fernandez-Hernando, C.; Eichmann, A.; Sessa, W.C. BMP-9 and LDL crosstalk regulates ALK-1 endocytosis and LDL transcytosis in endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 18179–18188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttmacher, A.E.; McKinnon, W.C.; Taylor, L.A.; Berg, J.; Porteous, M.E.M.; Korsenik, J.; Fayad, P.B.; Shovlin, C.; Burdge, C.M.; Jacobson, B.; et al. The natural history of hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia: Data from a patient questionnaire. In Proceedings of the HHT Foundation Int. Inc., Scientific Meeting, Willemstad, Curaçao, 5–8 December 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Shovlin, C.L. Ischaemic stroke and thrombolysis-time to consider the HHT question. BMJ 2009, 339, b4584. [Google Scholar]
- Junus, K.; Centlow, M.; Wikström, A.K.; Larsson, I.; Hansson, S.R.; Olovsson, M. Gene expression profiling of placentae from women with early- and late-onset pre-eclampsia: Down-regulation of the angiogenesis-related genes ACVRL1 and EGFL7 in early-onset disease. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 18, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Wild Type | Arg374 | Arg411 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant | Trp | Gln | Gln | Trp | ||
| Cont. | Countries | c.1120C>T | c.1121G>A | c.1232G>A | c.1231C>T | References |
| 1 | Canada | Abdalla et al., 2003 [89] | ||||
| 1 | Canada | Abdalla et al., 2004 [90] | ||||
| 1 | Canada | Abdalla et al., 2005 [91] | ||||
| 1 | US (Utah) | Bayrak-Toydemir et al., 2004 [92] | ||||
| 1, 2 | US and UK | Berg et al., 1997 [93] | ||||
| 2 | Denmark | Brusgaard et al., 2004 [94] | ||||
| 3 | Morocco, Senegal | Canzonieri et al., 2014 [95] | ||||
| 2 | Spain | Fernandez-L et al., 2005 [96] | ||||
| 2 | Spain | Fernandez-L et al., 2006 [97] | ||||
| 2 | Spain | Fontalba et al., 2008 [98] | ||||
| 1 | US (Utah) | Gedge et al., 2007 [99] | ||||
| 2 | UK | Harrison et al., 2003 [100] | ||||
| 1, 2 | US and UK | Johnson et al., 1996 [27] | ||||
| 2 | Denmark | Kjeldsen et al., 2001 [101] | ||||
| 2 | Germany | Kuehl et al., 2005 [102] | ||||
| 2 | Italy | Lenato et al., 2006 [103] | ||||
| 2 | France | Lesca et al., 2004 [104] | ||||
| 2 | France | Lesca et al., 2006 [105] | ||||
| 4 | China | Lin et al., 2001 [106] | ||||
| 2 | Netherlands | Letteboer et al., 2005 [107] | ||||
| 1 | US (Utah) | McDonald et al., 2011 [108] | ||||
| 3 | South Africa | Mutize et al., 2020 [41] | ||||
| 1 | Canada | Nishida et al., 2012 [109] | ||||
| 2 | Italy | Olivieri et al., 2006 [110] | ||||
| 2 | Italy | Olivieri et al., 2007 [111] | ||||
| 2 | France | Ricard et al., 2010 [79] | ||||
| 2 | Finland | Sankelo et al., 2008 [112] | ||||
| 2 | Spain | Sanz-Rodriguez et al., 2004 [113] | ||||
| 2 | Germany | Schulte et al., 2005 [114] | ||||
| 2 | UK | Trembath et al., 2001 [115] | ||||
| 2 | Germany | Wehner et al., 2006 [116] | ||||
| 4 | China | Zhang et al., 2004 [117] | ||||
| 1 | US | Reported ARUP Laboratories | ||||
| 2 | UK | Submitted by Edinburgh | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jain, K.; McCarley, S.C.; Mukhtar, G.; Ferlin, A.; Fleming, A.; Morris-Rosendahl, D.J.; Shovlin, C.L. Pathogenic Variant Frequencies in Hereditary Haemorrhagic Telangiectasia Support Clinical Evidence of Protection from Myocardial Infarction. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010250
Jain K, McCarley SC, Mukhtar G, Ferlin A, Fleming A, Morris-Rosendahl DJ, Shovlin CL. Pathogenic Variant Frequencies in Hereditary Haemorrhagic Telangiectasia Support Clinical Evidence of Protection from Myocardial Infarction. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(1):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010250
Chicago/Turabian StyleJain, Kinshuk, Sarah C. McCarley, Ghazel Mukhtar, Anna Ferlin, Andrew Fleming, Deborah J. Morris-Rosendahl, and Claire L. Shovlin. 2024. "Pathogenic Variant Frequencies in Hereditary Haemorrhagic Telangiectasia Support Clinical Evidence of Protection from Myocardial Infarction" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 1: 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010250
APA StyleJain, K., McCarley, S. C., Mukhtar, G., Ferlin, A., Fleming, A., Morris-Rosendahl, D. J., & Shovlin, C. L. (2024). Pathogenic Variant Frequencies in Hereditary Haemorrhagic Telangiectasia Support Clinical Evidence of Protection from Myocardial Infarction. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(1), 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010250





