Role of Complement Components in Asthma: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
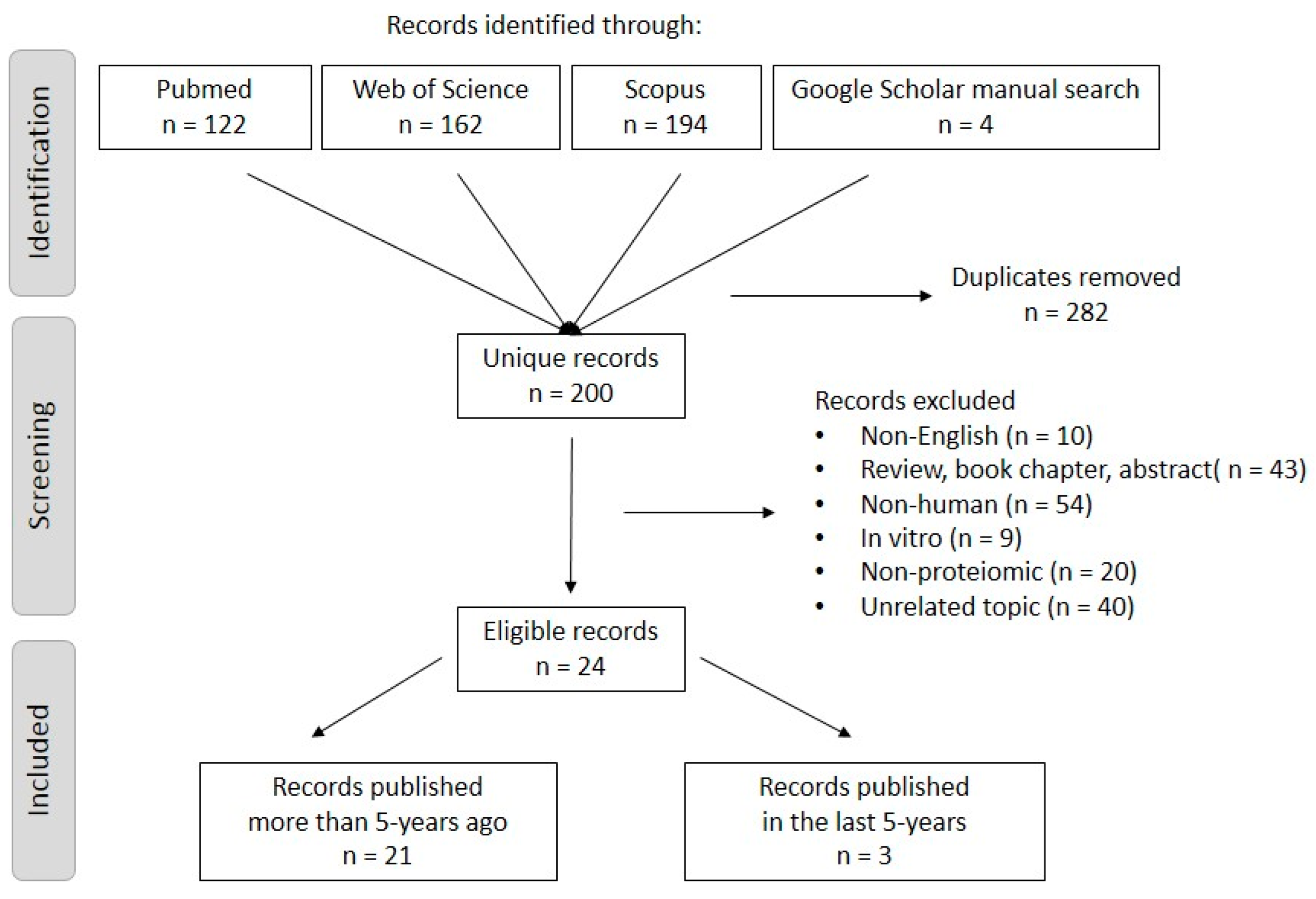
2.1. Searching Strategy and Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Quality Assessment
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Implication of the Findings
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bronte-Moreno, O.; González-Barcala, F.J.; Muñoz-Gall, X.; Pueyo-Bastida, A.; Ramos-González, J.; Urrutia-Landa, I. Impact of air pollution on asthma: A scoping review. Open Respir. Arch. 2023, 5, 100229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.A.; McKenzie, A.N.J. TH2 cell development and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloutier, M.M.; Baptist, A.P.; Blake, K.V.; Brooks, E.G.; Bryant-Stephens, T.; DiMango, E.; Dixon, A.E.; Elward, K.S.; Hartert, T.; Krishnan, J.A.; et al. 2020 focused updates to the asthma management guidelines: A report from the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Coordinating Committee Expert Panel Working Group. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 1217–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, D.D.; Man, J.; Sharpe, H.; Gan, W.Q.; Man, S.P. Pharmacological management to reduce exacerbations in adults with asthma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2004, 292, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, B.F.; Ducharme, F.M. Anti-leukotriene agents compared to inhaled corticosteroids in the management of recurrent and/or chronic asthma in adults and children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 5, CD002314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, M.L.; Bacharier, L.B.; Bateman, E.; Boulet, L.P.; Brightling, C.; Buhl, R.; Brusselle, G.; Cruz, A.A.; Drazen, J.M.; Duijts, L.; et al. Key recommendations for primary care from the 2022 Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) update. NPJ Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2023, 33, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni Chroinin, M.; Greenstone, I.R.; Danish, A.; Magdolinos, H.; Masse, V.; Zhang, X.; Ducharme, F.M. Long-acting beta2-agonists versus placebo in addition to inhaled corticosteroids in children and adults with chronic asthma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2005, 4, CD005535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayen, S.; Dachert, S.; Lashari, B.H.; Gordon, M.; Desai, P.; Criner, G.J.; Cardet, J.C.; Shenoy, K. Critical Care Management of Severe Asthma Exacerbations. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Via, L.; Sanfilippo, F.; Cuttone, G.; Dezio, V.; Falcone, M.; Brancati, S.; Crimi, C.; Astuto, M. Use of ketamine in patients with refractory severe asthma exacerbations: Systematic review of prospective studies. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 78, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellings, P.W.; Steelant, B. Epithelial barriers in allergy and asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, Y.; Ikizawa, K.; Kajiwara, K.; Koshio, T.; Basaki, Y.; Akiyama, K. Functional significance of IL-4 receptor on B cells in IL-4-induced human IgE production. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1995, 96, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocks, B.G.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; Galizzi, J.P.; de Vries, J.E.; Aversa, G. IL-13 induces proliferation and differentiation of human B cells activated by the CD40 ligand. Int. Immunol. 1993, 5, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.Y.; Bates, M.E.; Jarjour, N.N.; Busse, W.W.; Bertics, P.J.; Kelly, E.A. Generation of Th1 and Th2 chemokines by human eosinophils: Evidence for a critical role of TNF-α. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 4840–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munn, D.H.; Shafizadeh, E.; Attwood, J.T.; Bondarev, I.; Pashine, A.; Mellor, A.L. Inhibition of T cell proliferation by macrophage tryptophan catabolism. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1363–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahanonda, R.; Sa-Ard-Iam, N.; Montreekachon, P.; Pimkhaokham, A.; Yongvanichit, K.; Fukuda, M.M.; Pichyangkul, S. IL-8 and IDO expression by human gingival fibroblasts via TLRs. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutelspacher, S.C.; Tan, P.H.; McClure, M.O.; Larkin, D.F.; Lechler, R.I.; George, A.J. Expression of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase (IDO) by endothelial cells: Implications for the control of alloresponses. Am. J. Transplant. 2006, 6, 1320–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, A.L.; Munn, D.H. IDO expression by dendritic cells: Tolerance and tryptophan catabolism. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 762–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, G.X.; Ciric, B.; Rostami, A. IDO: A double-edged sword for TH1/TH2 regulation. Immunol. Lett. 2008, 121, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busse, W.W.; Rosenwasser, L.J. Mechanisms of asthma. J. Allergy. Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, S799–S804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayakannu, R.; Abdullah, N.A.; Radhakrishnan, A.K.; Raj, V.L.; Liam, C.K. Relationship between various cytokines implicated in asthma. Hum. Immunol. 2019, 80, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.; Weaver, C.; Berg, L. The complement system and innate immunity. In Janeway’s Immunobiology, 10th ed.; Twitchell, B., Bressack, C.B., Eds.; W.W. Norton & Company Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 169–215. [Google Scholar]
- Merle, N.S.; Church, S.E.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Roumenina, L.T. Complement system part I–molecular mechanisms of activation and regulation. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 134383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.B.; Wallis, R. Two mechanisms for mannose-binding protein modulation of the activity of its associated serine proteases. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 26058–26065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, S.C.; Sim, R.B.; Lea, S.M.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Blom, A.M. Complement factor I in health and disease. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, N.S.; Noe, R.; Halbwachs-Mecarelli, L.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Roumenina, L.T. Complement system part II: Role in immunity. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 136998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flierman, R.; Daha, M.R. The clearance of apoptotic cells by complement. Immunobiology 2007, 212, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markiewski, M.M.; DeAngelis, R.A.; Strey, C.W.; Foukas, P.G.; Gerard, C.; Gerard, N.; Wetsel, R.A.; Lambris, J.D. The regulation of liver cell survival by complement. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 5412–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, S.K.; Ozantürk, A.N.; Kulkarni, D.H.; Ma, L.; Barve, R.A.; Dannull, L.; Lu, A.; Starick, M.; McPhatter, J.N.; Garnica, L. Lung epithelial cell–derived C3 protects against pneumonia-induced lung injury. Sci. Immunol. 2023, 8, eabp9547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Kimura, Y.; Fang, C.; Zhou, L.; Sfyroera, G.; Lambris, J.D.; Wetsel, R.A.; Miwa, T.; Song, W.C. Regulation of Toll-like receptor–mediated inflammatory response by complement in vivo. Blood 2007, 110, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dempsey, P.W.; Allison, M.E.; Akkaraju, S.; Goodnow, C.C.; Fearon, D.T. C3d of complement as a molecular adjuvant: Bridging innate and acquired immunity. Science 1996, 271, 348–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, C.; Atkinson, J.P. T-cell regulation: With complements from innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skendros, P.; Mitsios, A.; Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Mastellos, D.C.; Metallidis, S.; Rafailidis, P.; Ntinopoulou, M.; Sertaridou, E.; Tsironidou, V.; Tsigalou, C.; et al. Complement and tissue factor-enriched neutrophil extracellular traps are key drivers in COVID-19 immunothrombosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 6151–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sárközi, A.; Tornyi, I.; Békési, E.; Horváth, I. Co-Morbidity Clusters in Post-COVID-19 Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiScipio, R.G.; Schraufstatter, I.U. The role of the complement anaphylatoxins in the recruitment of eosinophils. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 1909–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Assiri, A.M.; Broering, D.C. Complement mediators: Key regulators of airway tissue remodeling in asthma. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marqués-García, F.; Marcos-Vadillo, E. Review of Mouse Models Applied to the Study of Asthma. In Molecular Genetics of Asthma Methods in Molecular Biology, 1st ed.; Isidoro García, M., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1434, pp. 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajoie, S.; Lewkowich, I.P.; Suzuki, Y.; Clark, J.R.; Sproles, A.A.; Dienger, K.; Budelsky, A.L.; Wills-Karp, M. Complement-mediated regulation of the IL-17A axis is a central genetic determinant of the severity of experimental allergic asthma. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, N.; Goshima, H.; Nabe, T.; Yoshino, S. Complement C3a-induced IL-17 plays a critical role in an IgE-mediated late-phase asthmatic response and airway hyperresponsiveness via neutrophilic inflammation in mice. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 5694–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Follettie, M.T.; Ellis, D.K.; Donaldson, D.D.; Hill, A.A.; Diesl, V.; DeClercq, C.; Sypek, J.P.; Dorner, A.J.; Wills-Karp, M. Gene expression analysis in a murine model of allergic asthma reveals overlapping disease and therapy dependent pathways in the lung. Pharmacogenom. J. 2006, 6, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P.J. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. 2011. Available online: https://www.evidencebasedpublichealth.de/download/Newcastle_Ottowa_Scale_Pope_Bruce.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2023).
- Al Mutairi, S.S.; Mojiminiyi, O.A.; Shihab-Eldeen, A.; Al Rammah, T.; Abdella, N. Putative roles of circulating resistin in patients with asthma, COPD and cigarette smokers. Dis. Markers 2011, 31, 297591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabassi, H.M.; Al Nadawi, W. The complement component C9 and nitric oxide serum level in Iraqi patients with asthma. Ann. Trop. Med. Public Health 2020, 23, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohács, A.; Bikov, A.; Ivancsó, I.; Czaller, I.; Böcskei, R.; Müller, V.; Rigó, J.; Losonczy, G.; Tamási, L. Relationship of circulating C5a and complement factor H levels with disease control in pregnant women with asthma. Respir. Care 2016, 61, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaney, J.C.; Kay, A.B. Complement components and IgE in patients with asthma and aspirin idiosyncrasy. Thorax 1976, 31, 425–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejaz, S.; Nasim, F.U.; Ashraf, M.; Ahmad, S. Serum proteome profiling to identify proteins promoting pathogenesis of non-atopic asthma. Protein Pept. Lett. 2018, 25, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattah, M.A.; El Baz, M.; Sherif, A.; Adel, A. Complement components (C3, C4) as inflammatory markers in asthma. Indian J. Pediatr. 2010, 77, 771–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häfner, G.E.; Wüthrich, B.; Grob, P.J.; Arrenbrecht, S. Circulating immune complexes, complement factors C3, C4, C1-inhibitor, alpha-1-antitrypsin and immunoglobulins in asthmatic patients. Respiration 1981, 41, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbles, A.A.; Lu, B.; Nilsson, C.A.; Lilly, C.; Israel, E.; Fujiwara, Y.; Gerard, N.P.; Gerard, C. A role for the C3a anaphylatoxin receptor in the effector phase of asthma. Nature 2000, 406, 998–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, A.B.; Bacon, G.D.; Mercer, B.; Simpson, H.; Crofton, J.W. Complement components and IgE in bronchial asthma. Lancet 1974, 304, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschfink, M.; Castro, F.F.; Rother, U.; Nakhosteen, J.A.; Deppisch, R.; Schmitz-Schumann, M. Complement activation and C3 allotype distribution in patients with bronchial asthma. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 1993, 100, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, N.; Tschernig, T.; Erpenbeck, V.J.; Hohlfeld, J.M.; Kohl, J. Complement factors C3a and C5a are increased in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid after segmental allergen provocation in subjects with asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 1841–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Rhim, T.; Choi, Y.S.; Min, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, S.Y.; Paik, Y.K.; Park, C.S. Complement C3a and C4a increased in plasma of patients with aspirin-induced asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, Q.; Khudhier, A. Determination of Humoral Immunity in Adults Male Asthmatic patients. Iraqi J. Community Med. 2005, 18, 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Marc, M.M.; Korosec, P.; Kosnik, M.; Kern, I.; Flezar, M.; Suskovic, S.; Sorli, J. Complement factors c3a, c4a, and c5a in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2004, 31, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikus, M.S.; Kolmert, J.; Andersson, L.I.; Östling, J.; Knowles, R.G.; Gómez, C.; Ericsson, M.; Thörngren, J.O.; Khoonsari, P.E.; Dahlén, B.; et al. Plasma proteins elevated in severe asthma despite oral steroid use and unrelated to Type-2 inflammation. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 59, 2100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosca, T.; Menezes, M.; Dionigi, P.C.; Stirbulov, R.; Forte, W.C. C3 and C4 complement system components as biomarkers in the intermittent atopic asthma diagnosis. J. Pediatr. 2011, 87, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najam, F.E.; Shembesh, A.H.; Giasuddin, A.S. Complement components (C3, C4) in childhood asthma. Indian J. Pediatr. 2005, 72, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, Y.; Morita, S.; Kawamoto, A.; Suda, T.; Chida, K.; Nakamura, H. Elevated complement C3a in plasma from patients with severe acute asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, T.; Uchida, K.; Meno, K.; Ishii, T.; Aoki, T.; Imada, Y.; Makino, Y.; Hirata, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Arinami, T.; et al. Alpha-1-antitrypsin and complement component C7 are involved in asthma exacerbation. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2008, 2, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, T.; Choi, Y.S.; Nam, B.Y.; Uh, S.T.; Park, J.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Paik, Y.K.; Park, C.S. Plasma protein profiles in early asthmatic responses to inhalation allergen challenge. Allergy 2009, 64, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Graaf, E.A.; Jansen, H.M.; Bakker, M.M.; Alberts, C.; Schattenkerk, J.K.; Out, T.A. ELISA of complement C3a in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. J. Immunol. Methods 1992, 147, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedel-Krogh, S.; Rasmussen, K.L.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Nielsen, S.F. Complement C3 and allergic asthma: A cohort study of the general population. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2000645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiszhár, Z.; Bikov, A.; Gálffy, G.; Tamási, L.; Ungvári, I.; Szalai, C.; Losonczy, G.; Horváth, I. Elevated complement factor H levels in asthmatic sputa. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 33, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Kobayashi, M.; Sousa, E.A.; Liu, W.; Cai, J.; Goldman, S.J.; Dorner, A.J.; Projan, S.J.; Kavuru, M.S.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Differential Proteomic Analysis of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid in Asthmatics following Segmental Antigen Challenge* S. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2005, 4, 1251–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.L.; Ma, L.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yang, Z.H.; Huang, D.; Weng, H.; Zeng, X.T. Methodological quality (risk of bias) assessment tools for primary and secondary medical studies: What are they and which is better? Mil. Med. Res. 2020, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiszhar, Z.; Horváth, I. Induces sputum analysis: Step by step. Breathe 2013, 9, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Y.M.; Lynch, N.J.; Shaaban, A.A.; Rizk, D.E.; Abdel-Rahman, S.H.; Demopulos, G.; Schwaeble, W.J. Inhibition of the lectin pathway of complement activation reduces LPS-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome in mice. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1192767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detsika, M.G.; Palamaris, K.; Dimopoulou, I.; Kotanidou, A.; Orfanos, S.E. The complement cascade in lung injury and disease. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.M.; Tamasi, L.; Schleich, F.; Hoxha, M.; Horvath, I.; Louis, R.; Barnes, N. Clinically relevant subgroups in COPD and asthma. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2015, 24, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoda, U.; Pavlidis, S.; Bansal, A.T.; Takahashi, K.; Hu, S.; Ng Kee Kwong, F.; Rossios, C.; Sun, K.; Bhavsar, P.; Loza, M.; et al. Clinical and transcriptomic features of persistent exacerbation-prone severe asthma in U-BIOPRED cohort. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandsma, J.; Schofield, J.P.; Yang, X.; Strazzeri, F.; Barber, C.; Goss, V.M.; Koster, G.; Bakke, P.S.; Caruso, M.; Chanez, P.; et al. Stratification of asthma by lipidomic profiling of induced sputum supernatant. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 152, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, J.D.; Majoor, C.J.; van’t Veer, C.; Bel, E.H.; van der Poll, T. Asthma and coagulation. Blood 2012, 119, 3236–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimasuay, K.G.; Berg, B.; Schaunaman, N.; Nichols, T.; Chu, H.W. Parkin promotes airway inflammatory response to interferon gamma. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacionyte, J.; Januskevicius, A.; Vasyle, E.; Rimkunas, A.; Bajoriuniene, I.; Vitkauskiene, A.; Miliauskas, S.; Malakauskas, K. Novel Serum Biomarkers for Patients with Allergic Asthma Phenotype. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiemstra, P.S. Parallel activities and interactions between antimicrobial peptides and complement in host defense at the airway epithelial surface. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 68, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heggi, M.T.; Nour El-Din, H.T.; Morsy, D.I.; Abdelaziz, N.I.; Attia, A.S. Microbial evasion of the complement system: A continuous and evolving story. Front. Immunol. 2024, 14, 1281096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornyi, I.; Lazar, J.; Pettko-Szandtner, A.; Hunyadi-Gulyas, E.; Takacs, L. Epitomics: Analysis of Plasma C9 Epitope Heterogeneity in the Plasma of Lung Cancer Patients and Control Subjects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naviaux, R.K. Metabolic features of the cell danger response. Mitochondrion 2014, 16, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizi, É.; Huszár, É.; Csoma, Z.; Böszörményi-Nagy, G.; Barát, E.; Horváth, I.; Herjavecz, I.; Kollai, M. Plasma adenosine concentration increases during exercise: A possible contributing factor in exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenkamp, C.; Plümers, R.; Osterhage, M.R.; Vanakker, O.M.; Van Wynsberghe, J.; Knabbe, C.; Hendig, D. The Activation of JAK/STAT3 Signaling and the Complement System Modulate Inflammation in the Primary Human Dermal Fibroblasts of PXE Patients. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, E.E.; Kunz, N.; Kemper, C. Complement and human T cell metabolism: Location, location, location. Immunol. Rev. 2020, 295, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, P.; Veuskens, B.R.; de Jorge, E.G.; Józsi, M.; Baeumner, A.J.; Steiner, M.S.; Pouw, R.B.; Toonen, E.J.; Pauly, D.; Poppelaars, F. Evaluating the clinical utility of measuring levels of factor H and the related proteins. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 151, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardas, G.; Panek, M.; Kuna, P.; Damiański, P.; Kupczyk, M. Monoclonal antibodies in the management of asthma: Dead ends, current status and future perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 983852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Domain | Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Participants | - Asthmatic patients | - Other respiratory illness |
| Interventions | - Any intervention - No intervention | |
| Comparisons | - No control group - Healthy control group - Other respiratory illness | |
| Outcomes | - Quantitative data of any complement components | - No quantitative data of any complement components - Non proteomic measurement |
| Study design | - Case–control studies - Cohort studies | - Animal studies - In vitro studies - Systematic reviews - Meta-analyses - Book chapters |
| Publication—Author (Year) | Selection | Comparability | Outcome | Total | Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al Mutairi et al. (2011) [42] | 3 | 2 | 3 | 8 | High |
| Alabassi et al. (2020) [43] | 0 | 2 | 3 | 5 | Moderate |
| Bohács et al. (2016) [44] | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| Delaney et al. (1976) [45] | 2 | 1 | 3 | 6 | Moderate |
| Ejaz et al. (2018) [46] | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | Moderate |
| Fattah et al. (2010) [47] | 2 | 1 | 3 | 6 | Moderate |
| Häfner et al. (1981) [48] | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5 | Moderate |
| Humbles et al. (2000) [49] | 2 | 1 | 3 | 6 | Moderate |
| Kay et al. (1974) [50] | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5 | Moderate |
| Kirschfink et al. (1993) [51] | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 | High |
| Krug et al. (2001) [52] | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| Lee et al. (2006) [53] | 3 | 2 | 3 | 8 | High |
| Mahdi et al. (2005) [54] | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | Moderate |
| Marc et al. (2004) [55] | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 | High |
| Mikus et al. (2022) [56] | 3 | 2 | 3 | 8 | High |
| Mosca et al. (2011) [57] | 3 | 2 | 3 | 8 | High |
| Najam et al. (2005) [58] | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| Nakano et al. (2003) [59] | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| Nishioka et al. (2008) [60] | 3 | 2 | 3 | 8 | High |
| Rhim et al. (2009) [61] | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| van de Graaf et al. (1992) [62] | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| Vedel-Krogh et al. (2021) [63] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 | High |
| Weiszhár et al. (2012) [64] | 3 | 2 | 3 | 8 | High |
| Wu et al. (2005) [65] | 3 | 2 | 3 | 8 | High |
| Publication | Sample | Method | No. Subjects in Asthma | No. Subjects in Control | Complements Investigated in the Publication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al Mutairi et al. [42] | Blood | immunochemistry | 60 | 42 | C3 ↑↑↑, C4 ↑↑↑ |
| Alabassi et al. [43] | Serum | ELISA | 30 | 30 | C9 ↑↑↑ |
| Bohács et al. [44] | Plasma | ELISA | 41 | 34 | C5a ↑, Factor H ↔ |
| Delaney et al. [45] | Serum | SRID | 16 | N.A. *1 | C3 ↔, C4 ↔ |
| Ejaz et al. [46] | Serum | MS | 73 | 99 | C3 ↑, C4 ↓, C8 ↓ |
| Fattah et al. [47] | Serum | ELISA | 60 | 60 | C3 ↑↑↑, C4 ↔ |
| Häfner et al. [48] | Serum | SRID, “Monorocket” immunoelectrophoresis | 159 | 100 | C3 ‡1 ↔, C4↑ |
| Humbles et al. [49] | BALF | RIA | 8 | 5 | C3a ↑↑↑ |
| Kay et al. [50] | Serum | SRID | 93 | 59 *2 | C1q ↔, C2 ‡2 ↔, C3↔, C4 ‡3 ↑↑↑, C6 ‡4 ↔, C7 ‡5 ↑, Factor B ↑ |
| Kirschfink et al. [51] | Plasma | ELISA | 61 | 30 | C3d ↑↑↑, sC5b-9 ↑↑↑, Factor H ↑↑↑, Factor I ↑ |
| Krug et al. [52] | BALF | ABICAP assay | 14 | 9 | C3a ↑↑↑, C5a ↑↑↑ |
| Lee et al. [53] | Plasma | MS | 54 | 21 | C3 ↑, C3a ‡6 ↑↑↑, C4 ↑, C4a ‡6 ↑↑↑ |
| Mahdi et al. [54] | Serum | SRID | 60 | 28 *3 | C3 ↓↓↓, C4 ↓↓↓ |
| Marc et al. [55] | Sputum | CBA | 10 | 12 | C3a ↑, C4a ↑, C5a ↑↑↑ |
| Mikus et al. [56] | Plasma | Array-based protein profiling technique | 434 | 91 *4 | C9 ‡7 ↑↑↑, Factor I ‡7 ↑↑↑ |
| Mosca et al. [57] | Serum | SRID | 40 | 30 *5 | C3 ↑↑↑, C4 ↑↑↑ |
| Najam et al. [58] | Serum | SRID | 64 | 57 | C3 ‡8 ↑↑↑, C4 ↔ |
| Nakano et al. [59] | Plasma | RIA | 52 | 42 *6 | C3a ↑↑↑ |
| Nishioka et al. [60] | Plasma | ELISA | 16 | 6 | C7 ↔ |
| Rhim et al. [61] | Plasma | MS | 8 | 8 | C3 ↓, C3d ↑↑↑, C4a ↑↑↑ |
| van de Graaf et al. [62] | BALF, plasma | ELISA, RIA | 10 | 9 | C3a ‡9 ↑↑↑ |
| Vedel-Krogh et al. [63] | Plasma | Turbidimetry using polyclonal antibodies | 2248 | 101,029 *7 | C3 *8 ↑ |
| Weiszhár et al. [64] | Sputum, plasma | ELISA | 26 | 21 | sC5b-9 ↔, Factor H ‡10 ↑↑↑ |
| Wu et al. [65] | BALF | MS | 4 | 3 | C1q ↑, C6 ↑, C8 ↑, Factor H ↑, Factor B ↑, Factor D ↑ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tornyi, I.; Horváth, I. Role of Complement Components in Asthma: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3044. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13113044
Tornyi I, Horváth I. Role of Complement Components in Asthma: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(11):3044. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13113044
Chicago/Turabian StyleTornyi, Ilona, and Ildikó Horváth. 2024. "Role of Complement Components in Asthma: A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 11: 3044. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13113044
APA StyleTornyi, I., & Horváth, I. (2024). Role of Complement Components in Asthma: A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(11), 3044. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13113044







