Exercise Intolerance Is Associated with Cardiovascular Dysfunction in Long COVID-19 Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Respiratory Function Assessment
2.3. Chronic Dyspnoea and Fatigue Assessment
2.4. Ramp Incremental Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test
2.5. Resting Echocardiography
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Exercise Tolerance
3.3. Echocardiographic Findings
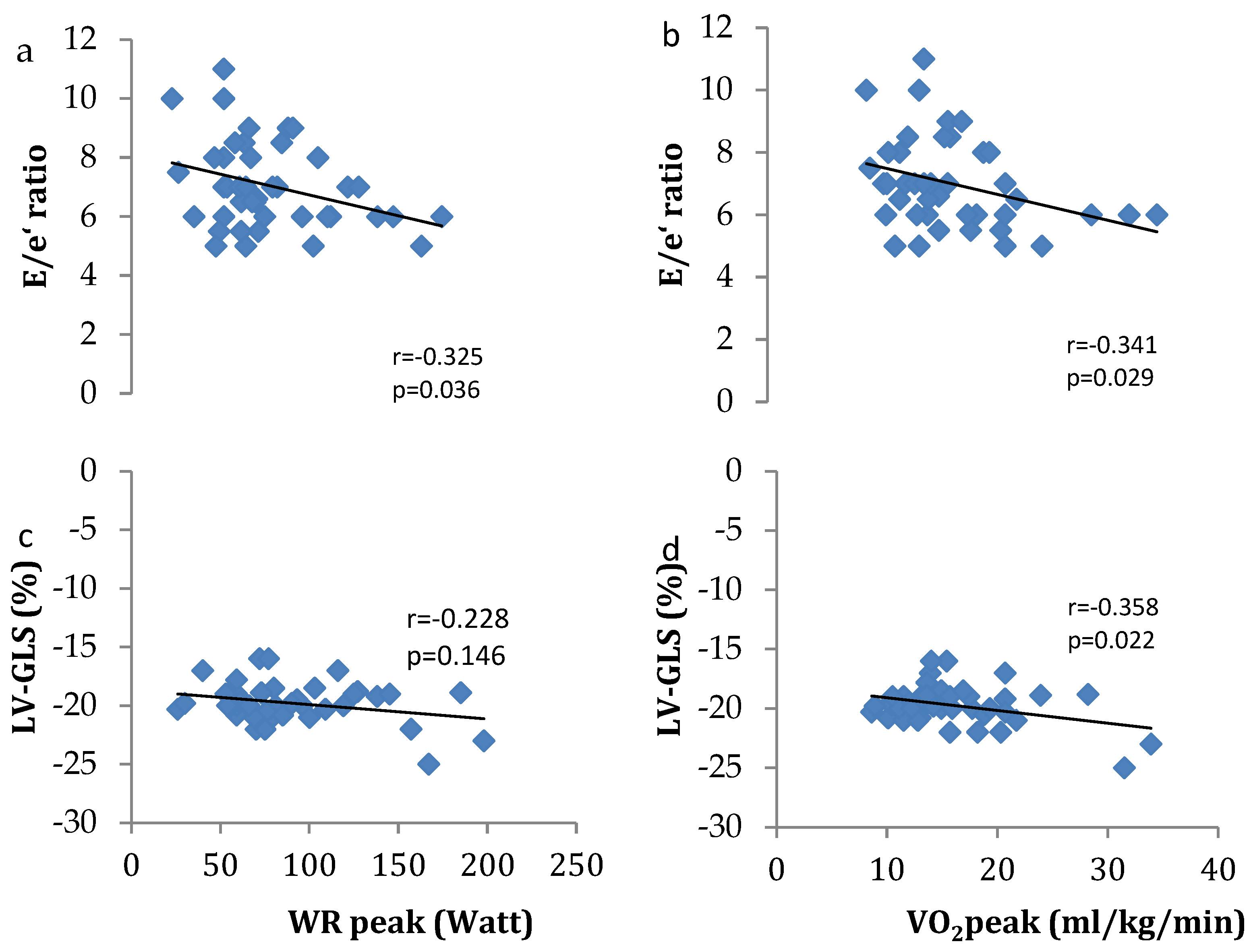
3.4. Associations between Exercise Tolerance and Cardiovascular Function
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Implications and Future Directions
4.2. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johns Hopkins University. Coronavirus Resource Centre. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (accessed on 3 October 2023).
- WHO. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/region/euro/country/gr (accessed on 4 October 2023).
- Vaes, A.W.; Goërtz, Y.M.J.; Van Herck, M.; Machado, F.V.C.; Meys, R.; Delbressine, J.M.; Houben-Wilke, S.; Gaffron, S.; Maier, D.; Burtin, C.; et al. Recovery from COVID-19: A sprint or marathon? 6-month follow-up data from online long COVID-19 support group members. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00141-2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durstenfeld, M.S.; Sun, K.; Tahir, P.; Peluso, M.J.; Deeks, S.G.; Aras, M.A.; Grandis, D.J.; Long, C.S.; Beatty, A.; Hsue, P.Y. Use of Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing to Evaluate Long COVID-19 Symptoms in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2236057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenko, E.; Badimon, L.; Bugiardini, R.; Claeys, M.J.; De Luca, G.; de Wit, C.; Derumeaux, G.; Dorobantu, M.; Duncker, D.J.; Eringa, E.C.; et al. Cardiovascular disease and COVID-19: A consensus paper from the ESC Working Group on Coronary Pathophysiology & Microcirculation, ESC Working Group on Thrombosis and the Association for Acute CardioVascular Care (ACVC), in collaboration with the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA). Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 2705–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonomou, E.; Lampsas, S.; Theofilis, P.; Souvaliotis, N.; Papamikroulis, G.A.; Katsarou, O.; Kalogeras, K.; Pantelidis, P.; Papaioannou, T.G.; Tsatsaragkou, A.; et al. Impaired left ventricular deformation and ventricular-arterial coupling in post-COVID-19: Association with autonomic dysregulation. Heart Vessel. 2023, 38, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonomou, E.; Souvaliotis, N.; Lampsas, S.; Siasos, G.; Poulakou, G.; Theofilis, P.; Papaioannou, T.G.; Haidich, A.B.; Tsaousi, G.; Ntousopoulos, V.; et al. Endothelial dysfunction in acute and long standing COVID-19: A prospective cohort study. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 144, 106975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theofilis, P.; Lampsas, S.; Oikonomou, E.; Siasos, G.; Vavuranakis, M.A.; Marinos, G.; Tsioufis, K.; Vavuranakis, M.; Tousoulis, D. Endothelial dysfunction in convalescent COVID-19 patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 115, 675–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NICE. COVID-19 Rapid Guideline: Managing the Longterm Effects of COVID-19. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng188/resources/covid19-rapid-guideline-managing-the-longterm-effects-of-covid19-pdf-51035515742 (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Venkatesan, P. NICE guideline on long COVID. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, E.; Prandi, E.; Marazzini, L.; Milic-Emili, J. Dependence of maximal flow-volume curves on time course of preceding inspiration in patients with chronic obstruction pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 150, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, R.C.; Cournand, A.; Richards, D.W. Studies on the intrapulmonary mixture of gases. III. An open circuit method for measuring residual air. J. Clin. Investig. 1940, 19, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macintyre, N.; Crapo, R.O.; Viegi, G.; Johnson, D.C.; van der Grinten, C.P.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Enright, P.; et al. Standardisation of the single-breath determination of carbon monoxide uptake in the lung. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 720–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quanjer, P.H.; Tammeling, G.; Cotes, J.E.; Pedersen, O.F.; Peslin, R.; Yernault, J.C. Standardized lung function testing. Official statement of the European Respiratory Society. Eur. Respir. J. 1993, 6 (Suppl. 16), 1–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ilsley, T.; Howden, E.J. Clinimetrics: Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-Fatigue). J. Physiother. 2023, 69, 273–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, G.A. Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1982, 14, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, R.M.; Badano, L.P.; Mor-Avi, V.; Afilalo, J.; Armstrong, A.; Ernande, L.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Foster, E.; Goldstein, S.A.; Kuznetsova, T.; et al. Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: An update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2015, 28, 1–39.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagueh, S.F.; Smiseth, O.A.; Appleton, C.P.; Byrd, B.F., 3rd; Dokainish, H.; Edvardsen, T.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Gillebert, T.C.; Klein, A.L.; Lancellotti, P.; et al. Recommendations for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function by Echocardiography: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 17, 1321–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudski, L.G.; Lai, W.W.; Afilalo, J.; Hua, L.; Handschumacher, M.D.; Chandrasekaran, K.; Solomon, S.D.; Louie, E.K.; Schiller, N.B. Guidelines for the echocardiographic assessment of the right heart in adults: A report from the American Society of Echocardiography endorsed by the European Association of Echocardiography, a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology, and the Canadian Society of Echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2010, 23, 685–713, quiz 786–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratto, C.; Caravita, S.; Faini, A.; Perego, G.B.; Senni, M.; Badano, L.P.; Parati, G. Impact of COVID-19 on exercise pathophysiology: A combined cardiopulmonary and echocardiographic exercise study. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 130, 1470–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendinger, F.; Knaier, R.; Radtke, T.; Schmidt-Trucksäss, A. Low Cardiorespiratory Fitness Post-COVID-19: A Narrative Review. Sports Med. 2023, 53, 51–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannini, L.; Quijada-Fumero, A.; Martín, M.P.R.; Pina, N.C.; Afonso, J.S.H. Cardiopulmonary exercise test with stress echocardiography in COVID-19 survivors at 6 months follow-up. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 94, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Joseph, P.; Heerdt, P.M.; Cullinan, M.; Lutchmansingh, D.D.; Gulati, M.; Possick, J.D.; Systrom, D.M.; Waxman, A.B. Persistent Exertional Intolerance after COVID-19: Insights from Invasive Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing. Chest 2022, 161, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekely, Y.; Lichter, Y.; Sadon, S.; Lupu, L.; Taieb, P.; Banai, A.; Sapir, O.; Granot, Y.; Hochstadt, A.; Friedman, S.; et al. Cardiorespiratory Abnormalities in Patients Recovering from Coronavirus Disease 2019. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2021, 34, 1273–1284.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churchill, T.W.; Bertrand, P.B.; Bernard, S.; Namasivayam, M.; Churchill, J.; Crousillat, D.; Davis, E.F.; Hung, J.; Picard, M.H. Echocardiographic Features of COVID-19 Illness and Association with Cardiac Biomarkers. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2020, 33, 1053–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szekely, Y.; Lichter, Y.; Taieb, P.; Banai, A.; Hochstadt, A.; Merdler, I.; Gal Oz, A.; Rothschild, E.; Baruch, G.; Peri, Y.; et al. Spectrum of Cardiac Manifestations in COVID-19: A Systematic Echocardiographic Study. Circulation 2020, 142, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.T.; Saigal, A.; Karia, N.; Patel, R.K.; Razvi, Y.; Constantinou, N.; Steeden, J.A.; Mandal, S.; Kotecha, T.; Fontana, M.; et al. Ongoing Exercise Intolerance Following COVID-19: A Magnetic Resonance-Augmented Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e024207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, S.J.; Voduc, N.; Corrales-Medina, V.F.; McGuinty, M.; Pratt, A.; Chopra, A.; Law, A.; Garuba, H.A.; Thavorn, K.; Reid, R.E.R.; et al. Symptoms, Pulmonary Function, and Functional Capacity Four Months after COVID-19. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2021, 18, 1912–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, D.M.; Brunjes, D.L.; Lala, A.; Trivieri, M.G.; Contreras, J.P.; Natelson, B.H. Use of Cardiopulmonary Stress Testing for Patients with Unexplained Dyspnea Post-Coronavirus Disease. JACC Heart Fail. 2021, 9, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladlow, P.; O’Sullivan, O.; Bennett, A.N.; Barker-Davies, R.; Houston, A.; Chamley, R.; May, S.; Mills, D.; Dewson, D.; Rogers-Smith, K.; et al. The effect of medium-term recovery status after COVID-19 illness on cardiopulmonary exercise capacity in a physically active adult population. J. Appl. Physiol. 2022, 132, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.; Haller, B.; Feuerstein, A.; Winzer, E.B.; Beckers, P.; Haykowsky, M.J.; Gevaert, A.B.; Hommel, J.; Azevedo, L.F.; Duvinage, A.; et al. Peak O(2)-pulse predicts exercise training-induced changes in peak VO(2) in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. ESC Heart Fail. 2022, 9, 3393–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.; Khera, R.; Park, B.; Haykowsky, M.; Borlaug, B.A.; Lewis, G.D.; Kitzman, D.W.; Butler, J.; Berry, J.D. Relative Impairments in Hemodynamic Exercise Reserve Parameters in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Study-Level Pooled Analysis. JACC Heart Fail. 2018, 6, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, K.; Duman, A. Pulmonary artery pressures and right ventricular dimensions of post-COVID-19 patients without previous significant cardiovascular pathology. Heart Lung J. Crit. Care 2023, 57, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounaridi, M.I.; Vontetsianos, A.; Oikonomou, E.; Theofilis, P.; Chynkiamis, N.; Lampsas, S.; Anastasiou, A.; Papamikroulis, G.A.; Katsianos, E.; Kalogeras, K.; et al. The Role of Rehabilitation in Arterial Function Properties of Convalescent COVID-19 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiado, L.D.C.; Azevedo, N.C.; Azevedo, R.R.C.; Caiado, B.R. Cardiac involvement in patients recovered from COVID-19 identified using left ventricular longitudinal strain. J. Echocardiogr. 2022, 20, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremonesi, M.; Felicetta, A.; Cannata, F.; Serio, S.; van Beek, J.J.P.; Bombace, S.; My, I.; Zanon, V.; Catalano, C.; Papadopoulou, V.; et al. Long COVID-19 Cardiac Complications Are Associated with Autoimmunity to Cardiac Self-Antigens Sufficient to Cause Cardiac Dysfunction. Circulation 2023, 148, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Buono, M.G.; Arena, R.; Borlaug, B.A.; Carbone, S.; Canada, J.M.; Kirkman, D.L.; Garten, R.; Rodriguez-Miguelez, P.; Guazzi, M.; Lavie, C.J.; et al. Exercise Intolerance in Patients with Heart Failure: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 2209–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donal, E.; Coquerel, N.; Bodi, S.; Kervio, G.; Schnell, F.; Daubert, J.C.; Carré, F. Importance of ventricular longitudinal function in chronic heart failure. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. J. Work. Group Echocardiogr. Eur. Soc. Cardiol. 2011, 12, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hasselberg, N.E.; Haugaa, K.H.; Sarvari, S.I.; Gullestad, L.; Andreassen, A.K.; Smiseth, O.A.; Edvardsen, T. Left ventricular global longitudinal strain is associated with exercise capacity in failing hearts with preserved and reduced ejection fraction. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 16, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellsten, Y.; Nyberg, M. Cardiovascular Adaptations to Exercise Training. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 6, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sista, A.K.; Miller, L.E.; Kahn, S.R.; Kline, J.A. Persistent right ventricular dysfunction, functional capacity limitation, exercise intolerance, and quality of life impairment following pulmonary embolism: Systematic review with meta-analysis. Vasc. Med. 2017, 22, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaCombe, P.; Jose, A.; Basit, H.; Lappin, S.L. Physiology, Starling Relationships. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hadzibegovic, S.; Lena, A.; Churchill, T.W.; Ho, J.E.; Potthoff, S.; Denecke, C.; Rösnick, L.; Heim, K.M.; Kleinschmidt, M.; Sander, L.E.; et al. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction according to the HFA-PEFF score in COVID-19 patients: Clinical correlates and echocardiographic findings. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 23, 1891–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudoran, C.; Tudoran, M.; Pop, G.N.; Giurgi-Oncu, C.; Cut, T.G.; Lazureanu, V.E.; Oancea, C.; Parv, F.; Ciocarlie, T.; Bende, F. Associations between the Severity of the Post-Acute COVID-19 Syndrome and Echocardiographic Abnormalities in Previously Healthy Outpatients Following Infection with SARS-CoV-2. Biology 2021, 10, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccone, G.; Tomasoni, D.; Italia, L.; Lombardi, C.M.; Metra, M. Myocardial Involvement in COVID-19: An Interaction Between Comorbidities and Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. A Further Indication of the Role of Inflammation. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2021, 18, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balady, G.J.; Arena, R.; Sietsema, K.; Myers, J.; Coke, L.; Fletcher, G.F.; Forman, D.; Franklin, B.; Guazzi, M.; Gulati, M.; et al. Clinician’s Guide to cardiopulmonary exercise testing in adults: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010, 122, 191–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
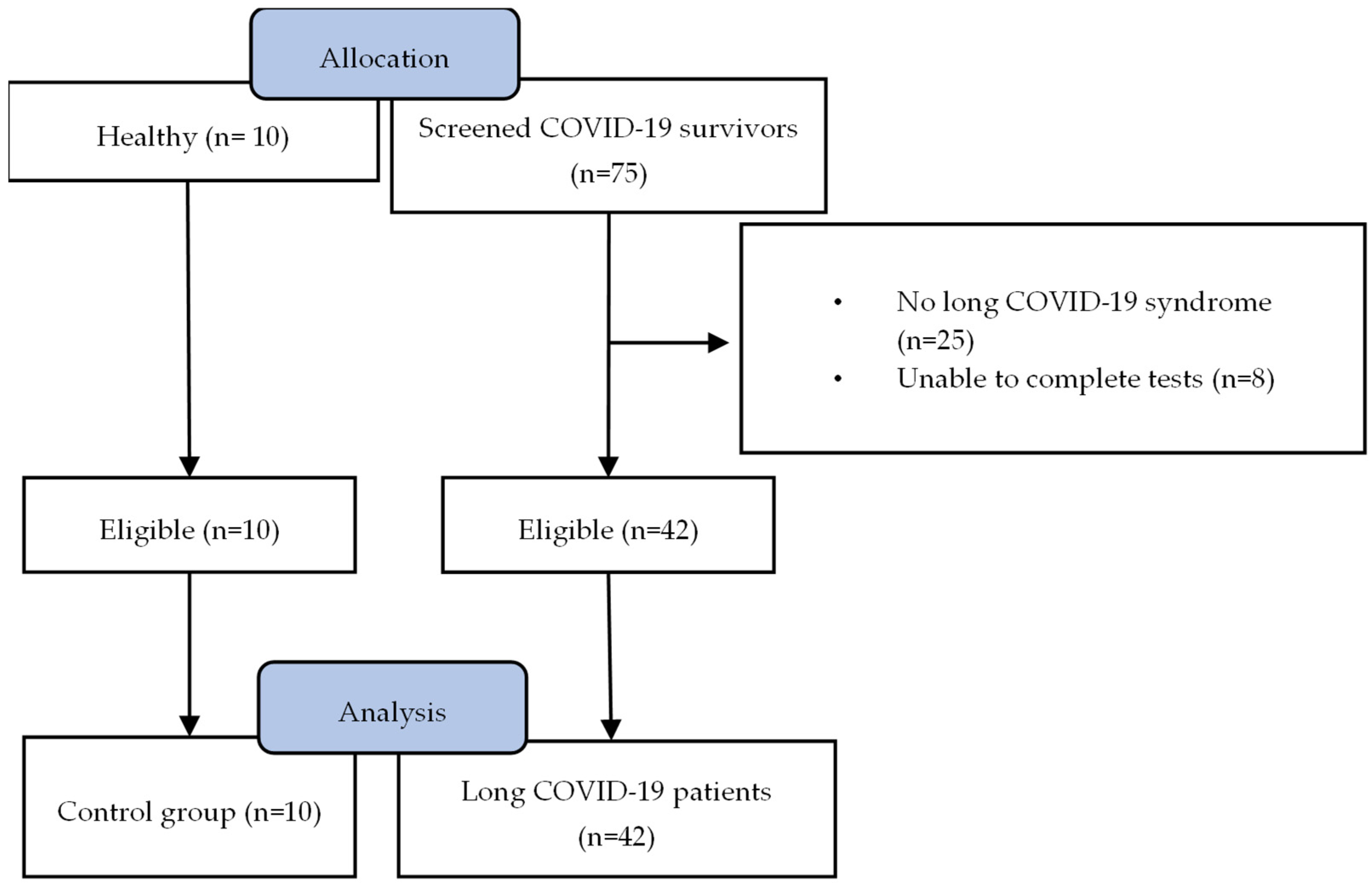

| Variable | Long COVID-19 Patients | Healthy Control | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (Male/Female) | 19/23 | 4/6 | 0.76 |
| Age (years) | 55 ± 13 | 52 ± 8 | 0.58 |
| Height (cm) | 166 ± 11 | 170 ± 12 | 0.293 |
| Weight (kg) | 80.8 ± 17.8 | 84.4 ± 20.0 | 0.579 |
| BMI | 29.0 ± 5.2 | 28.8 ± 3.7 | 0.916 |
| Days from discharge | 149 ± 92 | - | - |
| Smoking status | |||
| Current | 5 | 0 | |
| Ex | 6 | 3 | 0.57 |
| Never | 31 | 7 | |
| FEV1 (% predicted) | 98 ± 19 | 110 ± 17 | 0.065 |
| FVC (% predicted) | 96 ± 21 | 121 ± 20 | 0.002 |
| FEV1/FVC | 84 ± 6 | 77 ± 6 | 0.002 |
| TLC (% predicted) | 92 ± 27 | 100 ± 3 | 0.339 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Dyslipidaemia | 8 | ||
| Hypertension | 6 | ||
| Coronary artery disease | 3 | ||
| Diabetes mellitus | 4 | ||
| Asthma | 2 | ||
| Anxiety–Depression | 4 | ||
| DLco (% predicted) | 73 ± 21 | 98 ± 3 | 0.002 |
| mMRC | 2.1 ± 1.2 | 0.4 ± 0.5 | 0.001 |
| FACIT | 24 ± 10 | 48 ± 4 | 0.001 |
| Variable | Long COVID-19 Patients | Healthy Control | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| WRpeak (watts) | 88 ± 40 | 148 ± 63 | 0.001 |
| WRpeak (%pred) | 74 ± 27 | 115 ± 27 | 0.001 |
| VO2peak (mL/kg/min) | 16.1 ± 5.7 | 21.1 ± 4.3 | 0.014 |
| VO2peak (%pred) | 67 ± 18 | 89 ± 13 | 0.001 |
| RER | 1.12 ± 0.10 | 1.26 ± 0.11 | 0.001 |
| VE/VCO2 | 34 ± 6 | 37 ± 6 | 0.116 |
| O2 pulse (mL/kg/beat) | 10.4 ± 3.5 | 11.4 ± 4.0 | 0.465 |
| O2 pulse (%pred) | 90 ± 21 | 95 ± 12 | 0.495 |
| Heart rate (beats/minute) | 126 ± 18 | 159 ± 17 | 0.001 |
| Heart rate (%pred) | 79 ± 18 | 95 ± 10 | 0.007 |
| Mean arterial pressure (mmHg) | 108 ± 17 | 126 ± 14 | 0.003 |
| SpO2 (%) | 96 ± 5 | 99 ± 1 | 0.078 |
| Dyspnoea | 3.8 ± 2.3 | 4.4 ± 2.8 | 0.476 |
| Fatigue | 5.9 ± 2.5 | 6.0 ± 2.3 | 0.890 |
| Reason for termination (Dyspnoea/Fatigue/Both) (%) | 4 (10%)/34 (80%)/4 (10%) | 4 (40%)/6 (60%)/0 (0%) | - |
| Variable | Long COVID-19 Patients | Healthy Control | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| LVEDD (mm) | 54 ± 5 | 48 ± 2 | 0.001 |
| LVEF (%) | 54 ± 5 | 59 ± 4 | 0.010 |
| LVmass (g) | 135 ± 25 | 143 ± 29 | 0.412 |
| LAvol (ml) | 45 ± 11 | 45 ± 10 | 0.986 |
| E/e’ ratio | 7.0 ± 1.5 | 6.4 ± 1.0 | 0.230 |
| RV diameter (mm) | 31 ± 3 | 31 ± 4 | 0.706 |
| SRV (cm/s) | 12.0 ± 1.6 | 12.6 ± 1.8 | 0.325 |
| PASP (mmHg) | 28 ± 6 | 27 ± 4 | 0.892 |
| LV-GLS (%) | −20 ± 2 | −21 ± 1 | 0.020 |
| LVOT (mm) | 22.8 ± 2.3 | 22.2 ± 2.4 | 0.521 |
| SV (ml) | 75 ± 9 | 72 ± 7 | 0.325 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vontetsianos, A.; Chynkiamis, N.; Gounaridi, M.I.; Anagnostopoulou, C.; Lekka, C.; Zaneli, S.; Anagnostopoulos, N.; Oikonomou, E.; Vavuranakis, M.; Rovina, N.; et al. Exercise Intolerance Is Associated with Cardiovascular Dysfunction in Long COVID-19 Syndrome. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4144. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144144
Vontetsianos A, Chynkiamis N, Gounaridi MI, Anagnostopoulou C, Lekka C, Zaneli S, Anagnostopoulos N, Oikonomou E, Vavuranakis M, Rovina N, et al. Exercise Intolerance Is Associated with Cardiovascular Dysfunction in Long COVID-19 Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(14):4144. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144144
Chicago/Turabian StyleVontetsianos, Angelos, Nikolaos Chynkiamis, Maria Ioanna Gounaridi, Christina Anagnostopoulou, Christiana Lekka, Stavroula Zaneli, Nektarios Anagnostopoulos, Evangelos Oikonomou, Manolis Vavuranakis, Nikoletta Rovina, and et al. 2024. "Exercise Intolerance Is Associated with Cardiovascular Dysfunction in Long COVID-19 Syndrome" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 14: 4144. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144144
APA StyleVontetsianos, A., Chynkiamis, N., Gounaridi, M. I., Anagnostopoulou, C., Lekka, C., Zaneli, S., Anagnostopoulos, N., Oikonomou, E., Vavuranakis, M., Rovina, N., Papaioannou, A. I., Kaltsakas, G., Koulouris, N., & Vogiatzis, I. (2024). Exercise Intolerance Is Associated with Cardiovascular Dysfunction in Long COVID-19 Syndrome. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(14), 4144. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144144








