Exome Sequence Analysis to Characterize Undiagnosed Family Segregating Motor Impairment and Dystonia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Recruitment and Ethical Approval
2.2. Genomic DNA Isolation and Exome Sequencing
2.3. Exome Data Analysis and Sanger Sequencing
2.4. Protein–Protein Interaction
3. Results
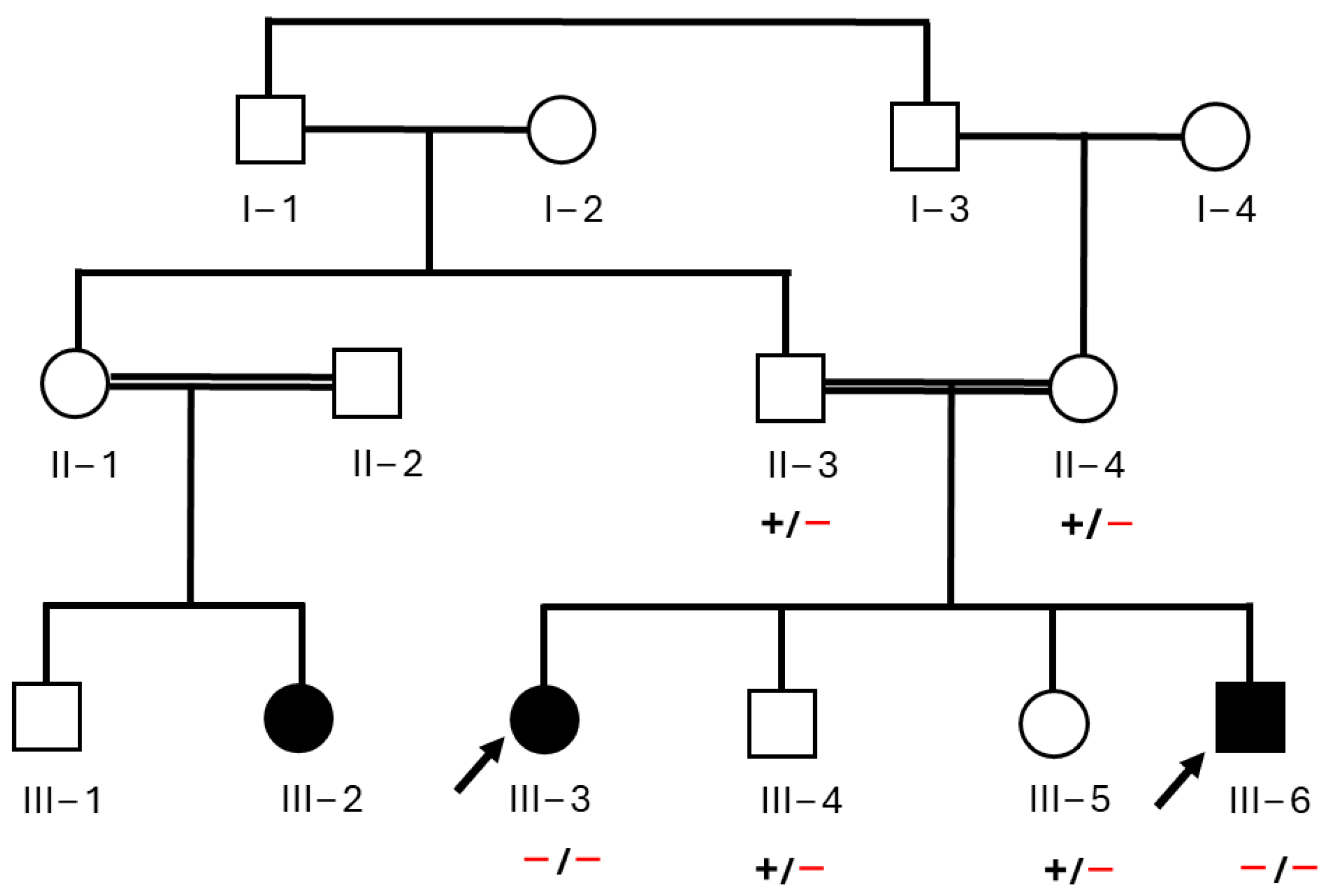
3.1. Clinical Features of Affected Individuals
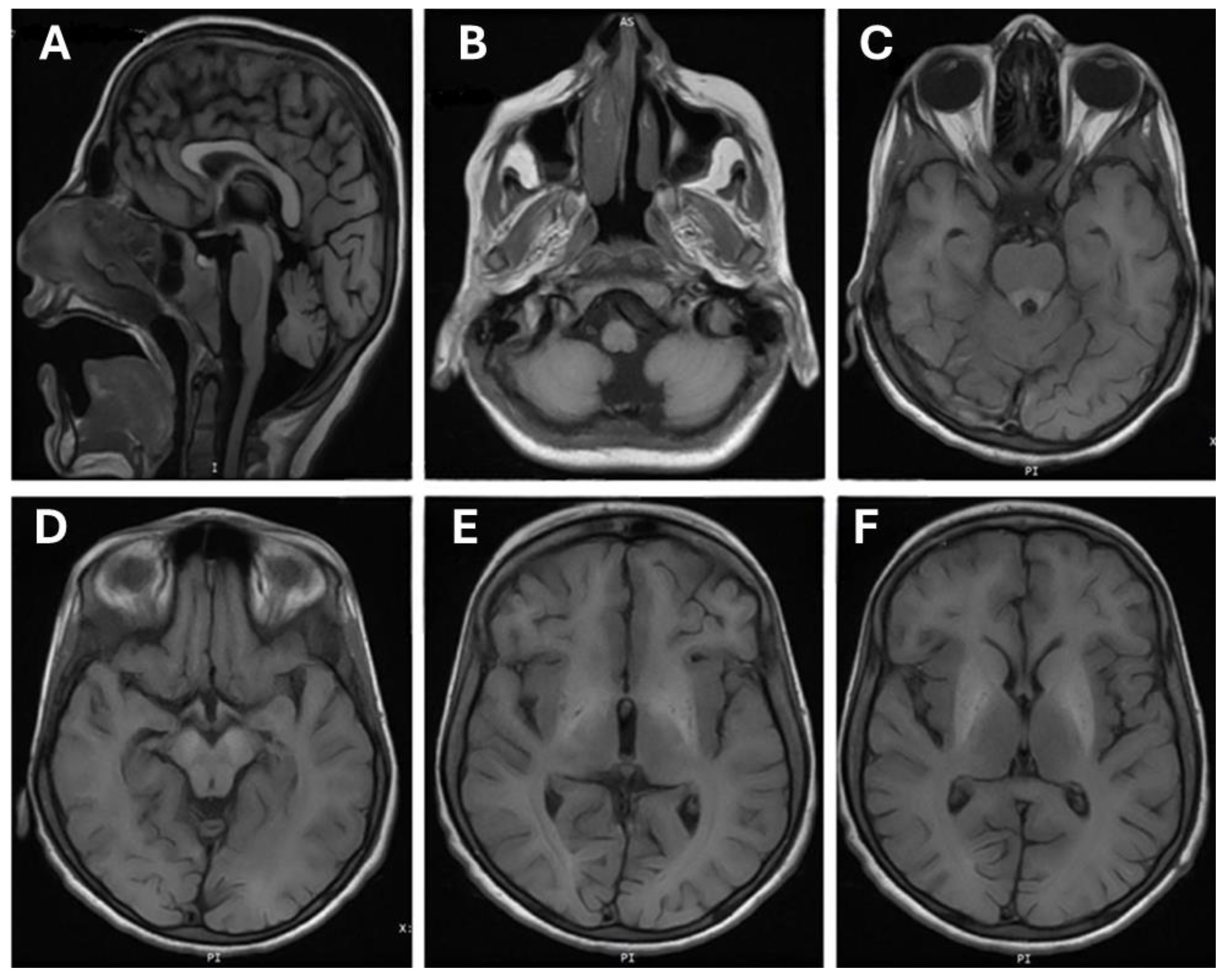
3.2. Brain MRI Finding
3.3. Exome Data Analysis and Genetic Assessment
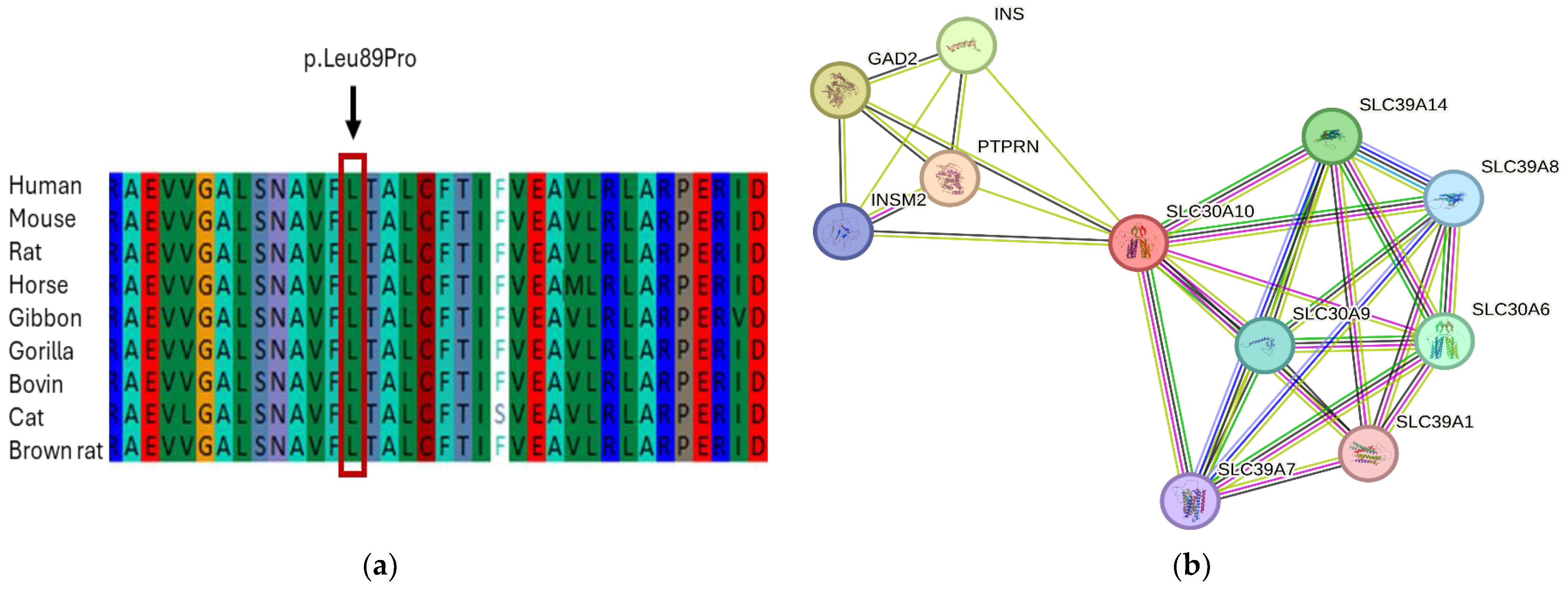
3.4. In Silico Analysis and Protein Network Interaction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balachandran, R.C.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; McBride, D.; Veevers, J.; Harrison, F.E.; Aschner, M.; Haynes, E.N.; Bowman, A.B. Brain manganese and the balance between essential roles and neurotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 6312–6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschner, J.L.; Aschner, M. Nutritional aspects of manganese homeostasis. Mol. Aspects Med. 2005, 26, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaassen, C.D. Biliary excretion of manganese in rats, rabbits, and dogs. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1974, 29, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, C.; Benedetto, A.; Aschner, M. Manganese transport in eukaryotes: The role of DMT1. Neurotoxicology 2008, 29, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furbee, B. Welding and parkinsonism. Neurol. Clin. 2011, 29, 623–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crossgrove, J.; Zheng, W. Manganese toxicity upon overexposure. NMR Biomed. 2004, 17, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikk, K.; Haldre, S.; Aquilonius, S.M.; Taba, P. Manganese-Induced Parkinsonism due to Ephedrone Abuse. Park. Dis. 2011, 2011, 865319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.C., Jr.; Gubert, P.; Villas Boas, G.R.; Meirelles Paes, M.; Santamaría, A.; Lee, E.; Tinkov, A.A.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschner, M. Manganese-induced neurodegenerative diseases and possible therapeutic approaches. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2020, 20, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouabid, S.; Tinakoua, A.; Lakhdar-Ghazal, N.; Benazzouz, A. Manganese neurotoxicity: Behavioral disorders associated with dysfunctions in the basal ganglia and neurochemical transmission. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachtman, J.P.; Tubben, R.E.; Commissaris, R.L. Behavioral effects of chronic manganese administration in rats: Locomotor activity studies. Neurobehav. Toxicol. Teratol. 1986, 8, 711–715. [Google Scholar]
- Calne, D.B.; Chu, N.S.; Huang, C.C.; Lu, C.S.; Olanow, W. Manganism and idiopathic parkinsonism: Similarities and differences. Neurology 1994, 44, 1583–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadri, M.; Federico, A.; Zhao, T.; Breedveld, G.J.; Battisti, C.; Delnooz, C.; Severijnen, L.A.; Di Toro Mammarella, L.; Mignarri, A.; Monti, L.; et al. Mutations in SLC30A10 cause parkinsonism and dystonia with hypermanganesemia, polycythemia, and chronic liver disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuschl, K.; Clayton, P.T.; Gospe, S.M., Jr.; Gulab, S.; Ibrahim, S.; Singhi, P.; Aulakh, R.; Ribeiro, R.T.; Barsottini, O.G.; Zaki, M.S.; et al. Syndrome of hepatic cirrhosis, dystonia, polycythemia, and hypermanganesemia caused by mutations in SLC30A10, a manganese transporter in man. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brna, P.; Gordon, K.; Dooley, J.M.; Price, V. Manganese toxicity in a child with iron deficiency and polycythemia. J. Child Neurol. 2011, 26, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahni, V.; Léger, Y.; Panaro, L.; Allen, M.; Giffin, S.; Fury, D.; Hamm, N. Case report: A metabolic disorder presenting as pediatric manganism. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1776–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sue, W.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, C.C. Dyskinesia from manganism in a hepatic dysfunction patient. Honghua Min Guo Xiao Er Ke Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi 1996, 37, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Tuschl, K.; Mills, P.B.; Parsons, H.; Malone, M.; Fowler, D.; Bitner-Glindzicz, M.; Clayton, P.T. Hepatic cirrhosis, dystonia, polycythemia and hypermanganesaemia--a new metabolic disorder. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2008, 31, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatrafi, A.; Umair, M.; Eldardear, A.; Al-Luqmani, M.; Hashmi, J.A.; Albalawi, A.M.; Alfadhel, M.; Ramzan, K.; Basit, S. A homozygous missense variant in the homeobox domain of the NKX6-2 results in progressive spastic ataxia type 8 associated with lower limb weakness and neurological manifestations. J. Gene Med. 2020, 22, e3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatrafi, A.M.; Hibshi, A.M.; Basit, S. Exome Sequencing to Identify Novel Variants Associated with Secondary Amenorrhea and Premature Ovarian Insufficiency (POI) in Saudi Women. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatrafi, A.M.; Alluqmani, M.M.; Basit, S. Homozygous Duplication in the CHRNE in a Family with Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome 4C: 18-Year Follow Up. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gospe, S.M., Jr.; Caruso, R.D.; Clegg, M.S.; Keen, C.L.; Pimstone, N.R.; Ducore, J.M.; Gettner, S.S.; Kreutzer, R.A. Paraparesis, hypermanganesaemia, and polycythaemia: A novel presentation of cirrhosis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2000, 83, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchens, S.; Liu, C.; Jursa, T.; Shawlot, W.; Chaffee, B.K.; Yin, W.; Gore, A.C.; Aschner, M.; Smith, D.R.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Deficiency in the manganese efflux transporter SLC30A10 induces severe hypothyroidism in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 9760–9773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, A.B.; Kwakye, G.F.; Herrero Hernández, E.; Aschner, M. Role of manganese in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2011, 25, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyva-Illades, D.; Chen, P.; Zogzas, C.E.; Hutchens, S.; Mercado, J.M.; Swaim, C.D.; Morrisett, R.A.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschner, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S. SLC30A10 is a cell surface-localized manganese efflux transporter, and parkinsonism-causing mutations block its intracellular trafficking and efflux activity. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 14079–14095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zogzas, C.E.; Aschner, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Structural Elements in the Transmembrane and Cytoplasmic Domains of the Metal Transporter SLC30A10 Are Required for Its Manganese Efflux Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 15940–15957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Clinical Features | III-3 | III-4 |
|---|---|---|
| Age of onset (years) | 2 | 1 |
| Age at examination (years) | 11 | 2 |
| Hepatomegaly | No | No |
| Liver cirrhosis | Yes | No |
| Dystonia | Yes | Yes |
| Hypertonia of the limbs | Yes | Yes |
| Fine motor impairment | Severe | Severe |
| Tremor | No | No |
| Bradykinesia | No | No |
| Rigidity | Yes | Yes |
| Postural instability | Yes | Yes |
| Spastic paraparesis | Yes | Yes |
| Laboratory Test Results | ||
| Polycythemia | Yes | Yes |
| Serum manganese | High | High |
| Hyperbilirubinemia, unconjugated | Yes | Yes |
| Low iron | Low | Low |
| Total iron-binding capacity | High | High |
| Brain MRI Findings | ||
| Hyperintensities in the basal ganglia | Yes | N/A |
| White matter lesions | Yes | N/A |
| Anterior pituitary lesions | No | N/A |
| Gene | Chr | Exon | Nucleotide Variant | Protein Variant | SNP No. | Zygosity | gnomAD Freq |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLC30A10 | 1 | 1 | c.266T>C | p.L89P | rs281860284 | Homo | 0.0 |
| Prediction bioinformatics tools | |||||||
| SIFT (v4.7) | CADD (v1.7) | VarSome | PolyPhen (v2) | PhyloP (V5.20) | ClinVar | HGMD variant class (v 2023.1) | ACMG classification |
| D | De | P | PD | HC | P | DC | VUS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almatrafi, A.M.; Alayoubi, A.M.; Alluqmani, M.; Hashmi, J.A.; Basit, S. Exome Sequence Analysis to Characterize Undiagnosed Family Segregating Motor Impairment and Dystonia. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4252. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144252
Almatrafi AM, Alayoubi AM, Alluqmani M, Hashmi JA, Basit S. Exome Sequence Analysis to Characterize Undiagnosed Family Segregating Motor Impairment and Dystonia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(14):4252. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144252
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmatrafi, Ahmad M., Abdulfatah M. Alayoubi, Majed Alluqmani, Jamil A. Hashmi, and Sulman Basit. 2024. "Exome Sequence Analysis to Characterize Undiagnosed Family Segregating Motor Impairment and Dystonia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 14: 4252. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144252
APA StyleAlmatrafi, A. M., Alayoubi, A. M., Alluqmani, M., Hashmi, J. A., & Basit, S. (2024). Exome Sequence Analysis to Characterize Undiagnosed Family Segregating Motor Impairment and Dystonia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(14), 4252. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144252






