A Literature Review of the Morphological Variability in the Intrinsic Muscles of the Foot: Traps Awaiting Clinicians during Ultrasound
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review Design and Methods
- -
- Manuscript written in any language other than English.
- -
- Lack of information regarding the description of the typical anatomy/morphological variability in a structure covered by the topic of this review/clinical significance/application of imaging studies/the use of US in diagnosis.
- -
- Articles focused mainly on methods of visualization other than US imaging.
- -
- Type of the article including expert opinion/letter to the editor/conference report.
- -
- Publication after March 2024.
3. Discussion
3.1. Dorsal Aspect of the Foot
3.1.1. Extensor Digitorum Brevis Muscle
3.1.2. Extensor Hallucis Brevis Muscle
3.2. Plantar Aspect of the Foot
3.2.1. Medial Plantar Muscles
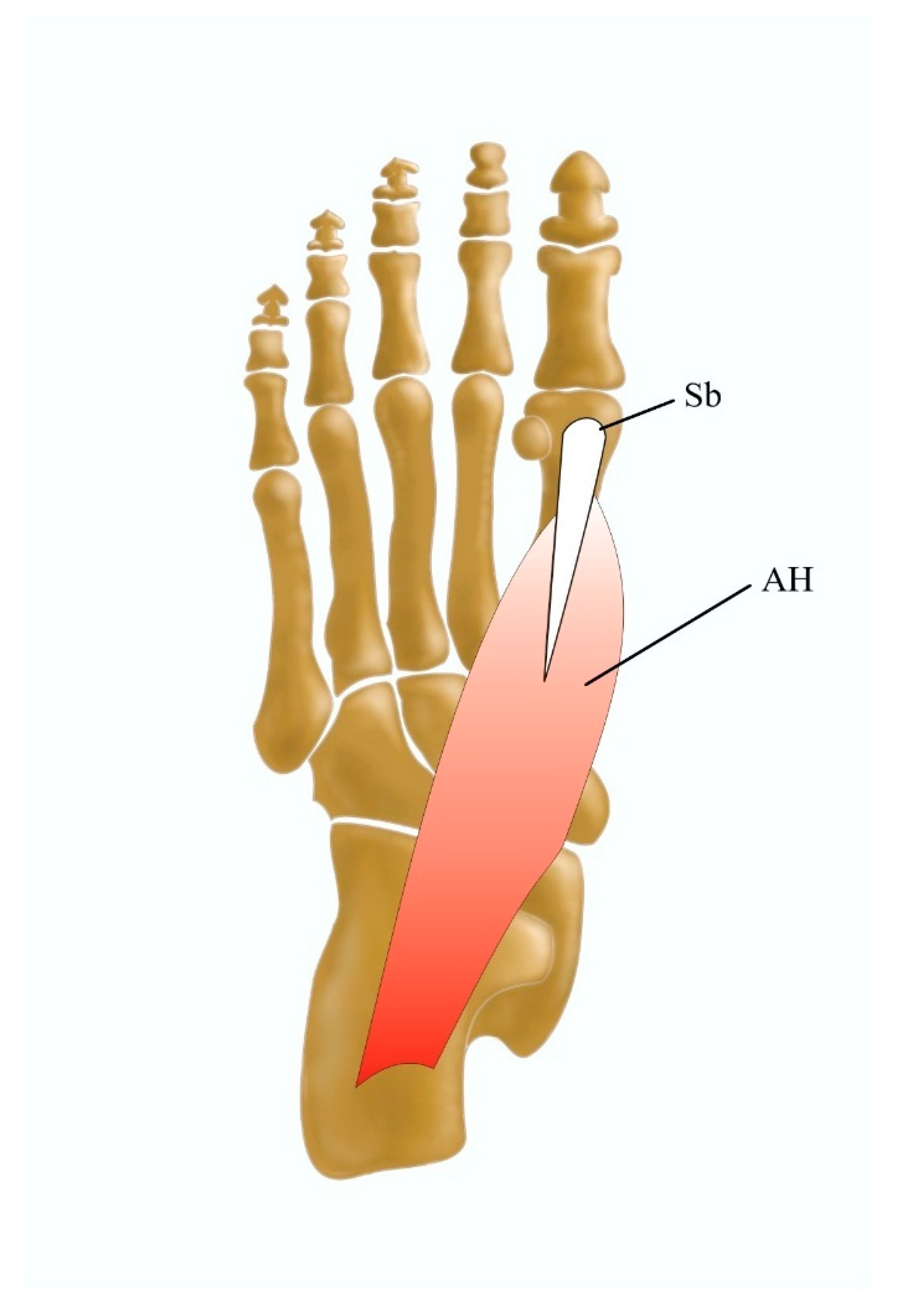
3.2.2. The Abductor Hallucis Muscle
3.2.3. The Adductor Hallucis Muscle
3.2.4. The Flexor Hallucis Brevis Muscle
3.3. Central Plantar Muscles
3.3.1. The Flexor Digitorum Brevis Muscle
3.3.2. Quadratus Plantae
3.3.3. Lumbrical Muscles
3.4. Lateral Plantar Muscles
The Abductor Digiti Minimi Muscle
4. Conclusions
5. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morton, D.J. The Human Foot, Its Evolution, Physiology, and Functional Disorders; Hafner Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1964; pp. 3–91. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, E.; Cooper, G.; Reeves, N.D.; Hodson-Tole, E.F. Intrinsic Foot Muscles Act to Stabilise the Foot When Greater Fluctuations in Centre of Pressure Movement Result from Increased Postural Balance Challenge. Gait Posture 2020, 79, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafka, R.M.; Aveytua, I.L.; Fiacco, R.C.; Ream, G.M.; DiLandro, A.C.; D’Antoni, A. Intrinsic Muscles of the Foot. In Bergman’s Comprehensive Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 438–448. [Google Scholar]
- Sirasanagandla, S.R.; Swamy, R.S.; Nayak, S.B.; Somayaji, N.S.; Rao, M.K.G.; Bhat, K.M.R. Analysis of the Morphometry and Variations in the Extensor Digitorum Brevis Muscle: An Anatomic Guide for Muscle Flap and Tendon Transfer Surgical Dissection. Anat. Cell Biol. 2013, 46, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdilla, M.J.; Paulet, J.E.; Lear, J.J.; Addie, K.M.; Lambert, H.W. A Review of Extensor Hallucis Longus Variants Featuring a Novel Extensor Primi Internodii Hallucis Muscle Merging with Extensor Hallucis Brevis. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2018, 57, 1218–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myerson, M.S.; Komenda, G.A. Results of Hallux Varus Correction Using an Extensor Hallucis Brevis Tenodesis. Foot Ankle Int. 1996, 17, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.J.; Chung, C.H. Upper-Lip Reconstruction Using a Free Dorsalis Pedis Flap Incorporating the Extensor Hallucis and Digitorum Brevis Muscles. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2011, 22, 998–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chittoria, R.K.; Pratap, H.; Yekappa, S.H. Abductor Hallucis: Anatomical Variation and Its Clinical Implications in the Reconstruction of Chronic Nonhealing Ulcers and Defects of Foot. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pośnik, M.; Zielinska, N.; Tubbs, R.S.; Ruzik, K.; Olewnik, Ł. Morphological variability of the leg muscles: Potential traps on ultrasound that await clinicians. Folia Morphol. 2023, 83, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olewnik, Ł.; Podgórski, M.; Polguj, M.; Ruzik, K.; Grzelak, P. Is ultrasound effective in determining variation of the insertion of the extensor hallucis longus tendon? Clin. Anat. 2020, 33, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijntjes, J.; van Alfen, N. Muscle ultrasound: Present state and future opportunities. Muscle Nerve 2021, 63, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberfehlner, H.; Maas, H.; Harlaar, J.; Becher, J.G.; Buizer, A.I.; Jaspers, R.T. Freehand three-dimensional ultrasound to assess semitendinosus muscle morphology. J. Anat. 2016, 229, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashir, A.; Jerban, S.; Barrère, V.; Wu, Y.; Shah, S.B.; Andre, M.P.; Chang, E.Y. Skeletal Muscle Assessment Using Quantitative Ultrasound: A Narrative Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhulst, F.v.; Leeuwesteijn, A.E.E.P.M.; Louwerens, J.W.K.; Geurts, A.C.H.; van Alfen, N.; Pillen, S. Quantitative Ultrasound of Lower Leg and Foot Muscles: Feasibility and Reference Values. Foot Ankle Surg. 2011, 17, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macchi, V.; Tiengo, C.; Porzionato, A.; Stecco, C.; Parenti, A.; Mazzoleni, F.; Ger, R.; de Caro, R. Correlation between the Course of the Medial Plantar Artery and the Morphology of the Abductor Hallucis Muscle. Clin. Anat. 2005, 18, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, M.; Okuda, R.; Morikawa, J.; Abe, M. Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Associated with an Accessory Muscle. Foot Ankle Int. 2003, 24, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, K.; Dalley, A.F.; Agur, A.M.R. Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 7th ed.; Wilkins, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kelikian, A. Sarrafian’s Anatomy of the Foot and Ankle: Descriptive, Topographic, Functional, 3rd ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chaney, D.; Lee, M.; Khan, M.; Krueger, W.; Mandracchia, V.; Yoho, R. Study of Ten Anatomical Variants of the Foot and Ankle. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 1996, 86, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkan, Y.; Öztürk, A.; Özdemir, R.; Aykut, S.; Yalşin, N. Interpositional Arthroplasty with Extensor Digitorum Brevis Tendon in Freiberg’s Disease: A New Surgical Technique. Foot Ankle Int. 2008, 29, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparisi Gómez, M.P.; Errani, C.; Lalam, R.; Vasilevska Nikodinovska, V.; Fanti, S.; Tagliafico, A.S.; Sconfienza, L.M.; Bazzocchi, A. The Role of Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Soft Tissue Tumors. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2020, 24, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.; Dupont, G.; Katsuta, J.; Iwanaga, J.; Olewnik, Ł.; Tubbs, R.S. Concomitant Variations of the Tibialis Anterior, and Extensor Hallucis Longus, and Extensor Hallucis Brevis Muscles. Anat. Cell Biol. 2023, 56, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaizumi, A.; Kadota, H.; Ishida, K. Extensor Hallucis Brevis Tendon Transfer for the Correction of Drop Toe Deformity after Dorsalis Pedis Tendocutaneous Free Flap Harvest. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 76, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.N.; Lui, T.H. Traumatic Hallux Varus Treated by Minimally Invasive Extensor Hallucis Brevis Tenodesis. Case Rep. Orthop. 2015, 2015, 179642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, G.C. Intrinsic Muscle Flaps for Coverage of Small Defects in the Foot. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Surg. 2020, 37, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fessell, D.P.; Jamadar, D.A.; Jacobson, J.A.; Caoili, E.M.; Dong, Q.; Pai, S.S.; van Holsbeeck, M.T. Sonography of Dorsal Ankle and Foot Abnormalities. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003, 181, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agawany, A.E.; Meguid, E.A. Mode of Insertion of the Abductor Hal- Lucis Muscle in Human Feet and Its Arterial Supply. Folia Morphol. 2010, 69, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, E. Insertion of the Abductor Hallucis Muscle in Feet with and without Hallux Valgus. Anat. Rec. 1999, 254, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calancie, B.; Molano, M.R.; Broton, J.G. Abductor Hallucis for Monitoring Lower-Limb Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury in Man. Spinal Cord 2004, 42, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korol, E.; Johnston, K.; Waser, N.; Sifakis, F.; Jafri, H.S.; Lo, M.; Kyaw, M.H. A Systematic Review of Risk Factors Associated with Surgical Site Infections among Surgical Patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, W.G.; Lincoln, C.R.; Bassett, F.H.; Goldner, J.L. The Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome. Diagnosis and Treatment. JAMA 1969, 207, 716–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhansali, R.; Bhansali, R. Accessory Abductor Hallucis Causing Entrapment of the Posterior Tibial Nerve. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1987, 69-B, 479–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- de Souza Reis Soares, O.; Duarte, M.L.; Brasseur, J.L. Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome: An Ultrasound Pictorial Review. J. Ultrasound Med. 2021, 41, 1247–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saar, W.E.; Bell, J. Accessory Flexor Digitorum Longus Presenting as Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome: A Case Report. Foot Ankle Spec. 2011, 4, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Tokita, K.; Miki, A.; Terashima, T. Anatomical Study of Human Adductor Hallucis Muscle with Respect to Its Origin and Insertion. Ann. Anat. 2003, 185, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cralley, J.C.; Schuberth, J.M. The Transverse Head of Adductor Hallucis. Ann. Anat. 1979, 146, 400–409. [Google Scholar]
- Sarrafian, S.K. Anatomy of Foot and Ankle; J.B. Lipincott: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1983; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar]
- McBride, E.D. A Conservative Operation for Bunions. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1928, 10, 735–739. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Nova, A.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, R.; Gómez-Martín, B.; Escamilla Martínez, E.; Expósito-Arcas, A.; Novel-Martí, V. The Effect of Adductor Tendon Transposition in the Modified McBride Procedure. Foot Ankle Spec. 2008, 1, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, S.; Thordarson, D.B. The Adductor Hallucis Revisited. Foot Ankle Int. 2001, 22, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerro de Bengoa Vallejo, R.; Losa Iglesias, M.E.; Jules, K.T. Tendon Insertion at the Base of the Proximal Phalanx of the Hallux: Surgical Implications. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2012, 51, 729–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- le Double, A.-F. Traité Des Variations Du Système Musculaire de l’Homme et de Leur Signification Au Point de Vue de l’Anthropologie Zoologique; Schleicher Freres: Paris, France, 1897; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Young, W.; Jiang, P.; Edelstein, Y. Congenital Absence of Tibial Sesamoids, with Alternate Insertions of the Flexor Hallucis Brevis Tendon. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2020, 59, 1079–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masadeh, S.; Liette, M.D.; Perry, W.; Bibbo, C. Distally-Based (Reverse) Medial Hemi-Flexor Hallucis Brevis Muscle Flap in a Series of High-Risk Patients: Retrospective Case Series. Plast Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2023, 11, E4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attinger, C.E.; Ducic, I.; Cooper, P.; Zelen, C.M. The Role of Intrinsic Muscle Flaps of the Foot for Bone Coverage in Foot and Ankle Defects in Diabetic and Nondiabetic Patients. Plast Reconstr. Surg. 2002, 110, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latey, P.J.; Burns, J.; Nightingale, E.J.; Clarke, J.L.; Hiller, C.E. Reliability and Correlates of Cross-Sectional Area of Abductor Hallucis and the Medial Belly of the Flexor Hallucis Brevis Measured by Ultrasound. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manter, J.T. Variations of the Interosseous Muscles of the Human Foot. Anat. Rec. 1945, 93, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalin, P.J.; Hirsch, B.E. The Origins and Functions of the Interosseous Muscles of the Foot. J. Anat. 1987, 152, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, A.; Miller, J.; Keeler, J.; Siesel, K.; Bridges, E. Absence of the Fourth Tendon of the Flexor Digitorum Brevis Muscle: A Cadaveric Study. Foot Ankle Spec. 2013, 6, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcin, B.; Ozan, H. Some Variations of the Musculus Flexor Digitorum Brevis. Anat. Sci. Int. 2005, 80, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, S.W.; Menezes, R.G.; Mamata, S.; Baral, P.; Hunnargi, S.A.; Kanchan, T.; Bodhe, A.V.; Bhat, N.B. Phylogenetic Variation in Flexor Digitorum Brevis: A Nepalese Cadaveric Study. Nepal Med. Coll. J. 2008, 10, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nathan, H.; Gloobe, H. Flexor Digitorum Brevis: Anatomical Variations. Ann. Anat. 1974, 135, 295–301. [Google Scholar]
- Macalister, A. Additional Observations on Muscular Anomalies in Human Anatomy (Third Series): With a Catalogue of the Principal Muscular Variations Hitherto Published. Trans. R. Ir. Acad. 1875, 25, 126–200. [Google Scholar]
- Beldame, J.; Lalevée, M.; Regnard, S.; Marguet, F.; Csanyi-Bastien, M.; Masse, M.; Duparc, F. Impact of Intertendinous Connections between the Flexor Digitorum Brevis and Longus on Percutaneous Tenotomy for the Treatment of Claw Toes: An Anatomic and Ultrasound Study. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2021, 43, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Prado, M.; Ripoll, P.L.; Golanó, P. Minimally Invasive Foot Surgery Surgical Techniques, Indications, Anatomical Basis; About Your Health Publisher’s: Barcelona, Spain, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Angin, S.; Crofts, G.; Mickle, K.J.; Nester, C.J. Ultrasound Evaluation of Foot Muscles and Plantar Fascia in Pes Planus. Gait Posture 2014, 40, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvius, J. Hippocratis et Galeni Physiologiae Partem Anatomicam Isagoge; Gorbinum A: Paris, France, 1560. [Google Scholar]
- Pretterklieber, B. Morphological Characteristics and Variations of the Human Quadratus Plantae Muscle. Ann. Anat. 2018, 216, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haratizadeh, S.; Seyyedin, S.; Nematollahi-mahani, S.N. Anatomical Variation of Quadratus Plantae in Relation with Flexor Hallucis Longus and Flexor Digitorum Longus: A Rare Case. Folia Morphol. 2022, 82, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hur, M.; Kim, J.; Woo, J.; Choi, B.; Kim, H.; Lee, K. An Anatomic Study Ofthe Quadratus Plantae in Relation to Tendinous Slips Ofthe Flexor Hallucis Longus for Gait Analysis. Clinic. Anat. 2011, 24, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nováková, Z.; Korbelár, P. Variability and Development of the Quadratus Plantae Muscle in Man. Folia Morphol. 1976, 24, 345–348. [Google Scholar]
- Mickle, K.J.; Nester, C.J.; Crofts, G.; Steele, J.R. Reliability of Ultrasound to Measure Morphology of the Toe Flexor Muscles. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2013, 6, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hur, M.S.; Kim, J.H.; Gil, Y.C.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, K.S. New Insights into the Origin of the Lumbrical Muscles of the Foot: Tendinous Slip of the Flexor Hallucis Longus Muscle. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2015, 37, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oukouchi, H.; Murakami, T.; Kikuta, A. Insertions of the Lumbrical and Interosseous Muscles in the Human Foot. Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn. 1992, 69, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Schmidt, R.; Reissig, D.; Heinrichs, H.J. Die m. Lumbricales Am Fuss Des Menschen. Ann. Anat. 1963, 113, 450–453. [Google Scholar]
- Severinsen, K.; Obel, A.; Jakobsen, J.; Andersen, H. Atrophy of Foot Muscles in Diabetic Patients Can Be Detected with Ultrasonography. 2007, 30, 3053–3057. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 3053–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Sol, M.; Olave, E.; Gabrielli, C.; Mandiola, E.; Prates, J. Innervation of the Abductor Digiti Minimi Muscle of the Human Foot: Anatomical Basis of the Entrapment of the Abductor Digiti Minimi Nerve. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2002, 24, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Number of EDB Muscle Bellies | Typical Site of Insertion |
|---|---|
| 2 | first and fourth toes |
| second and third toes | |
| first and fifth toes | |
| 3 | first, second, and third toes |
| second, third, and fourth toes | |
| 4 | first, second, third, and fourth toe |
| Type | Description of Insertion | Occurrence |
|---|---|---|
| I | single tendinous insertion onto the base of the proximal phalanx of the first toe | 46.7% |
| II | tendinous insertion onto the base of the proximal phalanx of the first toe with a slip onto the medial sesamoid bone | 33.3% |
| III | single insertion onto the medial sesamoid bone | 6.7% |
| IV | superficial tendinous slip onto the proximal phalanx and a deep slip onto the metatarsophalangeal joint capsule of the first toe | 13.3% |
| Type | Description of Insertion | Occurrence |
|---|---|---|
| A | single tendon inserted onto the proximal phalanx of the first toe | 38.5% |
| B | two insertion sites including the medial sesamoid bone and medial sesamoid ligament | 59.6% |
| C | single insertion onto medial sesamoid bone | 1.8% |
| Type | Description | Occurrence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Narrow type with three subtypes | 47% | |
| Subtype 1 | origin from the fibrous sheath of the peroneus longus muscle tendon, long plantar ligament, and the base of the second, third, and fourth metatarsals and the lateral cuneiform bone | ||
| Subtype 2 | all sites of origin comparable with those presented in subtype 1; however, no origin from the long plantar ligament | ||
| Subtype 3 | all sites of origin comparable with those presented in subtype 1; however, no origin from the lateral cuneiform bone | ||
| B | Lateral type; origin from the fibrous sheath of the peroneus longus muscle tendon, long plantar ligament, and the base of the second, third, and fourth metatarsals, the lateral cuneiform bone, and additionally from the base of the fifth metatarsal bone | 33% | |
| C | Wide type; compound origin: laterally from the fifth metatarsal bone, medially from the medial intermuscular septum/tibialis posterior tendon/plantar tarsometatarsal ligament/peroneus longus tendon, and classically from the fibrous sheath of the peroneus longus muscle tendon, the long plantar ligament, and the base of the second, third, and fourth metatarsals, and the lateral cuneiform bone | 9% | |
| D | Medial type; origin from the divided tendon of the tibialis posterior/medial intermuscular septum/tarsometatarsal ligament/peroneus longus tendon and from the fibrous sheath of the peroneus longus muscle tendon, the long plantar ligament, and the base of the second, third, and fourth metatarsals and the lateral cuneiform bone | 11% | |
| Type | Description | Occurrence |
|---|---|---|
| A | Narrow type; origin from the third and fourth metatarsophalangeal joint capsules and from the deep transverse metatarsal ligaments | 40% |
| B | Lateral type; origin from the third, fourth, and fifth metatarsophalangeal joint capsules and from the deep transverse metatarsal ligament | 30% |
| C | Wide type; origin from the aponeurosis between the third plantar interosseus muscle and fourth dorsal interosseus muscle and from the third and fourth (sometimes also the fifth) metatarsophalangeal joint capsules | 30% |
| Type | Description | Occurrence |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | two similarly sized muscle bellies from both the tendon of the FDL and the tendinous slip of the FHL for the second toe | 37.9% |
| 2 | two-thirds of the muscle arose from the FDL tendon for the second toe, one-third of the first lumbrical arose from the tendinous slip of the FHL for the second toe | 30.3% |
| 3 | origin solely from the FHL tendon for the second toe | 15.2% |
| 4 | origin from the tendon of the FDL for the second toe with a few muscle fibers arising from the tendinous slip of the FHL for the second toe | 12.1% |
| 5 | one-third of the muscle arises from the tendon of the FDL for the second toe and two-thirds from the tendinous slip of the FHL for the second toe | 3% |
| 6 | origin solely from the tendon of the FDL for the second toe | 1.5% |
| Accessory Slip Origin | Accessory Slip Insertion | Occurrence |
|---|---|---|
| The first lumbrical muscle | The base of the second proximal phalanx | 12% |
| The second lumbrical muscle | The base of the third proximal phalanx | 8% |
| The third lumbrical muscle | The base of the fourth proximal phalanx | 12% |
| The fourth lumbrical muscle | The base of the fifth proximal phalanx | 16% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pośnik, M.; Zielinska, N.; Gonera, B.; Olewnik, Ł.; Głowacka, M.; Maślanka, K.; Ruzik, K. A Literature Review of the Morphological Variability in the Intrinsic Muscles of the Foot: Traps Awaiting Clinicians during Ultrasound. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4286. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154286
Pośnik M, Zielinska N, Gonera B, Olewnik Ł, Głowacka M, Maślanka K, Ruzik K. A Literature Review of the Morphological Variability in the Intrinsic Muscles of the Foot: Traps Awaiting Clinicians during Ultrasound. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(15):4286. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154286
Chicago/Turabian StylePośnik, Marta, Nicol Zielinska, Bartosz Gonera, Łukasz Olewnik, Mariola Głowacka, Krystian Maślanka, and Kacper Ruzik. 2024. "A Literature Review of the Morphological Variability in the Intrinsic Muscles of the Foot: Traps Awaiting Clinicians during Ultrasound" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 15: 4286. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154286
APA StylePośnik, M., Zielinska, N., Gonera, B., Olewnik, Ł., Głowacka, M., Maślanka, K., & Ruzik, K. (2024). A Literature Review of the Morphological Variability in the Intrinsic Muscles of the Foot: Traps Awaiting Clinicians during Ultrasound. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(15), 4286. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154286





