Atlantoaxial Instability in the Course of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Relation to Selected Parameters of Sagittal Balance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neva, M.H.; Myllykangas-Luosujärvi, R.; Kautiainen, H.; Kauppi, M. Mortality associated with cervical spine disorders: A population—Based study of 1666 patients with rheumatoid arthritis who died in Finland in 1989. Rheumatology 2001, 40, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.V.; Ludwig, S.C.; Silber, J.; Gelb, D.E.; Anderson, P.A.; Frank, L.; Vaccaro, A.R. Rheumatoid arthritis of the cervical spine. Spine J. 2004, 4, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillick, J.L.; Wainwright, J.; Das, K. Rheumatoid arthritis and the cervical spine: A review on the role of surgery. Int. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 2015, 252456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, S. Upper cervical instability associated with rheumatoid arthritis: A case report. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2016, 24, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entezami, P.; Fox, D.A.; Clapham, P.J.; Chung, K.C. Historical perspective on the ethiology of rheumathoid arthritis. Hand. Clin. 2011, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, S. History of rheumatology. Med. J. Dr D Y Patil Univ. 2014, 7, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, B.R.; Moskovich, R.; Razi, A.E. Rheumatoid arthritis of the cervical spine—Clinical considerations. Bull. NYU Hosp. Jt. Dis. 2011, 69, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Barton, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Emery, P.; Firestein, G.S.; Kavanaugh, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Solomon, D.H.; Strand, V.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2018, 4, 18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheer, J.K.; Tang, J.A.; Smith, J.S.; Acosta, F.L., Jr.; Protopsaltis, T.S.; Blondel, B.; Bess, S.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Deviren, V.; Lafage, V.; et al. Cervical spine alignment, sagittal deformity, and clinical implications: A review. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2013, 19, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.A., 3rd; Panjabi, M.M. The basic kinematics of the human spine. A review of past and current knowledge. Spine 1978, 3, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, W.E.; Bledsoe, J.M.; Clarke, M.J.; Nottmeier, E.W.; Pichelmann, M.A. Rheumatoid arthritis of the craniovertebral junction. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mańczak, M.; Gasik, R. Cervical spine instability in the course of rheumatoid arthritis—Imaging methods. Reumatologia 2017, 55, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Pope, J. Cervical spine involvement in rheumatoid arthritis over time: Results from a meta-analysis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, F.C., Sr.; Rosenbaum, R.; Narayanan, M.; Koby, M.; Tuchman, K.; Rowe, P.C.; Francomano, C. Atlanto-axial rotary instability (Fielding type 1): Characteristic clinical and radiological findings, and treatment outcomes following alignment, fusion, and stabilization. Neurosurg. Rev. 2021, 44, 1553–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kapandji, A.I. Anatomiafunkcjonalnastawów. Tom3. Kregołsupaigłowa; Edra Urban & Partner: Wroclaw, Poland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Bochenek, A.; Reicher, M. Anatomiaczłowieka. Tom, I. Wyd. XII; WydawnictwoNaukowe PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bochenek, A.; Reicher, M. Anatomiaczłowieka. Tom, I.V; Ośrodkowyukładnerwowy. PZWL: Warszawa, Poland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Mukerji, N.; Todd, N.V. Cervical myelopathy in rheumatoid arthritis. Neurol. Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 153628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Janssen, I.; Nouri, A.; Tessitore, E.; Meyer, B. Cervical Myelopathy in Patients Suffering from Rheumatoid Arthritis-A Case Series of 9 Patients and A Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gallie, W.E. Fractures and dislocations of the cervical spine. Am. J. Surg. 1939, 46, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.L.; Jenkins, E.B. Atlanto-axial arthrodesis by the wedge compression method. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 1978, 60, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.R.; Goetz, D.D.; Menezes, A.H. Arthrodesis of the cervical spine in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Ser. A 1989, 71, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magerl, F.; Seeman, P. Stable posterior fusion of the atlas and axis by transarticular screw fixation. In Cervical Spine; Kehr, P., Weidner, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; pp. 322–327. [Google Scholar]
- Grob, D.; Magerl, F. Surgical stabilization of C1 and C2 fractures. Orthopade 1987, 16, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, A.; Laheri, V. Plate and screw fixation for atlanto-axial subluxation. Acta Neurochirurgica 1994, 129, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, J.; Melcher, R.P. Posterior C1–C2 fusion with polyaxial screw and rod fixation. Spine 2001, 26, 2467–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAfee, P.C.; Cassidy, J.R.; Davis, R.F.; North, R.B.; Ducker, T.B. Fusion of the occiput to the upper cervical spine: A review of 37 cases. Spine. 1991, 16, S490–S494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipson, S.J. Cervical myelopathy and posterior atlanto-axial subluxation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 1985, 67, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaidi, A.C.; Kim, H.J. Classification(s) of Cervical Deformity. Neurospine 2022, 19, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Grob, D.; Dvorak, J.; Panjabi, M.; Froehlich, M.; Hayek, J. Posterior occipitocervical fusion: A preliminary report of a new technique. Spine 1991, 16, S17–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Xu, W.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. Cervical spine involvement risk factors in rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurube, T.; Sumi, M.; Nishida, K.; Miyamoto, H.; Kohyama, K.; Matsubara, T.; Miura, Y.; Hirata, H.; Sugiyama, D.; Doita, M. Accelerated development of cervical spine instabilities in rheumatoid arthritis: A prospective minimum 5-year cohort study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, I.W.; Joo, Y.B.; Park, K.S.; Kim, K.J. Risk factors for cervical spine instability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashima, Y.; Yurube, T.; Hirata, H.; Sugiyama, D.; Sumi, M. Hyogo Organization of Spinal Disorders Predictive Risk Factors of Cervical Spine Instabilities in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Prospective Multicenter Over 10-Year Cohort Study. Spine 2017, 42, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaito, T.; Ohshima, S.; Fujiwara, H.; Makino, T.; Takenaka, S.; Sakai, Y.; Yoshikawa, H. Predictors for progression of two different types of cervical lesions in rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologic agents. J. Orthop. Sci. 2019, 24, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geraldo-Flores, N.A.; Merlos-López, R.J.; Rodríguez-Wong, J.A.; Ramírez-Hernández, S.; Espino-Lizarraga, M.J.; Pérez-Atanasio, J.M. La severidad de la artritisreumatoidecomo predictor oportuno de inestabilidad de la columna cervical asintomática [The severity of rheumatoid arthritis as a timely predictor of instability in the asymptomatic cervical spine]. Acta Ortop. Mex. 2018, 32, 342–346. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro-Franco, J.; Roussouly, P. Sagittal balance: The main parameters. In Sagittal Balance of the Spine: From Normal to Pathology: A Key for Treatment Strategy, 1st ed.; Roussouly, P., Pinheiro-Franco, J., Labelle, H., Gechren, M., Eds.; Normative Values Following Age and Populations; Thieme: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Roussouly, P.; Pinheiro-Franco, J.; Labelle, H.; Gechren, M. Sagittal Balance of the Spine: From Normal to Pathology: A Key for Treatment Strategy, 1st ed.; Normative Values Following Age and Populations; Thieme: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Błaszczyk, J. Biomechanika Kliniczna, Podręcznik dla Studentów Medycyny i Fizjoterapii; WydawnictwoLekarskie PZWL: Warszawa, Poland, 2004; pp. 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siempis, T.; Tsakiris, C.; Anastasia, Z.; Alexiou, G.A.; Voulgaris, S.; Argyropoulou, M.I. Radiological assessment and surgical management of cervical spine involvement in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2023, 43, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joaquim, A.F.; Ghizoni, E.; Tedeschi, H.; Appenzeller, S.; Riew, K.D. Radiological evaluation of cervical spine involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Neurosurg. Focus. 2015, 38, E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colebatch, A.N.; Edwards, C.J.; Østergaard, M.; van der Heijde, D.; Balint, P.V.; D’Agostino, M.-A.; Forslind, K.; Grassi, W.; Haavardsholm, E.A.; Haugeberg, G.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging of the joints in the clinical management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonezawa, T.; Tsuji, H.; Matsui, H.; Hirano, N. Subaxial lesions in rheumatoid arthritis. Radiographic factors suggestive of lower cervical myelopathy. Spine 1995, 20, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranawat, C.S.; O’Leary, P.; Pellicci, P.; Tsairis, P.; Marchisello, P.; Dorr, L. Cervical spine fusion in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1979, 61, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riew, K.D.; Hilibrand, A.S.; Palumbo, M.A.; Sethi, N.; Bohlman, H.H. Diagnosing basilar invagination in the rheumatoid patient. The reliability of radiographic criteria. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2001, 83, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faro, F.D.; Marks, M.C.; Pawelek, J.; Newton, P.O. Evaluation of a functional position for lateral radiograph acquisition in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 2004, 29, 2284–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, S.D.; Dodge, L.D.; Bohlman, H.H.; Rechtine, G.R. Rheumatoid arthritis of the cervical spine. A long-term analysis with predictors of paralysis and recovery. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1993, 75, 1282–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Sha, S.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, W.; Qiu, Y.; Zhu, Z. Influence of the Occipital Orientation on Cervical Sagittal Alignment: A Prospective Radiographic Study on 335 Normal Subjects. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vital, J.M.; Seneges, P.; Castelani, J.E. From Head do the feet: Anatomy of upriht position. In Sagittal Balance of the Spine: A Key for Treatment Strategy, 1st ed.; Rossouly, P., Piheiro-Franco, J., Labelle, H., Gechren, M., Eds.; Normative values following age and population; Thieme: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 24–42. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, K.T.; Seo, E.M.; Suk, K.S.; Kwack, Y.H.; Son, E.S. The influence of thoracic inlet alignment on the craniocervical sagittal balance in asymptomatic adults. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2012, 25, E41–E47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ames, C.P.; Blondel, B.; Scheer, J.K.; Schwab, F.J.; Le Huec, J.C.; Massicotte, E.M.; Patel, A.A.; Traynelis, V.C.; Kim, H.J.; Shaffrey, C.I.; et al. Cervical radiographical alignment: Comprehensive assessment techniques and potential importance in cervical myelopathy. Spine 2013, 38 (Suppl. 1), S149–S160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Hyun, S.J.; Kim, K.J. Odontoid Incidence: A Novel Cervical Parameter Influencing Cervical Alignment from Top to Bottom. Neurospine 2022, 19, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Passias, P.G.; Alas, H.; Bess, S.; Line, B.G.; Lafage, V.; Lafage, R.; Ames, C.P.; Burton, D.C.; Brown, A.; Bortz, C.; et al. Patient-related and radiographic predictors of inferior health-related quality-of-life measures in adult patients with nonoperative spinal deformity. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2021, 34, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ames, C.P.; Smith, J.S.; Scheer, J.K.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Lafage, V.; Deviren, V.; Moal, B.; Protopsaltis, T.; Mummaneni, P.V.; Mundis, G.M., Jr.; et al. A standardized nomenclature for cervical spine soft-tissue release and osteotomy for deformity correction: Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2013, 19, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ames, C.P.; Smith, J.S.; Eastlack, R.; Blaskiewicz, D.J.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Schwab, F.; Bess, S.; Kim, H.J.; Mundis, G.M., Jr.; Klineberg, E.; et al. Reliability assessment of a novel cervical spine deformity classification system. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2015, 23, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, H.; Ames, C.; Mehdian, H.; Bartels, R.; Ferch, R.; Deriven, V.; Toyone, H.; Shaffrey, C.; Smith, J.; Hitzl, W.; et al. Characteristics of deformity surgery in patients with severe and rigid cervical kyphosis (CK): Results of the CSRS-Europe multi-centre study project. Eur. Spine J. 2019, 28, 324–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Virk, S.; Elysee, J.; Passias, P.; Ames, C.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Mundis, G., Jr.; Protopsaltis, T.; Gupta, M.; Klineberg, E.; et al. The morphology of cervical deformities: A two-step cluster analysis to identify cervical deformity patterns. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Virk, S.; Elysee, J.; Ames, C.; Passias, P.; Shaffrey, C.; Mundis, G.; Protopsaltis, T.; Gupta, M.; Klineberg, E.; et al. Surgical strategy for the management of cervical deformity is based on type of cervical deformity. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, S.; Ozgen, S.; Pamir, M.N.; Ozek, M.M.; Erzen, C. Cervical spondylotic myelopathy: Surgical results and factors affecting prognosis. Neurosurgery 1998, 43, 43–49, discussion 49–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suk, K.S.; Kim, K.T.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.M. Significance of chin-brow vertical angle in correction of kyphotic deformity of ankylosing spondylitis patients. Spine 2003, 28, 2001–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.A.; Scheer, J.K.; Smith, J.S.; Deviren, V.; Bess, S.; Hart, R.A.; Lafage, V.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Schwab, F.; Ames, C.P.; et al. The impact of standing regional cervical sagittal alignment on outcomes in posterior cervical fusion surgery. Neurosurgery 2012, 71, 662–669, discussion 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terran, J.; Schwab, F.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Smith, J.S.; Devos, P.; Ames, C.P.; Fu, K.M.; Burton, D.; Hostin, R.; Klineberg, E.; et al. The SRS-Schwab adult spinal deformity classification: Assessment and clinical correlations based on a prospective operative and nonoperative cohort. Neurosurgery 2013, 73, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masamoto, K.; Otsuki, B.; Fujibayashi, S.; Shima, K.; Ito, H.; Furu, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Tanaka, M.; Lyman, S.; Yoshitomi, H.; et al. Factors influencing spinal sagittal balance, bone mineral density, and Oswestry Disability Index outcome measures in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, T.; Yano, K.; Shirahata, T.; Ikari, K.; Hiroshima, R.; Nasu, Y.; Okazaki, K. Spinal sagittal balance associated with age, vertebral fracture, and functional disability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A cross-sectional study. Mod. Rheumatol. 2020, 30, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramiro, K.R.B.; Mystro, S.; Veiga, I.G.; Rosa, A.F.; Lima, M.C.; Tebet, M.A.; Pasqualini, W.; Cavali, P.T.M.; Neto, M.I.R. Analysis of cervical sagittal parameters in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Coluna/Columna 2021, 20, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.C.; Qian, B.P.; Qiu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Ni, H.B. Surgical overreduction and hyperlordotic fusion of C1-C2 joint are associated with cervical sagittal malalignment. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2017, 137, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Okada, E.; Watanabe, K.; Tsuji, T.; Takaishi, H.; Nakamura, M.; Toyama, Y.; Chiba, K. Risk factors for development of subaxial subluxations following atlantoaxial arthrodesis for atlantoaxial subluxations in rheumatoid arthritis. Spine 2010, 35, 1551–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, H.; Ito, M.; Abumi, K.; Kotani, Y.; Shono, Y.; Takada, T.; Minami, A. A retrospective radiographic analysis of subaxial sagittal alignment after posterior C1-C2 fusion. Spine 2004, 29, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Qi, Y.; Tan, M.; Yi, P.; Yang, F.; Tang, X.; Hao, Q. Incidence and risk factors for adjacent segment degeneration following occipitoaxial fusion for atlantoaxial instability in non-rheumatoid arthritis. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2018, 138, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H.; Neo, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Fujibayashi, S.; Yoshitomi, H.; Nakamura, T. Subaxial subluxation after atlantoaxial transarticular screw fixation in rheumatoid patients. Eur. Spine J. 2009, 18, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Joaquim, A.F.; Osorio, J.A.; Riew, K.D. Occipitocervical Fixation: General Considerations and Surgical Technique. Glob. Spine J. 2020, 10, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pérez-Edo, L.; Díez-Pérez, A.; Mariñoso, L.; Vallés, A.; Serrano, S.; Carbonell, J. Bone metabolism and histomorphometric changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 31, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, J.Z.; Feldman, Z.M.; McAnany, S.; Hecht, A.C.; Qureshi, S.A.; Cho, S.K. Osteoporosis in Cervical Spine Surgery. Spine 2016, 41, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, D.E.; Harrison, D.D.; Cailliet, R.; Troyanovich, S.J.; Janik, T.J.; Holland, B. Cobb method or Harrison posterior tangent method: Which to choose for lateral cervical radiographic analysis. Spine 2000, 25, 2072–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussouly, P.; Pinheiro-Franco, J.L. Biomechanical analysis of the spino-pelvic organization and adaptation in pathology. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20 (Suppl. 5), 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Carreon, L.Y.; Smith, C.L.; Dimar, J.R., 2nd; Glassman, S.D. Correlation of cervical sagittal alignment parameters on full-length spine radiographs compared with dedicated cervical radiographs. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2016, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Le Huec, J.C.; Thompson, W.; Mohsinaly, Y.; Barrey, C.; Faundez, A. Sagittal balance of the spine. Eur. Spine J. 2019, 28, 1889–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubousset, J. Spinal alignment, balance and harmony throught the ages. Int. J. Orth. 2019, 2, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Panjabi, M.M. The stabilizing system of the spine. Part, I.I. Neutral zone and instability hypothesis. J. Spinal Disord. 1992, 5, 390–396, discussion 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toprak, C.Ş.; Duruöz, M.T.; Gündüz, O.H. Static and Dynamic Balance Disorders in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Relationships With Lower Extremity Function and Deformities: A Prospective Controlled Study. Arch. Rheumatol. 2018, 33, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Amabile, C.; Pillet, H.; Lafage, V.; Barrey, C.; Vital, J.M.; Skalli, W. A new quasi-invariant parameter characterizing the postural alignment of young asymptomatic adults. Eur. Spine J. 2016, 25, 3666–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Cui, C.; Pei, L.; Huang, Z. Preoperative cervical sagittal alignment parameters and their impacts on myelopathy in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy: A retrospective study. PeerJ 2017, 5, e4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mac-Thiong, J.M.; Transfeldt, E.E.; Mehbod, A.A.; Perra, J.H.; Denis, F.; Garvey, T.A.; Lonstein, J.E.; Wu, C.; Dorman, C.W.; Winter, R.B. Can c7 plumbline and gravity line predict health related quality of life in adult scoliosis? Spine 2009, 34, E519–E527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrey, C.; Roussouly, P.; Le Huec, J.C.; D’Acunzi, G.; Perrin, G. Compensatory mechanisms contributing to keep the sagittal balance of the spine. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22 (Suppl. 6), S834–S841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
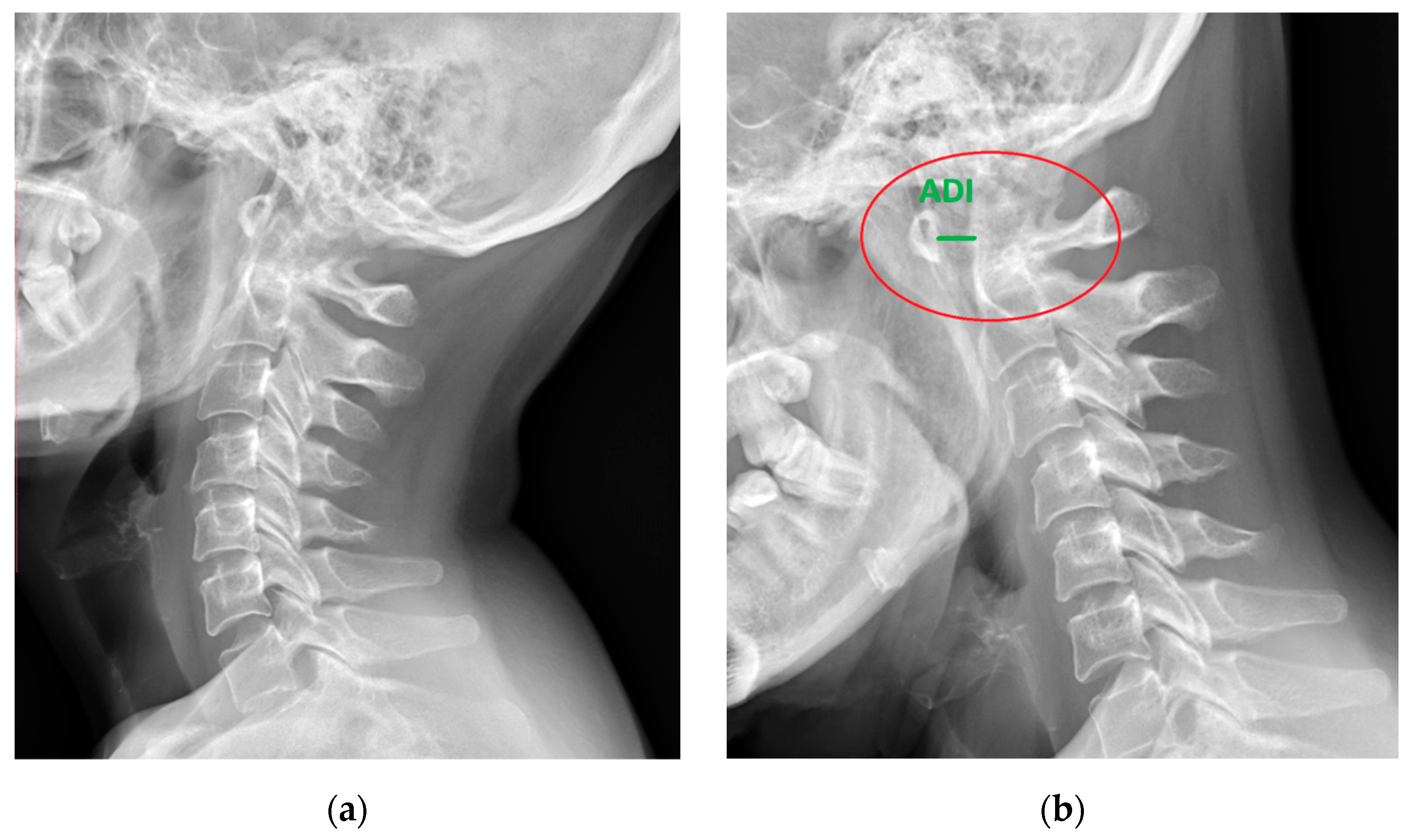
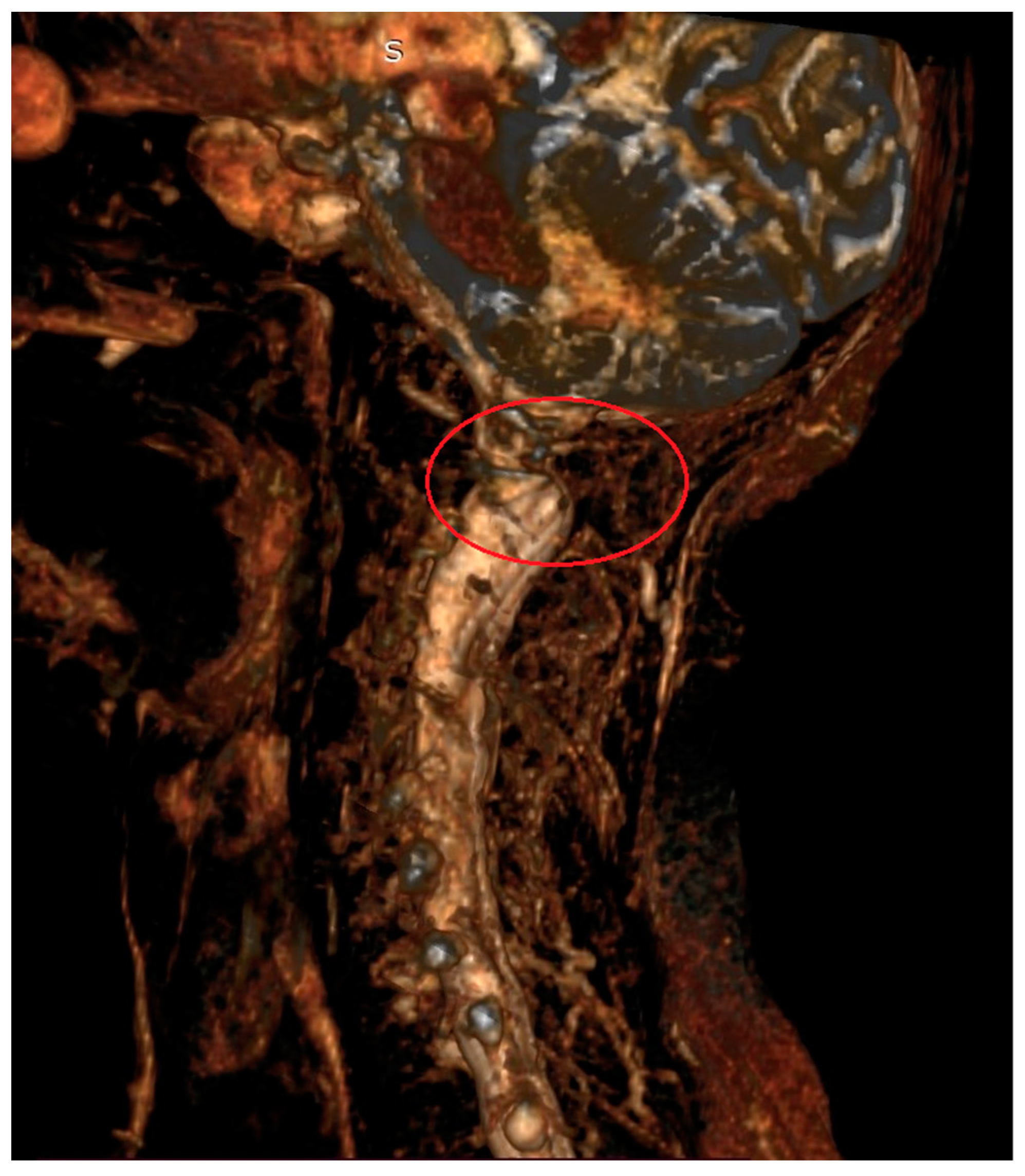
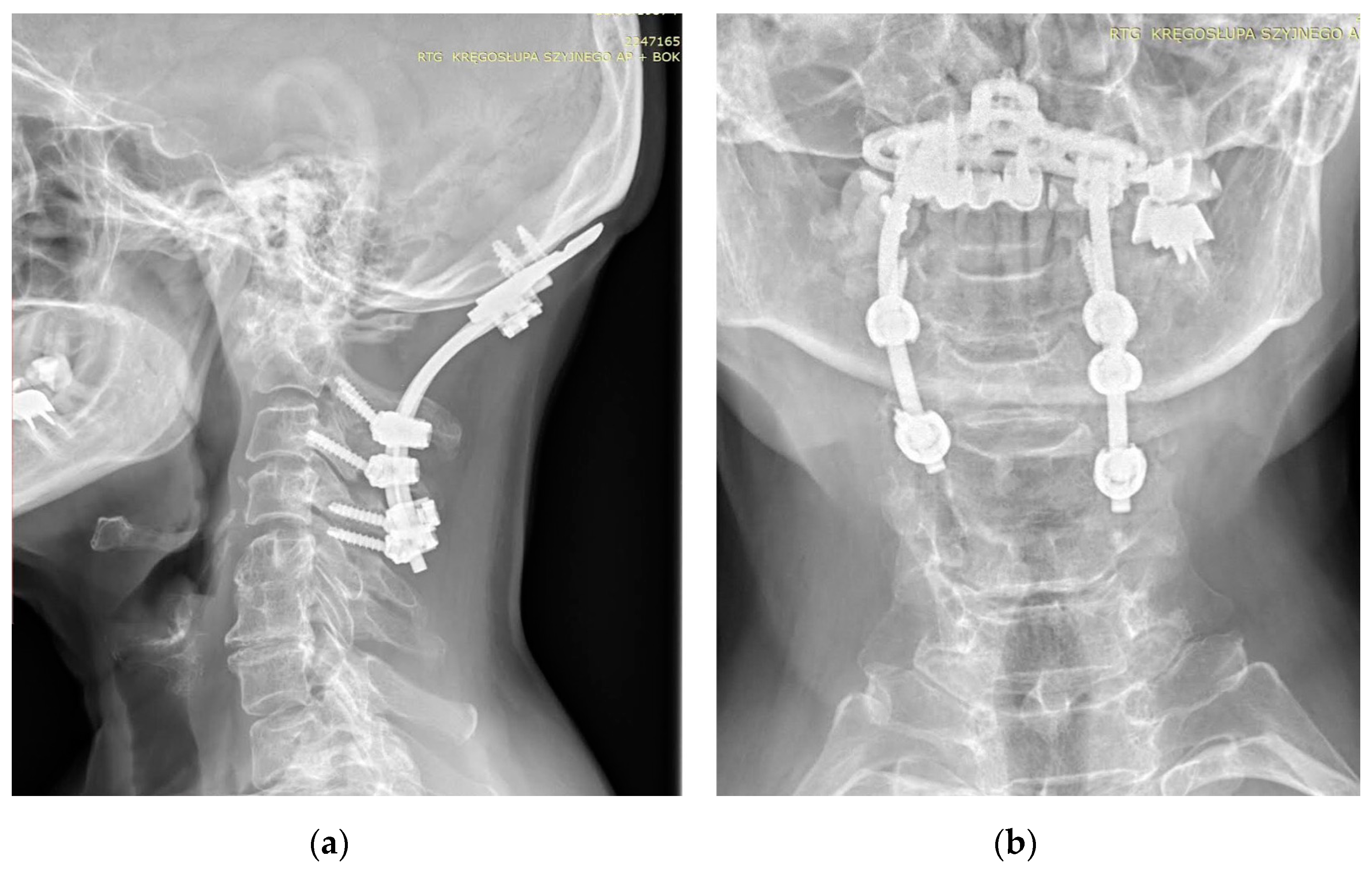
| Skull | |
| McGS | the angle between the line connecting the back edge of the pallatum with the caudal edge of foremen magnum and the horizontal line |
| OI | the angle between the line connecting the center of the skull and the center of foramen magnum and the line perpendicular to the foramen magnum |
| OT | the angle between the line directed through the center of the skull and the center of the foramen magnum and SVA |
| OS | the angle between the line parallel to the foremen magnum and the horizontal line (according to the W. Zhu modification) |
| Cervical | |
| COG-C7 SVA | the distance between the SVA—directed from COG—and the center of the C7 (vertebra) |
| C2–C7 SVA | the distance between the SVA—directed from the C2 vertebra—and the SVA directed from the center of C7 |
| Cobb angle C0–C2 | the angle between the McRea line and the lower surface of the C2 vertebra |
| Cobb angle C1–C7 | the angle between C1 and the lower surface of the C7 |
| Cobb angle C2–C7 | the angle between the lower surface of C2 and C7 |
| C7S | the angle between the upper surface of the C7 vertebra and the horizontal line |
| Thoracic, lumbar, sacral section and the pelvis | |
| ThK | the angle between the upper Th1 plate and the lower Th12 plate |
| T1S | the angle between the upper plate of Th1 and the horizontal line |
| LL | the angle between the upper L1 plate and the upper S1 plate |
| SS | the angle between the upper S1 plate and the horizontal line |
| PT | the angle between the upper plumb line from the femur head center and the center point of the superior sacrum endplate surface |
| Global | |
| C7SVA HD | the horizontal distance between the C7 SVA and the back edge of upper S1 plate |
| ODHA (degree) | the angle between the SVA directed through the center of the femur heads |
| ODHA (mm) | line connecting the center of the femur heads with the axis dense |
| Type of Instability | Cases of Instability | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| CrS | 3 | 3.4% |
| C1–C2 | 27 | 31% |
| C2–C3 | 10 | 11.5% |
| C3-C4 | 15 | 17.2% |
| C4-C5 | 21 | 24% |
| C5-C6 | 9 | 10.3% |
| C6-C7 | 2 | 2.3% |
| Assessment of the Relationship between Variables, Spearman Correlations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADI (mm) | ADI (mm)—Only among Patients with Subluxation | |||
| Spearman rho | COG-C7SVA (mm) | rho | −0.082 | 0.087 |
| p | 0.585 | 0.667 | ||
| C2–C7 SVA (mm) | rho | −0.203 | −0.203 | |
| p | 0.172 | 0.310 | ||
| C7 SVA (mm) | rho | 0.105 | −0.011 | |
| p | 0.489 | 0.956 | ||
| OD-HA (mm) | rho | −0.107 | 0.097 | |
| p | 0.452 | 0.630 | ||
| abs OD-HA (mm) | rho | 0.275 | 0.097 | |
| p | 0.065 | 0.528 | ||
| OD-HA (degree) | rho | −0.123 | 0.199 | |
| p | 0.423 | 0.329 | ||
| abs OD-HA (degree) | rho | 0.287 | 0.073 | |
| p | 0.053 | 0.653 | ||
| OI (degree) | rho | −0.077 | 0.005 | |
| p | 0.618 | 0.982 | ||
| OS (degree) (w mod. W. Zhu) | rho | −0.097 | 0.034 | |
| p | 0.530 | 0.876 | ||
| OT (degree) | rho | 0.016 | 0.015 | |
| p | 0.917 | 0.946 | ||
| McGS (degree) | rho | 0.006 | 0.243 | |
| p | 0.969 | 0.223 | ||
| C1–C7 (degree) | rho | −0.293 | −0.050 | |
| p | 0.046 | 0.805 | ||
| C0-C2 (degree) | rho | 0.108 | 0.095 | |
| p | 0.470 | 0.636 | ||
| C2–C7 (degree) | rho | −0.256 | 0.102 | |
| p | 0.082 | 0.612 | ||
| C7S (degree) | rho | −0.167 | −0.014 | |
| p | 0.261 | 0.944 | ||
| T1S (degree) | rho | −0.122 | −0.026 | |
| p | 0.493 | 0.911 | ||
| ThK (degree) | rho | −0.198 | −0.042 | |
| p | 0.198 | 0.844 | ||
| LL (degree) | rho | 0.082 | 0.006 | |
| p | 0.586 | 0.975 | ||
| PI (degree) | rho | 0.069 | −0.238 | |
| p | 0.650 | 0.232 | ||
| SS (degree) | rho | 0.004 | −0.316 | |
| p | 0.979 | 0.108 | ||
| PT (degree) | rho | 0.105 | −0.014 | |
| p | 0.487 | 0.944 | ||
| Assessment of the Relationship between Variables, Spearman Correlations | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| C7 SVA HD (mm) | |||
| Spearman rho | OD-HA (mm) | rho | 0.636 |
| abs OD-HA (mm) | rho | −0.029 | |
| OD-HA (degree) | rho | 0.602 | |
| abs OD-HA (degree) | rho | 0.023 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wróblewski, R.; Mańczak, M.; Gasik, R. Atlantoaxial Instability in the Course of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Relation to Selected Parameters of Sagittal Balance. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4441. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154441
Wróblewski R, Mańczak M, Gasik R. Atlantoaxial Instability in the Course of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Relation to Selected Parameters of Sagittal Balance. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(15):4441. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154441
Chicago/Turabian StyleWróblewski, Robert, Małgorzata Mańczak, and Robert Gasik. 2024. "Atlantoaxial Instability in the Course of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Relation to Selected Parameters of Sagittal Balance" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 15: 4441. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154441
APA StyleWróblewski, R., Mańczak, M., & Gasik, R. (2024). Atlantoaxial Instability in the Course of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Relation to Selected Parameters of Sagittal Balance. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(15), 4441. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154441





