Predictivity of the Prognostic Nutritional Index and Systemic Inflammation Index for All-Cause In-Hospital Mortality in Geriatric and Adult COVID-19 Inpatients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Measures
2.3. Statistical Analyses
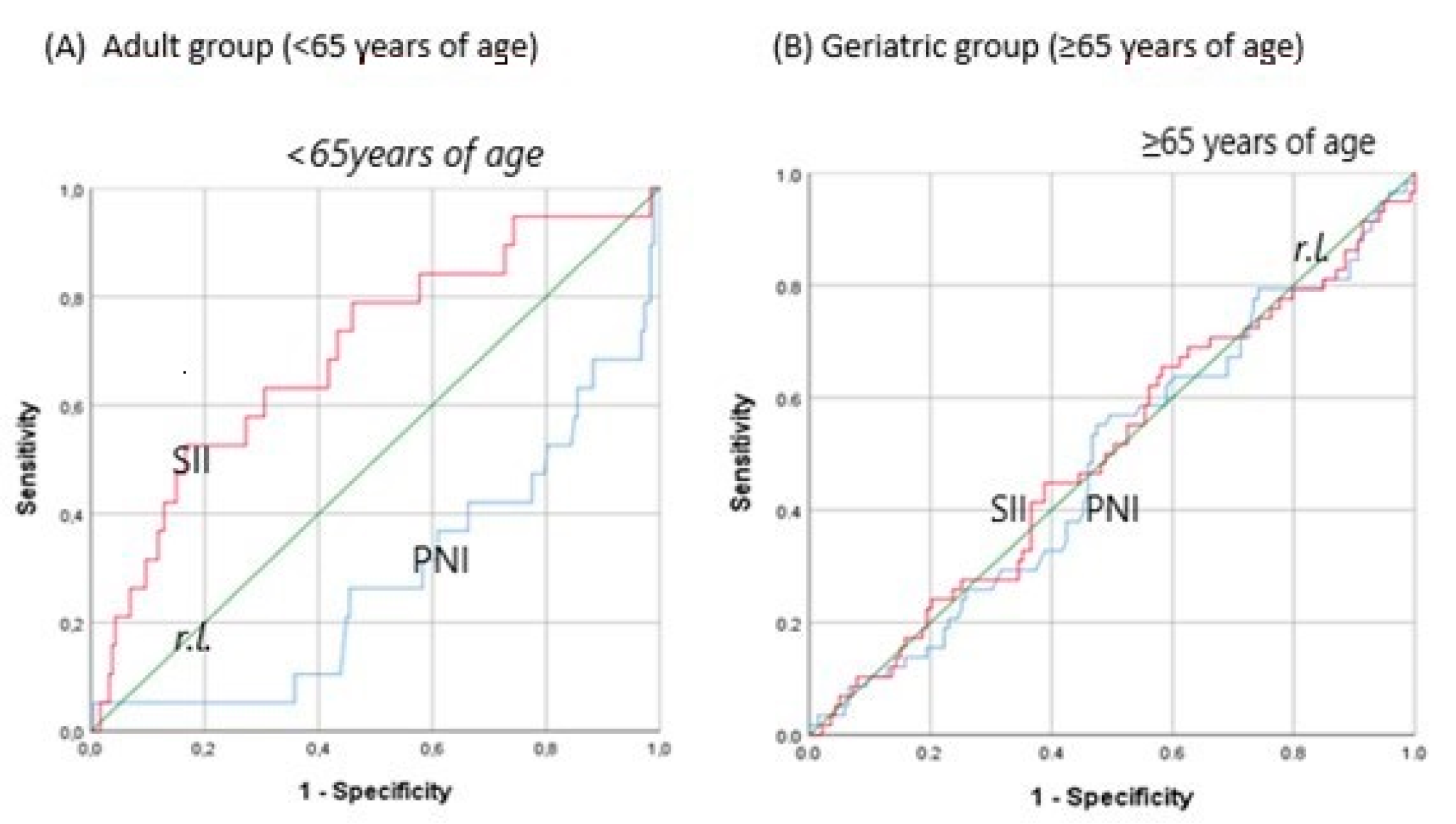
3. Results
Predictive Accuracy of Inflammation Indices According to Age Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations and Strengths
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.-J.; Dong, X.; Liu, G.-H.; Gao, Y.-D. Risk and Protective Factors for COVID-19 Morbidity, Severity, and Mortality. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 64, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Huang, L.; Chen, J.; Yuan, X.; Shen, Q.; Dong, S.; Cheng, B.; Guo, T.-M. Clinical features predicting mortality risk in older patients with COVID-19. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2020, 36, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidoriki, I.; Frountzas, M.; Schizas, D. Could nutritional and functional status serve as prognostic factors for COVID-19 in the elderly? Med. Hypotheses 2020, 144, 109946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.-J.; Jung, S.I. Age-Related Morbidity and Mortality among Patients with COVID-19. Infect. Chemother. 2020, 52, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, S.; Fischer, I.; Naderi, S.; Faghih Jouibari, M.; Abdolreza, S.; Karimialavijeh, E.; Aslzadeh, S.; Mashayekhi, M.; Zojaji, M.; Kahlert, U.D.; et al. Systemic Inflammatory Index Is a Novel Predictor of Intubation Requirement and Mortality after SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Pathogens 2021, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, A.; Shobeiri, P.; Kulasinghe, A.; Rezaei, N. Novel Systemic Inflammation Markers to Predict COVID-19 Prognosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 741061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fois, A.G.; Paliogiannis, P.; Scano, V.; Cau, S.; Babudieri, S.; Perra, R.; Ruzzittu, G.; Zinellu, E.; Pirina, P.; Carru, C.; et al. The Systemic Inflammation Index on Admission Predicts In-Hospital Mortality in COVID-19 Patients. Molecules 2020, 25, 5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Huang, H.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, C.; Liao, H.; Chen, X. Increased Pretreatment C-Reactive Protein-to-Albumin Ratio Predicts Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019. Res. Sq. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; He, M.; Yin, W.; Liao, X.; Wang, B.; Jin, X.; Ma, Y.; Yue, J.; Bai, L.; Liu, D.; et al. The Prognostic Nutritional Index is associated with mortality of COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, China. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Gan, X.; Wu, Z.; Xie, D.; Xiong, Y.; Hua, L.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, N.; Xiang, J.; Li, J. Novel serological biomarkers for inflammation in predicting disease severity in patients with COVID-19. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 89, 107065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastug, A.; Bodur, H.; Erdogan, S.; Gokcinar, D.; Kazancioglu, S.; Kosovali, B.D.; Ozbay, B.O.; Gok, G.; Turan, I.O.; Yilmaz, G.; et al. Clinical and laboratory features of COVID-19: Predictors of severe prognosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 88, 106950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliogiannis, P.; Zinellu, A.; Scano, V.; Mulas, G.; De Riu, G.; Pascale, R.M.; Arru, L.B.; Carru, C.; Pirina, P.; Mangoni, A.A.; et al. Laboratory test alterations in patients with COVID-19 and non COVID-19 interstitial pneumonia: A preliminary report. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2020, 14, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizo-Téllez, S.A.; Méndez-García, L.A.; Flores-Rebollo, C.; Alba-Flores, F.; Alcántara-Suárez, R.; Manjarrez-Reyna, A.N.; Baltazar-López, N.; Hernández-Guzmán, V.A.; León-Pedroza, J.I.; Zapata-Arenas, R.; et al. The Neutrophil-to-Monocyte Ratio and Lymphocyte-to-Neutrophil Ratio at Admission Predict In-Hospital Mortality in Mexican Patients with Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection (COVİD-19). Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosovali, B.D.; Kucuk, B.; Balkiz Soyal, O.; Mehmet Mutlu, N. Can prognostic nutritional index predict mortality in intensive care patients with COVID-19? Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çınar, T.; Hayıroğlu, M.; Çiçek, V.; Kılıç, Ş.; Asal, S.; Yavuz, S.; Selçuk, M.; Yalçınkaya, E.; Keser, N.; Orhan, A.L. Is prognostic nutritional index a predictive marker for estimating all-cause in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients with cardiovascular risk factors? Heart Lung J. Crit. Care 2021, 50, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashedi, S.; Keykhaei, M.; Pazoki, M.; Ashraf, H.; Najafi, A.; Kafan, S.; Peirovi, N.; Najmeddin, F.; Jazayeri, S.A.; Kashani, M.; et al. Clinical significance of prognostic nutrition index in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: Results from single-center experience with systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2021, 36, 970–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, K.-C.; Ko, C.-C.; Wang, L.-K.; Liu, P.-H.; Chen, I.-W.; Huang, Y.-T.; Sun, C.-K. Association of Prognostic Nutritional Index with Severity and Mortality of Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilge, M.; Akilli, I.K.; Karaayvaz, E.B.; Yesilova, A.; Yasar, K.K. Comparison of systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), early warning score (ANDC) and prognostic nutritional index (PNI) in hospitalized patients with malignancy, and their influence on mortality from COVID-19. Infect. Agents Cancer 2021, 16, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalbant, A.; Demirci, T.; Kaya, T.; Aydın, A.; Altındiş, M.; Güçlü, E. Can prognostic nutritional index and systemic im-mune-inflammatory index predict disease severity in COVID-19? Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L. Prognostic Value of Preoperative Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index in Patients with Cervical Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-L.; Wu, C.-H.; Hsu, P.-F.; Chen, S.-C.; Huang, S.-S.; Chan, W.L.; Lin, S.-J.; Chou, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-W.; Pan, J.-P.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) predicted clinical outcome in patients with coronary artery disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 50, e13230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosidło, J.W.; Wolszczak-Biedrzycka, B.; Matowicka-Karna, J.; Dymicka-Piekarska, V.; Dorf, J. Clinical Significance and Diagnostic Utility of NLR, LMR, PLR and SII in the Course of COVID-19: A Literature Review. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 539–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witkowski, J.M.; Fulop, T.; Bryl, E. Immunosenescence and COVID-19. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2022, 204, 111672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meftahi, G.H.; Jangravi, Z.; Sahraei, H.; Bahari, Z. The possible pathophysiology mechanism of cytokine storm in elderly adults with COVID-19 infection: The contribution of “inflame-aging”. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 69, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghobadi, H.; Mohammadshahi, J.; Javaheri, N.; Fouladi, N.; Mirzazadeh, Y.; Aslani, M.R. Role of leukocytes and systemic inflammation indexes (NLR, PLR, MLP, dNLR, NLPR, AISI, SIR-I, and SII) on admission predicts in-hospital mortality in non-elderly and elderly COVID-19 patients. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 916453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candeloro, M.; Di Nisio, M.; Balducci, M.; Genova, S.; Valeriani, E.; Pierdomenico, S.D.; Porreca, E. Prognostic nutritional index in elderly patients hospitalized for acute heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2020, 7, 2479–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaluźniak-Szymanowska, A.; Krzymińska-Siemaszko, R.; Lewandowicz, M.; Deskur-Śmielecka, E.; Stachnik, K.; Wieczorowska-Tobis, K. Diagnostic Performance and Accuracy of the MNA-SF against GLIM Criteria in Community-Dwelling Older Adults from Poland. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acar, E.; Demir, A.; Yıldırım, B.; Kaya, M.G.; Gökçek, K. The role of hemogram parameters and C-reactive protein in predicting mortality in COVID-19 infection. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elouadani, M.; Konzi, C.; Addi, Y.; Mourji, D.; Biaz, A.; Elmechtani, S.; Ennibi, K.; Dami, A.; Bouhsain, S. C-Reactive Protein, Ferritin, and Procalcitonin in 300 Moroccan Patients with COVID 19. Clin. Lab. 2022, 68, 2158–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrentieva, A.; Kaimakamis, E.; Voutsas, V.; Bitzani, M. An observational study on factors associated with ICU mortality in Covid-19 patients and critical review of the literature. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasmi, A.; Peana, M.; Pivina, L.; Srinath, S.; Benahmed, A.G.; Semenova, Y.; Menzel, A.; Dadar, M.; Bjørklund, G. Interrelations between COVID-19 and other disorders. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 224, 108651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becerra-Muñoz, V.M.; Núñez-Gil, I.J.; Eid, C.M.; Aguado, M.G.; Romero, R.; Huang, J.; Mulet, A.; Ugo, F.; Rametta, F.; Liebetrau, C.; et al. Clinical profile and predictors of in-hospital mortality among older patients hospitalised for COVID-19. Age Ageing 2020, 50, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babel, N.; Hugo, C.; Westhoff, T.H. Vaccination in patients with kidney failure: Lessons from COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 708–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covino, M.; De Matteis, G.; Della Polla, D.A.; Santoro, M.; Burzo, M.L.; Torelli, E.; Simeoni, B.; Russo, A.; Sandroni, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Predictors of in-hospital mortality and death risk stratification among COVID-19 patients aged ≥ 80 years old. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2021, 95, 104383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ticinesi, A.; Lauretani, F.; Nouvenne, A.; Porro, E.; Fanelli, G.; Maggio, M.; Meschi, T. C-reactive protein (CRP) measurement in geriatric patients hospitalized for acute infection. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 37, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhwani, S.K.; Mirza, T.; Khatoon, A.; Shaikh, F.; Khan, R.; Shaikh, O.A.; Nashwan, A.J. Inflammatory markers and COVID-19 disease pro-gression. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 1386–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotnis, A.; Mittal, R.; Chourasia, N.; Bharti, V.; Singh, S.; Sarkar, P.; Agrawal, A.; Ghosh, A.; Pal, R.; Kanwar, J. Blood-based biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, and severity prediction of COVID-19: Opportunities and challenges. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2022, 11, 4330–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakirca, G.; Cakirca, T.D.; Bindal, A.; Olcen, M. Inflammation-based Indices Predicting Mortality in COVID-19. J. Coll. Physicians Surg.-Pak. JCPSP 2023, 33, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Rincon, J.M.; Buonaiuto, V.; Ricci, M.; Martín-Carmona, J.; Paredes-Ruíz, D.; Calderón-Moreno, M.; Rubio-Rivas, M.; Beato-Pérez, J.L.; Arnalich-Fernández, F.; Monge-Monge, D.; et al. Clinical Character-istics and Risk Factors for Mortality in Very Old Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in Spain. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, e28–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelagatti, L.; Fabiani, G.; De Paris, A.; Lagomarsini, A.; Paolucci, E.; Pepe, F.; Villanti, M.; Todde, F.; Matteini, S.; Caldi, F.; et al. 4C mortality score and COVID-19 mortality risk score: An analysis in four different age groups of an Italian population. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, E.; Chapman, M.S.; Williams, N.; Dawson, K.J.; Mende, N.; Calderbank, E.F.; Jung, H.; Mitchell, T.; Coorens, T.H.H.; Spencer, D.H.; et al. Clonal dynamics of haematopoiesis across the human lifespan. Nature 2022, 606, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, S.S.; Oberoi, S.; Iqbal, K.; Bhattar, K.; Benítez-López, G.A.; Nieto-Salazar, M.A.; Velasquez-Botero, F.; Moreno Cortes, G.A.; Hilliard, J.; Madekwe, C.C.; et al. Prognostic value of novel serum bi-omarkers, including C-reactive protein to albumin ratio and fibrinogen to albumin ratio, in COVID-19 disease: A meta-analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Wu, X.; Jin, C.; Mu, T.; Gu, G.; Min, M.; Mu, S.; Han, Y. Predictive Significance of the Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) in Patients with Severe COVID-19. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 17302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzo, F.M.; Buan-Mayo, M. Nutritional biomarkers as predictors of clinical outcomes between COVID-19 severity groups in a tertiary government hospital. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 53, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangoni, A.A.; Zinellu, A. Systemic inflammation index, disease severity, and mortality in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1212998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Tian, J.; Wen, L. Meta-analysis of the systemic immune-inflammatory index and in-hospital mortality of COVID-19 patients. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudlinski, B.; Zgoła, D.; Stolińska, M.; Murkos, M.; Kania, J.; Nowak, P.; Noga, A.; Wojciech, M.; Zaborniak, G.; Zembron-Lacny, A. Systemic Inflammatory Predictors of In-Hospital Mor-tality in COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citu, C.; Gorun, F.; Motoc, A.; Sas, I.; Gorun, O.M.; Burlea, B.; Tuta-Sas, I.; Tomescu, L.; Neamtu, R.; Malita, D.; et al. The Predictive Role of NLR, d-NLR, MLR, and SIRI in COVID-19 Mortality. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shami, I.; Hourani, H.M.; Alkhatib, B. The use of prognostic nutritional index (PNI) and selected inflammatory indicators for predicting malnutrition in COVID-19 patients: A retrospective study. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahavvori, A.; Mosaddeghi-Heris, R.; Sevari, F.G.; Alavi, S.M.A.; Panahi, P.; Abbasi, N.; Youshanlouei, H.R.; Hejazian, S.S. Combined systemic inflammatory indexes as reflectors of outcome in patients with COVID-19 infection admitted to ICU. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 2337–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M.; Shaarawy, S.; Abdellateif, M.S. The Role of Different Inflammatory Indices in the Diagnosis of COVID-19. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 7843–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celik, C.O.; Ozer, N.; Ciftci, O.; Torun, S.; Çolak, M.Y.; Muderrisoglu, I.H. Evaluation of Inflammation-Based Prognostic Risk Scores in Predicting in-Hospital Mortality Risk in COVID-19 Patients: A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study. Infect. Dis. Clin. Microbiol. 2023, 5, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covino, M.; De Matteis, G.; Burzo, M.L.; Russo, A.; Forte, E.; Carnicelli, A.; Piccioni, A.; Simeoni, B.; Gasbarrini, A.; Franceschi, F.; et al. Predicting In-Hospital Mortality in COVID-19 Older Patients with Specifically Developed Scores. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2020, 69, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.J.; Govindarajan, P.; Bennett, C.L.; Matheson, L.; Kohn, M.A.; Camargo, C.; Kline, J. External validation of the 4C Mortality Score for hospitalised patients with COVID-19 in the RECOVER network. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e054700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | <65 Years | <65 Years | ≥65 Years | ≥65 Years | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survivors (n = 190) | Non-Survivors (n = 20) | p | Survivors (n = 139) | Non-Survivors (n = 58) | p | |
| Age, y | 51 (18–64) | 59.5 (34–64) | 0.001 | 72 (65–91) | 78.5 (65–95) | <0.001 |
| Male, N (%) | 109 (57.4) | 14 (70) | 0.275 | 80 (57.6) | 35 (60.3) | 0.717 |
| Female, N (%) | 81 (42.6) | 6 (30) | 0.275 | 59 (42.4) | 23 (39.7) | 0.717 |
| Respiratory rate, min−1 | 20 (14–40) | 20 (18–32) | 0.058 | 20 (16–36) | 20.5 (16–30) | 0.002 |
| Heart rate, bpm | 88.5 (37–149) | 86.5 (60–128) | 0.995 | 86 (55–142) | 88 (63–141) | 0.106 |
| Comorbidity, N (%) | 115 (60.5) | 17 (85) | 0.031 | 120 (87) | 53 (91.4) | 0.380 |
| CHF, N (%) | 3 (1.6) | 2 (10) | 0.019 | 10 (7.2) | 3 (5.3) | 0.759 |
| CAD, N (%) | 15 (7.9) | 1 (5) | 1.000 | 22 (15.9) | 14 (24.6) | 0.158 |
| HT, N (%) | 43 (22.6) | 5 (25) | 0.783 | 76 (55.1) | 35 (61.4) | 0.417 |
| DM, N (%) | 36 (18.9) | 4 (20) | 1.000 | 50 (36.2) | 16 (28.1) | 0.273 |
| CVD, N (%) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0) | 0.745 | 12 (8.7) | 7 (12.3) | 0.443 |
| Remission Ca, N (%) | 7 (3.7) | 0 (0) | 0.383 | 9 (6.5) | 0 (0) | 0.060 |
| Active Ca, N (%) | 7 (3.7) | 5 (25) | <0.001 | 10 (7.2) | 5 (8.6) | 0.772 |
| Liver disease, N (%) | 2 (1.1) | 1 (5) | 0.157 | 0 (0) | 1 (1.8) | 0.292 |
| CRF, N (%) | 9 (4.7) | 3 (15) | 0.093 | 8 (5.8) | 11 (19.3) | 0.004 |
| COPD, N (%) | 5 (2.6) | 1 (5) | 0.545 | 15 (10.9) | 5 (8.8) | 0.661 |
| ILD, N (%) | 2 (1.1) | 3 (15) | <0.001 | 3 (2.2) | 1 (1.8) | 1.000 |
| Asthma, N (%) | 15 (7.9) | 0 (0) | 0.371 | 5 (3.6) | 1 (1.8) | 0.673 |
| Drug treatment (yes) | 77 (48.1) | 9 (64.3) | 0.246 | 95 (81.2) | 33 (76.7) | 0.533 |
| Immunosuppression use | 23 (12.2) | 8 (40) | 0.003 | 13 (9.4) | 5 (8.8) | 0.898 |
| ICU transfer | 39 (20.5) | 19 (95) | <0.001 | 36 (26.1) | 56 (96.6) | <0.001 |
| Length of hospital stay, days | 7 (1–50) | 15 (1–36) | 0.005 | 9 (2–45) | 12 (1–38) | 0.006 |
| Variables | <65 Years | <65 Years | ≥65 Years | ≥65 Years | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survivors (n = 190) | Non-Survivors (n = 20) | p | Survivors (n = 139) | Non-Survivors (n = 58) | p | |
| WBC count (mcL) | 6395 (580–27,180) | 8695 (2930–54,730) | 0.015 | 6680 (1640–18,620) | 7835 (2440–34,060) | 0.076 |
| Lymph count (mcL) | 1140 (220–18,620) | 935 (440–20,880) | 0.028 | 980 (170–7480) | 975 (190–23,680) | 0.640 |
| Neu count (mcL) | 4050 (80–24,400) | 7345 (920–21,060) | 0.001 | 5100 (980–15,980) | 6075 (570–17,930 | 0.155 |
| Neu/Lymph | 3.32 (0.09–30.89) | 8.67 (0.71–29.09) | 0.001 | 5.01 (0.69–37.19) | 6.13 (0.39–22.94) | 0.235 |
| PLT count (mcL) | 203,000 (49,000–613,000) | 202,000 (25,000–415,000) | 0.478 | 219,000 (17,000–929,000) | 177,500 (69,000–515,000) | 0.007 |
| Urea (mg/dL | 26 (10–144) | 45 (24–183) | <0.001 | 39 (18–183) | 63.5 (23–319) | <0.001 |
| Crea (mg/dL) | 0.88 (0.31–7.8) | 1.12 (0.62–10.77) | <0.001 | 0.93 (0.33–8.97) | 1.27 (0.48–8.56) | <0.001 |
| ALB (g/L) | 39.7 (18.2–50.3) | 35.85 (21.9–41.9) | 0.001 | 35.8 (17.7–45.6) | 35.65 (19.3–42.6) | 0.753 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 36.2 (0.31–396.9) | 90.78 (30.8–338) | <0.001 | 74.57 (1.18–396.89) | 108.6 (8.9–364.4) | 0.119 |
| Procalcitonin (mcg/L) | 0.07 (0.02–5.35) | 0.34 (0.08–6.93) | 0.023 | 0.115 (0.02–14.38) | 0.29 (0.09–19.12) | 0.01 |
| Ferritin (mcg/L) | 363.5 (3.75–7371) | 1048 (277–10,540) | <0.001 | 362.5 (14.8–2685) | 585 (32.9–3498) | 0.039 |
| LDH (IU/L) | 249.5 (116–1285) | 520 (240–926) | <0.001 | 280 (126–644) | 322 (157–1289) | 0.04 |
| PNI | 45.65 (21.1–141.4) | 40.4 (24.7–136.9) | 0.003 | 40.75 (26.15–74.9) | 41.62 (25.2–158.7) | 0.739 |
| SII | 646 (16.5–18,935) | 1854 (25–5672) | 0.005 | 1104 (76.5–9196) | 1111 (62–7096) | 0.993 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cavdar, S.; Savas, S.; Tasbakan, S.; Sayıner, A.; Basoglu, O.; Korkmaz, P.; Akcicek, F. Predictivity of the Prognostic Nutritional Index and Systemic Inflammation Index for All-Cause In-Hospital Mortality in Geriatric and Adult COVID-19 Inpatients. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4466. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154466
Cavdar S, Savas S, Tasbakan S, Sayıner A, Basoglu O, Korkmaz P, Akcicek F. Predictivity of the Prognostic Nutritional Index and Systemic Inflammation Index for All-Cause In-Hospital Mortality in Geriatric and Adult COVID-19 Inpatients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(15):4466. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154466
Chicago/Turabian StyleCavdar, Sibel, Sumru Savas, Sezai Tasbakan, Abdullah Sayıner, Ozen Basoglu, Pervin Korkmaz, and Fehmi Akcicek. 2024. "Predictivity of the Prognostic Nutritional Index and Systemic Inflammation Index for All-Cause In-Hospital Mortality in Geriatric and Adult COVID-19 Inpatients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 15: 4466. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154466
APA StyleCavdar, S., Savas, S., Tasbakan, S., Sayıner, A., Basoglu, O., Korkmaz, P., & Akcicek, F. (2024). Predictivity of the Prognostic Nutritional Index and Systemic Inflammation Index for All-Cause In-Hospital Mortality in Geriatric and Adult COVID-19 Inpatients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(15), 4466. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13154466






