Sphingolipids and Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
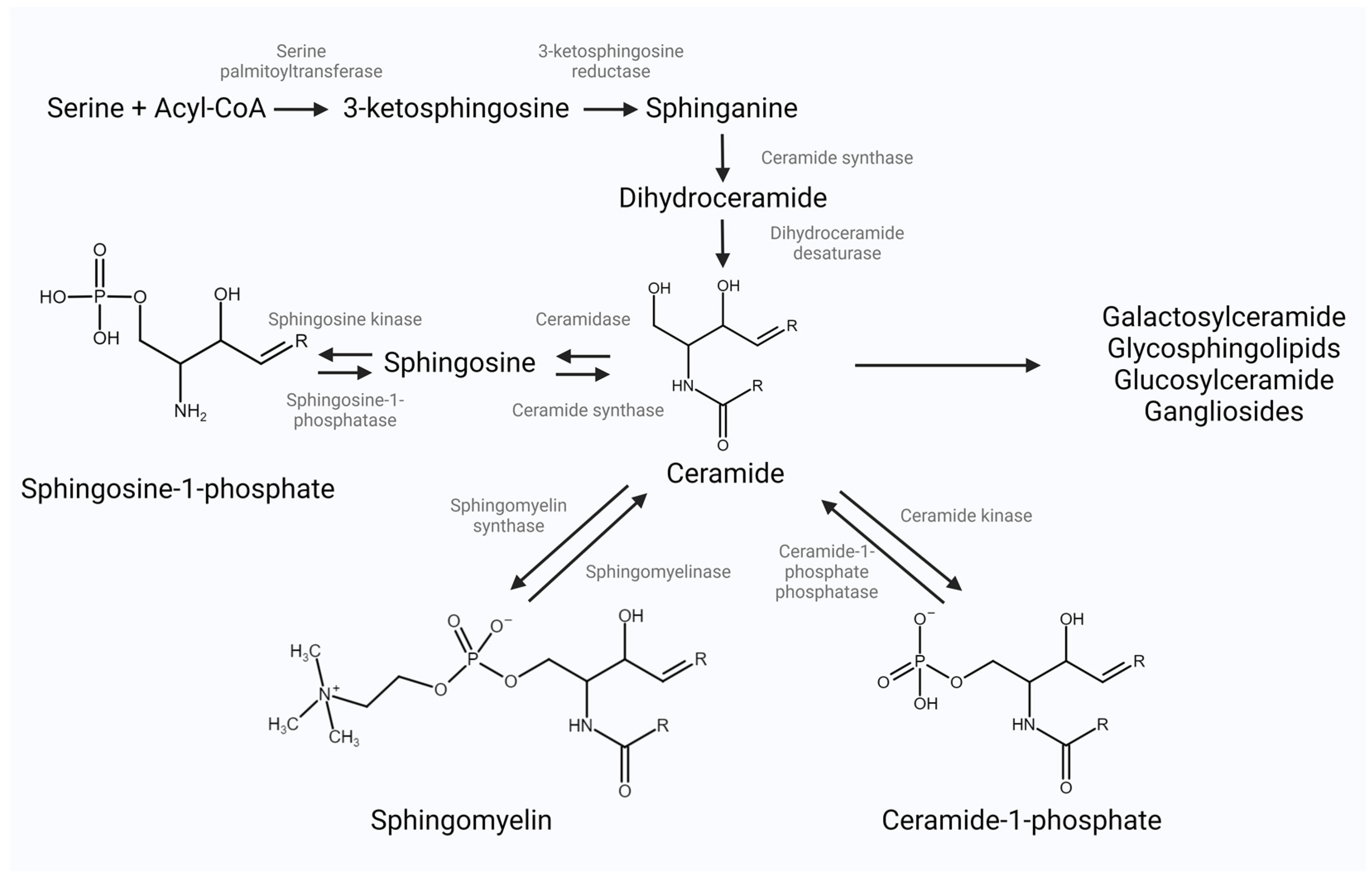
2. Bioactive Sphingolipid Classes and Their Metabolism
2.1. Ceramide
2.2. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate
2.3. Ceramide-1-Phosphate
2.4. Complex Sphingolipids
3. Sphingolipid Role in Normal Renal Function
4. Role of Sphingolipids in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Kidney Disease
5. The Role of Sphingolipids in Diabetic Kidney Disease
6. Sphingolipids in Kidney Transplantation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Sphingolipids and their metabolism in physiology and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Dev, S.; Khalid, M.U.; Siddenthi, S.M.; Noman, M.; John, C.; Mohamad, T. The Bidirectional Link Between Diabetes and Kidney Disease: Mechanisms and Management. Cureus 2023, 15, e45615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, C.Y.; Baek, J.Y.; Kim, A.R.; Hong, C.H.; Yoon, J.E.; Kim, H.S.; Koh, E.H. Inhibition of Ceramide Accumulation in Podocytes by Myriocin Prevents Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes Metab. J. 2020, 44, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaabia, Z.; Poirier, J.; Moughaizel, M.; Aguesse, A.; Billon-Crossouard, S.; Fall, F.; Durand, M.; Dagher, E.; Krempf, M.; Croyal, M. Plasma lipidomic analysis reveals strong similarities between lipid fingerprints in human, hamster and mouse compared to other animal species. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruett, S.T.; Bushnev, A.; Hagedorn, K.; Adiga, M.; Haynes, C.A.; Sullards, M.C.; Liotta, D.C.; Merrill, A.H.J. Biodiversity of sphingoid bases (“sphingosines”) and related amino alcohols. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1621–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gault, C.R.; Obeid, L.M.; Hannun, Y.A. An overview of sphingolipid metabolism: From synthesis to breakdown. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 688, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yokota, R.; Bhunu, B.; Toba, H.; Intapad, S. Sphingolipids and Kidney Disease: Possible Role of Preeclampsia and Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR). Kidney 360 2021, 2, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, R.J.; Pezzolesi, M.G.; Summers, S.A. Rotten to the Cortex: Ceramide-Mediated Lipotoxicity in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 622692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, K. Serine palmitoyltransferase, a key enzyme of sphingolipid metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1632, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiban, J.; Perera, M. Very long chain ceramides interfere with C16-ceramide-induced channel formation: A plausible mechanism for regulating the initiation of intrinsic apoptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1848, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raichur, S.; Brunner, B.; Bielohuby, M.; Hansen, G.; Pfenninger, A.; Wang, B.; Bruning, J.C.; Larsen, P.J.; Tennagels, N. The role of C16:0 ceramide in the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes: CerS6 inhibition as a novel therapeutic approach. Mol. Metab. 2019, 21, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckes, T.; Trautmann, S.; Djudjaj, S.; Beyer, S.; Patyna, S.; Schwalm, S.; Pfeilschifter, J. Consistent alteration of chain length-specific ceramides in human and mouse fibrotic kidneys. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 158821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, R.J.; Holland, W.L.; Summers, S.A. Ceramides and Acute Kidney Injury. Semin. Nephrol. 2022, 42, 151281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, L.P.; Ren, S.; Schwalm, S.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Huwiler, A. Sphingosine kinase 1 and 2 regulate the capacity of mesangial cells to resist apoptotic stimuli in an opposing manner. Biol. Chem. 2008, 389, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intapad, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling in blood pressure regulation. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2019, 317, F638–F640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maceyka, M.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: The Swiss army knife of sphingolipid signaling. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S272–S276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsutake, S.; Yokose, U.; Kato, M.; Matsuoka, I.; Yoo, J.M.; Kim, T.J.; Igarashi, Y. The generation and behavioral analysis of ceramide kinase-null mice, indicating a function in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 363, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallela, S.K.; Mitrofanova, A.; Merscher, S.; Fornoni, A. Regulation of the amount of ceramide-1-phosphate synthesized in differentiated human podocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 158517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyne, S.; Long, J.S.; Ktistakis, N.T.; Pyne, N.J. Lipid phosphate phosphatases and lipid phosphate signalling. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005, 33, 1370–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Wada, R.; Sasaki, T.; Deng, C.; Bierfreund, U.; Sandhoff, K.; Proia, R.L. A vital role for glycosphingolipid synthesis during development and differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallela, S.K.; Merscher, S.; Fornoni, A. Implications of Sphingolipid Metabolites in Kidney Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, N. A Rheostat of Ceramide and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate as a Determinant of Oxidative Stress-Mediated Kidney Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, O.M.; Yuan, X.; Li, G.; Lee, R.; Li, P.-L. Sphingolipids and Redox Signaling in Renal Regulation and Chronic Kidney Diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 1008–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, N. Ceramide-induced apoptosis in renal tubular cells: A role of mitochondria and sphingosine-1-phoshate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 5076–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, H.; Ellström, P.; Ekström, K.; Gustafsson, L.; Gustafsson, M.; Svanborg, C. Ceramide as a TLR4 agonist; a putative signalling intermediate between sphingolipid receptors for microbial ligands and TLR4. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Daher, A.; Francis, M.; Azzam, P.; Ahmad, A.; Eid, A.A.; Fornoni, A.; Marples, B.; Zeidan, Y.H. Modulation of radiation-induced damage of human glomerular endothelial cells by SMPDL3B. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 7915–7926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zager, R.A.; Conrad, D.S.; Burkhart, K. Ceramide accumulation during oxidant renal tubular injury: Mechanisms and potential consequences. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1998, 9, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Van Veldhoven, P.P.; Zhang, L.; Hanigan, M.H.; Alexander, H.; Alexander, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase regulates sensitivity of human cells to select chemotherapy drugs in a p38-dependent manner. Mol. Cancer Res. 2005, 3, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camaré, C.; Augé, N.; Pucelle, M.; Saint-Lebes, B.; Grazide, M.-H.; Nègre-Salvayre, A.; Salvayre, R. The neutral sphingomyelinase-2 is involved in angiogenic signaling triggered by oxidized LDL. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 93, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.C.; Nica, A.F.; Kurinna, S.M.; Jiffar, T.; Mumby, M.; Ruvolo, P.P. Mitochondrial protein phosphatase 2A regulates cell death induced by simulated ischemia in kidney NRK-52E cells. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuma, S.; Hada, Y.; Ueda, T.; Shiojima, S.; Hirasawa, A.; Tanoue, A.; Takagaki, K.; Ohgi, T.; Yano, J.; Tsujimoto, G. Signalling mechanisms in sphingosine 1-phosphate-promoted mesangial cell proliferation. Genes Cells 2002, 7, 1217–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantalupo, A.; Di Lorenzo, A.S. 1.P. Signaling and De Novo Biosynthesis in Blood Pressure Homeostasis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 358, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomone, S.; Potts, E.M.; Tyndall, S.; Ip, P.C.; Chun, J.; Brinkmann, V.; Waeber, C. Analysis of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors involved in constriction of isolated cerebral arteries with receptor null mice and pharmacological tools. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nofer, J.R.; Van Der Giet, M.; Tölle, M.; Wolinska, I.; von Wnuck Lipinski, K.; Baba, H.A.; Levkau, B. HDL induces NO-dependent vasorelaxation via the lysophospholipid receptor S1P3. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, A.; Czyborra, P.; Fetscher, C.; Meyer Zu Heringdorf, D.; Jakobs, K.H.; Michel, M.C. Sphingosine-1-phosphate and sphingosylphosphorylcholine constrict renal and mesenteric microvessels in vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 130, 1871–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, A.; Meyer Zu Heringdorf, D.; Jakobs, K.H.; Michel, M.C. Lysosphingolipid receptor-mediated diuresis and natriuresis in anaesthetized rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 132, 1925–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Xia, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, P.-L.; Li, N. A novel lipid natriuretic factor in the renal medulla: Sphingosine-1-phosphate. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2011, 301, F35–F41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantalupo, A.; Zhang, Y.; Kothiya, M.; Galvani, S.; Obinata, H.; Bucci, M.; Giordano, F.J.; Jiang, X.-C.; Hla, T.; Di Lorenzo, A. Nogo-B regulates endothelial sphingolipid homeostasis to control vascular function and blood pressure. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spijkers, L.J.; van den Akker, R.F.; Janssen, B.J.; Debets, J.J.; De Mey, J.G.; Stroes, E.S.; Peters, S.L. Hypertension is associated with marked alterations in sphingolipid biology: A potential role for ceramide. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, L.M.P.; Almeida, F.G.; Grelle, G.M.R.S.; Vieyra, A.; Caruso-Neves, C.; Einicker-Lamas, M. Ceramide-1-Phosphate as a Potential Regulator of the Second Sodium Pump from Kidney Proximal Tubules by Triggering Distinct Protein Kinase Pathways in a Hierarchic Way. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 998–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zager, R.A.; Burkhart, K.M.; Johnson, A. Sphingomyelinase and membrane sphingomyelin content: Determinants of Proximal tubule cell susceptibility to injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2000, 11, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natoli, T.A.; Modur, V.; Ibraghimov-Beskrovnaya, O. Glycosphingolipid metabolism and polycystic kidney disease. Cell. Signal. 2020, 69, 109526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-J.; Chae, S.-K.; Kim, J.-W.; Yang, S.-G.; Jung, J.-M.; Kim, M.-J.; Wee, G.; Lee, D.-S.; Kim, S.-U.; Koo, D.-B. Ganglioside GM3 induces cumulus cell apoptosis through inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathways during in vitro maturation of pig oocytes. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2017, 84, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degroote, S.; Wolthoorn, J.; van Meer, G. The cell biology of glycosphingolipids. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 15, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowart, L.A. (Ed.) Sphingolipids and Metabolic Disease, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolerico, M.; Merscher, S.; Fornoni, A. Normal and Dysregulated Sphingolipid Metabolism: Contributions to Podocyte Injury and Beyond. Cells 2024, 13, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merscher, S.; Fornoni, A. Podocyte pathology and nephropathy—Sphingolipids in glomerular diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, C.; Touyz, R.; Dominiczak, A.F.; Webb, R.C.; Johns, D.G. Angiotensin receptors: Signaling, vascular pathophysiology, and interactions with ceramide. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2001, 281, H2337–H2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, A.; Miro, F.; Jiménez-Altayó, F.; Jurado, A.; Vila, E.; Planas, A.M. Sphingosine-1-phosphate signalling-a key player in the pathogenesis of Angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Cardiovasc. Res. 2017, 113, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornoni, A.; Sageshima, J.; Wei, C.; Merscher-Gomez, S.; Aguillon-Prada, R.; Jauregui, A.N.; Burke, G.W., III. Rituximab targets podocytes in recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 85ra46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drexler, Y.; Molina, J.; Elfassy, T.; Ma, R.; Christoffersen, C.; Kurano, M.; Fornoni, A. Identification of Glomerular and Plasma Apolipoprotein M as Novel Biomarkers in Glomerular Disease. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 884–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammad, S.M.; Hunt, K.J.; Baker, N.L.; Klein, R.L.; Lopes-Virella, M.F. Diabetes and kidney dysfunction markedly alter the content of sphingolipids carried by circulating lipoproteins. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2022, 16, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górska, M.; Dobrzyń, A.; Baranowski, M. Concentrations of sphingosine and sphinganine in plasma of patients with type 2 diabetes. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2005, 11, CR35–CR38. [Google Scholar]
- Mitrofanova, A.; Drexler, Y.; Merscher, S.; Fornoni, A. Role of Sphingolipid Signaling in Glomerular Diseases: Focus on DKD and FSGS. J. Cell. Signal. 2020, 1, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schümann, J.; Grevot, A.; Ledieu, D.; Wolf, A.; Schubart, A.; Piaia, A.; Walker, U.J. Reduced Activity of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Lyase Induces Podocyte-related Glomerular Proteinuria, Skin Irritation, and Platelet Activation. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 43, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imeri, F.; Stepanovska Tanturovska, B.; Manaila, R.; Pavenstädt, H.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Huwiler, A. Loss of S1P Lyase Expression in Human Podocytes Causes a Reduction in Nephrin Expression That Involves PKCδ Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Kidd, J.; Kaspar, C.; Dempsey, S.; Bhat, O.M.; Camus, S.; Ritter, J.K.; Gehr, T.W.B.; Gulbins, E.; Li, P.-L. Podocytopathy and Nephrotic Syndrome in Mice with Podocyte-Specific Deletion of the Asah1 Gene: Role of Ceramide Accumulation in Glomeruli. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 1211–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafft, C.A.; Fervenza, F.C.; Semret, M.H.; Orloff, S.; Sethi, S. Renal involvement in Neimann-Pick Disease. NDT Plus 2009, 2, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebau, M.C.; Braun, F.; Höpker, K.; Weitbrecht, C.; Bartels, V.; Müller, R.U.; Kurschat, C.E. Dysregulated Autophagy Contributes to Podocyte Damage in Fabry’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, D.; Rosenbloom, B.E.; Cohen, A.H. Gaucher disease with nephrotic syndrome: Response to enzyme replacement therapy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2002, 40, E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, S.; Aeddula, N. Chronic Kidney Disease; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.; Nath, K.A. Chapter 18—Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney Disease Progression: Organ and Cellular Considerations. In Chronic Renal Disease; Kimmel, P.L., Rosenberg MEBT-CRD, Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 263–278. [Google Scholar]
- Altamura, S.; Pietropaoli, D.; Lombardi, F.; Del Pinto, R.; Ferri, C. An Overview of Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology: The Impact of Gut Dysbiosis and Oral Disease. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remuzzi, G.; Perico, N.; Macia, M.; Ruggenenti, P. The role of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the progression of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, S57–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehanna, M.; McDonough, C.W.; Smith, S.M.; Gong, Y.; Gums, J.G.; Chapman, A.B.; Johnson, J.A.; McIntyre, L.; Cooper-DeHoff, R.M. Metabolomics Signature of Plasma Renin Activity and Linkage with Blood Pressure Response to Beta Blockers and Thiazide Diuretics in Hypertensive European American Patients. Metabolites 2021, 11, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaulding, S.C.; Bollag, W.B. The role of lipid second messengers in aldosterone synthesis and secretion. J. Lipid Res. 2022, 63, 100191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Beyene, H.B.; Kuokkanen, M.; Miao, G.; Magliano, D.J.; Umans, J.G.; Zhao, J. Lipidomic profiling in the Strong Heart Study identified American Indians at risk of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, 1154–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, M.; Böttcher, A.; Schmitz, G.; Liebisch, G. Sphingolipid profiling of human plasma and FPLC-separated lipoprotein fractions by hydrophilic interaction chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1811, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, S.M.; Al Gadban, M.M.; Semler, A.J.; Klein, R.L. Sphingosine 1-phosphate distribution in human plasma: Associations with lipid profiles. J. Lipids 2012, 2012, 180705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoffersen, C.; Obinata, H.; Kumaraswamy, S.B.; Galvani, S.; Ahnström, J.; Sevvana, M.; Dahlbäck, B. Endothelium-protective sphingosine-1-phosphate provided by HDL-associated apolipoprotein M. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9613–9618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argraves, K.M.; Gazzolo, P.J.; Groh, E.M.; Wilkerson, B.A.; Matsuura, B.S.; Twal, W.O.; Hammad, S.M.; Argraves, W.S. High density lipoprotein-associated sphingosine 1-phosphate promotes endothelial barrier function. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25074–25081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, A.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Huwiler, A. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in Renal Diseases. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 31, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Mitrofanova, A.; Bielawski, J.; Yang, Y.; Marples, B.; Fornoni, A.; Zeidan, Y.H. Sphingomyelinase-like phosphodiesterase 3b mediates radiation-induced damage of renal podocytes. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2017, 31, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitiyakara, C.; Eggers, P.; Kopp, J.B. Twenty-one-year trend in ESRD due to focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2004, 44, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, T.H.; Pedigo, C.E.; Guzman, J.; Correa-Medina, M.; Wei, C.; Villarreal, R.; Merscher, S. Sphingomyelinase-like phosphodiesterase 3b expression levels determine podocyte injury phenotypes in glomerular disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative. Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes and CKD: 2012 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2012, 60, 850–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruotsalainen, V.; Ljungberg, P.; Wartiovaara, J.; Lenkkeri, U.; Kestilä, M.; Jalanko, H.; Holmberg, C.; Tryggvason, K. Nephrin is specifically located at the slit diaphragm of glomerular podocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7962–7967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes-Virella, M.F.; Baker, N.L.; Hunt, K.J.; Hammad, S.M.; Arthur, J.; Virella, G.; Klein, R.L. Glycosylated sphingolipids and progression to kidney dysfunction in type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2019, 13, 481–491.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, K.E.; Bilous, R.W.; Marshall, S.M.; El Nahas, M.; Remuzzi, G.; Piras, G.; De Cosmo, S.; Viberti, G. Podocyte number in normotensive type 1 diabetic patients with albuminuria. Diabetes 2002, 51, 3083–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasumov, T.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Gulshan, K.; Kirwan, J.P.; Liu, X.; Previs, S.; Willard, B.; Smith, J.D.; McCullough, A. Ceramide as a Mediator of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Associated Atherosclerosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boini, K.M.; Zhang, C.; Xia, M.; Poklis, J.L.; Li, P.-L. Role of sphingolipid mediator ceramide in obesity and renal injury in mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 334, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Snider, A.J. Sphingolipids in High Fat Diet and Obesity-Related Diseases. Mediators Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 520618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasia, B.; Summers, S.A. Ceramides—Lipotoxic Inducers of Metabolic Disorders. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, S.M.; Lopes-Virella, M.F. Circulating Sphingolipids in Insulin Resistance, Diabetes and Associated Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez, J.A.; Siddique, M.M.; Wang, S.T.; Ching, J.; Shayman, J.A.; Summers, S.A. Ceramides and glucosylceramides are independent antagonists of insulin signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haus, J.M.; Kashyap, S.R.; Kasumov, T.; Zhang, R.; Kelly, K.R.; Defronzo, R.A.; Kirwan, J.P. Plasma ceramides are elevated in obese subjects with type 2 diabetes and correlate with the severity of insulin resistance. Diabetes 2009, 58, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongrac Barlovic, D.; Harjutsalo, V.; Sandholm, N.; Forsblom, C.; Groop, P.-H. Sphingomyelin and progression of renal and coronary heart disease in individuals with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofte, N.; Suvitaival, T.; Ahonen, L.; Winther, S.A.; Theilade, S.; Frimodt-Møller, M.; Ahluwalia, T.S.; Rossing, P. Lipidomic analysis reveals sphingomyelin and phosphatidylcholine species associated with renal impairment and all-cause mortality in type 1 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, T.; Kurano, M.; Tokuhara, Y.; Ohkubo, S.; Hara, M.; Ikeda, H.; Tsukamoto, K.; Yatomi, Y. Modulation of sphingosine-1-phosphate and apolipoprotein M levels in the plasma, liver and kidneys in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. J. Diabetes Investig. 2014, 5, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; He, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; He, Y.; Shi, B. Sphingolipid metabolism in type 2 diabetes and associated cardiovascular complications. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 3603–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imeri, F.; Stepanovska Tanturovska, B.; Schwalm, S.; Saha, S.; Zeng-Brouwers, J.; Pavenstädt, H.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Schaefer, L.; Huwiler, A. Loss of sphingosine kinase 2 enhances Wilm’s tumor suppressor gene 1 and nephrin expression in podocytes and protects from streptozotocin-induced podocytopathy and albuminuria in mice. Matrix Biol. 2021, 98, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.S.; Rouse, M.D.; Khutsishvili, K.; Huang, L.; Bolton, W.K.; Lynch, K.R.; Okusa, M.D. Chronic sphingosine 1-phosphate 1 receptor activation attenuates early-stage diabetic nephropathy independent of lymphocytes. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajwa, A.; Jo, S.-K.; Ye, H.; Huang, L.; Dondeti, K.R.; Rosin, D.L.; Haase, V.H.; Macdonald, T.L.; Lynch, K.R.; Okusa, M.D. Activation of sphingosine-1-phosphate 1 receptor in the proximal tubule protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Zheng, S.; Kharel, Y.; Fritzemeier, R.G.; Huang, T.; Foster, D.; Okusa, M.D. Sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling in perivascular cells enhances inflammation and fibrosis in the kidney. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabj2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Jin, Y.; Ni, H.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Q. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor agonist, FTY720, restores coronary flow reserve in diabetic rats. Circ. J. 2014, 78, 2979–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Morita, Y.; Kurano, M.; Sakai, E.; Nishikawa, T.; Nishikawa, M.; Sawabe, M.; Aoki, J.; Yatomi, Y. Analysis of urinary sphingolipids using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in diabetic nephropathy. J. Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, J.M.; Ottenhoff, R.; Powlson, A.S.; Grefhorst, A.; Van Eijk, M.; Dubbelhuis, P.F.; Overkleeft, H.S. Pharmacological inhibition of glucosylceramide synthase enhances insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subathra, M.; Korrapati, M.; Howell, L.A.; Arthur, J.M.; Shayman, J.A.; Schnellmann, R.G.; Siskind, L.J. Kidney glycosphingolipids are elevated early in diabetic nephropathy and mediate hypertrophy of mesangial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2015, 309, F204–F215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savas, B.; Astarita, G.; Aureli, M.; Sahali, D.; Ollero, M. Gangliosides in Podocyte Biology and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ene, C.D.; Penescu, M.; Anghel, A.; Neagu, M.; Budu, V.; Nicolae, I. Monitoring Diabetic Nephropathy by Circulating Gangliosides. J. Immunoassay Immunochem. 2016, 37, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, K.; Adachi, K. Discovery of fingolimod, the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator and its application for the therapy of multiple sclerosis. Future Med. Chem. 2012, 4, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budde, K.; Schütz, M.; Glander, P.; Peters, H.; Waiser, J.; Liefeldt, L.; Neumayer, H.-H.; Böhler, T. FTY720 (fingolimod) in renal transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2006, 20 (Suppl. S1), 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.S.; Ye, H.; Huang, L.; Li, L.; Foss, F.W.J.; Macdonald, T.L.; Lynch, K.R.; Okusa, M.D. Selective sphingosine 1-phosphate 1 receptor activation reduces ischemia-reperfusion injury in mouse kidney. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2006, 290, F1516–F1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, Y.; Ahmadian, E.; Hejazian, S.M.; Raeesi, M.; Zununi Vahed, S.; Ardalan, M. The Effect of Fingolimod on Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in a Rat Model. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2024, 17, e250823220363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uffing, A.; Pérez-Sáez, M.J.; Mazzali, M.; Manfro, R.C.; Bauer, A.C.; de Sottomaior Drumond, F.; Riella, L.V. Recurrence of FSGS after Kidney Transplantation in Adults. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrofanova, A.; Mallela, S.K.; Ducasa, G.M.; Yoo, T.H.; Rosenfeld-Gur, E.; Zelnik, I.D.; Fornoni, A. SMPDL3b modulates insulin receptor signaling in diabetic kidney disease. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drexler, Y.; Molina, J.; Mitrofanova, A.; Fornoni, A.; Merscher, S. Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Metabolism and Signaling in Kidney Diseases. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 9–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Injury Type/Disease | Model | Pathway/Phenotype | Sphingolipid | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nephrotoxic drugs/irradiation/bacterial toxin | In vitro and in vivo studies | Mitochondrial membrane permeability/ROS generation → apoptosis/cell survival | Ceramide ↑ and S1P ↓ | Ueda N [24] |
| Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system | Mice and in vitro | Second messenger/Rho–kinase pathway; vascular dysfunction (S1P); aldosterone synthesis | Ceramide; S1P | Berry et al. [48]; Meissner et al. [49] |
| Podocyte dysfunction | ||||
| Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis | Human | Actin cytoskeleton remodeling, apoptosis | SMPDL3b overexpression; GM3 ↓, S1P (?) | Fornoni et al. [50]; Drexler et al. [51] |
| Diabetic kidney disease | In vitro, mice, in vivo | Podocyte insulin signaling dysregulation; podocyte dysfunction; promotion of fibrosis | iS1P ↑, iGM3 ↓, iC1P ↓, ceramide ↑, SMPDL3b activity ↑ | Hammad et al. [52]; Gorska et al. [53]; Malella et al. [21]; Mitrofanova et al. [54] |
| S1P lyase deficiency | Human, mice, rats | Sphingolipid accumulation, foot process effacement | S1P ↑, ceramide ↑ | Schumann et al. [55]; Imeri et al. [56] |
| Farber disease | Human | Foot process effacement | Ceramide ↑ | Li et al. [57] |
| Niemann-Pick disease | Human | Lipid accumulation, glomerular sclerosis | Sphingomyelin ↑ | Grafft et al. [58] |
| Fabry disease | Human | Increased autophagy, mTOR dysregulation (?) | Gb3 ↑ | Liebau et al. [59] |
| Gaucher disease | Human | Podocyte dysfunction, Gaucher cell formation | Glucosyceramide | Santoro et al. [60] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šakić, Z.; Atić, A.; Potočki, S.; Bašić-Jukić, N. Sphingolipids and Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5050. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175050
Šakić Z, Atić A, Potočki S, Bašić-Jukić N. Sphingolipids and Chronic Kidney Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(17):5050. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175050
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠakić, Zrinka, Armin Atić, Slavica Potočki, and Nikolina Bašić-Jukić. 2024. "Sphingolipids and Chronic Kidney Disease" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 17: 5050. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175050
APA StyleŠakić, Z., Atić, A., Potočki, S., & Bašić-Jukić, N. (2024). Sphingolipids and Chronic Kidney Disease. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(17), 5050. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13175050






