Sera from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Induce Oxidative Stress and Pro-Angiogenic and Profibrotic Phenotypes in Human Endothelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
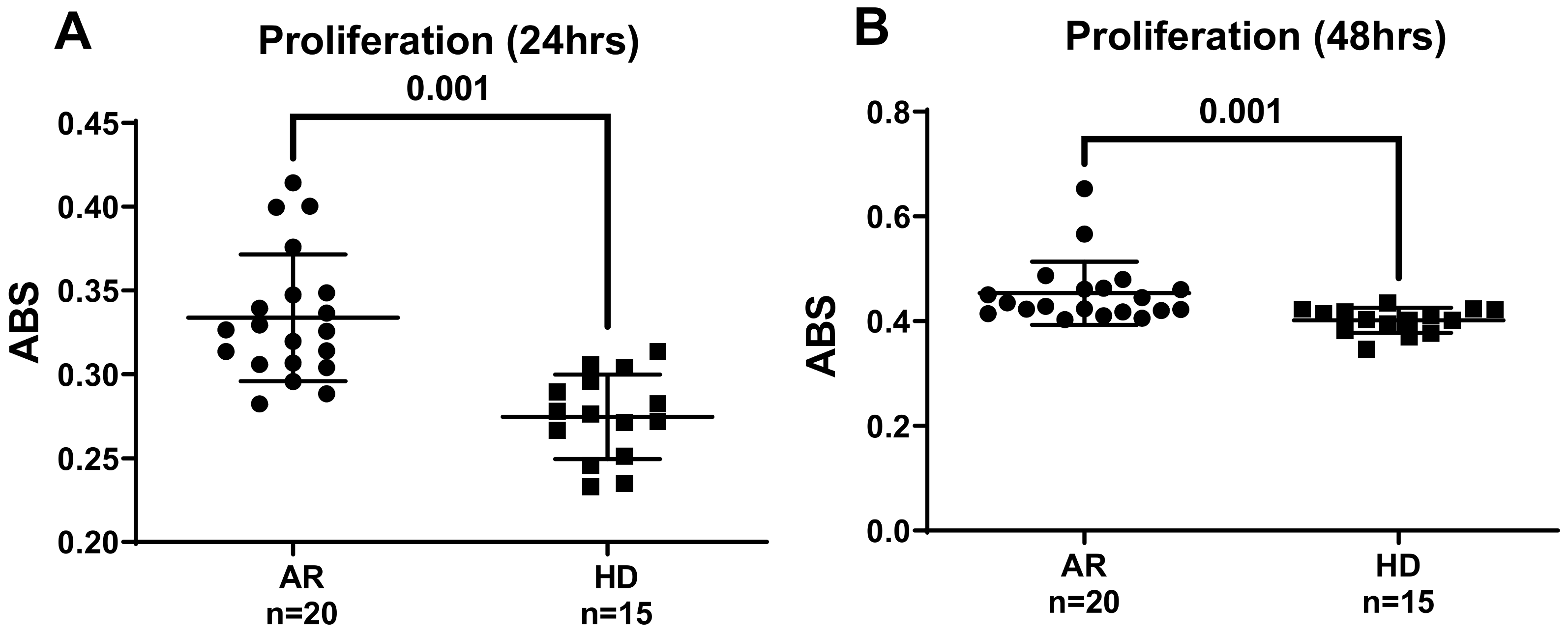
2.3. Determination of Cell Viability
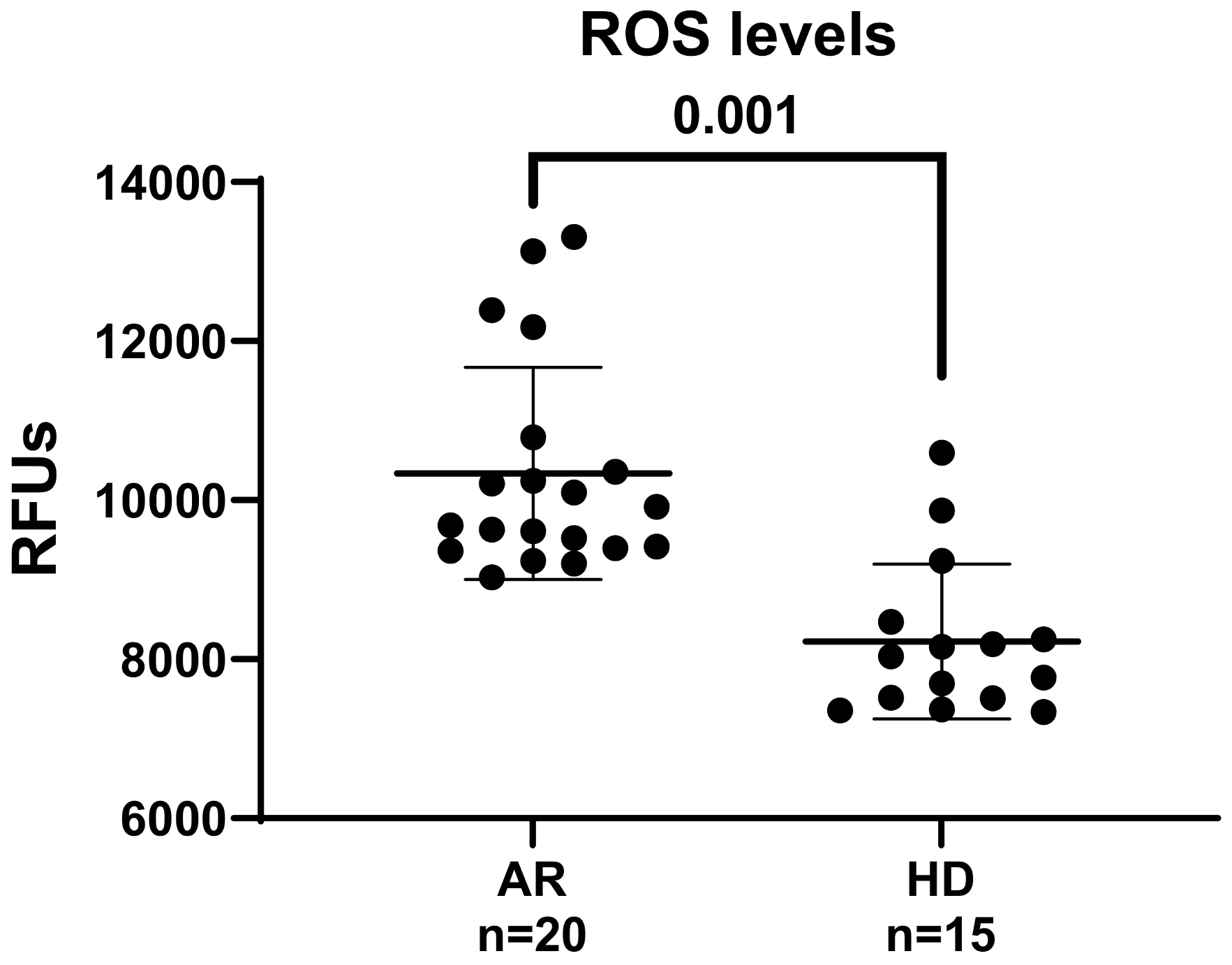
2.4. Determination of Intracellular ROS
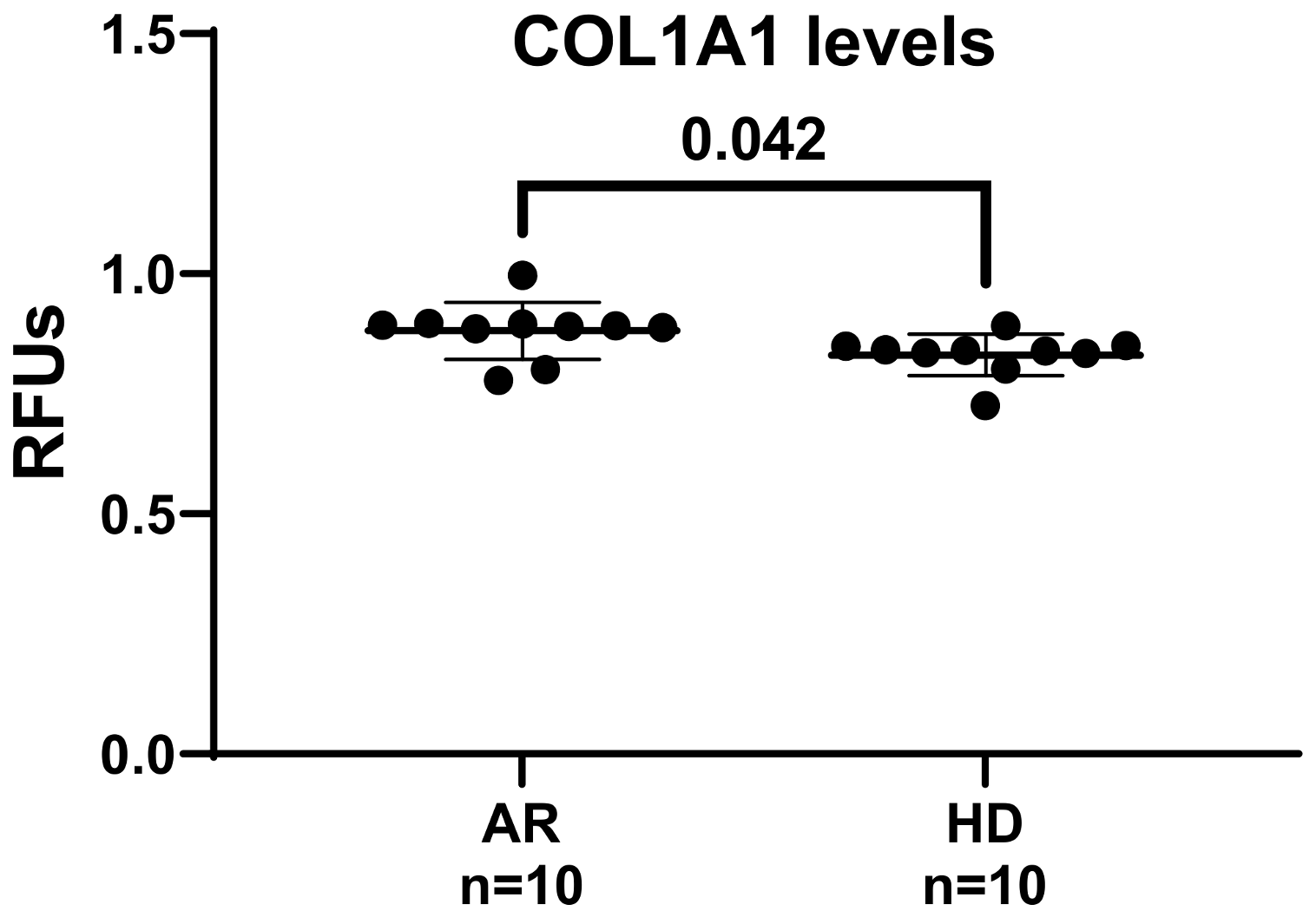
2.5. Collagen Type I Synthesis Determination
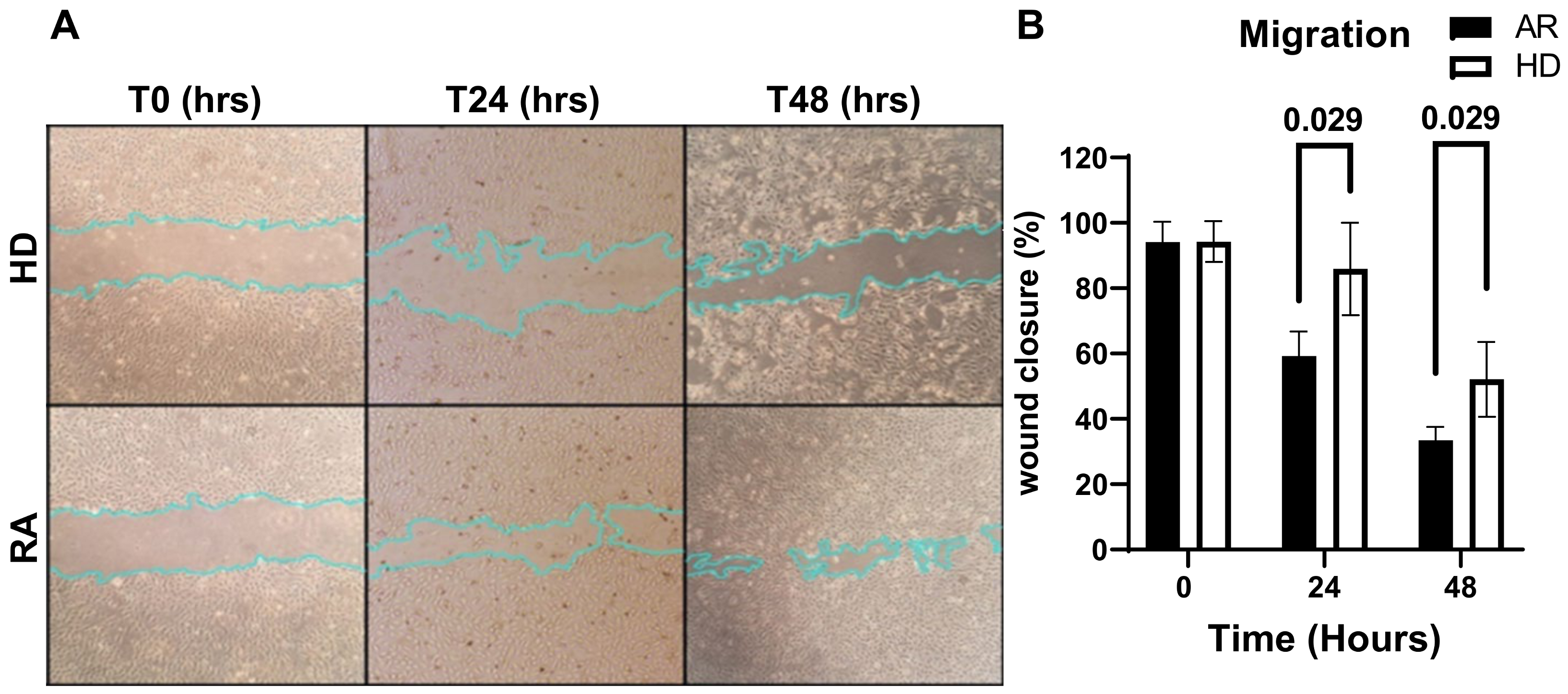
2.6. Cell Migration
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Future Perspectives
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Firestein, G.S. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 2003, 423, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radu, A.-F.; Bungau, S.G. Management of rheumatoid arthritis: An overview. Cells 2021, 10, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, R.J.; Cross, M.; Haile, L.M.; Culbreth, G.T.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Hagins, H.; Kopec, J.A.; Brooks, P.M.; Woolf, A.D.; Ong, K.L. Global, regional, and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis, 1990–2020, and projections to 2050: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e594–e610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, I.B.; O’Dell, J.R. State-of-the-art: Rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1898–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, M.; Erre, G.L.; Bach, H.; Slavin, Y.N.; Manchia, P.A.; Passiu, G.; Sechi, L.A. PtpA and PknG proteins secreted by Mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis are recognized by sera from patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A case–Control study. J. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 12, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conforti, A.; Di Cola, I.; Pavlych, V.; Ruscitti, P.; Berardicurti, O.; Ursini, F.; Giacomelli, R.; Cipriani, P. Beyond the joints, the extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkshoorn, B.; Raadsen, R.; Nurmohamed, M.T. Cardiovascular disease risk in rheumatoid arthritis anno 2022. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erre, G.; Cacciapaglia, F.; Sakellariou, G.; Manfredi, A.; Bartoloni, E.; Viapiana, O.; Fornaro, M.; Cauli, A.; Mangoni, A.; Woodman, R. Cardiovascular, Obesity and Rheumatic Disease Study (CORDIS) Group of the Italian Society of Rheumatology (SIR). C-reactive protein and 10-year cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 104, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordy, R.; Totoson, P.; Prati, C.; Marie, C.; Wendling, D.; Demougeot, C. Microvascular endothelial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resano-Barrio, P.; Alfaro, E.; Solano-Pérez, E.; Coso, C.; Cubillos-Zapata, C.; Díaz-García, E.; Romero-Peralta, S.; Izquierdo-Alonso, J.L.; Barbé, F.; García-Rio, F. Analysis of the Ischemia-Modified Albumin as a Potential Biomarker for Cardiovascular Damage in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampa, M.; Mitran, C.I.; Mitran, M.I.; Amuzescu, A.; Matei, C.; Georgescu, S.R. Ischemia-modified albumin—A potential new marker of oxidative stress in dermatological diseases. Medicina 2022, 58, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erre, G.L.; Piras, A.; Mura, S.; Mundula, N.; Piras, M.; Taras, L.; Longu, M.G.; Saba, P.S.; Ganau, A.; Carru, C. Asymmetric dimethylarginine and arterial stiffness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A case–control study. J. Int. Med. Res. 2016, 44, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erre, G.L.; Chessa, I.; Bassu, S.; Cavagna, L.; Carru, C.; Pintus, G.; Giordo, R.; Mangoni, A.A.; Damiano Sanna, G.; Zinellu, A. Association between ischemia-modified albumin (IMA) and peripheral endothelial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadi, H.A.; Carr, C.S.; Al Suwaidi, J. Endothelial dysfunction: Cardiovascular risk factors, therapy, and outcome. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2005, 1, 183–198. [Google Scholar]
- Erre, G.L.; Bosincu, L.; Faedda, R.; Fenu, P.; Masala, A.; Sanna, M.; Taras, L.; Longu, M.G.; Piras, M.; Soro, G. Antiphospholipid syndrome nephropathy (APSN) in patients with lupus nephritis: A retrospective clinical and renal pathology study. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 34, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogita, H.; Liao, J.K. Endothelial function and oxidative stress. Endothelium 2004, 11, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaito, A.; Aramouni, K.; Assaf, R.; Parenti, A.; Orekhov, A.; El Yazbi, A.; Pintus, G.; Eid, A.H. Oxidative Stress-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2022, 27, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, L.J.S.D.; Nunes-Souza, V.; Goulart, M.O.F.; Rabelo, L.A. Oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis: What the future might hold regarding novel biomarkers and add-on therapies. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 7536805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassu, S.; Zinellu, A.; Sotgia, S.; Mangoni, A.A.; Floris, A.; Farina, G.; Passiu, G.; Carru, C.; Erre, G.L. Oxidative stress biomarkers and peripheral endothelial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis: A monocentric cross-sectional case-control study. Molecules 2020, 25, 3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, E.; Veale, D.J.; McGarry, T.; Orr, C.; Szekanecz, Z.; Ng, C.-T.; Fearon, U.; Biniecka, M. Oxidative stress impairs energy metabolism in primary cells and synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Kundu, S.; Ghosh, P.; De, S.; Ghosh, A.; Chatterjee, M. Correlation of oxidant status with oxidative tissue damage in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 33, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Armada, M.J.; Fernández-Rodríguez, J.A.; Blanco, F.J. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biniecka, M.; Kennedy, A.; Fearon, U.; Ng, C.T.; Veale, D.J.; O’Sullivan, J.N. Oxidative damage in synovial tissue is associated with in vivo hypoxic status in the arthritic joint. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitchon, C.A.; El-Gabalawy, H.S. Oxidation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2004, 6, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshabrawy, H.A.; Chen, Z.; Volin, M.V.; Ravella, S.; Virupannavar, S.; Shahrara, S. The pathogenic role of angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Angiogenesis 2015, 18, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O., III; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevoo, M.; Van’T Hof, M.A.; Kuper, H.; Van Leeuwen, M.; Van De Putte, L.; Van Riel, P. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. Off. J. Am. Coll. Rheumatol. 1995, 38, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintus, G.; Tadolini, B.; Posadino, A.M.; Sanna, B.; Debidda, M.; Carru, C.; Deiana, L.; Ventura, C. PKC/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway modulates native-LDL-induced E2F-1 gene expression and endothelial cell proliferation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2003, 59, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fois, A.G.; Posadino, A.M.; Giordo, R.; Cossu, A.; Agouni, A.; Rizk, N.M.; Pirina, P.; Carru, C.; Zinellu, A.; Pintus, G. Antioxidant activity mediates pirfenidone antifibrotic effects in human pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cells exposed to sera of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patients. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 2639081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordo, R.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Posadino, A.M.; Galimi, F.; Capobianco, G.; Eid, A.H.; Pintus, G. Resveratrol-elicited pkc inhibition counteracts nox-mediated endothelial to mesenchymal transition in human retinal endothelial cells exposed to high glucose. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadino, A.M.; Cossu, A.; Giordo, R.; Zinellu, A.; Sotgia, S.; Vardeu, A.; Hoa, P.T.; Deiana, L.; Carru, C.; Pintus, G. Coumaric acid induces mitochondrial damage and oxidative-mediated cell death of human endothelial cells. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2013, 13, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vono, R.; Fuoco, C.; Testa, S.; Pirrò, S.; Maselli, D.; Ferland McCollough, D.; Sangalli, E.; Pintus, G.; Giordo, R.; Finzi, G. Activation of the pro-oxidant PKCβII-p66Shc signaling pathway contributes to pericyte dysfunction in skeletal muscles of patients with diabetes with critical limb ischemia. Diabetes 2016, 65, 3691–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boin, F.; Erre, G.L.; Posadino, A.M.; Cossu, A.; Giordo, R.; Spinetti, G.; Passiu, G.; Emanueli, C.; Pintus, G. Oxidative stress-dependent activation of collagen synthesis is induced in human pulmonary smooth muscle cells by sera from patients with scleroderma-associated pulmonary hypertension. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posadino, A.M.; Erre, G.L.; Cossu, A.; Emanueli, C.; Eid, A.H.; Zinellu, A.; Pintus, G.; Giordo, R. NADPH-derived ROS generation drives fibrosis and endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in systemic sclerosis: Potential cross talk with circulating miRNAs. Biomol. Concepts 2022, 13, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordo, R.; Thuan, D.T.B.; Posadino, A.M.; Cossu, A.; Zinellu, A.; Erre, G.L.; Pintus, G. Iloprost attenuates oxidative stress-dependent activation of collagen synthesis induced by sera from scleroderma patients in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posadino, A.M.; Cossu, A.; Giordo, R.; Zinellu, A.; Sotgia, S.; Vardeu, A.; Hoa, P.T.; Carru, C.; Pintus, G. Resveratrol alters human endothelial cells redox state and causes mitochondrial-dependent cell death. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 78, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossu, A.; Posadino, A.M.; Giordo, R.; Emanueli, C.; Sanguinetti, A.M.; Piscopo, A.; Poiana, M.; Capobianco, G.; Piga, A.; Pintus, G. Apricot melanoidins prevent oxidative endothelial cell death by counteracting mitochondrial oxidation and membrane depolarization. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, E.; Yoon, H. Modeling and predicting the cell migration properties from scratch wound healing assay on cispla-tin-resistant ovarian cancer cell lines using artificial neural network. Healthcare 2021, 9, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamudio-Cuevas, Y.; Martínez-Flores, K.; Martínez-Nava, G.A.; Clavijo-Cornejo, D.; Fernández-Torres, J.; Sánchez-Sánchez, R. Rheumatoid arthritis and oxidative stress. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2022, 68, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Sharma, A.; Bhatnagar, A. Role of oxidative stress in pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis: Insights into NRF2-KEAP1 signalling. Autoimmunity 2021, 54, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñonez-Flores, C.M.; González-Chávez, S.A.; Del Río Nájera, D.; Pacheco-Tena, C. Oxidative stress relevance in the pathogenesis of the rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6097417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, A.; Bagchi, A.; De, S.; Mitra, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Ghosh, P.; Ghosh, A.; Chatterjee, M. Role of redox imbalance and cytokines in mediating oxidative damage and disease progression of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Free Radic. Res. 2019, 53, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjevic, K.; Milojevic Samanovic, A.; Veselinovic, M.; Zivkovic, V.; Mikhaylovsky, V.; Mikerova, M.; Reshetnikov, V.; Jakovljevic, V.; Nikolic Turnic, T. Oxidative Stress Mediated Therapy in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarry, T.; Biniecka, M.; Veale, D.J.; Fearon, U. Hypoxia, oxidative stress and inflammation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 125, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-R.; Kim, K.-W.; Kim, B.-M.; Cho, M.-L.; Lee, S.-H. The effect of vascular endothelial growth factor on osteoclastogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krock, B.L.; Skuli, N.; Simon, M.C. Hypoxia-induced angiogenesis: Good and evil. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 1117–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Fan, D.; Cao, X.; Ye, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, C. The role of reactive oxygen species in the rheumatoid arthritis-associated synovial microenvironment. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Joo, Y.; Kim, W.; Min, D.; Min, J.; Park, S.H.; Cho, C.; Kim, H. Vascular endothelial growth factor levels in the serum and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2001, 19, 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Aslanalp, Z.; Tikiz, C.; Ulusoy, A.; Orguc, Ş.; Yedekci, A.B.; Ulman, C. The relationship between serum angiogenic factor levels and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arch. Rheumatol. 2020, 35, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordo, R.; Cossu, A.; Porcu, M.C.; Cappuccinelli, R.; Biosa, G.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Pretti, L.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Pintus, G.; Posadino, A.M. Cytoprotective, antioxidant, and anti-migratory activity of Pistacia lentiscus L. supercritical carbon dioxide extract on primary human endothelial cells. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 37, 2681–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M.; Collins, B.F.; Ho, L.A.; Raghu, G. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated lung disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2015, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diesler, R.; Cottin, V. Pulmonary fibrosis associated with rheumatoid arthritis: From pathophysiology to treatment strategies. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2022, 16, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKleroy, W.; Lee, T.-H.; Atabai, K. Always cleave up your mess: Targeting collagen degradation to treat tissue fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2013, 304, L709–L721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A. The role of immunosuppressive myofibroblasts in the aging process and age-related diseases. J. Mol. Med. 2023, 101, 1169–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, E.; Rosa, I.; Fioretto, B.S.; Manetti, M. The contribution of endothelial cells to tissue fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2024, 36, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Zhao, M.; Lian, H.; Ma, S.; Xu, K.; Li, Z.; Yu, G. Injured endothelial cell: A risk factor for pulmonary fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, J. Study Design, Sample Size Estimation, and Selection of Statistical Method. In Textbook of Medical Statistics: For Medical Students; Guo, X., Xue, F., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 7–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, M.H.; Paparozzi, E.T.; Stroup, W.W. Best practices for presenting statistical information in a research article. HortScience 2019, 54, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intriago, M.; Maldonado, G.; Cárdenas, J.; Ríos, C. Clinical characteristics in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Differences between genders. Sci. World J. 2019, 2019, 8103812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | RA (n = 20) | HD (n = 15) |
|---|---|---|
| Age at serum sampling (years) * | 58 ± 7 | 52 ± 11 |
| Male n (%) | 11 (55) | 4 (27) |
| Female n (%) | 9 (45) | 11 (73) |
| Smoking status n (%) | 14 (70) | 6 (40) |
| ACPA positivity n (%) | 10 (50) | |
| RF positivity n (%) | 16 (80) | |
| DMARD use n (%) | 16 (80) | |
| MTX use n (%) | 11 (55) | |
| TNFi use n (%) | 5 (25) | |
| Steroids use n (%) | 10 (50) | |
| Steroids dose (mg/day) * | 4.8 ± 0.8 | |
| ESR * | 19.4 ± 12.5 | |
| CRP level mg/dL | 0.5 ± 0.5 | |
| Disease duration before sampling (months) | 130 ± 91 | |
| DAS-28 * | 3.7 ± 1.3 | |
| 6 (30) 2 (10) 8 (40) 4 (20) | |
| Ln-RHI * | 0.6 ± 0.4 | |
| MDA (µmol/L) * | 3.7 ± 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giordo, R.; Posadino, A.M.; Maccioccu, P.; Capobianco, G.; Zinellu, A.; Erre, G.L.; Pintus, G. Sera from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Induce Oxidative Stress and Pro-Angiogenic and Profibrotic Phenotypes in Human Endothelial Cells. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5913. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195913
Giordo R, Posadino AM, Maccioccu P, Capobianco G, Zinellu A, Erre GL, Pintus G. Sera from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Induce Oxidative Stress and Pro-Angiogenic and Profibrotic Phenotypes in Human Endothelial Cells. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(19):5913. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195913
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiordo, Roberta, Anna Maria Posadino, Paola Maccioccu, Giampiero Capobianco, Angelo Zinellu, Gian Luca Erre, and Gianfranco Pintus. 2024. "Sera from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Induce Oxidative Stress and Pro-Angiogenic and Profibrotic Phenotypes in Human Endothelial Cells" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 19: 5913. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195913
APA StyleGiordo, R., Posadino, A. M., Maccioccu, P., Capobianco, G., Zinellu, A., Erre, G. L., & Pintus, G. (2024). Sera from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Induce Oxidative Stress and Pro-Angiogenic and Profibrotic Phenotypes in Human Endothelial Cells. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(19), 5913. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195913








