Extracellular DNA and Markers of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Saliva from Patients with Periodontitis—A Case–Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Salivary DNA
2.3. ELISA Assays
2.4. Statistical Analysis
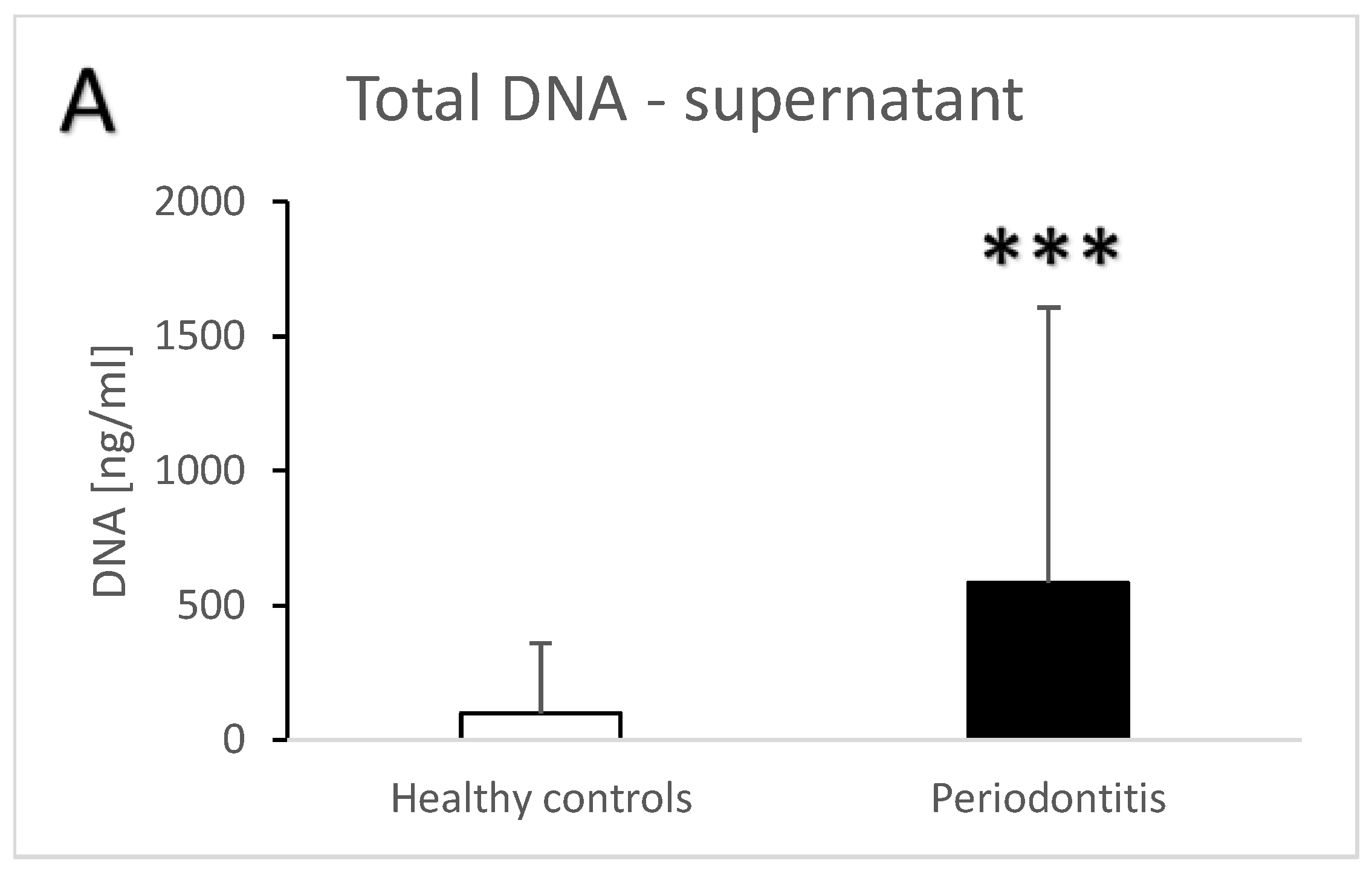
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kinane, D.F.; Stathopoulou, P.G.; Papapanou, P.N. Periodontal diseases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krutyhołowa, A.; Strzelec, K.; Dziedzic, A.; Bereta, G.P.; Łazarz-Bartyzel, K.; Potempa, J.; Gawron, K. Host and bacterial factors linking periodontitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 980805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.A.; Krauss, J. Neutrophils in Periodontal Inflammation. Front. Oral Biol. 2012, 15, 56–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filep, J.G. Targeting Neutrophils for Promoting the Resolution of Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 866747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, M.J.; Radic, M. Neutrophil extracellular traps: Double-edged swords of innate immunity. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2689–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, J.S.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; Kaplan, M.J. Proteins derived from neutrophil extracellular traps may serve as self-antigens and mediate organ damage in autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigerblad, G.; Kaplan, M.J. Neutrophil extracellular traps in systemic autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magán-Fernández, A.; Rasheed Al-Bakri, S.M.; O’Valle, F.; Benavides-Reyes, C.; Abadía-Molina, F.; Mesa, F. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Periodontitis. Cells 2020, 9, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannopoulos, V.; Metzler, K.D.; Hakkim, A.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil elastase and myeloperoxidase regulate the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 191, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisareva, E.; Mihalovičová, L.; Pastor, B.; Kudriavtsev, A.; Mirandola, A.; Mazard, T.; Badiou, S.; Maus, U.; Ostermann, L.; Weinmann-Menke, J.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps have auto-catabolic activity and produce mononucleosome-associated circulating DNA. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitkov, L.; Klappacher, M.; Hannig, M.; Krautgartner, W.D. Extracellular neutrophil traps in periodontitis. J. Periodontal Res. 2009, 44, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.S.; Silva, L.M.; Theofilou, V.I.; Greenwell-Wild, T.; Li, L.; Williams, D.W.; Ikeuchi, T.; Brenchley, L.; Bugge, T.H.; Diaz, P.I.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps and extracellular histones potentiate IL-17 inflammation in periodontitis. J. Exp. Med. 2023, 220, e20221751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonaka, T.; Wong, D.T.W. Saliva Diagnostics. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 15, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baňasová, L.; Kamodyová, N.; Janšáková, K.; Tóthová, Ľ.; Stanko, P.; Turňa, J.; Celec, P. Salivary DNA and markers of oxidative stress in patients with chronic periodontitis. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2015, 19, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Gornitsky, M.; Velly, A.M.; Yu, H.; Benarroch, M.; Schipper, H.M. Salivary DNA, lipid, and protein oxidation in nonsmokers with periodontal disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chu, C.J.; Pan, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhao, L. The Correlation between Periodontal Parameters and Cell-Free DNA in the Gingival Crevicular Fluid, Saliva, and Plasma in Chinese Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisetsky, D.S. The origin and properties of extracellular DNA: From PAMP to DAMP. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 144, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stortz, J.A.; Hawkins, R.B.; Holden, D.C.; Raymond, S.L.; Wang, Z.; Brakenridge, S.C.; Cuschieri, J.; Moore, F.A.; Maier, R.V.; Moldawer, L.L.; et al. Cell-free nuclear, but not mitochondrial, DNA concentrations correlate with the early host inflammatory response after severe trauma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorber, L.; Zwaenepoel, K.; Jacobs, J.; De Winne, K.; Goethals, S.; Reclusa, P.; Van Casteren, K.; Augustus, E.; Lardon, F.; Roeyen, G.; et al. Circulating Cell-Free DNA and RNA Analysis as Liquid Biopsy: Optimal Centrifugation Protocol. Cancers 2019, 11, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Chen, K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Lin, L.; Shao, Y.; Gao, L.; Yin, H.; Cui, C.; et al. DNA in serum extracellular vesicles is stable under different storage conditions. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapin, M.; Tjensvoll, K.; Nedrebø, K.; Taksdal, E.; Janssen, H.; Gilje, B.; Nordgård, O. Extracellular vesicles as a potential source of tumor-derived DNA in advanced pancreatic cancer. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0291623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konečná, B.; Gaál Kovalčíková, A.; Pančíková, A.; Novák, B.; Kovaľová, E.; Celec, P.; Tóthová, Ľ. Salivary Extracellular DNA and DNase Activity in Periodontitis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janovičová, Ľ.; Konečná, B.; Vlková, B.; Celec, P. Isolation and Quantification of Extracellular DNA from Biofluids. Bio-Protocol 2020, 10, e3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronkhorst, A.J.; Ungerer, V.; Diehl, F.; Anker, P.; Dor, Y.; Fleischhacker, M.; Gahan, P.B.; Hui, L.; Holdenrieder, S.; Thierry, A.R. Towards systematic nomenclature for cell-free DNA. Hum. Genet. 2021, 140, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meddeb, R.; Dache, Z.A.A.; Thezenas, S.; Otandault, A.; Tanos, R.; Pastor, B.; Sanchez, C.; Azzi, J.; Tousch, G.; Azan, S.; et al. Quantifying circulating cell-free DNA in humans. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisetsky, D.S.; Gauley, J.; Ullal, A.J. Microparticles as a source of extracellular DNA. Immunol. Res. 2011, 49, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Feng, Y.; Tang, H.; Huang, L.; Tong, Z.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Tan, J. A Simplified and Effective Method for Generation of Experimental Murine Periodontitis Model. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitkov, L.; Hartl, D.; Minnich, B.; Hannig, M. Janus-Faced Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Periodontitis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.C.; Chicca, I.J.; Cooper, P.R.; Milward, M.R.; Chapple, I.L. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Periodontitis: A Web of Intrigue. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, S.R.; de Arruda, J.A.A.; Schneider, A.H.; Carvalho, V.F.; Machado, C.C.; Corrêa, J.D.; Moura, M.F.; Duffles, L.F.; de Souza, F.F.L.; Ferreira, G.A.; et al. Are neutrophil extracellular traps the link for the cross-talk between periodontitis and rheumatoid arthritis physiopathology? Rheumatology 2021, 61, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilherme Neto, J.L.; Rodrigues Venturini, L.G.; Schneider, A.H.; Taira, T.M.; Duffles Rodrigues, L.F.; Veras, F.P.; Oliveira, S.R.; da Silva, T.A.; Cunha, F.Q.; Fukada, S.Y. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Aggravate Apical Periodontitis by Stimulating Osteoclast Formation. J. Endod. 2023, 49, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magán-Fernández, A.; O’Valle, F.; Abadía-Molina, F.; Muñoz, R.; Puga-Guil, P.; Mesa, F. Characterization and comparison of neutrophil extracellular traps in gingival samples of periodontitis and gingivitis: A pilot study. J. Periodontal. Res. 2019, 54, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.; Sakellari, D.; Roberts, H.; Risafi, I.; Ling, M.; Cooper, P.; Milward, M.; Chapple, I. Peripheral blood neutrophil extracellular trap production and degradation in chronic periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, C.; Kobayashi, T.; Ito, S.; Sugita, N.; Murasawa, A.; Nakazono, K.; Yoshie, H. Circulating levels of carbamylated protein and neutrophil extracellular traps are associated with periodontitis severity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A pilot case-control study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.M.; Salma, U.; Irahara, T.; Watanabe, E.; Takeyama, N. Quantifying Myeloperoxidase-DNA and Neutrophil Elastase-DNA Complexes from Neutrophil Extracellular Traps by Using a Modified Sandwich ELISA. J. Vis. Exp. 2023, 195, e64644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, H.; Ibrahim, N.; Klopf, J.; Zagrapan, B.; Mauracher, L.M.; Hell, L.; Hofbauer, T.M.; Ondracek, A.S.; Schoergenhofer, C.; Jilma, B.; et al. ELISA detection of MPO-DNA complexes in human plasma is error-prone and yields limited information on neutrophil extracellular traps formed in vivo. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakash, K.; Demirel, I.; Khalaf, H.; Bengtsson, T. The role of phagocytosis, oxidative burst and neutrophil extracellular traps in the interaction between neutrophils and the periodontal pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2015, 30, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.; Cooper, P.; Milward, M.; Chapple, I. Differential activation of neutrophil extracellular traps by specific periodontal bacteria. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 75 (Suppl. S1), S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celecová, V.; Kamodyová, N.; Tóthová, L.; Kúdela, M.; Celec, P. Salivary markers of oxidative stress are related to age and oral health in adult non-smokers. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2013, 42, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóthová, L.; Celecová, V.; Celec, P. Salivary markers of oxidative stress and their relation to periodontal and dental status in children. Dis. Markers 2013, 34, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Aguilar, M.D.; Escribano, D.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Martínez-Miró, S.; Rubio, M.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Tecles, F.; Cerón, J.J. Influence of the way of reporting alpha-Amylase values in saliva in different naturalistic situations: A pilot study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, J.S.; Tait, S.W. Mitochondrial DNA in inflammation and immunity. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e49799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Groups | Healthy Controls | Periodontitis |
|---|---|---|
| Number of subjects (n) | 71 | 49 |
| Age (years) | 31.6 ± 9.5 | 48.5 ± 9.4 |
| Papillary bleeding index | 17.4 ± 11.8 | 41.0 ± 22.3 |
| Probing depth (mm) | 0.6 ± 0.4 | 6.2 ± 1.6 |
| Clinical attachment level | - | 3.2 ± 1.6 |
| Bleeding on probing | - | 1.4 ± 0.8 |
| Total ecDNA—s | Total ecDNA—p | Nc ecDNA—s | Nc ecDNA—p | Mt ecDNA—s | Mt ecDNA—p | Myeloperoxidase | Neutrophil Elastase | Nucleosomes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | r | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.12 | −0.09 | 0.04 | −0.06 | 0.33 | −0.09 |
| p | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.53 | 0.43 | 0.55 | 0.77 | 0.69 | 0.02 | 0.53 | |
| PBI | r | −0.08 | 0.00 | −0.12 | −0.17 | −0.02 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.07 | −0.32 |
| p | 0.58 | 0.98 | 0.40 | 0.24 | 0.92 | 0.78 | 0.48 | 0.61 | 0.03 | |
| Probing depth | r | 0.26 | 0.41 | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.31 | −0.07 |
| p | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.64 | |
| Clinicalattachment level | r | 0.25 | 0.41 | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.31 | −0.08 |
| p | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.61 | |
| Total ecDNA—s | Total ecDNA—p | Nc ecDNA—s | Nc ecDNA—p | Mt ecDNA—s | Mt ecDNA—p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Myeloperoxidase | r | 0.38 | 0.47 | 0.35 | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.45 |
| p | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Neutrophil elastase | r | 0.37 | 0.48 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.17 | 0.25 |
| p | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.24 | 0.08 | |
| Nucleosomes | r | 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.13 | −0.04 | −0.09 |
| p | 0.36 | 0.80 | 0.25 | 0.38 | 0.77 | 0.55 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovalčíková, A.G.; Novák, B.; Roshko, O.; Kovaľová, E.; Pastorek, M.; Vlková, B.; Celec, P. Extracellular DNA and Markers of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Saliva from Patients with Periodontitis—A Case–Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020468
Kovalčíková AG, Novák B, Roshko O, Kovaľová E, Pastorek M, Vlková B, Celec P. Extracellular DNA and Markers of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Saliva from Patients with Periodontitis—A Case–Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(2):468. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020468
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovalčíková, Alexandra Gaál, Bohuslav Novák, Oksana Roshko, Eva Kovaľová, Michal Pastorek, Barbora Vlková, and Peter Celec. 2024. "Extracellular DNA and Markers of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Saliva from Patients with Periodontitis—A Case–Control Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 2: 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020468
APA StyleKovalčíková, A. G., Novák, B., Roshko, O., Kovaľová, E., Pastorek, M., Vlková, B., & Celec, P. (2024). Extracellular DNA and Markers of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Saliva from Patients with Periodontitis—A Case–Control Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(2), 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020468







