Pars Interarticularis Fractures Treated with Minimally Invasive Surgery: A Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Etiology and Risk Factors
1.2. Natural History
1.3. Clinical Presentation
1.4. Physical Examination
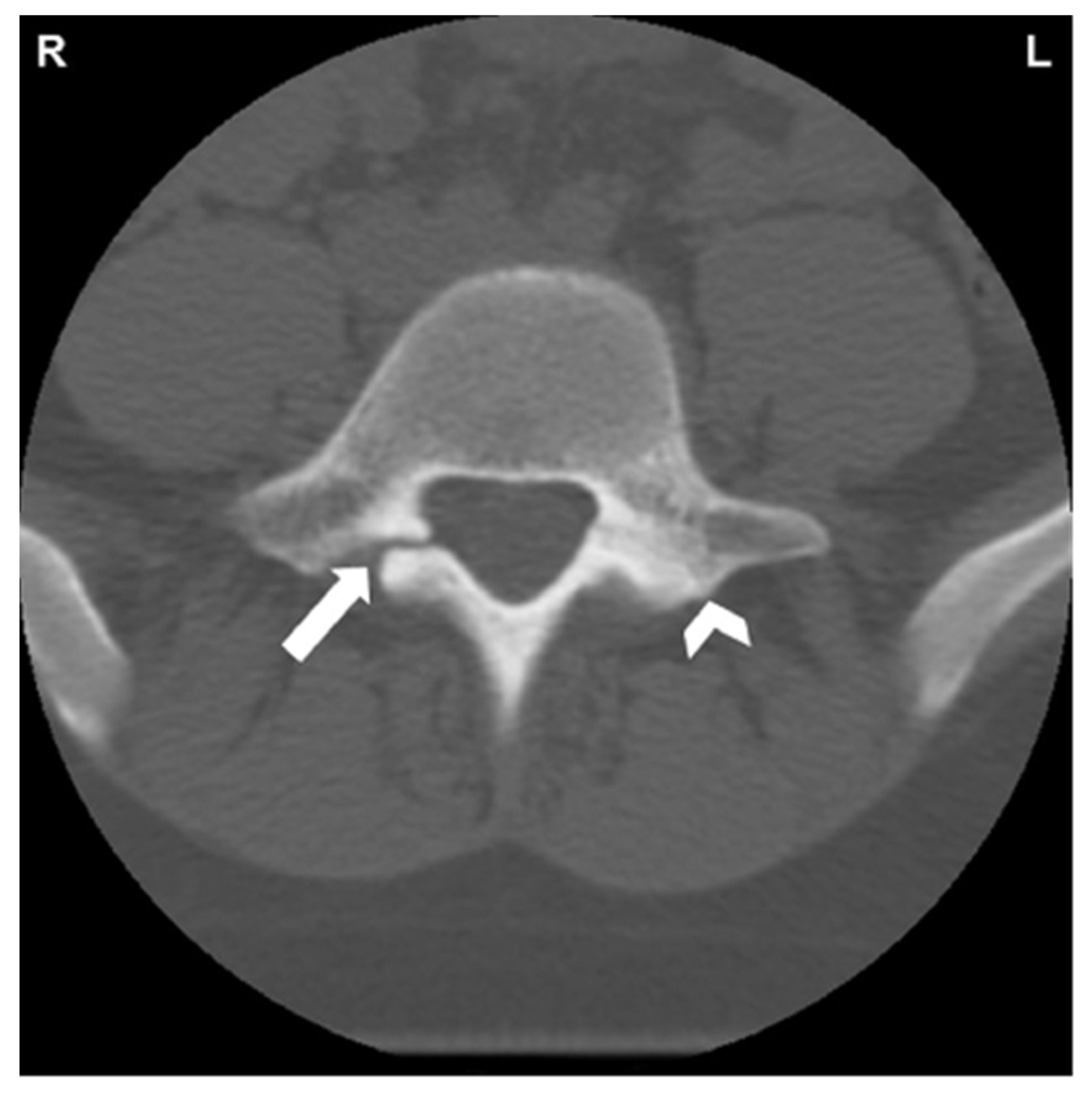
1.5. Imaging
1.6. Non-Operative Management
1.7. Follow-Up Evaluation
1.8. Surgical Repair Indications
1.9. Conventional Surgical Repair Techniques
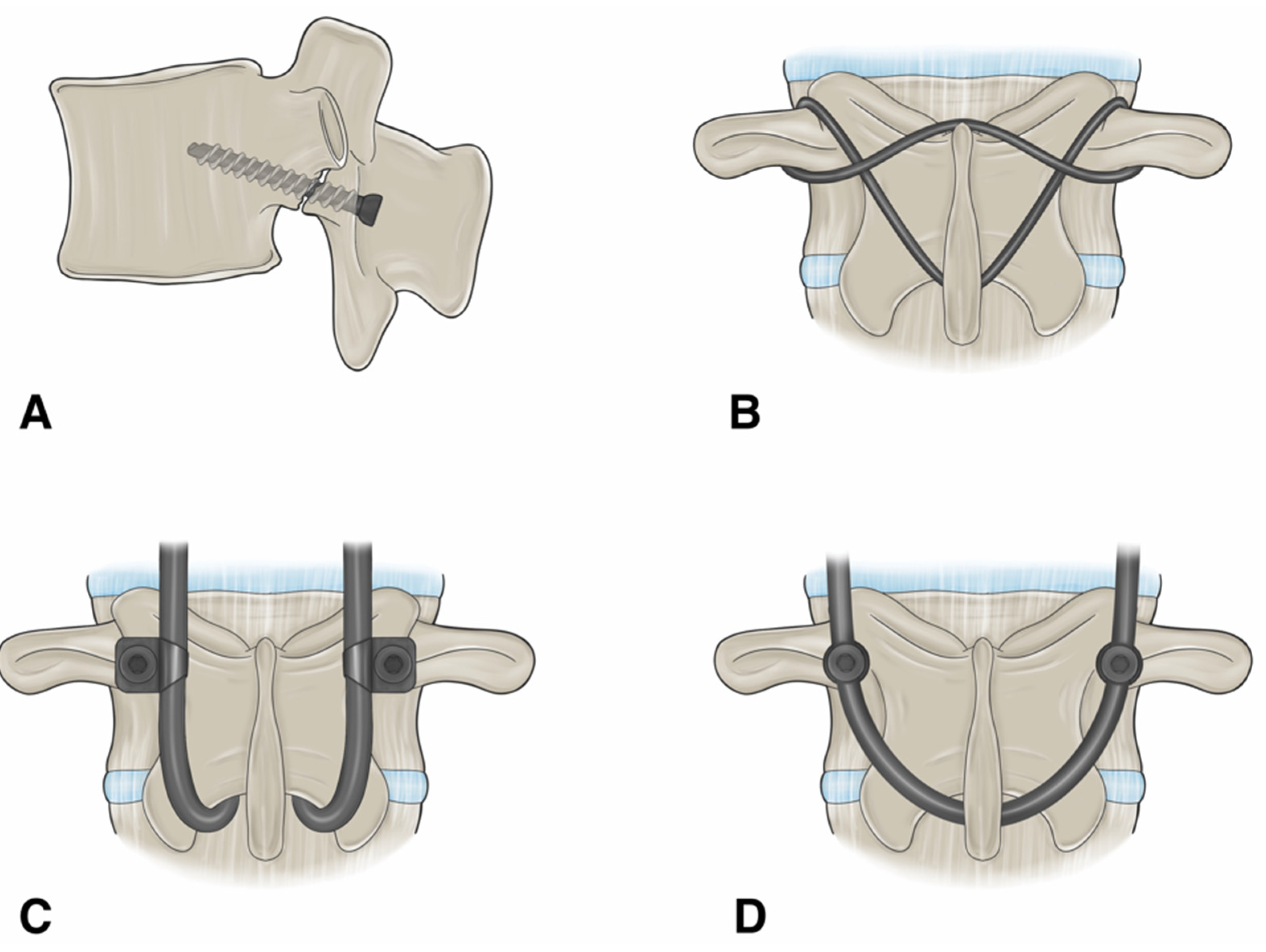
1.9.1. Buck’s Repair
1.9.2. Morscher Screw-Hook Repair
1.9.3. Scott’s Wiring Technique
1.9.4. Pedicle Screw Based Repairs
1.10. Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
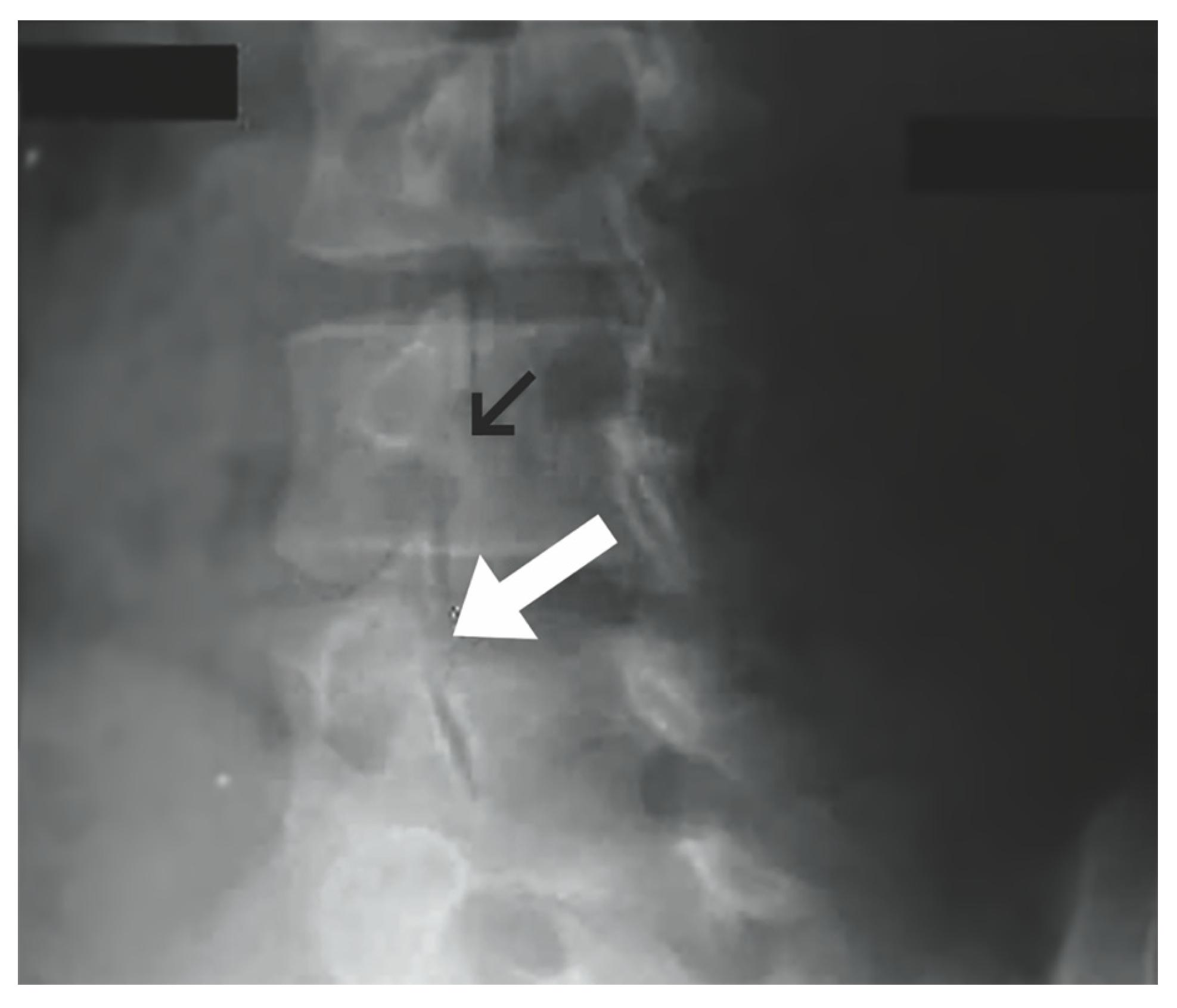
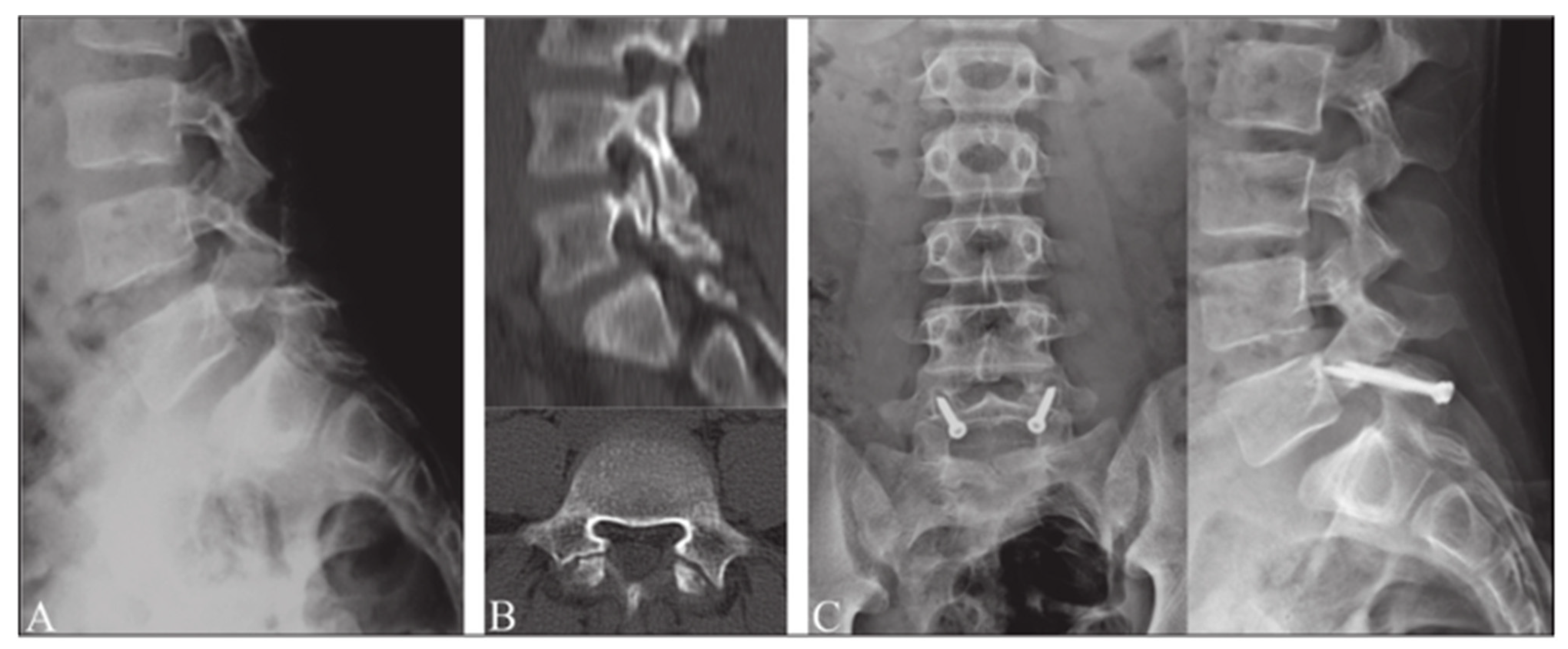
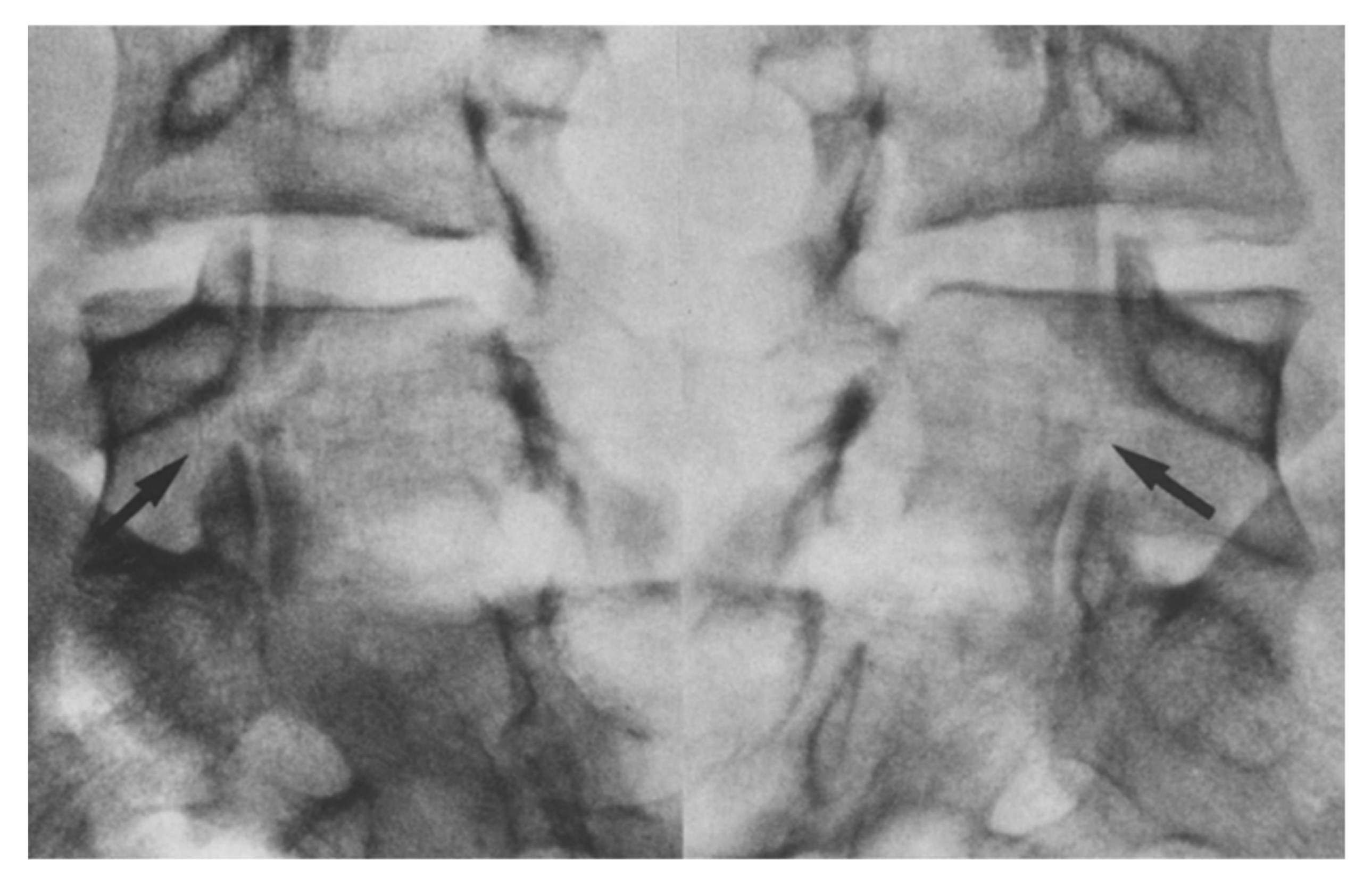
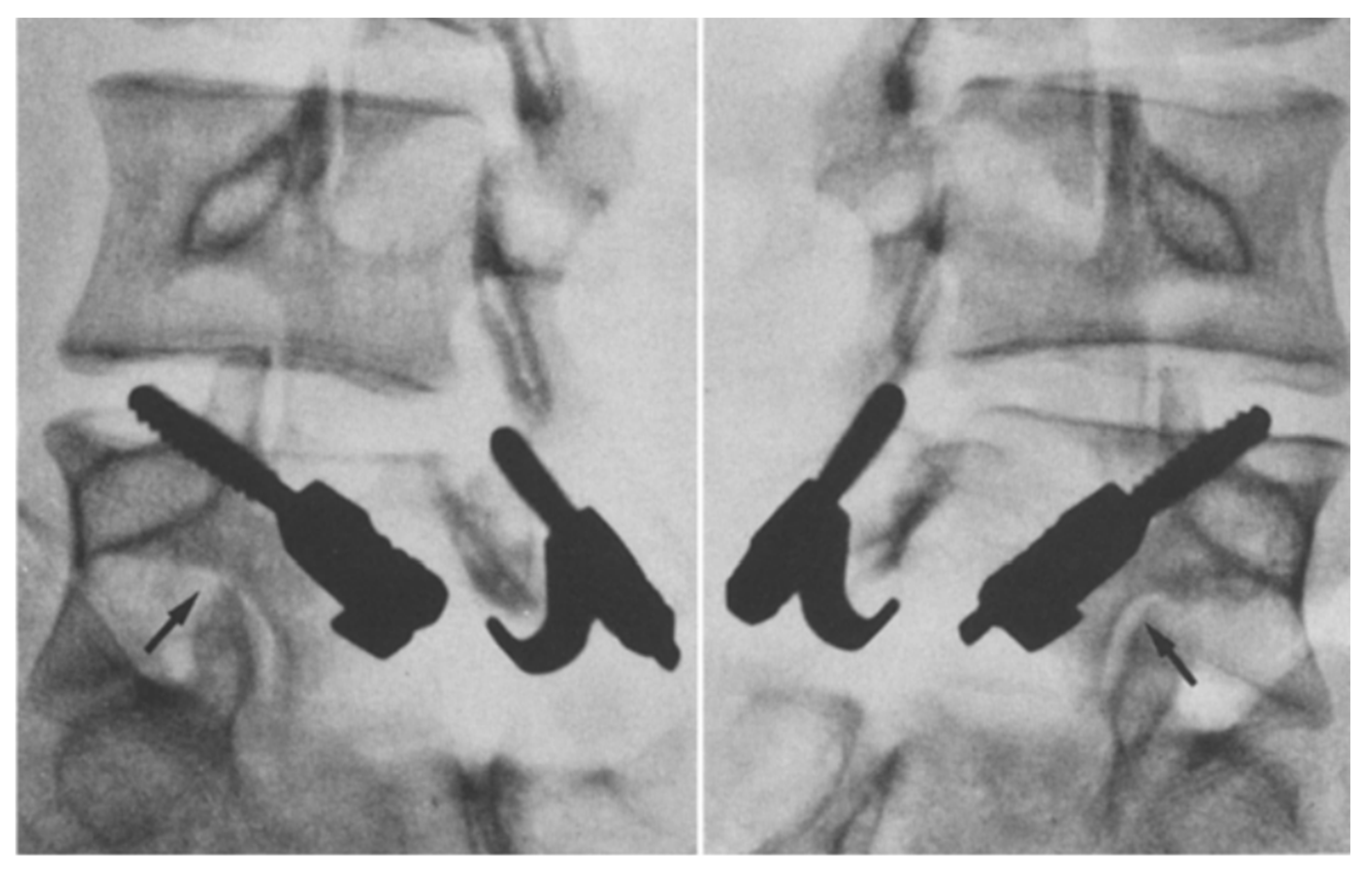
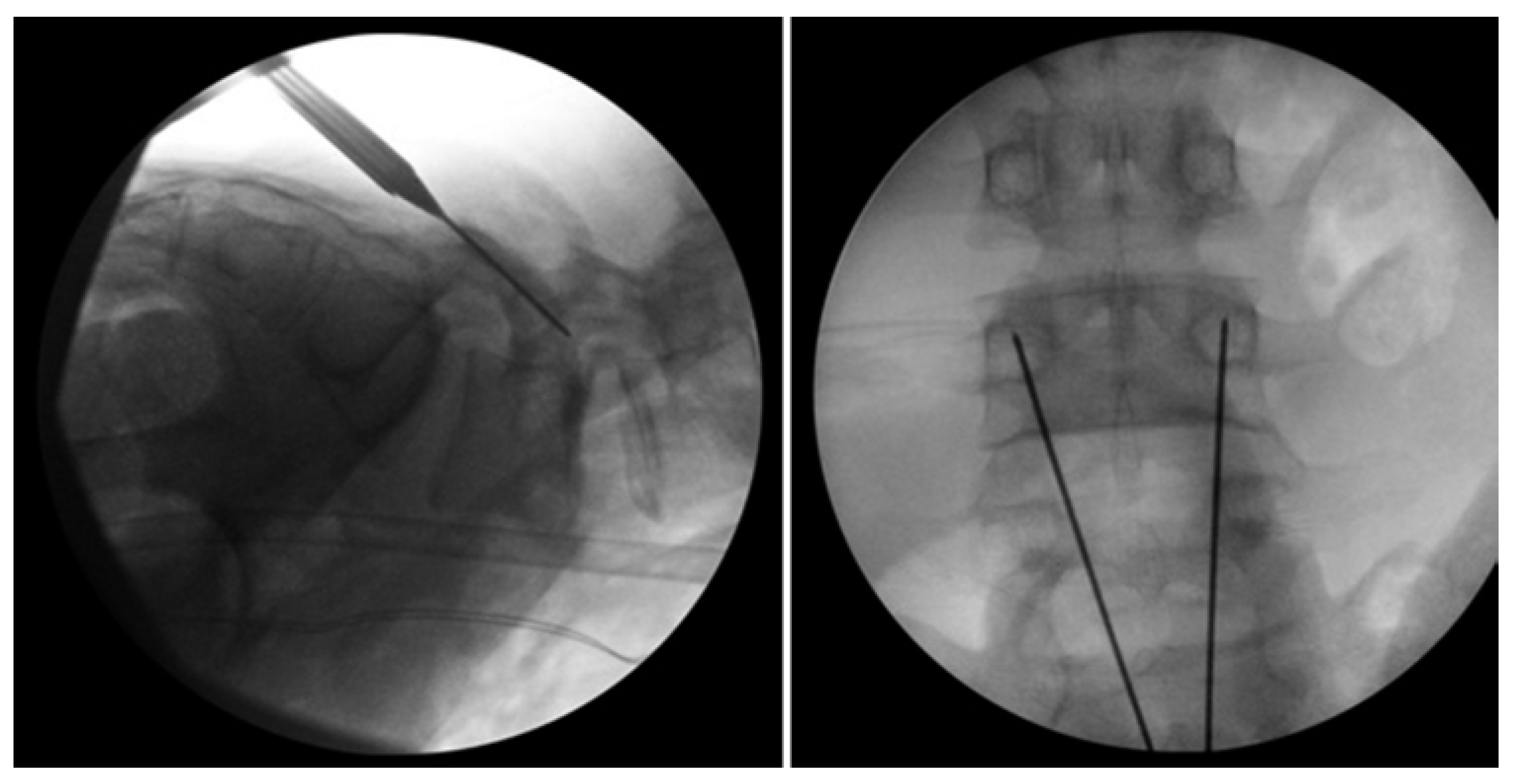
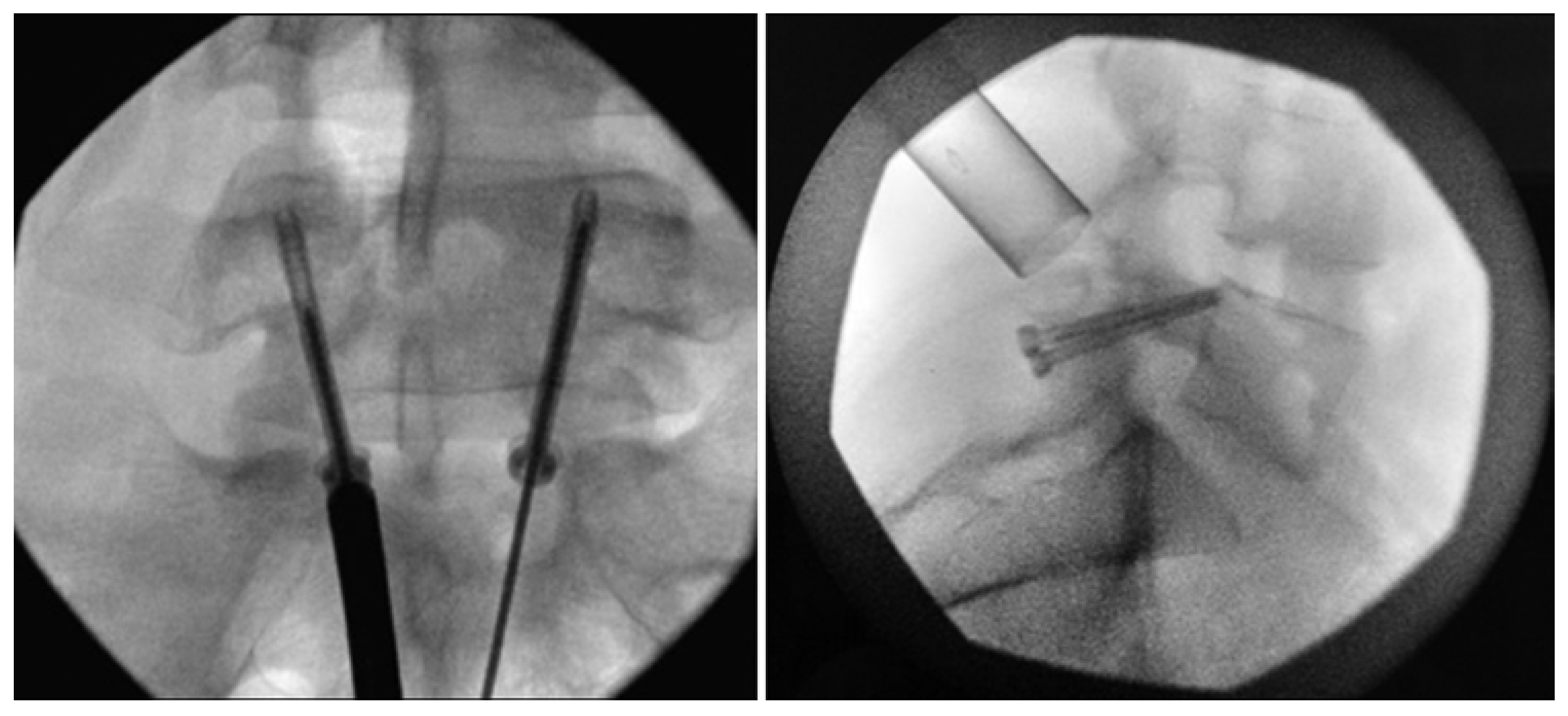
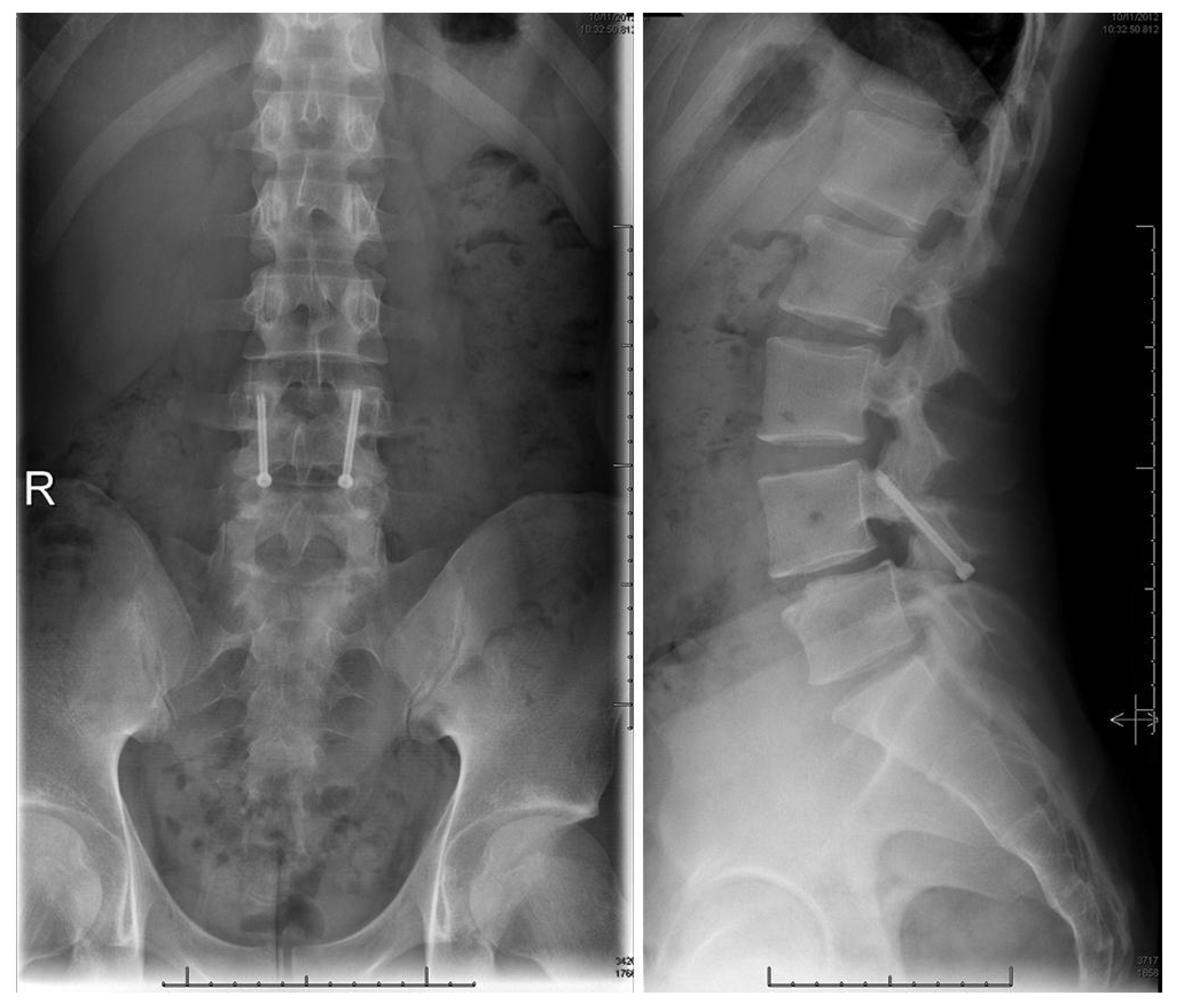
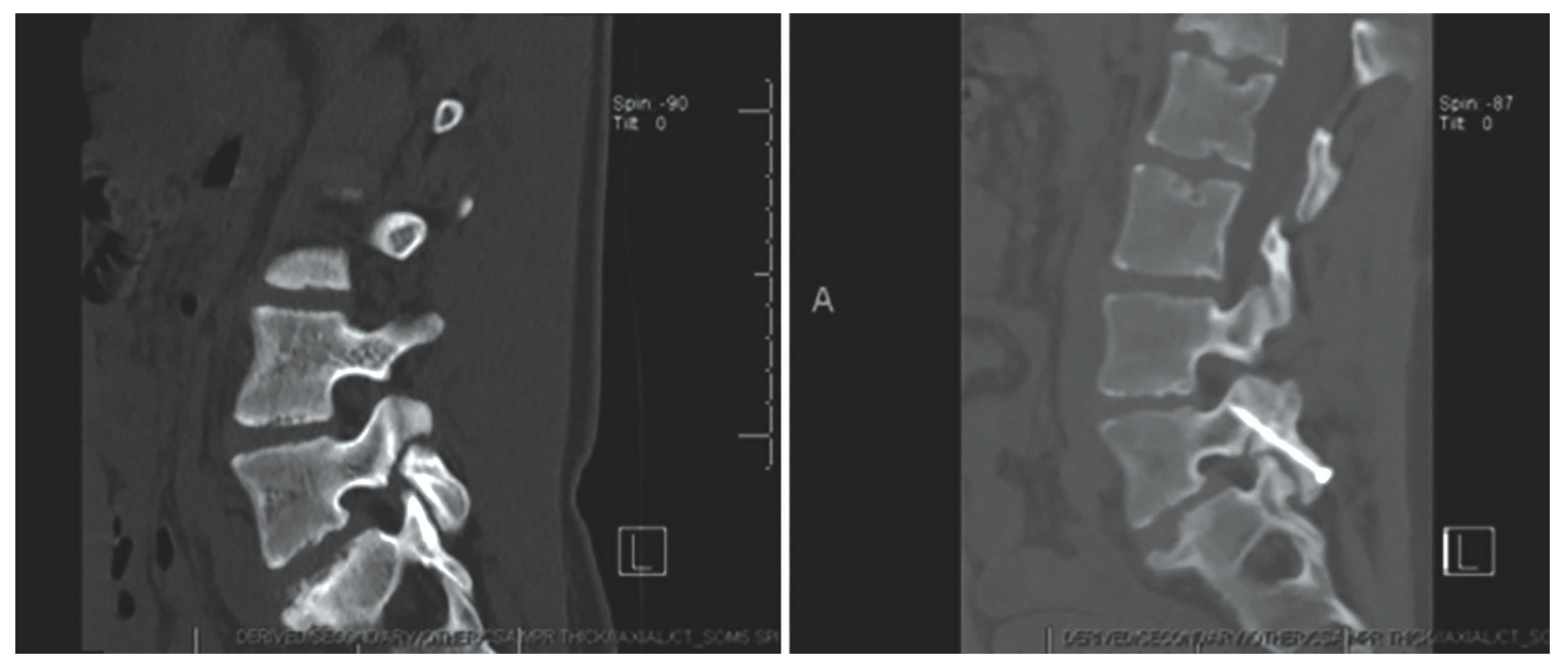
Levi Technique—Minimally Invasive Direct Pars Screw Placement
2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mansfield, J.T.; Wroten, M. Pars Interarticularis Defect. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Kashlan, O.N.; Singh, R.; Adsul, N.M.; Yong, Z.; Oh, S.W.; Noh, J.H.; Jang, I.T.; Oh, S.H. Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Radiofrequency Ablation of the Sinuvertebral Nerve in an Olympian with a Left L5 Pedicle/Pars Interarticularis Fracture-Associated Left L5-S1 Disk Desiccation. World Neurosurg. X 2019, 3, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, N.; Patra, D.P.; Narayan, V.; Savardekar, A.R.; Dossani, R.H.; Bollam, P.; Bir, S.; Nanda, A. A comparison of the techniques of direct pars interarticularis repairs for spondylolysis and low-grade spondylolisthesis: A meta-analysis. Neurosurg. Focus. 2018, 44, E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredrickson, B.E.; Baker, D.; McHolick, W.J.; Yuan, H.A.; Lubicky, J.P. The natural history of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1984, 66, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffa, S.J.; Luther, E.; Levi, A.D. Repair of isthmic pars interarticularis fractures: A literature review of conventional and minimally invasive techniques. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2019, 63, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.K.; Bisson, E.F.; Bydon, M.; Glassman, S.D.; Foley, K.T.; Potts, E.A.; Shaffrey, C.I.; Shaffrey, M.E.; Coric, D.; Knightly, J.J.; et al. Obese patients benefit, but do not fare as well as nonobese patients, following lumbar spondylolisthesis surgery: An analysis of the quality outcomes database. Neurosurgery 2020, 86, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, S.; Phan, K.; Mobbs, R.J.; Rao, P.J. The incidence of pars interarticularis defects in athletes. Glob. Spine J. 2020, 10, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makovitch, S.; Eng, C. Spine injuries in gymnasts. In Gymnastics Medicine: Evaluation, Management and Rehabilitation; Sweeney, E., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 135–176. ISBN 978-3-030-26287-7. [Google Scholar]
- Tanveer, F.; Arslan, S.A.; Darain, H.; Ahmad, A.; Gilani, S.A.; Hanif, A. Prevailing treatment methods for lumbar spondylolysis: A systematic review. Medicine 2021, 100, e28319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira Duarte, M.; Camino Willhuber, G.O. Pars Interarticularis Injury. In Pars InteStatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, K.; Hakozaki, M.; Mashiko, R.; Konno, S.-I. Familial development of lumbar spondylolysis: A familial case report of 7- and 4-year-old brothers and their father. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 3000605211015559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, A.; Sairyo, K.; Shibuya, I.; Kato, K.; Dezawa, A.; Sakai, T. Lumbar spondylolysis in juveniles from the same family: A report of three cases and a review of the literature. Case Rep. Orthop. 2013, 2013, 272514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurube, T.; Kakutani, K.; Okamoto, K.; Manabe, M.; Maeno, K.; Yoshikawa, M.; Sha, N.; Kuroda, R.; Nishida, K. Lumbar spondylolysis: A report of four cases from two generations of a family. J. Orthop. Surg. 2017, 25, 2309499017713917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, M.B.; Rowe, G.G. The incidence of separate neural arch and coincident bone variations; a survey of 4,200 skeletons. Anat. Rec. 1951, 109, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatsumura, M.; Gamada, H.; Ishimoto, R.; Okuwaki, S.; Eto, F.; Ogawa, T.; Mammoto, T.; Hirano, A. Prevalence of curable and pseudoarthrosis stages of adolescent lumbar spondylolysis. J. Rural Med. 2018, 13, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Ochoa, J.K.; Lubinus, A.; Timon, S.; Lee, Y.-P.; Bhatia, N.N. Management of lumbar spondylolysis in the adolescent athlete: A review of over 200 cases. Spine J. 2022, 22, 1628–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, N.J.; Bargar, W.L.; Friedman, B. The incidence of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in nonambulatory patients. Spine 1981, 6, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, U.K. Lumbar spondylolysis—Current concepts review. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2021, 21, 101535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newell, R.L. Spondylolysis. An historical review. Spine 1995, 20, 1950–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphry, G.M. A Treatise on the Human Skeleton (Including the Joints); Macmillan and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1858; Volume 57. [Google Scholar]
- Wiltse, L.L.; Widell, E.H.; Jackson, D.W. Fatigue fracture: The basic lesion in inthmic spondylolisthesis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1975, 57, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciullo, J.V.; Jackson, D.W. Pars interarticularis stress reaction, spondylolysis, and spondylolisthesis in gymnasts. Clin. Sports Med. 1985, 4, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logroscino, G.; Mazza, O.; Aulisa, G.; Pitta, L.; Pola, E.; Aulisa, L. Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in the pediatric and adolescent population. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2001, 17, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libson, E.; Bloom, R.A.; Dinari, G. Symptomatic and asymptomatic spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in young adults. Int. Orthop. 1982, 6, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrmou, E.; Tsitsopoulos, P.P.; Marinopoulos, D.; Tsonidis, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Tsitsopoulos, P.D. Spondylolysis: A review and reappraisal. Hippokratia 2010, 14, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, B.T.; Hanna, A.; Lucas, J.A. Spondylolysis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Linton, A.A.; Hsu, W.K. A review of treatment for acute and chronic pars fractures in the lumbar spine. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2022, 15, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.; Beck, N.A.; Sampson, N.R.; Zhu, X.; Flynn, J.M.; Drummond, D. Imaging modalities for low back pain in children: A review of spondyloysis and undiagnosed mechanical back pain. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2013, 33, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohile, N.V.; Kuczmarski, A.S.; Lee, D.; Warburton, C.; Rakoczy, K.; Butler, A.J. Spondylolysis and isthmic spondylolisthesis: A guide to diagnosis and management. J. Am. Board. Fam. Med. 2022, 35, 1204–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, A.; Cianfoni, A.; Cerase, A.; Magarelli, N.; Bonomo, L. Lumbar spondylolysis: A review. Skelet. Radiol. 2011, 40, 683–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.; Nischal, N.; Murphy, J.; Azzopardi, C.; Iyengar, K.P.; Haleem, S.; Botchu, R. Does chemical shift magnetic resonance imaging improve visualization of pars interarticularis defect? Indian. J. Radiol. Imaging 2023, 33, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, M.R.; Dowling, T.J.; Mesfin, F.B. Isthmic Spondylolisthesis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- [Figure, Oblique Plain Radiograph of the…]—StatPearls—NCBI Bookshelf. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538292/figure/article-26700.image.f1/?report=objectonly (accessed on 28 October 2023).
- Ruff, A.N.; Cornelson, S.M.; Wells, C.B.; Kettner, N.W. Neural arch bone marrow edema and spondylolysis in adolescent cheerleaders: A case series. J. Chiropr. Med. 2019, 18, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.C.; Shimer, A.L. Lumbosacral spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. Clin. Sports Med. 2021, 40, 471–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selhorst, M.; Fischer, A.; Graft, K.; Ravindran, R.; Peters, E.; Rodenberg, R.; Welder, E.; MacDonald, J. Timing of physical therapy referral in adolescent athletes with acute spondylolysis: A retrospective chart review. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2017, 27, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetzinger, S.; Courtney, S.; Yee, K.; Welz, M.; Kalani, M.; Neal, M. Spondylolysis in young athletes: An overview emphasizing nonoperative management. J. Sports Med. 2020, 2020, 9235958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sri Vijay Anand, K.S.; Eamani, N.; Shetty, A.; Rajasekaran, S. Spondylolysis and pars repair technique: A comprehensive literature review of the current concepts. Indian Spine J. 2021, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, J.E. Direct repair of the defect in spondylolisthesis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 1970, 52-B, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, H.; Chang, X.; Hu, Z.; Mu, X.; Liu, C.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, C. Retrospective comparative study of pedicle screw fixation via quadrant retractor and buck’s technique in the treatment of adolescent spondylolysis. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 14, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnet, P.; Kern, K.; Andrews, K.; Elgafy, H.; Ebraheim, N. Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis: A review of the literature. J. Orthop. 2018, 15, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, A.K.; Hagen, R. Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. Treatment by internal fixation and bone-grafting of the defect. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1988, 70, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnici, A.V.; Koka, S.R.; Richards, D.J. Results of Buck screw fusion in grade I spondylolisthesis. J. R. Soc. Med. 1991, 84, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, L.A.; Shufflebarger, H.; O’Brien, M.F.; Thind, H.; Theodore, N.; Kakarla, U.K. Spondylolysis outcomes in adolescents after direct screw repair of the pars interarticularis. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2014, 21, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefti, F.; Seelig, W.; Morscher, E. Repair of lumbar spondylolysis with a hook-screw. Int. Orthop. 1992, 16, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, R.O.; Scott, J.H. Lytic spondylolysis. Repair by wiring. Spine 1986, 11, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.V.; Thompson, A.G. The Scott wiring technique for direct repair of lumbar spondylolysis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 1992, 74, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hioki, A.; Miyamoto, K.; Sadamasu, A.; Nozawa, S.; Ogawa, H.; Fushimi, K.; Hosoe, H.; Shimizu, K. Repair of pars defects by segmental transverse wiring for athletes with symptomatic spondylolysis: Relationship between bony union and postoperative symptoms. Spine 2012, 37, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.H.L.; Chang, C.-W.; Chen, W.-C.; Lin, T.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Wong, C.-B.; Yolcu, Y.U.; Alvi, M.A.; Bydon, M.; Fu, T.-S. Does Direct Surgical Repair Benefit Pars Interarticularis Fracture? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Pain Physician 2022, 25, 265–282. [Google Scholar]
- Tokuhashi, Y.; Matsuzaki, H. Repair of defects in spondylolysis by segmental pedicular screw hook fixation. A preliminary report. Spine 1996, 21, 2041–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debusscher, F.; Troussel, S. Direct repair of defects in lumbar spondylolysis with a new pedicle screw hook fixation: Clinical, functional and Ct-assessed study. Eur. Spine J. 2007, 16, 1650–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakiuchi, M. Repair of the defect in spondylolysis. Durable fixation with pedicle screws and laminar hooks. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 1997, 79, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songer, M.N.; Rovin, R. Repair of the pars interarticularis defect with a cable-screw construct. A preliminary report. Spine 1998, 23, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudenbush, B.L.; Chambers, R.C.; Silverstein, M.P.; Goodwin, R.C. Indirect pars repair for pediatric isthmic spondylolysis: A case series. J. Spine Surg. 2017, 3, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhao, C.; Luo, L.; Liu, L.; Liang, L.; Jiang, D.; Li, P.; Zhou, Q. Surgical Reduction and Direct Repair Using Pedicle Screw-Rod-Hook Fixation in Adult Patients with Low-Grade Isthmic Spondylolisthesis. Pain Res. Manag. 2022, 2022, 8410519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Yu, G.; Liu, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, W. A biomechanical study on the direct repair of spondylolysis by different techniques of fixation. Orthop. Surg. 2010, 2, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayed, I.; Conte, A.G.; Voyadzis, J.-M. Success and failure of percutaneous minimally invasive direct pars repair: Analysis of fracture morphology. World Neurosurg. 2019, 126, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Madhu, S.; Pandita, N.; Ramos, M.R.D.; Tan, B.W.L.; Lopez, K.G.; Alathur Ramakrishnan, S.; Jonathan, P.; Nolan, C.P.; Shree Kumar, D. Is there a place for surgical repair in adults with spondylolysis or grade-I spondylolisthesis—A systematic review and treatment algorithm. Spine J. 2021, 21, 1268–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillet, P.; Petit, M. Direct repair of spondylolysis without spondylolisthesis, using a rod-screw construct and bone grafting of the pars defect. Spine 1999, 24, 1252–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulibarri, J.A.; Anderson, P.A.; Escarcega, T.; Mann, D.; Noonan, K.J. Biomechanical and clinical evaluation of a novel technique for surgical repair of spondylolysis in adolescents. Spine 2006, 31, 2067–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis, C.C.; Eichholz, K.; Thoman, W.J.; Fessler, R.G. A minimally invasive approach to defects of the pars interarticularis: Restoring function in competitive athletes. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2015, 139, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, W.; Zhang, Q.; Han, X.-G.; Yuan, Q.; He, D.; Liu, Y.-J. Robot-assisted direct repair of spondylolysis: A case report. Medicine 2020, 99, e18944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, M.; Tezuka, F.; Chikawa, T.; Hibino, N.; Takahashi, Y.; Yamasaki, Y.; Momota, K.; Henmi, T.; Maeda, T.; Sairyo, K. Consecutive double-level lumbar spondylolysis successfully treated with the double “smiley face” rod method. J. Med. Investig. 2020, 67, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurac, R.; Bravo, J.T.; Silva, Á.; Marré, B. Spondylolysis Repair Using a Minimally Invasive Modified Buck Technique with Neuronavigation and Neuromonitoring in High School and Professional Athletes: Technical Notes, Case Series, and Literature Review. World Neurosurg. 2021, 155, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumura, M.; Okuwaki, S.; Gamada, H.; Asai, R.; Eto, F.; Nagashima, K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Funayama, T.; Yamazaki, M. A Novel Technique for Pars Defect Direct Repair with a Modified Smiley Face Rod for Spondylolysis and Isthmic Spondylolisthesis. Spine Surg. Relat. Res. 2023, 7, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ma, J.-S.; Feng, P.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J.-L.; Kong, Q.-Q. Clinical efficacy of minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (MIS-TLIF) in the treatment of II° lumbar isthmic spondylolisthesis: A retrospective cohort study. Medicine 2023, 102, e35420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widi, G.A.; Williams, S.K.; Levi, A.D. Minimally invasive direct repair of bilateral lumbar spine pars defects in athletes. Case Rep. Med. 2013, 2013, 659078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobrial, G.M.; Crandall, K.M.; Lau, A.; Williams, S.K.; Levi, A.D. Minimally invasive direct pars repair with cannulated screws and recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein: Case series and review of the literature. Neurosurg. Focus 2017, 43, E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, P. Pars Interarticularis Defect. Orthop. Nurs. 2021, 40, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minor, A.; Klein, B.R.; Sowah, M.N.; Etienne, K.; Levi, A.D. Pars Interarticularis Fractures Treated with Minimally Invasive Surgery: A Literature Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020581
Minor A, Klein BR, Sowah MN, Etienne K, Levi AD. Pars Interarticularis Fractures Treated with Minimally Invasive Surgery: A Literature Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(2):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020581
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinor, Adrienne, Benjamin R. Klein, Mareshah N. Sowah, Kayla Etienne, and Allan D. Levi. 2024. "Pars Interarticularis Fractures Treated with Minimally Invasive Surgery: A Literature Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 2: 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020581
APA StyleMinor, A., Klein, B. R., Sowah, M. N., Etienne, K., & Levi, A. D. (2024). Pars Interarticularis Fractures Treated with Minimally Invasive Surgery: A Literature Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(2), 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020581





