Brucella Spondylitis: Current Knowledge and Recent Advances
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
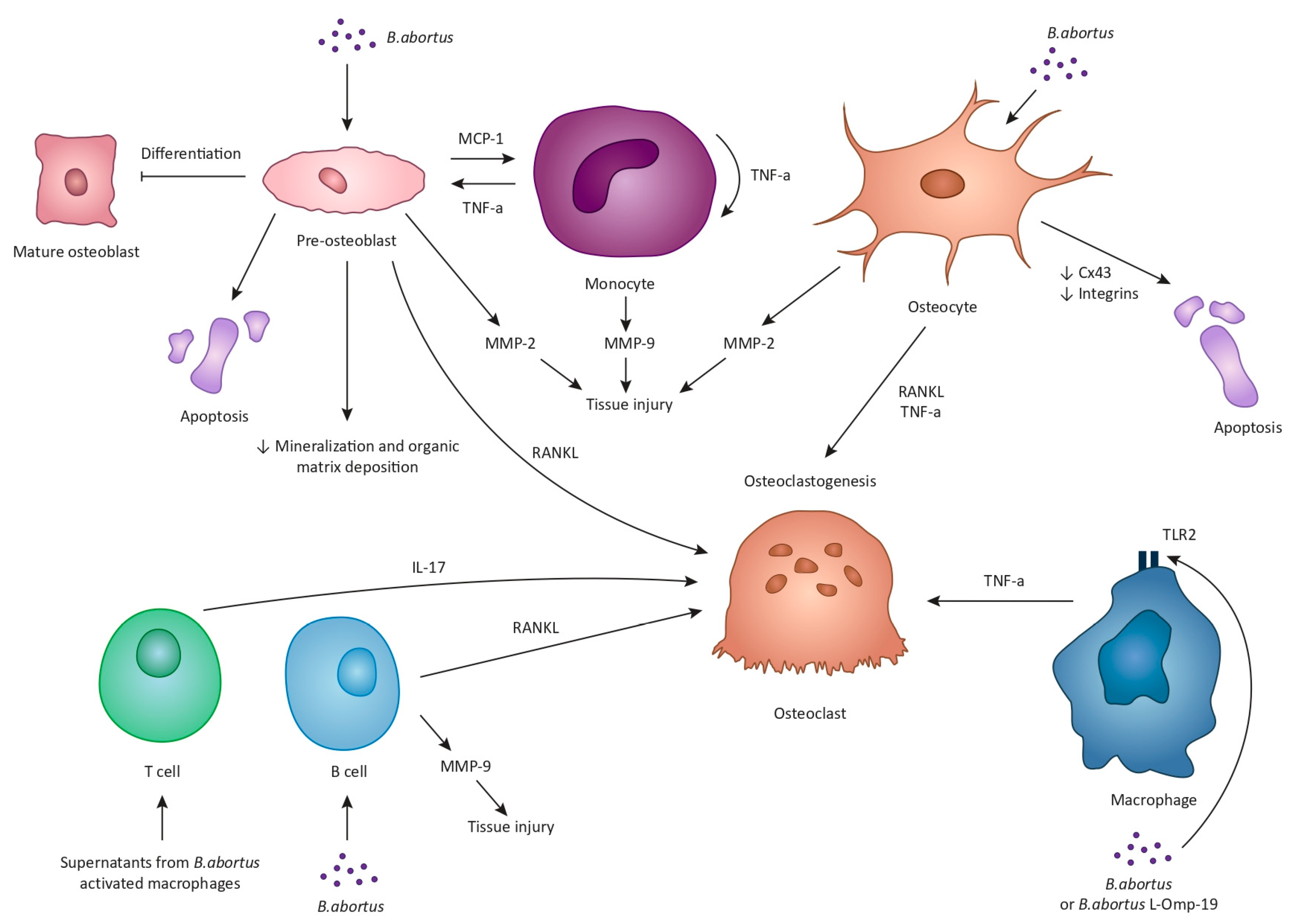
3. Pathogenesis
4. Clinical Features
5. Diagnosis
5.1. Microbiological Diagnosis
5.2. Radiological Diagnosis
6. Treatment
6.1. Conservative Management
6.2. Surgical Management
6.2.1. Open Surgery
6.2.2. Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tali, E.T.; Koc, A.M.; Oner, A.Y. Spinal brucellosis. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2015, 25, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percin, D. Microbiology of Brucella. Recent. Pat. Antiinfect. Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, D. Note on Discovery of a Micrococcus in Malta Fever. Practicioner 1887, 39, 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sayed, A.; Awad, W. Brucellosis: Evolution and expected comeback. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2018, 6, S31–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendhran, J. Genomic insights into Brucella. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 87, 104635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, G.; Akritidis, N.; Bosilkovski, M.; Tsianos, E. Brucellosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 2325–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuon, F.F.; Gondolfo, R.B.; Cerchiari, N. Human-to-human transmission of Brucella—A systematic review. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2017, 22, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. CDC Yellow Book 2024: Health Information for International Travel; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2023.
- Pappas, G.; Papadimitriou, P.; Akritidis, N.; Christou, L.; Tsianos, E.V. The new global map of human brucellosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleem, M.N.; Boyle, S.M.; Sriranganathan, N. Brucellosis: A re-emerging zoonosis. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosilkovski, M.; Krteva, L.; Caparoska, S.; Dimzova, M. Osteoarticular involvement in brucellosis: Study of 196 cases in the Republic of Macedonia. Croat. Med. J. 2004, 45, 727–733. [Google Scholar]
- Geyik, M.F.; Gur, A.; Nas, K.; Cevik, R.; Sarac, J.; Dikici, B.; Ayaz, C. Musculoskeletal involvement of brucellosis in different age groups: A study of 195 cases. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2002, 132, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzgan, T.; Karahocagil, M.K.; Irmak, H.; Baran, A.I.; Karsen, H.; Evirgen, O.; Akdeniz, H. Clinical manifestations and complications in 1028 cases of brucellosis: A retrospective evaluation and review of the literature. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14, e469–e478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkun, R.; Mete, B.D. Musculoskeletal brucellosis. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2011, 15, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turan, H.; Serefhanoglu, K.; Karadeli, E.; Togan, T.; Arslan, H. Osteoarticular involvement among 202 brucellosis cases identified in Central Anatolia region of Turkey. Intern. Med. 2011, 50, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosilkovski, M.; Kirova-Urosevic, V.; Cekovska, Z.; Labacevski, N.; Cvetanovska, M.; Rangelov, G.; Cana, F.; Bogoeva-Tasevska, S. Osteoarticular involvement in childhood brucellosis: Experience with 133 cases in an endemic region. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2013, 32, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeilnejad-Ganji, S.M.; Esmaeilnejad-Ganji, S.M.R. Osteoarticular manifestations of human brucellosis: A review. World J. Orthop. 2019, 10, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turgut, M.; Turgut, A.T.; Kosar, U. Spinal brucellosis: Turkish experience based on 452 cases published during the last century. Acta Neurochir. 2006, 148, 1033–1044, discussion 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulu-Kilic, A.; Karakas, A.; Erdem, H.; Turker, T.; Inal, A.S.; Ak, O.; Turan, H.; Kazak, E.; Inan, A.; Duygu, F.; et al. Update on treatment options for spinal brucellosis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O75–O82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozgeyik, Z.; Ozdemir, H.; Demirdag, K.; Ozden, M.; Sonmezgoz, F.; Ozgocmen, S. Clinical and MRI findings of brucellar spondylodiscitis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2008, 67, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozgeyik, Z.; Aglamis, S.; Bozdag, P.G.; Denk, A. Magnetic resonance imaging findings of musculoskeletal brucellosis. Clin. Imaging 2014, 38, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaksoy, D.; Yucesoy, K.; Yucesoy, M.; Kovanlikaya, I.; Yuce, A.; Naderi, S. Brucellar spondylitis: MRI findings. Eur. Spine J. 2001, 10, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harman, M.; Unal, O.; Onbasi, K.T.; Kiymaz, N.; Arslan, H. Brucellar spondylodiscitis: MRI diagnosis. Clin. Imaging 2001, 25, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrogenis, A.F.; Megaloikonomos, P.D.; Igoumenou, V.G.; Panagopoulos, G.N.; Giannitsioti, E.; Papadopoulos, A.; Papagelopoulos, P.J. Spondylodiscitis revisited. EFORT Open Rev. 2017, 2, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, H. Infectious Spondylitis Mimics: Mechanisms of Disease and Imaging Findings. Semin. Ultrasound CT MR 2018, 39, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batson, O.V. The Function of the Vertebral Veins and Their Role in the Spread of Metastases. Ann. Surg. 1940, 112, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turunc, T.; Demiroglu, Y.Z.; Uncu, H.; Colakoglu, S.; Arslan, H. A comparative analysis of tuberculous, brucellar and pyogenic spontaneous spondylodiscitis patients. J. Infect. 2007, 55, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliffe, J.F. Anatomic basis for the pathogenesis and radiologic features of vertebral osteomyelitis and its differentiation from childhood discitis. A microarteriographic investigation. Acta Radiol. Diagn. 1985, 26, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratcliffe, J.F. An evaluation of the intra-osseous arterial anastomoses in the human vertebral body at different ages. A microarteriographic study. J. Anat. 1982, 134, 373–382. [Google Scholar]
- Chelli Bouaziz, M.; Ladeb, M.F.; Chakroun, M.; Chaabane, S. Spinal brucellosis: A review. Skelet. Radiol. 2008, 37, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, D.; Martins-Cruz, C.; Oliveira, M.B.; Mano, J.F. Bone physiology as inspiration for tissue regenerative therapies. Biomaterials 2018, 185, 240–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neve, A.; Corrado, A.; Cantatore, F.P. Osteoblast physiology in normal and pathological conditions. Cell Tissue Res. 2011, 343, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Xie, X.; Gu, F.; Sui, Z.; Zhang, K.; Yu, T. Recent Advances in Osteoclast Biological Behavior. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 788680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Cai, X.; Ren, F.; Ye, Y.; Wang, F.; Zheng, C.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, M. The Macrophage-Osteoclast Axis in Osteoimmunity and Osteo-Related Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 664871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprangers, S.; Schoenmaker, T.; Cao, Y.; Everts, V.; de Vries, T.J. Different Blood-Borne Human Osteoclast Precursors Respond in Distinct Ways to IL-17A. J. Cell Physiol. 2016, 231, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, N.; Kawakami, A. The monocyte-to-osteoclast transition in rheumatoid arthritis: Recent findings. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 998554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roop, R.M., 2nd; Barton, I.S.; Hopersberger, D.; Martin, D.W. Uncovering the Hidden Credentials of Brucella Virulence. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2021, 85, e00021-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delpino, M.V.; Fossati, C.A.; Baldi, P.C. Proinflammatory response of human osteoblastic cell lines and osteoblast-monocyte interaction upon infection with Brucella spp. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scian, R.; Barrionuevo, P.; Fossati, C.A.; Giambartolomei, G.H.; Delpino, M.V. Brucella abortus invasion of osteoblasts inhibits bone formation. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 2333–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. ERK1/2 MAP kinases: Structure, function, and regulation. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 66, 105–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrage, P.S.; Mix, K.S.; Brinckerhoff, C.E. Matrix metalloproteinases: Role in arthritis. Front. Biosci. 2006, 11, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scian, R.; Barrionuevo, P.; Giambartolomei, G.H.; Fossati, C.A.; Baldi, P.C.; Delpino, M.V. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor- and tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated matrix metalloproteinase production by human osteoblasts and monocytes after infection with Brucella abortus. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce Viglietti, A.I.; Arriola Benitez, P.C.; Gentilini, M.V.; Velasquez, L.N.; Fossati, C.A.; Giambartolomei, G.H.; Delpino, M.V. Brucella abortus Invasion of Osteocytes Modulates Connexin 43 and Integrin Expression and Induces Osteoclastogenesis via Receptor Activator of NF-kappaB Ligand and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Secretion. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civitelli, R. Cell-cell communication in the osteoblast/osteocyte lineage. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2008, 473, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoghegan, I.P.; Hoey, D.A.; McNamara, L.M. Integrins in Osteocyte Biology and Mechanotransduction. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2019, 17, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpino, M.V.; Barrionuevo, P.; Macedo, G.C.; Oliveira, S.C.; Genaro, S.D.; Scian, R.; Miraglia, M.C.; Fossati, C.A.; Baldi, P.C.; Giambartolomei, G.H. Macrophage-elicited osteoclastogenesis in response to Brucella abortus infection requires TLR2/MyD88-dependent TNF-alpha production. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambartolomei, G.H.; Zwerdling, A.; Cassataro, J.; Bruno, L.; Fossati, C.A.; Philipp, M.T. Lipoproteins, not lipopolysaccharide, are the key mediators of the proinflammatory response elicited by heat-killed Brucella abortus. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 4635–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambartolomei, G.H.; Scian, R.; Acosta-Rodriguez, E.; Fossati, C.A.; Delpino, M.V. Brucella abortus-infected macrophages modulate T lymphocytes to promote osteoclastogenesis via IL-17. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce Viglietti, A.I.; Arriola Benitez, P.C.; Giambartolomei, G.H.; Delpino, M.V. Brucella abortus-infected B cells induce osteoclastogenesis. Microbes Infect. 2016, 18, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Shang, X.; Wang, L.; Fan, J.; Wang, Y.; Lv, J.; Nazierhan, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Ma, X. The role of CXCR3 and its ligands expression in Brucellar spondylitis. BMC Immunol. 2020, 21, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; He, H.Y.; Ojha, S.C.; Shi, H.; Sun, C.F.; Deng, C.L.; Sheng, Y.J. Association of IL-6, IL-10 and TGF-beta1 gene polymorphisms with brucellosis: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 135, 103640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafari, P.; Zarifian, A.; Alizadeh-Navaei, R.; Taghadosi, M.; Rafiei, A. Association between polymorphisms of cytokine genes and brucellosis: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. Cytokine 2020, 127, 154949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Du, L.; Zhen, H.; Li, M.; An, S.; Fan, W.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, M.; Han, X.; Li, Z.; et al. Follow-up outcomes of asymptomatic brucellosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2185464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cama, B.A.V.; Ceccarelli, M.; Venanzi Rullo, E.; Ferraiolo, F.; Paolucci, I.A.; Maranto, D.; Mondello, P.; Lo Presti Costantino, M.R.; Marano, F.; D’Andrea, G.; et al. Outbreak of Brucella melitensis infection in Eastern Sicily: Risk factors, clinical characteristics and complication rate. New Microbiol. 2019, 42, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.G.; Song, Z.Y.; Wang, W.X.; Xi, W.N.; Jin, D.; Ai, M.X.; Wu, Y.C.; Lan, Y.; Song, S.F.; Zhang, G.C.; et al. Human brucellosis and fever of unknown origin. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solera, J.; Solis Garcia Del Pozo, J. Treatment of pulmonary brucellosis: A systematic review. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2017, 15, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiangsheng, F.; Xiaoqin, H.; Tong, L.; Wenyun, G.; Yuejuan, S. Brucella cultures characteristics, clinical characteristics, and infection biomarkers of human Brucellosis. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, A.S.; Crump, L.; Greter, H.; Hattendorf, J.; Schelling, E.; Zinsstag, J. Clinical manifestations of human brucellosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namiduru, M.; Karaoglan, I.; Gursoy, S.; Bayazit, N.; Sirikci, A. Brucellosis of the spine: Evaluation of the clinical, laboratory, and radiological findings of 14 patients. Rheumatol. Int. 2004, 24, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmenero, J.D.; Jimenez-Mejias, M.E.; Sanchez-Lora, F.J.; Reguera, J.M.; Palomino-Nicas, J.; Martos, F.; Garcia de las Heras, J.; Pachon, J. Pyogenic, tuberculous, and brucellar vertebral osteomyelitis: A descriptive and comparative study of 219 cases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1997, 56, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannitsioti, E.; Papadopoulos, A.; Nikou, P.; Athanasia, S.; Kelekis, A.; Economopoulos, N.; Drakou, A.; Papagelopoulos, P.; Papakonstantinou, O.; Sakka, V.; et al. Long-term triple-antibiotic treatment against brucellar vertebral osteomyelitis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 40, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, H.; Elaldi, N.; Batirel, A.; Aliyu, S.; Sengoz, G.; Pehlivanoglu, F.; Ramosaco, E.; Gulsun, S.; Tekin, R.; Mete, B.; et al. Comparison of brucellar and tuberculous spondylodiscitis patients: Results of the multicenter “Backbone-1 Study”. Spine J. 2015, 15, 2509–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosilkovski, M.; Krteva, L.; Dimzova, M.; Vidinic, I.; Sopova, Z.; Spasovska, K. Human brucellosis in Macedonia-10 years of clinical experience in endemic region. Croat. Med. J. 2010, 51, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Moreno, S.; Soto-Guzman, O.; Bernaldo-de-Quiros, J.; Reverte-Cejudo, D.; Bascones-Casas, C. Pancytopenia due to hemophagocytosis in patients with brucellosis: A report of four cases. J. Infect. Dis. 1983, 147, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, E.J.; Tarry, A.; Genta, R.M.; Ayden, N.; Gotuzzo, E. Thrombocytopenic purpura associated with brucellosis: Report of 2 cases and literature review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pappas, G.; Kitsanou, M.; Christou, L.; Tsianos, E. Immune thrombocytopenia attributed to brucellosis and other mechanisms of Brucella-induced thrombocytopenia. Am. J. Hematol. 2004, 75, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Brucellosis (Brucella spp.) 2010 Case Definition. Available online: https://ndc.services.cdc.gov/case-definitions/brucellosis-2010/ (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- Di Bonaventura, G.; Angeletti, S.; Ianni, A.; Petitti, T.; Gherardi, G. Microbiological Laboratory Diagnosis of Human Brucellosis: An Overview. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, G.; Papadimitriou, P. Challenges in Brucella bacteraemia. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2007, 30 (Suppl. S1), S29–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Mirrett, S.; Reller, L.B.; Weinstein, M.P. Detection of bloodstream infections in adults: How many blood cultures are needed? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3546–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberlin, D.W.; Barnett, E.D.; Lynfield, R.; Sawyer, M.H. Red Book: 2021–2024 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases, 32nd ed.; American Academy of Pediatrics: Elk Grove, IL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- CDC. Brucellosis Reference Guide 2017. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/brucellosis/pdf/brucellosi-reference-guide.pdf (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- Gotuzzo, E.; Carrillo, C.; Guerra, J.; Llosa, L. An evaluation of diagnostic methods for brucellosis—The value of bone marrow culture. J. Infect. Dis. 1986, 153, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.; Casanova, A.; Ariza, J.; Moriyon, I. The Rose Bengal Test in human brucellosis: A neglected test for the diagnosis of a neglected disease. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memish, Z.A.; Almuneef, M.; Mah, M.W.; Qassem, L.A.; Osoba, A.O. Comparison of the Brucella Standard Agglutination Test with the ELISA IgG and IgM in patients with Brucella bacteremia. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2002, 44, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagupsky, P.; Morata, P.; Colmenero, J.D. Laboratory Diagnosis of Human Brucellosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, P. Real-time PCR assays for diagnosing brucellar spondylitis using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues. Medicine 2018, 97, e0062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, N.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Lou, C.; Ji, J.; Zhai, X.; Niu, N. Pathological features of Brucella spondylitis: A single-center study. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2022, 58, 151910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, S.; He, Y.; Tiheiran, M.; Liu, W.; Guo, H. The Angiopoietin-like protein 4: A promising biomarker to distinguish brucella spondylitis from tuberculous spondylitis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 4289–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raptopoulou, A.; Karantanas, A.H.; Poumboulidis, K.; Grollios, G.; Raptopoulou-Gigi, M.; Garyfallos, A. Brucellar spondylodiscitis: Noncontiguous multifocal involvement of the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine. Clin. Imaging 2006, 30, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, H.S.; Clark, D.C.; Aabed, M.Y.; Haddad, M.C.; al Deeb, S.M.; Yaqub, B.; al Moutaery, K.R. Granulomatous spinal infections: MR imaging. Radiology 1990, 177, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- al-Shahed, M.S.; Sharif, H.S.; Haddad, M.C.; Aabed, M.Y.; Sammak, B.M.; Mutairi, M.A. Imaging features of musculoskeletal brucellosis. Radiographics 1994, 14, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Lan, S.; He, Y.; Tiheiran, M.; Liu, W. Differentiating brucella spondylitis from tuberculous spondylitis by the conventional MRI and MR T2 mapping: A prospective study. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2021, 26, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, Y.H.; Liu, J.; Duan, Y.W.; Gao, M.; Lu, Y.T.; Yao, L.; Li, S.L. Imaging diagnosis of brucella spondylitis and tuberculous spondylitis. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2018, 98, 2341–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resorlu, H.; Sacar, S.; Inceer, B.S.; Akbal, A.; Gokmen, F.; Zateri, C.; Savas, Y. Cervical Spondylitis and Epidural Abscess Caused by Brucellosis: A Case Report and Literature Review. Folia Medica 2016, 58, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi-Nooraie, R.; Mortaz-Hejri, S.; Mehrani, M.; Sadeghipour, P. Antibiotics for treating human brucellosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 10, CD007179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marianelli, C.; Graziani, C.; Santangelo, C.; Xibilia, M.T.; Imbriani, A.; Amato, R.; Neri, D.; Cuccia, M.; Rinnone, S.; Di Marco, V.; et al. Molecular epidemiological and antibiotic susceptibility characterization of Brucella isolates from humans in Sicily, Italy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2923–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maves, R.C.; Castillo, R.; Guillen, A.; Espinosa, B.; Meza, R.; Espinoza, N.; Nunez, G.; Sanchez, L.; Chacaltana, J.; Cepeda, D.; et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Brucella melitensis isolates in Peru. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1279–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevtsov, A.; Syzdykov, M.; Kuznetsov, A.; Shustov, A.; Shevtsova, E.; Berdimuratova, K.; Mukanov, K.; Ramankulov, Y. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Brucella melitensis in Kazakhstan. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2017, 6, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkaman Asadi, F.; Hashemi, S.H.; Alikhani, M.Y.; Moghimbeigi, A.; Naseri, Z. Clinical and Diagnostic Aspects of Brucellosis and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Brucella Isolates in Hamedan, Iran. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 70, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosilkovski, M.; Keramat, F.; Arapovic, J. The current therapeutical strategies in human brucellosis. Infection 2021, 49, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solera, J. Update on brucellosis: Therapeutic challenges. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 36 (Suppl. S1), S18–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariza, J.; Gudiol, F.; Pallares, R.; Viladrich, P.F.; Rufi, G.; Corredoira, J.; Miravitlles, M.R. Treatment of human brucellosis with doxycycline plus rifampin or doxycycline plus streptomycin. A randomized, double-blind study. Ann. Intern. Med. 1992, 117, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariza, J.; Bosilkovski, M.; Cascio, A.; Colmenero, J.D.; Corbel, M.J.; Falagas, M.E.; Memish, Z.A.; Roushan, M.R.; Rubinstein, E.; Sipsas, N.V.; et al. Perspectives for the treatment of brucellosis in the 21st century: The Ioannina recommendations. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solis Garcia del Pozo, J.; Vives Soto, M.; Solera, J. Vertebral osteomyelitis: Long-term disability assessment and prognostic factors. J. Infect. 2007, 54, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbar, M.; Keramat, F.; Mamani, M.; Kia, A.R.; Khalilian, F.O.; Hashemi, S.H.; Nojomi, M. Comparison between doxycycline-rifampin-amikacin and doxycycline-rifampin regimens in the treatment of brucellosis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 11, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannou, S.; Karadima, D.; Pneumaticos, S.; Athanasiou, H.; Pontikis, J.; Zormpala, A.; Sipsas, N.V. Efficacy of prolonged antimicrobial chemotherapy for brucellar spondylodiscitis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unuvar, G.K.; Kilic, A.U.; Doganay, M. Current therapeutic strategy in osteoarticular brucellosis. North. Clin. Istanb. 2019, 6, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, E.; Koc, R.K.; Durak, A.C.; Yildiz, O.; Aygen, B.; Sumerkan, B.; Doganay, M. Doxycycline plus streptomycin versus ciprofloxacin plus rifampicin in spinal brucellosis [ISRCTN31053647]. BMC Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmenero, J.D.; Ruiz-Mesa, J.D.; Plata, A.; Bermudez, P.; Martin-Rico, P.; Queipo-Ortuno, M.I.; Reguera, J.M. Clinical findings, therapeutic approach, and outcome of brucellar vertebral osteomyelitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.M.; Jia, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.N.; Yao, Y.; Yin, Y.L.; Tian, Y. Clinical Effect of Doxycycline Combined with Compound Sulfamethoxazole and Rifampicin in the Treatment of Brucellosis Spondylitis. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2021, 15, 4733–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayindir, Y.; Sonmez, E.; Aladag, A.; Buyukberber, N. Comparison of five antimicrobial regimens for the treatment of brucellar spondylitis: A prospective, randomized study. J. Chemother. 2003, 15, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smailnejad Gangi, S.M.; Hasanjani Roushan, M.R.; Janmohammadi, N.; Mehraeen, R.; Soleimani Amiri, M.J.; Khalilian, E. Outcomes of treatment in 50 cases with spinal brucellosis in Babol, Northern Iran. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2012, 6, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koubaa, M.; Maaloul, I.; Marrakchi, C.; Lahiani, D.; Hammami, B.; Mnif, Z.; Ben Mahfoudh, K.; Hammami, A.; Ben Jemaa, M. Spinal brucellosis in South of Tunisia: Review of 32 cases. Spine J. 2014, 14, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulsun, S.; Aslan, S.; Satici, O.; Gul, T. Brucellosis in pregnancy. Trop. Doct 2011, 41, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebesoy, F.B.; Balat, O.; Mete, A. An extraordinary cause of vertebral fracture in pregnant woman: Brucellosis. Arch. Gynecol. Obs. 2009, 280, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solera, J.; Lozano, E.; Martinez-Alfaro, E.; Espinosa, A.; Castillejos, M.L.; Abad, L. Brucellar spondylitis: Review of 35 cases and literature survey. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 29, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katonis, P.; Tzermiadianos, M.; Gikas, A.; Papagelopoulos, P.; Hadjipavlou, A. Surgical treatment of spinal brucellosis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2006, 444, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Long, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Mansuerjiang, M.; Tian, Z.; Younusi, A.; Cao, L.; Wang, C. Biportal endoscopic decompression, debridement, and interbody fusion, combined with percutaneous screw fixation for lumbar brucellosis spondylitis. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 1024510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraj, A.A.; Webb, J.K. Spinal instrumentation for primary pyogenic infection report of 31 patients. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2000, 66, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alp, E.; Doganay, M. Current therapeutic strategy in spinal brucellosis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 12, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, P.; Mingzhi, Y.; Yin, X.; Chen, Y. Surgical management for lumbar brucella spondylitis: Posterior versus anterior approaches. Medicine 2021, 100, e26076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Liu, K.; Deng, X.; Sheng, W.; Mamat, M.; Guo, H.; Li, H.; Deng, Q. One-stage posterior surgery combined with anti-Brucella therapy in the management of lumbosacral brucellosis spondylitis: A retrospective study. BMC Surg. 2022, 22, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Wang, X.; Yin, X.; Han, J.; Tang, W. Analysis of the Curative Effect of Posterior Approach on Lumbar Brucellar Spondylitis with Abscess through Magnetic Resonance Imaging under Improved Watershed Algorithm. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2021, 2021, 1933706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aliberti, G.; Talamonti, G.; Villa, F.; Debernardi, A. The anterior stand-alone approach (ASAA) during the acute phase of spondylodiscitis: Results in 40 consecutively treated patients. Eur. Spine J. 2012, 21 (Suppl. S1), S75–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.H.; Liu, Z.K.; He, B.R.; Hao, D.J. One-stage surgical management for lumber brucella spondylitis with anterior debridement, autogenous graft, and instrumentation. Medicine 2018, 97, e11704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safran, O.; Rand, N.; Kaplan, L.; Sagiv, S.; Floman, Y. Sequential or simultaneous, same-day anterior decompression and posterior stabilization in the management of vertebral osteomyelitis of the lumbar spine. Spine 1998, 23, 1885–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Ma, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Sun, G.; Jia, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Comparison of two surgical interventions for lumbar brucella spondylitis in adults: A retrospective analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zuo, X.; Jia, Y.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ren, Y. Comparison of effectiveness between two surgical methods in treatment of thoracolumbar brucella spondylitis. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi 2014, 28, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cingoz, I.D. Role of Surgery in Brucella Spondylodiscitis: An Evaluation of 28 Patients. Cureus 2023, 15, e33542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjipavlou, A.G.; Crow, W.N.; Borowski, A.; Mader, J.T.; Adesokan, A.; Jensen, R.E. Percutaneous transpedicular discectomy and drainage in pyogenic spondylodiscitis. Am. J. Orthop. 1998, 27, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjipavlou, A.G.; Katonis, P.K.; Gaitanis, I.N.; Muffoletto, A.J.; Tzermiadianos, M.N.; Crow, W. Percutaneous transpedicular discectomy and drainage in pyogenic spondylodiscitis. Eur. Spine J. 2004, 13, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pola, E.; Pambianco, V.; Autore, G.; Cipolloni, V.; Fantoni, M. Minimally invasive surgery for the treatment of thoraco lumbar pyogenic spondylodiscitis: Indications and outcomes. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.J.; Kim, J.E.; Jung, J.T.; Kim, Y.S.; Jang, H.J.; Yoo, B.; Kang, I.H. Biportal Endoscopic Spine Surgery for Various Foraminal Lesions at the Lumbosacral Lesion. Asian Spine J. 2018, 12, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.C.; Fu, T.S.; Chen, L.H.; Niu, C.C.; Lai, P.L.; Chen, W.J. Percutaneous endoscopic discectomy and drainage for infectious spondylitis. Int. Orthop. 2007, 31, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, T.S.; Chen, L.H.; Chen, W.J. Minimally invasive percutaneous endoscopic discectomy and drainage for infectious spondylodiscitis. Biomed. J. 2013, 36, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, A.; Beisse, R.; Schmidt, M.H. Thoracoscopic debridement and stabilization of pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis. Surg. Laparosc. Endosc. Percutan Tech. 2007, 17, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spernovasilis, N.; Karantanas, A.; Markaki, I.; Konsoula, A.; Ntontis, Z.; Koutserimpas, C.; Alpantaki, K. Brucella Spondylitis: Current Knowledge and Recent Advances. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020595
Spernovasilis N, Karantanas A, Markaki I, Konsoula A, Ntontis Z, Koutserimpas C, Alpantaki K. Brucella Spondylitis: Current Knowledge and Recent Advances. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(2):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020595
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpernovasilis, Nikolaos, Apostolos Karantanas, Ioulia Markaki, Afroditi Konsoula, Zisis Ntontis, Christos Koutserimpas, and Kalliopi Alpantaki. 2024. "Brucella Spondylitis: Current Knowledge and Recent Advances" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 2: 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020595
APA StyleSpernovasilis, N., Karantanas, A., Markaki, I., Konsoula, A., Ntontis, Z., Koutserimpas, C., & Alpantaki, K. (2024). Brucella Spondylitis: Current Knowledge and Recent Advances. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(2), 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020595






