Characterisation of Paediatric Neuroblastic Tumours by Quantitative Structural and Diffusion-Weighted MRI
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Clinical and Qualitative Imaging Features
2.3. Imaging Examinations
2.3.1. MRI Data Acquisition
2.3.2. MRI Interpretation
2.3.3. Reference Standard
2.3.4. Effect Size Related to Available Sample Size
2.4. Statistical Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Lonergan, G.J.; Schwab, C.M.; Suarez, E.S.; Carlson, C.L. Neuroblastoma, ganglioneuroblastoma, and ganglioneuroma: Radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 2002, 22, 911–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, C.C.; Eklund, M.J.; Kraveka, J.M.; Alazraki, A.L. Updates in Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment of Neuroblastoma. Radiographics 2018, 38, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zheng, J.; Li, Q. Application of imaging modalities for evaluating neuroblastoma. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 26, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.G.; Yan, Y.; Tang, W.; Cai, R.; Ren, G. Clinical and biological features of neuroblastic tumors: A comparison of neuroblastoma and ganglioneuroblastoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 37730–37739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Arendonk, K.J.; Chung, D.H. Neuroblastoma: Tumor Biology and Its Implications for Staging and Treatment. Children 2019, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, D.; Totadri, S.; Chinnaswamy, G.; Agarwala, S.; Vora, T.; Arora, B.; Prasad, M.; Kapoor, G.; Radhakrishnan, V.; Laskar, S.; et al. Management of Neuroblastoma: ICMR Consensus Document. Indian J. Pediatr. 2017, 84, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serin, H.I.; Gorkem, S.B.; Doganay, S.; Cıracı, S.; Unal, E.; Guzel, M.; Kucuk, A.; Kurtsoy, A.; Coskun, A. Diffusion weighted imaging in differentiating malignant and benign neuroblastic tumors. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2016, 34, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisse, H.J.; McCarville, M.B.; Granata, C.; Krug, K.B.; Wootton-Gorges, S.L.; Kanegawa, K.; Giammarile, F.; Schmidt, M.; Shulkin, B.L.; Matthay, K.K.; et al. Guidelines for imaging and staging of neuroblastic tumors: Consensus report from the International Neuroblastoma Risk Group Project. Radiology 2011, 261, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, H.; Li, M.; Müller, V.R.; Pabst, T.; Beer, M. Diagnostic Value of Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Tumor Characterization, Differentiation and Monitoring in Pediatric Patients with Neuroblastic Tumors. RöFo 2017, 189, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Peng, Y.; Duan, X.M.; Zhang, N. Role of diffusion-weighted imaging in distinguishing thoracoabdominal neuroblastic tumours of various histological types and differentiation grades. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 61, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, H.; Ambros, I.M.; Dehner, L.P.; Hata, J.-i.; Joshi, V.V.; Roald, B.; Stram, D.O.; Gerbing, R.B.; Lukens, J.N.; Matthay, K.K.; et al. The International Neuroblastoma Pathology Classification (the Shimada system). Cancer 1999, 86, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgues, O.; Navarro, S.; Noguera, R.; Pellín, A.; Ruiz, A.; Castel, V.; Llombart-Bosch, A. Prognostic value of the International Neuroblastoma Pathology Classification in Neuroblastoma (Schwannian stroma-poor) and comparison with other prognostic factors: A study of 182 cases from the Spanish Neuroblastoma Registry. Virchows Arch. 2006, 449, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokol, E.; Desai, A.V. The Evolution of Risk Classification for Neuroblastoma. Children 2019, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, N.R.; Applebaum, M.A.; Volchenboum, S.L.; Matthay, K.K.; London, W.B.; Ambros, P.F.; Nakagawara, A.; Berthold, F.; Schleiermacher, G.; Park, J.R.; et al. Advances in Risk Classification and Treatment Strategies for Neuroblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3008–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthay, K.K.; Maris, J.M.; Schleiermacher, G.; Nakagawara, A.; Mackall, C.L.; Diller, L.; Weiss, W.A. Neuroblastoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisse, H.J.; Blanc, T.; Schleiermacher, G.; Mosseri, V.; Philippe-Chomette, P.; Janoueix-Lerosey, I.; Pierron, G.; Lapouble, E.; Peuchmaur, M.; Fréneaux, P.; et al. Radiogenomics of neuroblastomas: Relationships between imaging phenotypes, tumor genomic profile and survival. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharbach, A.; Bellach, B.; Ramoune, M.; Rahmoun, M.; Hadj Kacem, H. Towards a Novel Approach for Tumor Volume Quantification. J. Imaging 2017, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassenmaier, S.; Tsiflikas, I.; Fuchs, J.; Grimm, R.; Urla, C.; Esser, M.; Maennlin, S.; Ebinger, M.; Warmann, S.W.; Schäfer, J.F. Feasibility and possible value of quantitative semi-automated diffusion weighted imaging volumetry of neuroblastic tumors. Cancer Imaging 2020, 20, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliyan, V.; Das, C.J.; Sharma, R.; Gupta, A.K. Diffusion weighted imaging: Technique and applications. World J. Radiol. 2016, 8, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla-Dave, A.; Obuchowski, N.A.; Chenevert, T.L.; Jambawalikar, S.; Schwartz, L.H.; Malyarenko, D.; Huang, W.; Noworolski, S.M.; Young, R.J.; Shiroishi, M.S.; et al. Quantitative imaging biomarkers alliance (QIBA) recommendations for improved precision of DWI and DCE-MRI derived biomarkers in multicenter oncology trials. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, e101–e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahr, N.; Darge, K.; Hahn, G.; Kreher, B.W.; von Buiren, M.; Uhl, M. Diffusion-weighted MRI for differentiation of neuroblastoma and ganglioneuroblastoma/ganglioneuroma. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 79, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan, M.; Aslan, A.; Arıöz Habibi, H.; Kalyoncu Uçar, A.; Özmen, E.; Bakan, S.; Kuruğoğlu, S.; Adaletli, İ. Diffusion-weighted MRI for differentiating Wilms tumor from neuroblastoma. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 23, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeus, E.M.; Zarinabad, N.; Manias, K.A.; Novak, J.; Rose, H.E.L.; Dehghani, H.; Foster, K.; Morland, B.; Peet, A.C. Diffusion-weighted MRI and intravoxel incoherent motion model for diagnosis of pediatric solid abdominal tumors. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 47, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschmann, A.L.; Beer, M.; Ammann, B.; Dreyhaupt, J.; Kneer, K.; Beer, A.J.; Beltinger, C.; Steinbach, D.; Cario, H.; Neubauer, H. Quantitative DWI predicts event-free survival in children with neuroblastic tumours: Preliminary findings from a retrospective cohort study. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2019, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, E.; Ren, A.; Gao, B.; Yang, M.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, W.; Li, K. ROI for outlining an entire tumor is a reliable approach for quantification of lung cancer tumor vascular parameters using CT perfusion. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 2377–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jafari-Khouzani, K.; Paynabar, K.; Hajighasemi, F.; Rosen, B. Effect of Region of Interest Size on the Repeatability of Quantitative Brain Imaging Biomarkers. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 66, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Monclair, T.; Brodeur, G.M.; Ambros, P.F.; Brisse, H.J.; Cecchetto, G.; Holmes, K.; Kaneko, M.; London, W.B.; Matthay, K.K.; Nuchtern, J.G.; et al. The International Neuroblastoma Risk Group (INRG) staging system: An INRG Task Force report. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tolbert, V.P.; Matthay, K.K. Neuroblastoma: Clinical and biological approach to risk stratification and treatment. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 372, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bagatell, R.; McHugh, K.; Naranjo, A.; Van Ryn, C.; Kirby, C.; Brock, P.; Lyons, K.A.; States, L.J.; Rojas, Y.; Miller, A.; et al. Assessment of Primary Site Response in Children with High-Risk Neuroblastoma: An International Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, D.G. Practical Statistics for Medical Research; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1991; pp. 404–408. [Google Scholar]
- Okamatsu, C.; London, W.B.; Naranjo, A.; Hogarty, M.D.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Look, A.T.; LaQuaglia, M.; Maris, J.M.; Cohn, S.L.; Matthay, K.K.; et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of ganglioneuroma and ganglioneuroblastoma: A report from the CCG and COG. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2009, 53, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambasco, D.; Medeleanu, M.; Moineddin, R.; Harris, S.; Morgenstern, D.; Villani, A.; Malkin, D.; Doria, A. Diagnostic Accuracy of MRI for Pediatric Neuroblastic Tumour Differentiation: Review and Subgroup Meta-Analysis. Available online: http://ipr2021.org/pdf/finale_completo_IPR_2021.pdf (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- Yang, S.; Cai, S.; Ma, X.; Zeng, Q.; Qin, H.; Han, W.; Peng, X.; Wang, H. Discrimination of histopathologic types of childhood peripheral neuroblastic tumors based on clinical and biological factors. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdá Alberich, L.; Sangüesa Nebot, C.; Alberich-Bayarri, A.; Carot Sierra, J.M.; Martínez de las Heras, B.; Veiga Canuto, D.; Cañete, A.; Martí-Bonmatí, L. A Confidence Habitats Methodology in MR Quantitative Diffusion for the Classification of Neuroblastic Tumors. Cancers 2020, 12, 3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.; Miceli, R.; Meazza, C.; Casanova, M.; Favini, F.; Morosi, C.; Trecate, G.; Marchianò, A.; Luksch, R.; Cefalo, G.; et al. Comparison of the Prognostic Value of Assessing Tumor Diameter Versus Tumor Volume at Diagnosis or in Response to Initial Chemotherapy in Rhabdomyosarcoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.M.; Rasalkar, D.D.; Hu, Y.J.; Cheng, F.W.; Li, C.K.; Chu, W.C. Clinical presentations and imaging findings of neuroblastoma beyond abdominal mass and a review of imaging algorithm. Br. J. Radiol. 2011, 84, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trout, A.T. Finding the Best Ways to Measure Neuroblastoma Tumors. Leopard C, ed. Cincinnati Children’s Blog. Available online: http://blog.cincinnatichildrens.org/radiology/finding-the-best-ways-to-measure-neuroblastoma-tumors (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- Abele, N.; Langner, S.; Felbor, U.; Lode, H.; Hosten, N. Quantitative Diffusion-Weighted MRI of Neuroblastoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bharwani, N.; Miquel, M.E.; Sahdev, A.; Narayanan, P.; Malietzis, G.; Reznek, R.H.; Rockall, A.G. Diffusion-weighted imaging in the assessment of tumour grade in endometrial cancer. Br. J. Radiol. 2011, 84, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nougaret, S.; Vargas, H.A.; Lakhman, Y.; Sudre, R.; Do, R.K.; Bibeau, F.; Azria, D.; Assenat, E.; Molinari, N.; Pierredon, M.A.; et al. Intravoxel Incoherent Motion-derived Histogram Metrics for Assessment of Response after Combined Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy in Rectal Cancer: Initial Experience and Comparison between Single-Section and Volumetric Analyses. Radiology 2016, 280, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, C.; Bignone, R.; Bruno, A.; Bruno, A.; Bruno, F.; Calandri, M.; Caruso, D.; Coppolino, P.; Robertis, R.; Gentili, F.; et al. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Oncology: An Update. Cancers 2020, 12, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tyng, C.J.; Guimarães, M.D.; Bitencourt, A.G.V.; dos Santos, L.C.M.; Barbosa, P.N.V.P.; Zurstrassen, C.E.; Pereira, E.N.; Gross, J.L.; Chojniak, R. Correlation of the ADC values assessed by diffusion-weighted MRI and 18F–FDG PET/CT SUV in patients with lung cancer. Appl. Cancer Res. 2018, 38, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jin, G.Q.; Liu, J.J.; Su, D.K.; Luo, N.B.; Xie, D.; Lai, S.L.; Huang, X.Y.; Huang, W.L. Diagnostic performance of ADCs in different ROIs for breast lesions. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 12096–12104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thuy, T.T.M.; Trang, N.T.H.; Vy, T.T.; Duc, V.T.; Nam, N.H.; Chien, P.C.; Nhi, L.H.H.; Minh, L.H.N. Role of diffusion-weighted MRI in differentiation between benign and malignant anterior mediastinal masses. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 985735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]


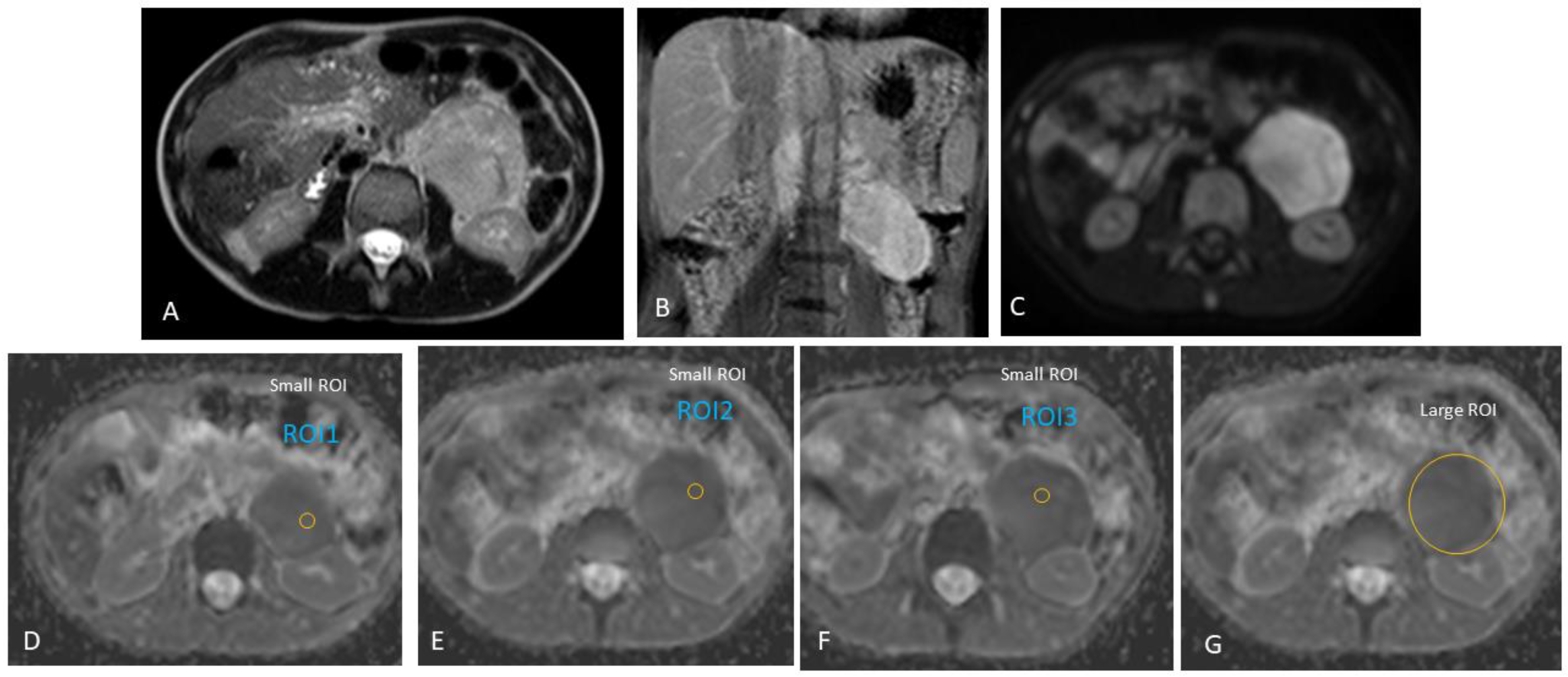
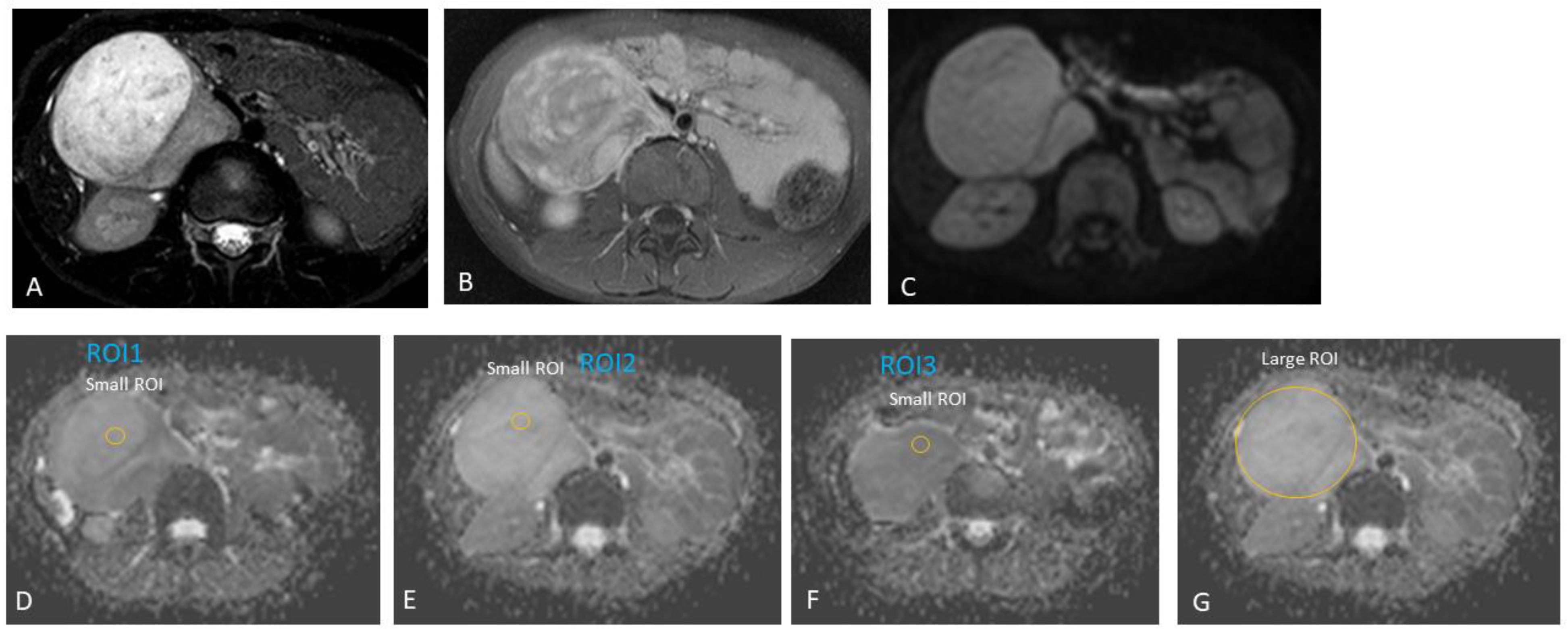

| Case # | Gender | Age at Diagnosis | Diagnosis | Tumour Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 7 y | GN | Posterior mediastinum |
| 2 | F | 7 days | NB | Presacral |
| 3 | F | 9 m | NB | Posterior mediastinum |
| 4 | M | 12 m | NB | Presacral |
| 5 | M | 8 y 3 m | GN | Retroperitoneum |
| 6 | M | 32 m | GNB | Carotid bifurcation |
| 7 | M | 3 y 8 m | NB | Retroperitoneum |
| 8 | M | 3 m | NB | Retroperitoneum |
| 9 | M | 9 y 8 m | GN | Presacral |
| 10 | F | 9 m | NB | Paravertebral |
| 11 | F | 5 y 7 m | GNB | Paravertebral |
| 12 | F | 9 m | NB | Presacral |
| 13 | M | 3 days | NB | Posterior mediastinum |
| 14 | F | 15 y 11 m | GN | Suprarenal |
| 15 | F | 12 y 1 m | GN | Suprarenal |
| 16 | M | 6 y 4 m | GNB | Suprarenal |
| 17 | M | 7 m | NB | Posterior mediastinum |
| 18 | F | 17 m | NB | Posterior mediastinum |
| 19 | F | 4 y | NB | Retroperitoneum |
| 20 | M | 17 m | NB | Posterior mediastinum |
| 21 | M | 5 m | NB | Suprarenal |
| 22 | M | 13 m | NB | Suprarenal |
| 23 | F | 13 m | GNB | Posterior mediastinum |
| 24 | M | 9 y 10 m | NB | Suprarenal |
| 25 | M | 3 y 11 m | NB | Suprarenal |
| 26 | F | 3 y 8 m | NB | Presacral |
| 27 | M | 11 y 7 m | GNB | Retroperitoneum |
| 28 | F | 36 m | NB | Suprarenal |
| 29 | F | 3 y 2 m | GN | Posterior mediastinum |
| 30 | F | 1 m | NB | Posterior mediastinum |
| 31 | M | 17 days | NB | Neck |
| 32 | F | 2 y 4 m | NB | Paravertebral |
| 33 | F | 4 y 4 m | GNB | Suprarenal |
| 34 | M | 14 y 7 m | GN | Retroperitoneum |
| 35 | M | 16 y 7 m | GN | Posterior mediastinum |
| 36 | F | 6 y 11 m | GN | Retroperitoneum—intramuscular |
| 37 | F | 1 y 9 m | NB | Posterior mediastinum |
| 38 | M | 3 m | NB | Retroperitoneum |
| 39 | M | 1 m 22 d | NB | Retroperitoneum—intramuscular |
| 40 | M | 15 y 7 m | GN | Retroperitoneum |
| Median (months) | 34 (2 y 10 m) | |||
| Females = 18 (45%) | Mean (months) | 54.7 (4 y 6 m) | ||
| Min. | 7 days | |||
| Max. | 16 y 7 m | |||
| SD (months) | 60.2 (5 y) | |||
| Case # | Diagnosis | International Neuroblastoma Risk Group (INGRSS) | MYCN Status | Pre-Treatment Risk Group | Multiple Body Compartments (Y/N) | Multi-Focal (Y/N) | Size of Tumour (AP Diam.) in mm | Size of Tumour (CC Diam.) in mm | Size of Tumour (TRV Diam.) in mm | Total Tumour Volume (cc) | Lobulated (Y/N) | Heterogenous (Y/N) | Calcification (Y/N) | Necrosis (Y/N) | Metastases (Y/N) | Metastases Type | Vascular Encasement (Y/N) | Vascular Encasement Vessels Involved | Adjacent Organ Infiltration (Y/N) | Type of Organ Infiltrated | Lymphadenopathy (Y/N) | Intraspinal Invasion (Y/N) | IDRF (Y/N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GN | NA | N | N | 37 | 43 | 28 | 23.32 | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | Right vertebral artery | N | N | N | Y | ||||
| 2 | NB | MS | Non-amplified | Low risk | N | N | 42 | 65 | 39 | 55.75 | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | Left sacral bone | N | Y | Y | ||
| 3 | NB | MS | Non-amplified | Low risk | Y | N | 35 | 69 | 49 | 61.96 | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Right cutaneous neck | Y | Right subclavian artery, proximal vertebral artery | Y | Right posterior 4th rib | Y | Y | Y |
| 4 | NB | L1 | Non-amplified | Low risk (surgery only) | N | N | 65 | 57 | 53 | 102.11 | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | |||
| 5 | GN | NA | N | N | 80 | 96 | 66 | 263.58 | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | |||||
| 6 | GNB | NA | N | N | 16 | 32 | 23 | 6.17 | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | ||||||
| 7 | NB | M | Non-amplified | High risk | N | N | 23 | 31 | 26 | 9.71 | N | Y | N | N | Y | Bones | N | N | Y | N | N | ||
| 8 | NB | MS | Non-amplified | Low risk | N | N | 63 | 61 | 56 | 111.91 | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Liver, paraspinal, skull base, left orbital, left proximal femur | Y | Celiac, SMA | N | N | N | Y | |
| 9 | GN | NA | N | N | 36 | 60 | 40 | 44.93 | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | |||||
| 10 | NB | L1 | Non-amplified | Low risk (surgery only) | N | N | 13 | 18 | 8 | 0.98 | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | |||
| 11 | GNB | NA | N | N | 34 | 64 | 26 | 29.42 | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Thoracic aorta | N | N | N | Y | ||||
| 12 | NB | L2 | Non-amplified | Intermediate risk | N | N | 74 | 115 | 97 | 432.22 | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Left paraaortic lymph nodes | N | N | Y | Y | Y | ||
| 13 | NB | L2 | Non-amplified | Intermediate risk | N | N | 47 | 52 | 50 | 63.98 | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Left paravertebral muscles | N | Y | Y | ||
| 14 | GN | NA | N | N | 30 | 29 | 15 | 6.83 | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | |||||
| 15 | GN | NA | N | N | 86 | 80 | 47 | 168.15 | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | IVC | N | N | N | Y | ||||
| 16 | GNB | NA | N | N | 33 | 30 | 30 | 15.44 | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | |||||
| 17 | NB | L2 | Non-amplified | Intermediate risk | N | N | 56 | 93 | 92 | 249.15 | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Aorta | N | N | Y | Y | ||
| 18 | NB | L1 | Non-amplified | Low risk (surgery only) | N | N | 38 | 39 | 25 | 19.27 | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | |||
| 19 | NB | L2 | Non-amplified | Intermediate risk | N | N | 83 | 127 | 95 | 520.73 | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y | Left common iliac artery, left renal artery and vein | Y | Left psoas muscle | N | N | Y | |
| 20 | NB | L1 | Non-amplified | Low risk (surgery only) | N | N | 23 | 43 | 24 | 12.34 | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | |||
| 21 | NB | MS | Non-amplified | Low risk | N | N | 43 | 57 | 58 | 73.92 | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Liver | Y | Aorta, IVC, celiac, SMA, left renal artery and vein | N | N | N | Y | |
| 22 | NB | L1 | Non-amplified | Low risk (surgery only) | N | N | 19 | 24 | 13 | 3.08 | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | |||
| 23 | GNB | NA | N | N | 16 | 16 | 8 | 1.06 | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | |||||
| 24 | NB | M | Unknown | High risk | N | N | 104 | 170 | 104 | 962.75 | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Liver, pelvic bones, sacrum, spine, left iliac bone | Y | SMA, left renal vessels | Y | Left kidney | N | N | Y |
| 25 | NB | M | Unknown | High risk | N | N | 44 | 49 | 28 | 31.39 | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Liver, bones (right prox femur, left iliac bone, right sacrum, T12, L3 vertebral bodies) | N | N | Y | N | N | ||
| 26 | NB | L2 | Non-amplified | Low risk | N | N | 106 | 121 | 76 | 510.39 | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | |||
| 27 | GNB | NA | N | N | 63 | 100 | 61 | 199.84 | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | |||||
| 28 | NB | M | Non-amplified | High risk | N | N | 74 | 90 | 60 | 207.79 | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Vertebral bodies, pelvic bones | Y | Left renal artery and vein | N | N | N | N | |
| 29 | GN | NA | N | N | 11 | 22 | 7 | 0.88 | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | |||||
| 30 | NB | L2 | Non-amplified | Intermediate risk | N | N | 28 | 42 | 50 | 30.58 | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Descending aorta | Y | Left paraspinal muscles | N | N | Y | |
| 31 | NB | L2 | Non-amplified | Low risk | N | N | 22 | 38 | 24 | 10.43 | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Right internal jugular vein | N | N | N | Y | ||
| 32 | NB | L1 | Non-amplified | Low risk (surgery only) | N | N | 34 | 17 | 24 | 7.26 | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | Bilateral common iliac arteries | N | N | N | Y | ||
| 33 | GNB | NA | N | N | 79 | 107 | 105 | 464.73 | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Right renal artery and vein | N | N | N | Y | ||||
| 34 | GN | NA | N | N | 60 | 89 | 63 | 176.15 | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | |||||
| 35 | GN | N | N | 24 | 30 | 30 | 11.31 | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | ||||||
| 36 | GN | NA | N | N | 32 | 60 | 50 | 50.27 | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | |||||
| 37 | NB | L1 | Non-amplified | Low risk (surgery only) | N | N | 37 | 18 | 55 | 19.18 | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | |||
| 38 | NB | L2 | Non-amplified | Intermediate risk | N | N | 26 | 41 | 42 | 23.44 | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Right paraspinal muscles | N | Y | Y | ||
| 39 | NB | L2 | Non-amplified | Intermediate risk | N | N | 37 | 48 | 30 | 27.9 | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | Right paraspinal muscles L2–3 | N | Y | Y | ||
| 40 | GN | NA | N | N | 47 | 86 | 63 | 133.33 | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Case # | Diagnosis | Tumour Location | T1 | T2 | Diffusion Restriction (Y/N) | b-Value (s/mm2) | Mean ADC Value | Whole Lesion (10−3 mm2/s) | Enhancement Type (Heterogenous, Homogenous, None) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GN | Posterior mediastinum | iso | hyper | Y | 800 | 1484.07 | 1713.60 | heterogenous |
| 2 | NB | Presacral | iso | intermediate | Y | 800 | 643.17 | 677.70 | heterogenous |
| 3 | NB | Posterior mediastinum | iso | hyper | Y | 1000 | 325.33 | 360.30 | Homogenous |
| 4 | NB | Presacral | iso | hyper | Y | 600 | 781.07 | 932.80 | Homogenous |
| 5 | GN | Retroperitoneum | hypo | hyper | Y | 600 | 1752.20 | 2173.80 | heterogenous |
| 6 | GNB | Carotid bifurcation | hypo | hyper | Y | 1000 | 3650.60 | 3956.70 | Homogenous |
| 7 | NB | Retroperitoneum | hypo | hyper | Y | 600 | 383.47 | 475.40 | No contrast |
| 8 | NB | Retroperitoneum | iso | hyper | Y | 600 | 678.33 | 810.70 | heterogenous |
| 9 | GN | Presacral | hypo | hyper | Y | 600 | 2015.53 | 2385.10 | heterogenous |
| 10 | NB | Paravertebral | iso | hyper | Y | 800 | 1071.17 | 1048.50 | homogenous |
| 11 | GNB | Paravertebral | hypo | hyper | Y | 800 | 1581.13 | 1522.40 | heterogenous |
| 12 | NB | Presacral | hypo | hyper | Y | 600 | 849.87 | 1011.60 | heterogenous |
| 13 | NB | Posterior mediastinum | hyper | hyper | Y | 600 | 649.33 | 710.10 | Homogenous |
| 14 | GN | Suprarenal | hypo | hyper | N | 600 | 1125.53 | 1048.00 | homogenous |
| 15 | GN | Suprarenal | hypo | hyper | Y | 600 | 968.07 | 1020.80 | heterogenous |
| 16 | GNB | Suprarenal | hypo | hyper | Y | 600 | 810.80 | 814.10 | heterogenous |
| 17 | NB | Posterior mediastinum | iso | hyper | Y | 600 | 773.20 | 774.30 | heterogenous |
| 18 | NB | Posterior mediastinum | hypo | hyper | Y | 600 | 1080.87 | 1066.30 | Homogenous |
| 19 | NB | Retroperitoneum | hypo | hyper | Y | 800 | 1226.33 | 1421.50 | heterogenous |
| 20 | NB | Posterior mediastinum | iso | hyper | Y | 600 | 981.20 | 980.00 | Homogenous |
| 21 | NB | Suprarenal | hypo | iso | Y | 600 | 517.93 | 525.90 | heterogenous |
| 22 | NB | Suprarenal | hypo | iso | Y | 600 | 772.33 | 951.40 | heterogenous |
| 23 | GNB | Posterior mediastinum | hypo | hyper | Y | 600 | 1437.53 | 1442.40 | Homogenous |
| 24 | NB | Suprarenal | hypo | hyper | Y | 1000 | 649.00 | 1075.30 | heterogenous |
| 25 | NB | Suprarenal | iso | hyper | Y | 600 | 657.43 | 747.70 | heterogenous |
| 26 | NB | Presacral | hypo | hyper | Y | 600 | 1657.10 | 1897.00 | heterogenous |
| 27 | GNB | Retroperitoneum | hypo | hyper | Y | 500 | 1048.93 | 1073.00 | heterogenous |
| 28 | NB | Suprarenal | hypo | hyper | Y | 800 | 741.20 | 791.60 | heterogenous |
| 29 | GN | Posterior mediastinum | hypo | hyper | Y | 600 | 803.80 | 965.00 | Homogenous |
| 30 | NB | Posterior mediastinum | iso | hyper | Y | 600 | 862.63 | 791.70 | heterogenous |
| 31 | NB | Neck | iso | iso | Y | 1000 | 243.97 | 237.50 | No contrast |
| 32 | NB | Paravertebral | hypo | hyper | Y | 600 | 1200 | 1228.20 | heterogenous |
| 33 | GNB | Suprarenal | iso | hyper | Y | 600 | 736.07 | 763.70 | heterogenous |
| 34 | GN | Retroperitoneum | hypo | hyper | N | 800 | 1700.47 | 1853.20 | heterogenous |
| 35 | GN | Posterior mediastinum | iso | hyper | N | 800 | 1189.07 | 1126.20 | Homogenous |
| 36 | GN | Retroperitoneum—intramuscular | iso | hyper | N | 800 | 1577.77 | 1708.90 | No contrast |
| 37 | NB | Posterior mediastinum | No | hyper | Y | 600 | 1040 | 1000.00 | Homogenous |
| 38 | NB | Retroperitoneum | iso | hyper | Y | 1000 | 426.67 | 470.00 | homogenous |
| 39 | NB | Retroperitoneum—intramuscular | iso | hyper | Y | 800 | 706.33 | 835.70 | heterogenous |
| 40 | GN | Retroperitoneum | hypo | hyper | Y | 800 | 1475.33 | 2125.50 | heterogenous |
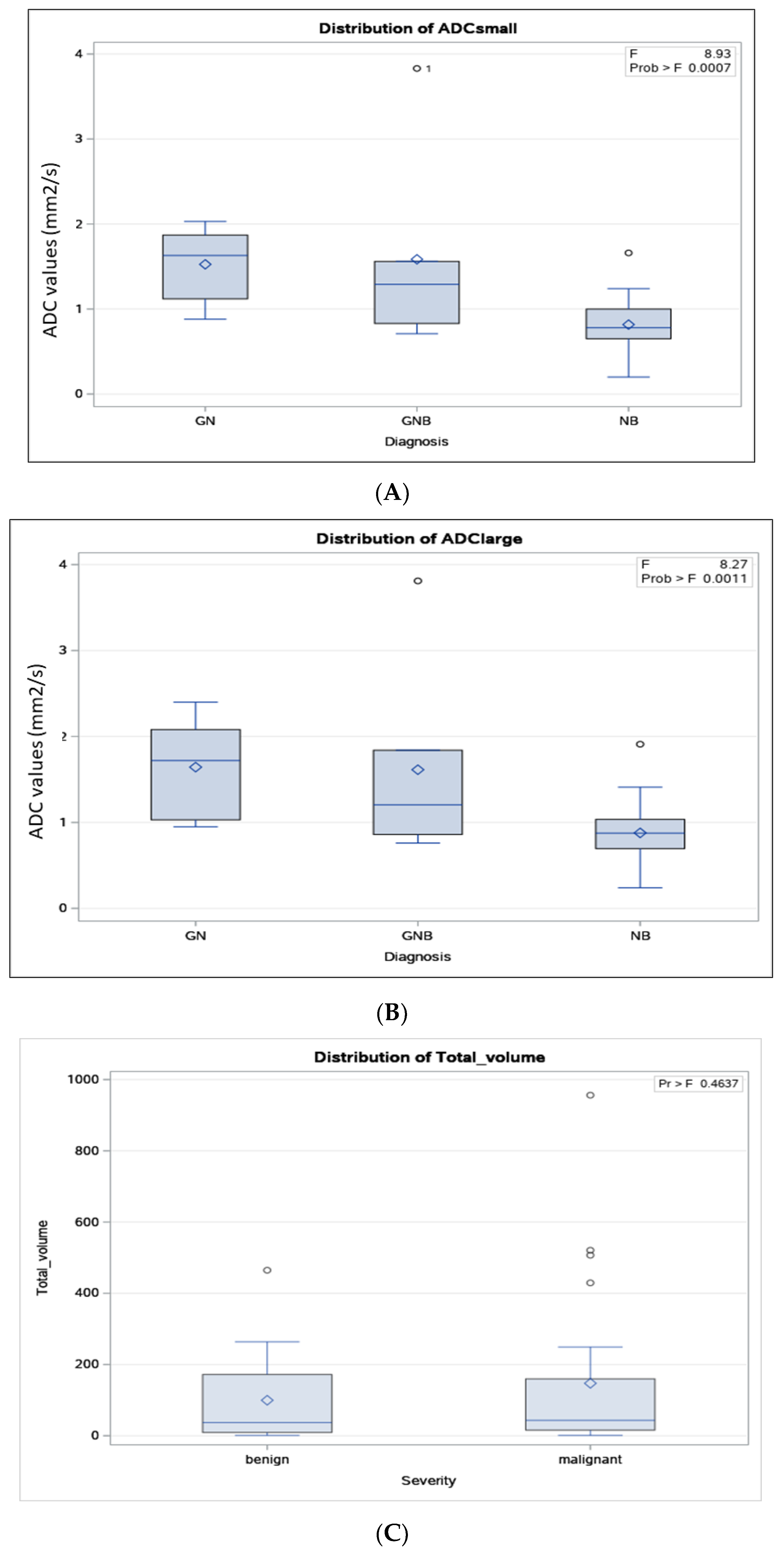
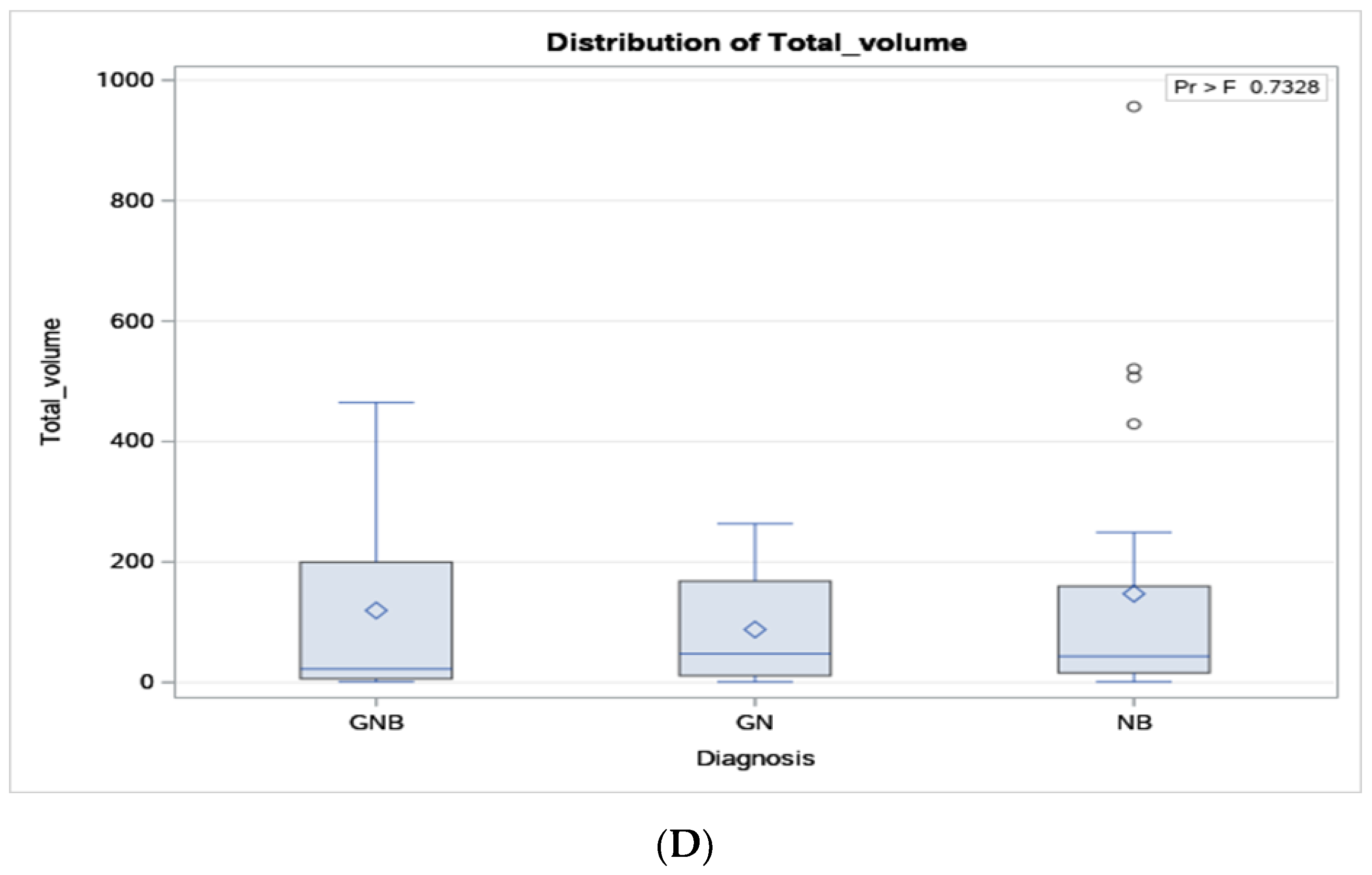
| Severity | Variable | Mean | SD | LCLM 95% | UCLM 95% | Median | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benign (N = 16) | Total volume (cc) | 155 | 266 | 31 | 168 | 37 | 1 | 1166 |
| ADC small | 1.54 | 0.69 | 1.15 | 1.94 | 1.53 | 0.71 | 3.82 | |
| ADC large | 1.63 | 0.71 | 1.21 | 2.05 | 1.52 | 0.76 | 3.81 | |
| Age at diagnosis (months) | 101 | 1 | 75 | 139 | 96 | 14 | 193 | |
| Malignant (N = 24) | Total volume (cc) | 147 | 234 | 49 | 246 | 43 | 1 | 956 |
| ADC small | 0.85 | 0.38 | 0.68 | 0.95 | 0.78 | 0.20 | 1.92 | |
| ADC large | 0.91 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 1.03 | 0.88 | 0.76 | 1.94 | |
| Age at diagnosis (months) | 20 | 1 | 9 | 32 | 10 | 0 | 119 | |
| Diagnosis | Variable | Mean | SD | LCLM 95% | UCLM 95% | Median | Minimum | Maximum |
| GN (N = 10) | Total volume (cc) | 93 | 90 | 23 | 153 | 48 | 1 | 264 |
| ADC small | 1.52 | 0.44 | 1.22 | 1.83 | 1.63 | 0.88 | 2.16 | |
| ADC large | 1.64 | 0.51 | 1.24 | 2.04 | 1.72 | 0.95 | 2.40 | |
| Age at diagnosis (months) | 121 | 54 | 93 | 173 | 132 | 34 | 193 | |
| GNB (N = 6) | Total volume (cc) | 269 | 430 | 75 | 314 | 22 | 1 | 1166 |
| ADC small | 1.59 | 1.05 | 0.38 | 2.79 | 1.29 | 0.71 | 3.83 | |
| ADC large | 1.63 | 1.04 | 0.41 | 2.81 | 1.21 | 0.76 | 3.81 | |
| Age at diagnosis (months) | 63 | 40 | 18 | 110 | 58 | 14 | 140 | |
| NB (N = 24) | Volume | 147 | 234 | 49 | 246 | 43 | 1 | 956 |
| ADC small | 0.82 | 0.32 | 0.68 | 0.95 | 0.78 | 0.20 | 1.66 | |
| ADC large | 0.88 | 0.35 | 0.73 | 1.03 | 0.88 | 0.24 | 1.66 | |
| Age at diagnosis (months) | 21 | 26 | 9 | 32 | 10 | 0 | 119 |
| Imaging Features | NB (n = 24) | GNB (n = 6) | GN (n = 10) | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total No. | % | Total No. | % | Total No. | % | ||
| Multifocal disease | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Multiple body compartments | 1 * | 4.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Lobulated (presence) | 22 | 91.6 | 4 | 66.7 | 5 | 50 | 0.01 |
| Heterogeneous (presence) | 20 | 83.3 | 4 | 66.7 | 7 | 70 | 0.74 |
| Calcifications (presence) | 6 | 25 | 1 | 16.7 | 2 | 20 | 1.0 |
| Necrosis (presence) | 4 | 16.7 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 10 | 0.82 |
| Predominant T1 signal | 0.53 | ||||||
| Hypointense | 10 | 41.7 | 5 | 83.3 | 7 | 70 | |
| Isointense | 13 | 54.2 | 1 | 16.7 | 3 | 30 | |
| Hyperintense | 1 | 4.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Predominant T2 signal | 0.83 | ||||||
| Hypointense | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Isointense | 4 | 16.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Hyperintense | 20 | 83.3 | 6 | 100 | 10 | 100 | |
| Contrast enhancement | 1.0 | ||||||
| Homogeneous | 8 | 33.3 | 2 | 33.3 | 3 | 30 | |
| Heterogeneous | 14 | 58.3 | 4 | 66.7 | 6 | 60 | |
| No contrast | 2 | 8.3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 10 | |
| Image-defined risk factors (IDRFs) | 15 | 62.5 | 2 | 33.3 | 2 | 20 | 0.07 |
| Vascular encasement (presence) | 10 | 41.7 | 2 | 33.3 | 2 | 20 | 0.53 |
| Intraspinal invasion (presence) | 8 | 33.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.04 |
| Adjacent organ infiltration (presence) | 8 | 33.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.04 |
| Tracheal compression (presence) | 3 | 12.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.72 |
| Metastatic disease at diagnosis (presence) | 8 | 33.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.04 |
| Diffusion restriction (presence) | 24 | 100 | 6 | 100 | 6 | 60 | 0.005 |
| Feature | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | Positive LR (95% CI) | Accuracy (95% CI) | DOR and Log DOR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADC cut-off small ROI, 1.06 × 10−3 mm2/s | 0.83 (0.68, 0.98) | 0.75 (0.54, 0.98) | 3.33 (1.40, 7.94) | 0.80 (0.64, 0.91) | DOR = 15.14 Log DOR = 2.71 |
| ADC cut-off large ROI, 1.22 × 10−3 mm2/s | 0.79 (0.63, 0.94) | 0.83 (0.62, 1.00) | 2.44 (1.28, 4.65) | 0.80 (0.64, 0.91%) | DOR = 18.33 Log DOR = 2.91 |
| Tumour volume cut-off, 56 cc | 0.50 (0.29, 0.71) | 0.63 (0.35, 0.85) | 1.33 (0.63, 2.83) | 0.55 (0.38, 0.71) | DOR = 1.67 Log DOR = 0.51 |
| Age at diagnosis cut-off, 48 months | 0.96 (0.79, 1.00) | 0.81 (0.54, 0.96) | 5.11 (1.84, 14.22) | 0.90 (0.76, 0.97) | DOR = 99.66 Log DOR = 4.60 |
| Variable | Likelihood Ratio 1 | p-Value | Point Estimate 2 | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADC small ROI | 18.77 | <0.0001 | 3.88 | 48.52 | 4.09, 575.36 | 0.002 |
| ADC large ROI | 16.10 | <0.0001 | 3.07 | 21.58 | 2.63, 177.01 | 0.004 |
| Tumour volume | 0.61 | 0.44 | 0.001 | 1.001 | 1.00, 1.005 | 0.46 |
| Age at diagnosis | 25.40 | <0.0001 | 0.05 | 1.05 | 1.02, 1.08 | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tambasco, D.; Zlotnik, M.; Joshi, S.; Moineddin, R.; Harris, S.; Villani, A.; Malkin, D.; Morgenstern, D.A.; Doria, A.S. Characterisation of Paediatric Neuroblastic Tumours by Quantitative Structural and Diffusion-Weighted MRI. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6660. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13226660
Tambasco D, Zlotnik M, Joshi S, Moineddin R, Harris S, Villani A, Malkin D, Morgenstern DA, Doria AS. Characterisation of Paediatric Neuroblastic Tumours by Quantitative Structural and Diffusion-Weighted MRI. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(22):6660. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13226660
Chicago/Turabian StyleTambasco, Domenica, Margalit Zlotnik, Sayali Joshi, Rahim Moineddin, Shelley Harris, Anita Villani, David Malkin, Daniel A. Morgenstern, and Andrea S. Doria. 2024. "Characterisation of Paediatric Neuroblastic Tumours by Quantitative Structural and Diffusion-Weighted MRI" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 22: 6660. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13226660
APA StyleTambasco, D., Zlotnik, M., Joshi, S., Moineddin, R., Harris, S., Villani, A., Malkin, D., Morgenstern, D. A., & Doria, A. S. (2024). Characterisation of Paediatric Neuroblastic Tumours by Quantitative Structural and Diffusion-Weighted MRI. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(22), 6660. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13226660






