Middle Molecular Uremic Toxin and Blood Purification Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Classification of Middle Molecular Uremic Toxin
2. Middle Molecules and the Blood Purification Setting (Figure 1)
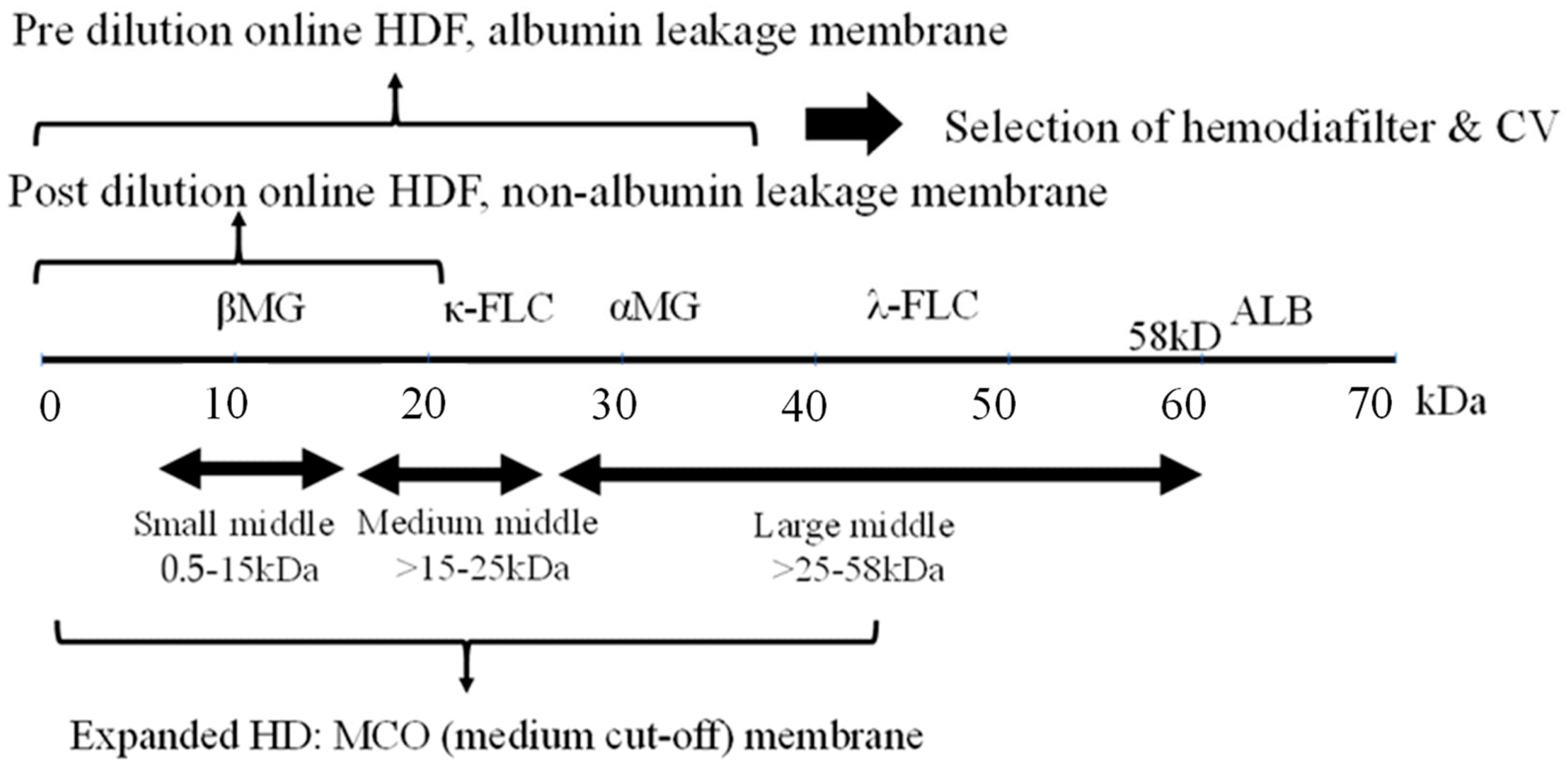
3. Impact of Highly Efficient Blood Purification on Patient Survival
3.1. Impact on HDF for Survival
3.2. Efficacy of Expanded HD
4. The Functional Classification of Dialyzer
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scribner, B.H.; Caner, J.E.; Buri, R.; Quinton, W. The technique of continous hemodialysis. Trans. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1960, 6, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henderson, L.W.; Sanfelippo, M.L.; Beans, E. “On line” preparation of sterile pyrogen-free electrolyte solution. Trans. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1978, 24, 465–467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ward, R.A.; Vienken, J.; Silverstein, D.M.; Ash, S.; Canaud, B. Regulatory Considerations for Hemodiafiltration in the United States. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rindi, P.; Pilone, N.; Riccò, V.; Cioni, L. Clinical experience with a new hemodiafiltration (HDF) system. ASAIO Trans. 1988, 34, 765–768. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Canaud, B.; Köhler, K.; Sichart, J.M.; Möller, S. Global prevalent use, trends and practices in haemodiafiltration. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergström, J.; Fürst, P. Uremic toxins. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1978, S9–S12. [Google Scholar]
- Vanholder, R.; De Smet, R.; Glorieux, G.; Argilés, A.; Baurmeister, U.; Brunet, P.; Clark, W.; Cohen, G.; De Deyn, P.P.; Deppisch, R.; et al. Review on uremic toxins: Classification, concentration, and interindividual variability. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1934–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanholder, R.; Pletinck, A.; Schepers, E.; Glorieux, G. Biochemical and Clinical Impact of Organic Uremic Retention Solutes: A Comprehensive Update. Toxins 2018, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, M.H.; Reis, T.; Husain-Syed, F.; Vanholder, R.; Hutchison, C.; Stenvinkel, P.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Cozzolino, M.; Juillard, L.; Kashani, K.; et al. Classification of uremic toxins and their role in kidney failure. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1918–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribner, B.H. Discussion. Trans. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1965, 11, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Babb, A.L.; Popovich, R.P.; Christopher, T.G.; Scribner, B.H. The genesis of the square meter-hour hypothesis. Trans. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs. 1971, 17, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Babb, A.L.; Ahmad, S.; Bergström, J.; Scribner, B.H. The middle molecule hypothesis in perspective. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1981, 1, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gejyo, F.; Yamada, T.; Odani, S.; Nakagawa, Y.; Arakawa, M.; Kunitomo, T.; Kataoka, H.; Suzuki, M.; Hirasawa, Y.; Shirahama, T. A new form of amyloid protein associated with chronic hemodialysis was identified as beta 2-microglobulin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1985, 129, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gelder, M.K.; Middel, I.R.; Vernooij, R.W.M.; Bots, M.L.; Verhaar, M.C.; Masereeuw, R.; Grooteman, M.P.; Nubé, M.J.; van den Dorpel, M.A.; Blankestijn, P.J.; et al. Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins in Hemodialysis Patients Relate to Residual Kidney Function, Are Not Influenced by Convective Transport, and Do Not Relate to Outcome. Toxins 2020, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madero, M.; Cano, K.B.; Campos, I.; Tao, X.; Maheshwari, V.; Brown, J.; Cornejo, B.; Handelman, G.; Thijssen, S.; Kotanko, P. Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins during Hemodialysis Using a Binding Competitor. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Marchionna, N.; Brendolan, A.; Neri, M.; Lorenzin, A.; Martínez Rueda, A.J. Expanded haemodialysis: From operational mechanism to clinical results. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33 (Suppl. 3), iii41–iii47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maduell, F.; Rodas, L.; Broseta, J.J.; Gomez, M.; Xipell, M.; Guillen, E.; Montagud-Marrahi, E.; Arias-Guillén, M.; Fontseré, N.; Vera, M.; et al. Medium cut-off dialyzer versus eight hemodiafiltration dialyzers: Comparison using a global removal score. Blood Purif. 2019, 48, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grooteman, M.P.; van den Dorpel, M.A.; Bots, M.L.; Penne, E.L.; van der Weerd, N.C.; Mazairac, A.H.; den Hoedt, C.H.; van der Tweel, I.; Lévesque, R.; Nubé, M.J.; et al. Effect of Online Hemodiafiltration on All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, E.; Asci, G.; Toz, H.; Ok, E.S.; Kircelli, F.; Yilmaz, M.; Hur, E.; Demirci, M.S.; Demirci, C.; Duman, S.; et al. Mortality and cardiovascular events in online haemodiafiltration (OL-HDF) compared with high-flux dialysis: Results from the Turkish OL-HDF Study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduell, F.; Moreso, F.; Pons, M.; Ramos, R.; Mora-Macià, J.; Carreras, J.; Soler, J.; Torres, F.; Campistol, J.M.; Martinez-Castelao, A. High-Efficiency Postdilution Online Hemodiafiltration Reduces All-Cause Mortality in Hemodialysis Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morena, M.; Jaussent, A.; Chalabi, L.; Leray-Moragues, H.; Chenine, L.; Debure, A.; Thibaudin, D.; Azzouz, L.; Patrier, L.; Maurice, F.; et al. Treatment tolerance and patient-reported outcomes favor online hemodiafiltration compared to high-flux hemodialysis in the elderly. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 1495–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernooij, R.W.M.; Bots, M.L.; Strippoli, G.F.M.; Canaud, B.; Cromm, K.; Woodward, M.; Blankestijn, P.J. CONVINCE scientific committee. CONVINCE in the context of existing evidence on haemodiafiltration. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, F.; Karaboyas, A.; Pisoni, R.L.; Robinson, B.M.; Fort, J.; Vanholder, R.; Rayner, H.C.; Kleophas, W.; Jacobson, S.H.; Combe, C.; et al. Mortality risk in patients on hemodiafiltration versus hemodialysis: A ‘real-world’ comparison from the DOPPS. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, A.; Arnold, R.; Gallagher, M.; Snelling, P.; Green, J.; Fernando, M.; Kiernan, M.C.; Hand, S.; Grimley, K.; Burman, J.; et al. Effect of Hemodiafiltration on the Progression of Neuropathy with Kidney Failure: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankestijn, P.J.; Vernooij, R.W.M.; Hockham, C.; Strippoli, G.F.M.; Canaud, B.; Hegbrant, J.; Barth, C.; Covic, A.; Cromm, K.; Cucui, A.; et al. Effect of Hemodiafiltration or Hemodialysis on Mortality in Kidney Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shroff, R.; Basile, C.; van der Sande, F.; Mitra, S. Haemodiafiltration for all: Are we CONVINCE? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38, 2663–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, K. Biomarkers for evaluation of clinical outcomes of hemodiafiltration. Blood Purif. 2013, 35 (Suppl. 1), 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, K.; Hosoya, H.; Kurihara, Y.; Takeshi, S. Suitability of α1-microglobulin reduction rate as a biomarker of removal efficiency of online hemodiafiltration: A retrospective cohort study. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2021, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, K.; Hamano, T.; Wada, A.; Nakai, S.; Masakane, I. Predilution online hemodiafiltration is associated with improved survival compared with hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, K.; Saito, T.; Yamauchi, F.; Hosoya, H.; Kurihara, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Ishi, D.; Kokubo, K. Comparison of the effects of pre-and post-dilution on-line hemodiafiltration on the cell surface and other inflammatory markers. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31 (Suppl. 1), i493. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Gan, L.; Niu, Q.; Ni, M.; Zuo, L. Efficacy and safety of expanded hemodialysis in hemodialysis patients: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Ren. Fail. 2022, 44, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, C.R.; Hornig, C.; Canaud, B. Systematic review to compare the outcomes associated with the modalities of expanded hemodialysis (HDx) versus high-flux hemodialysis and/or hemodiafiltration (HDF) in patients with end-stage kidney disease (ESKD). Semin. Dial. 2023, 36, 86–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, M.; Masakane, I.; Wada, A.; Nakai, S.; Nitta, K.; Nakamoto, H. Super high-flux membrane dialyzers improve mortality in patients on hemodialysis: A 3-year nationwide cohort study. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 15, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eknoyan, G.; Beck, G.J.; Cheung, A.K.; Daugirdas, J.T.; Greene, T.; Kusek, J.W.; Allon, M.; Bailey, J.; Delmez, J.A.; Depner, T.A.; et al. Effect of dialysis dose and membrane flux in maintenance hemodialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 2010–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, F.; Martin-Malo, A.; Hannedouche, T.; Loureiro, A.; Papadimitriou, M.; Wizemann, V.; Jacobson, S.H.; Czekalski, S.; Ronco, C.; Vanholder, R. Effect of membrane permeability on survival of hemodialysis patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depner, T.; Daugirdas, J.; Greene, T.; Allon, M.; Beck, G.; Chumlea, C.; Delmez, J.; Gotch, F.; Kusek, J.; Levin, N.; et al. Dialysis dose and the effect of gender and body size on outcome in the HEMO Study. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmez, J.A.; Yan, G.; Bailey, J.; Beck, G.J.; Beddhu, S.; Cheung, A.K.; Kaysen, G.A.; Levey, A.S.; Sarnak, M.J.; Schwab, S.J. Cerebrovascular disease in maintenance hemodialysis patients: Results of the HEMO Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2006, 47, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storr, M.; Ward, R.A. Membrane innovation: Closer to native kidneys. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, iii22–iii27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijers, B.; Vega, A.; Juillard, L.; Kawanishi, H.; Kirsch, A.H.; Maduell, F.; Massy, Z.A.; Mitra, S.; Vanholder, R.; Ronco, C.; et al. Extracorporeal Techniques in End-Stage Kidney Disease. Blood Purif. 2023, 2, 929–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, A. Definition of high-performance membranes—From the clinical point of view. Contrib. Nephrol. 2011, 173, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Naganuma, T.; Takemoto, Y.; Kamada, N.; Kawanishi, H. Hemodiafiltration in Japan: Current status and future directions. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2023, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanishi, H. Development of online hemodiafiltration in Japan. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2021, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuyoshi, S.; Nakatani, M.; Taman, J.; Kutsuki, H.; Takata, S.; Tani, N. New adsorption column (Lixelle) to eliminate beta2-microglobulin for direct hemoperfusion. Ther. Apher. 1998, 2, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Tian, H.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Ding, F. Improved Dialysis Removal of Protein-Bound Uraemic Toxins with a Combined Displacement and Adsorption Technique. Blood Purif. 2022, 51, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronco, C. Combined Hemoperfusion-Hemodialysis in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients. Contrib. Nephrol. 2023, 200, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
| Modality | Europe | Japan | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDF | Post-dilution, use non-albumin leakage membered | Pre-dilution, use albumin leakage membrane | |
| CV | 20–25 L/session | 48–58 L/session | |
| Blood flow rate | ≥300 mL/min | 250–300 mL/min | |
| Target MMs | Small middle, e.g., β2-microglobulin | Large-middle, e.g., α1-microglobulin | |
| Evidence | RCT: benefit to survival on higher CV | National cohort: enhanced survival was found to be substitution volume 50.5 L (limitation of CV) | |
| Expanded HD | MCO membrane | Note: This term is not common in Japan. The 2013 functional classification II-b: super high-flux-albumin leaking membrane HD is the equivalent. | |
| Target MM | Medium middle, e.g., κ free light chain protein | Medium to large-middle |
| 1996 |
| Classified by β2-microglobulin (βMG) clearance (CL), in vitro on QB200, QD500 mL/min |
| Type I βMG-CL 0–10 mL/min, standard dialyzer |
| Type II βMG-CL >10 mL/min, high performance dialyzer: |
| 2006 |
| Classified by βMG-CL, in vitro on QB200, QD500 mL/min |
| Type I < βMG-CL 10 mL/min |
| Type II < βMG-CL 30 mL/min |
| Type III < βMG-CL 50 mL/min |
| Type IV < βMG-CL 70 mL/min |
| Type V ≥ βMG-CL 70 mL/min |
| 2013 |
| Classified byβMG-CL, in vitro on QB200, QD500 mL/min and abumin (alb) sieving ecoefficiency (SC), in vitro, bromocresol green (BCG) method |
| Type I-a βMG-CL < 70 mL/min & alb-SC < 0.03, standard high-flux (including low flux) |
| Type I-b βMG-CL < 70 mL/min & alb-SC ≥ 0.03, high-flux-albumin leaking |
| Type II-a βMG-CL ≥ 70 mL/min & alb-SC < 0.03, super high-flux |
| Type II-b βMG-CL ≥ 70 mL/min & alb-SC ≥ 0.03, super high-flux-albumin leaking |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawanishi, H. Middle Molecular Uremic Toxin and Blood Purification Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030647
Kawanishi H. Middle Molecular Uremic Toxin and Blood Purification Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(3):647. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030647
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawanishi, Hideki. 2024. "Middle Molecular Uremic Toxin and Blood Purification Therapy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 3: 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030647
APA StyleKawanishi, H. (2024). Middle Molecular Uremic Toxin and Blood Purification Therapy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(3), 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030647






