A Comparison of Miller Straight Blade and Macintosh Blade Laryngoscopes for Intubation in Morbidly Obese Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
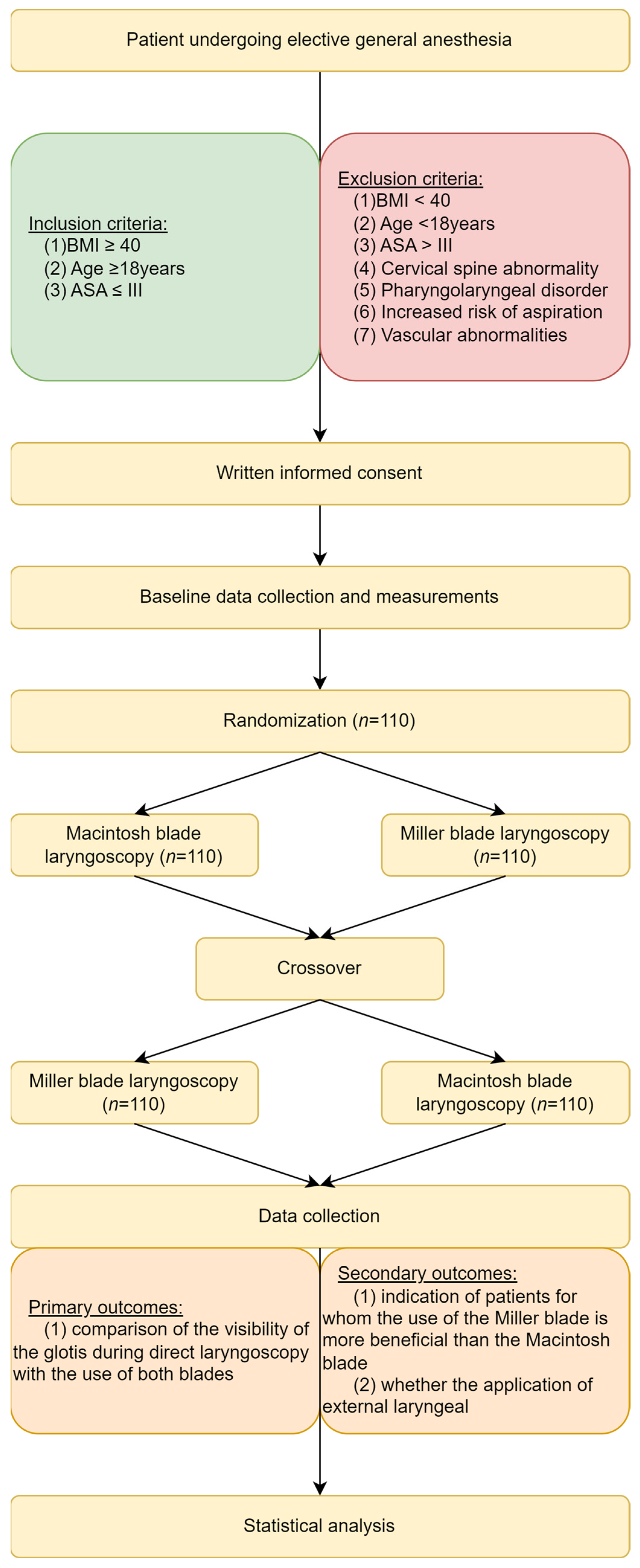
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Settings
2.2. Safety Conditions
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Group Characteristic
3.2. Primary Endpoint
3.3. Secondary Endpoints
3.3.1. Cormack–Lehane Scale without and with Laryngeal Pressure
3.3.2. POGO without and with Laryngeal Pressure
3.3.3. Optimal Cut-Off Points for Glottis Visualization When Using Miller Blade in Morbidly Obese Patients
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicholson, A.; Smith, A.F.; Lewis, S.R.; Cook, T.M. Tracheal intubation with a flexible intubation scope versus other intubation techniques for obese patients requiring general anaesthesia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, CD010320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, Z.I.; Yörükoğlu, H.U. Tracheal intubation with the McGrath MAC X-blade videolaryngoscope in morbidly obese and nonobese patients. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 49, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langeron, O.; Birenbaum, A.; Le Saché, F.; Raux, M. Airway management in obese patient. Minerva Anestesiol. 2014, 80, 382–392. [Google Scholar]
- Prathep, S.; Jitpakdee, W.; Woraathasin, W.; Oofuvong, M. Predicting difficult laryngoscopy in morbidly obese Thai patients by ultrasound measurement of distance from skin to epiglottis: A prospective observational study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022, 22, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ydemann, M.; Rovsing, L.; Lindekaer, A.L.; Olsen, K.S. Intubation of the morbidly obese patient: GlideScope(®) vs. Fastrach™. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2012, 56, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, M.S.; Berkow, L.C.; Kudenchuk, P.J.; Halperin, H.R.; Hess, E.P.; Moitra, V.K.; Neumar, R.W.; O’Neil, B.J.; Paxton, J.H.; Silvers, S.M.; et al. Part 7: Adult advanced cardiovascular life support: 2015 American Heart Association guidelines update for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation 2015, 132 (Suppl. S2), S444–S464, Correction in Circulation 2015, 132, e385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwin, K.; Bialka, S.; Czyzewski, L.; Smereka, J.; Dabrowski, M.; Dabrowska, A.; Ladny, J.R.; Ruetzler, K.; Szarpak, L. Video laryngoscopy for endotracheal intubation of adult patients with suspected/confirmed COVID-19. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Disaster Emerg. Med. J. 2020, 5, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.; Baker, P.A. How did the Macintosh laryngoscope become so popular? Pediatr. Anesth. 2009, 19 (Suppl. S1), 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak-Tim, J.; Gaszynski, T.; Ratajczyk, P. A comparison of face-to-face endotracheal intubation and standard intubation using Airtraq video laryngoscope in morbidly obese patients: A randomized controlled trial. Medicine 2022, 101, e32046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Shen, N.; Ma, C.; Hei, Z. Improvement of glottis visualisation during video laryngoscopy by lifting a flopy epiglottis similarly to direct laryngoscopy with a Miller blade. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain Med. 2021, 40, 100871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, W.; Arai, Y.-C.P. The use of a stylet to aid the lifting of the epiglottis with a video laryngoscope. Anesthesiol. Pain Med. 2016, 6, e38507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carron, M.; Ieppariello, G.; Linassi, F. Videolaryngoscopy versus direct laryngoscopy in obese surgical patients. Step by step toward more convincing evidence. J. Anesthesiol. Res. Pract. 2022, 2, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshjima, H.; Denawa, Y.; Tominaga, A.; Nakamura, C.; Shiga, T.; Nagasaka, H. Videolaryngoscope versus Macintosh laryngoscope for tracheal intubation in adut with obesity: A systemic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Anesth. 2018, 44, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carron, M.; Ieppariello, G.; Linassi, F. Videoalaryngoscopy versus direct laryngoscopy for tracheal intubation in obese adults: A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Anesth. 2021, 71, 110216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carron, M.; Linassi, F.; Ieppariello, G. Videolaryngoscopy Versus Direct Laryngoscopy for Patients with Obesity Requring Tracheal Intubation: A Meta-analysis. Obes. Surg. 2021, 31, 3327–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A.P.; Tirmanwar, A.S. Comparison of glottic visualisation and ease of intubation with different laryngoscope blades. Indian J. Anaesth. 2013, 57, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moritz, A.; Holzhauser, L.; Fuchte, T.; Kremer, S.; Schmidt, J.; Irouschek, A. Comparison of Glidescope Core, C-MAC Miller and conventional Miller laryngoscope for difficult airway management by anesthetists with limited and extensive experience in a simulated Pierre Robin sequence: A randomized crossover manikin study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, W.B., 3rd; Nossaman, B.D. Airway risk factors for the Miller laryngoscope blade. J. Clin. Anesth. 2016, 33, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochroch, E.A.; Hollander, J.E.; Kush, S.; Shofer, F.S.; Levitan, R.M. Assessment of laryngeal view: Percentage of glottic opening score vs Cormack and Lehane grading. Can. J. Anaesth. 1999, 46, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, J.K.; Pinchalk, M.E.; Wang, H.E. Reliability of paramedic ratings of laryngoscopic views during endotracheal intubation. Prehospital Emerg. Care 2005, 9, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitan, R.M.; Ochroch, E.A.; Rush, S.; Shofer, F.S.; Hollander, J.E. Assessment of airway visualization: Validation of the percentage of glottic opening (POGO) scale. Acad. Emerg. Med. 1998, 5, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Jang, E.-A.; Hong, M.; Bae, H.-B.; Kim, J. Ramped versus sniffing position in the videolaryngoscopy-guided tracheal intubation of morbidly obese patients: A prospective randomized study. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2023, 76, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, A.; Kulshrestha, M.; Mathews, J.J.; Bhandari, M. Are the obese difficult to intubate? Br. J. Anaesth. 2014, 112, 770–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wakabayashi, R.; Ishida, T.; Yamada, T.; Kawamata, M. Effect of an aerosol box on tracheal intubation difficulty. J. Anesth. 2020, 34, 790–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achen, B.; Terblanche, O.C.; Finucane, B.T. View of the larynx obtained using the Miller blade and paraglossal approach, compared to that with the Macintosh blade. Intensiv. Care 2008, 36, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arino, J.J.; Velasco, J.M.; Gasco, C.; Lopez-Timoneda, F. Straight blades improve visualization of the larynx while curved blades increase ease of intubation: A comparison of the Macintosh, Miller, McCoy, Belscope and Lee-Fiberview blades. Can. J. Anaesth. 2003, 50, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benumof, J.L.; Cooper, S.D. Quantitative improvement in laryngoscopic view by optimal external laryngeal manipulation. J. Clin. Anesth. 1996, 8, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruetzler, K.; Rivas, E.; Cohen, B.; Mosteller, L.; Martin, A.; Keebler, A.; Maheshwari, K.; Steckner, K.; Wang, M.; Praveen, C.; et al. McGrath Video Laryngoscope Versus Macintosh Direct Laryngoscopy for Intubation of Morbidly Obese Patients: A Randomized Trial. Obstet. Anesth. Dig. 2020, 131, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of patients | 110 (100%) |
| Sex [Female] | 65 (59.09%) |
| Age [years] | 43 (IQR: 36–49.75) |
| Neck circumference [cm] | 44 (IQR: 41–47) |
| Sternomental distance [cm] | 16 (IQR: 15–17) |
| Thyromental distance [cm] | 6 (IQR: 6–8) |
| Mouth opening ≥ 4 cm: | 71 (64.54%) |
| Mouth opening < 4 cm: | 39 (35.46%) |
| Weight [kg] | 130 (IQR: 118–145) |
| Height [cm] | 166 (IQR: 162.25–175) |
| BMI [km/m2] | 45.83 (IQR: 43.56–49.12) |
| Mallampati score | 3 (IQR: 2–3) |
| Cormack–Lehane for Macintosh laryngoscope without laryngeal pressure | 2 (IQR: 1–3) |
| Cormack–Lehane for Macintosh laryngoscope with laryngeal pressure | 1 (IQR: 1–2) |
| Cormack–Lehane for Miller laryngoscope without laryngeal pressure | 1 (IQR: 1–2) |
| Cormack–Lehane for Miller laryngoscope with laryngeal pressure | 1 (IQR: 1–2) |
| POGO for Macintosh laryngoscope without laryngeal pressure | 65% (IQR: 20–100%) |
| POGO for Macintosh laryngoscope with laryngeal pressure | 100% (IQR: 50–100%) |
| POGO for Miller laryngoscope without laryngeal pressure | 100% (IQR: 50–100%) |
| POGO for Miller laryngoscope with laryngeal pressure | 100% (IQR: 50–100%) |
| A. Cormack–Lehane Scale | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cormack–Lehane without Laryngeal Pressure | Cormack–Lehane with Laryngeal Pressure | |
| Higher score | 9 (8.18%) | 12 (10.91%) |
| The same score | 56 (50.91%) | 80 (72.73%) |
| Lower score | 45 (40.91%) | 18 (16.36%) |
| B. POGO Scale | ||
| POGO without Laryngeal Pressure | POGO with Laryngeal Pressure | |
| Lower score | 13 (11.82%) | 17 (15.45%) |
| The same score | 52 (47.27%) | 74 (67.27%) |
| Higher score | 45 (40.91%) | 19 (17.27%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ratajczyk, P.; Kluj, P.; Szmyd, B.; Resch, J.; Hogendorf, P.; Durczynski, A.; Gaszynski, T. A Comparison of Miller Straight Blade and Macintosh Blade Laryngoscopes for Intubation in Morbidly Obese Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030681
Ratajczyk P, Kluj P, Szmyd B, Resch J, Hogendorf P, Durczynski A, Gaszynski T. A Comparison of Miller Straight Blade and Macintosh Blade Laryngoscopes for Intubation in Morbidly Obese Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(3):681. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030681
Chicago/Turabian StyleRatajczyk, Pawel, Przemysław Kluj, Bartosz Szmyd, Julia Resch, Piotr Hogendorf, Adam Durczynski, and Tomasz Gaszynski. 2024. "A Comparison of Miller Straight Blade and Macintosh Blade Laryngoscopes for Intubation in Morbidly Obese Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 3: 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030681
APA StyleRatajczyk, P., Kluj, P., Szmyd, B., Resch, J., Hogendorf, P., Durczynski, A., & Gaszynski, T. (2024). A Comparison of Miller Straight Blade and Macintosh Blade Laryngoscopes for Intubation in Morbidly Obese Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(3), 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030681







