The Impact of Climate Change and Extreme Weather Conditions on Cardiovascular Health and Acute Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
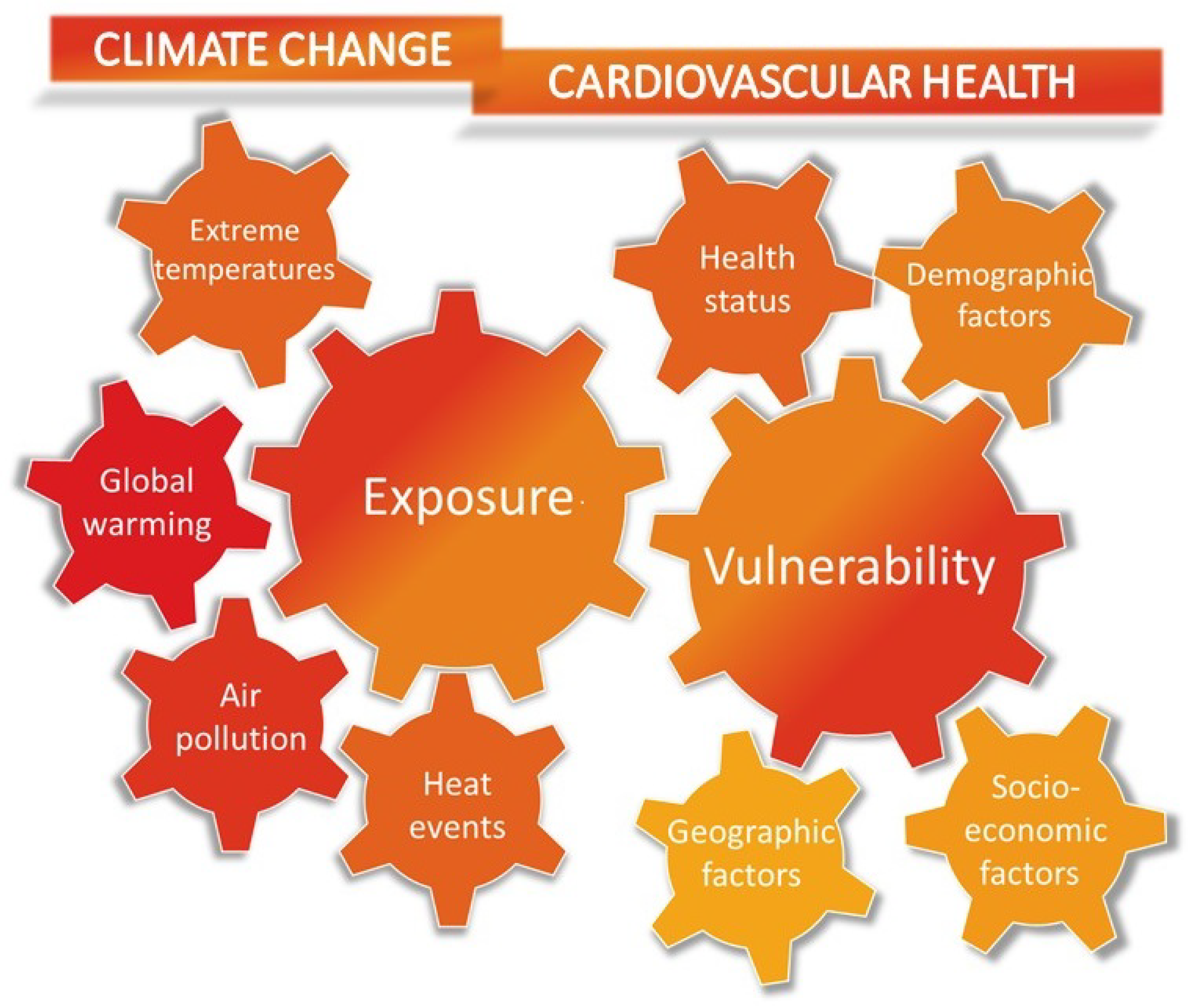
:1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
3. Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Diseases
3.1. Cardiovascular Mortality
3.2. Acute Myocardial Infarction
3.3. Heart Failure
3.4. Arrhythmias
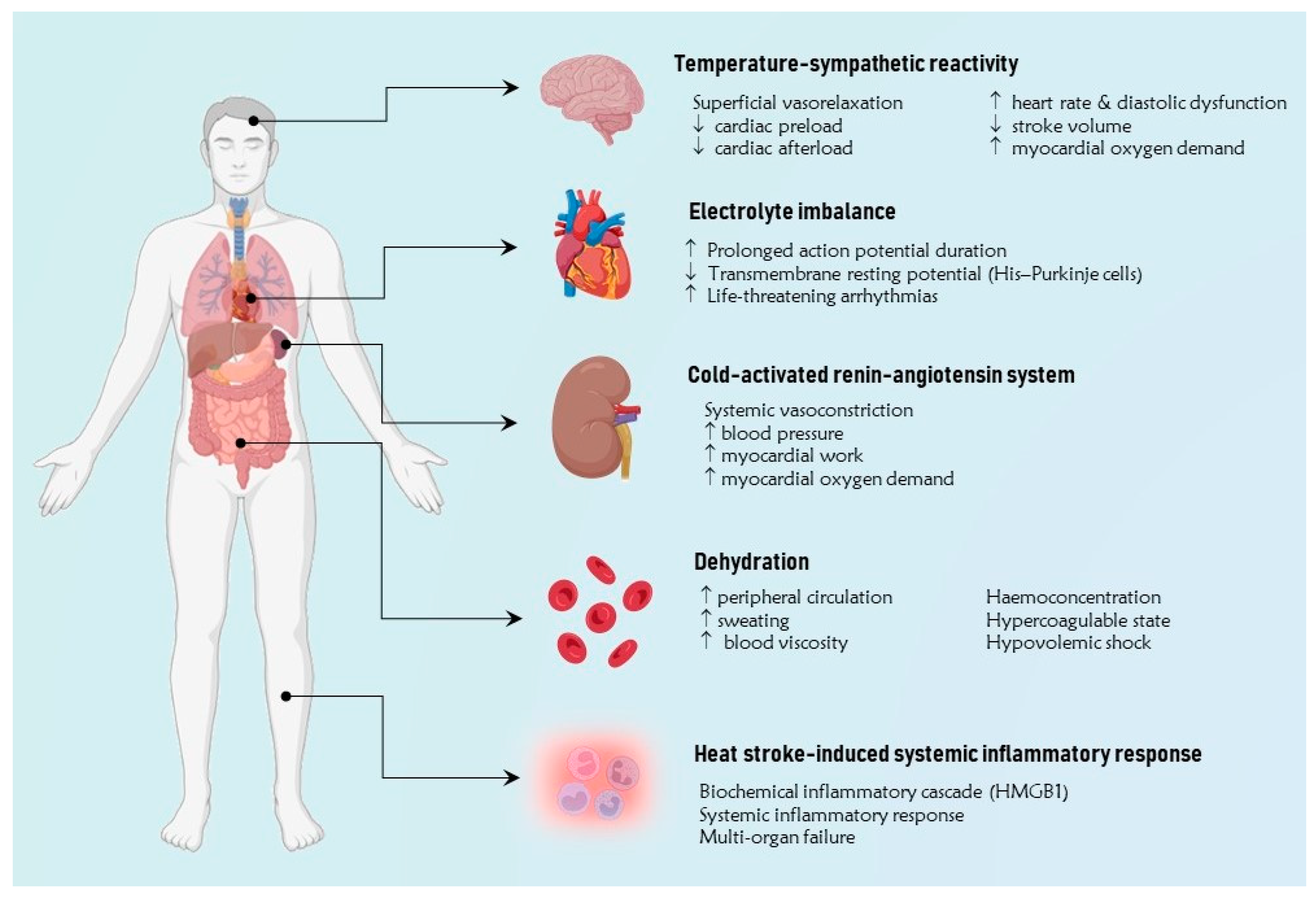
4. Extreme Temperatures and Cardiovascular Disease
4.1. Temperature-Sympathetic Reactivity
4.2. Cold-Activated Renin-Angiotensin System
4.3. Dehydration
4.4. Extreme Temperature-Induced Disionemias
4.5. Heat Stroke-Induced Systemic Inflammatory Response
5. Epidemiology of Temperature-Related Cardiovascular Disease
5.1. Cardiovascular Mortality
5.2. Acute Myocardial Infarction
5.3. Heart Failure
5.4. Arrhythmias
6. Discussion and Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zanobetti, A.; Peters, A. Disentangling interactions between atmospheric pollution and weather. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2015, 69, 613–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Fuller, R.; Acosta, N.J.R.; Adeyi, O.; Arnold, R.; Basu, N.N.; Baldé, A.B.; Bertollini, R.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Boufford, J.I.; et al. The Lancet Commission on pollution and health. Lancet 2018, 391, 462–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. COP24 Special Report: Health and Climate Change. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241514972 (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Brauer, M.; Casadei, B.; Harrington, R.A.; Kovacs, R.; Sliwa, K.; WHF Air Pollution Expert Group. Taking a Stand Against Air Pollution-The Impact on Cardiovascular Disease: A Joint Opinion from the World Heart Federation, American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association, and the European Society of Cardiology. Circulation 2021, 143, e800–e804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Schneider, A. Cardiovascular risks of climate change. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, A.; Wireko, A.A.; Jiffry, R.; Ng, J.C.; Patel, H.; Zahid, M.J.; Mehta, A.; Huang, H.; Abdul-Rahman, T.; Isik, A. The impact of natural disasters on healthcare and surgical services in low- and middle-income countries. Ann. Med. Surg. 2023, 85, 3774–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, M.S.; Zanobetti, A.; Schwartz, J. Disparities by race in heat-related mortality in four US cities: The role of air conditioning prevalence. J. Urban Health 2005, 82, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyce, S.C.; Schenker, M. Migrant Workers and Their Occupational Health and Safety. Ann. Rev. Public Health 2018, 39, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandentorren, S.; Bretin, P.; Zeghnoun, A.; Mandereau-Bruno, L.; Croisier, A.; Cochet, C.; Ribéron, J.; Siberan, I.; Declercq, B.; Ledrans, M. August 2003 heat wave in France: Risk factors for death of elderly people living at home. Eur. J. Public Health 2006, 16, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bernhard, G.H.; Neale, R.E.; Barnes, P.W.; Neale, P.J.; Zepp, R.G.; Wilson, S.R.; Andrady, A.L.; Bais, A.F.; McKenzie, R.L.; Aucamp, P.J.; et al. Environmental effects of stratospheric ozone depletion, UV radiation and interactions with climate change: UNEP Environmental Effects Assessment Panel, update 2019. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2020, 19, 542–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, S.; Al-Kindi, S.G.; Brook, R.D. Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2054–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khraishah, H.; Alahmad, B.; Ostergard, R.L., Jr.; AlAshqar, A.; Albaghdadi, M.; Vellanki, N.; Chowdhury, M.M.; Al-Kindi, S.G.; Zanobetti, A.; Gasparrini, A.; et al. Climate change and cardiovascular disease: Implications for global health. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 798–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A., 3rd; Bhatnagar, A.; McCracken, J.P.; Abplanalp, W.; Conklin, D.J.; O’Toole, T. Exposure to Fine Particulate Air Pollution Is Associated with Endothelial Injury and Systemic Inflammation. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, P.; Luo, X.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Han, M.; Qie, R.; Wu, X.; Liu, D.; et al. Long-term association of ambient air pollution and hypertension in adults and in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, G.; Mora, S.; Greenland, P.; Tsai, M.; Gill, E.; Kaufman, J.D. Association of Air Pollution Exposures with High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Particle Number: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Münzel, T.; Sørensen, M.; Gori, T.; Schmidt, F.P.; Rao, X.; Brook, F.R.; Chen, L.C.; Brook, R.D.; Rajagopalan, S. Environmental stressors and cardio-metabolic disease: Part II-mechanistic insights. Eur. Heart. J. 2017, 38, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newby, D.E.; Mannucci, P.M.; Tell, G.S.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Brook, R.D.; Donaldson, K.; Forastiere, F.; Franchini, M.; Franco, O.H.; Graham, I.; et al. Expert position paper on air pollution and cardiovascular disease. Eur. Heart. J. 2015, 36, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, S.; Brook, R.D. Air pollution and type 2 diabetes: Mechanistic insights. Diabetes 2012, 61, 3037–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.Y.; Fan, S.; Thiering, E.; Seissler, J.; Nowak, D.; Dong, G.H.; Heinrich, J. Ambient air pollution and diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2020, 180, 108817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, X.; Ruan, Y.; Lian, H.; Fan, Z. Effect of exposure to PM2.5 on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hypertens 2014, 32, 2130–2140; discussion 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ke, W.; Feng, B.; Lin, H.; Xiao, J.; Zeng, W.; Li, X.; Tao, J.; Yang, Z.; et al. Associations of Short-Term and Long-Term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollutants with Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hypertension 2016, 68, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.Y.; Qian, Z.; Howard, S.W.; Vaughn, M.G.; Fan, S.J.; Liu, K.K.; Dong, G.H. Global association between ambient air pollution and blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuźma, Ł.; Struniawski, K.; Pogorzelski, S.; Bachórzewska-Gajewska, H.; Dobrzycki, S. Gender Differences in Association between Air Pollution and Daily Mortality in the Capital of the Green Lungs of Poland-Population-Based Study with 2,953,000 Person-Years of Follow-Up. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurston, G.D.; Ahn, J.; Cromar, K.R.; Shao, Y.; Reynolds, H.R.; Jerrett, M.; Lim, C.C.; Shanley, R.; Park, Y.; Hayes, R.B. Ambient Particulate Matter Air Pollution Exposure and Mortality in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinault, L.L.; Weichenthal, S.; Crouse, D.L.; Brauer, M.; Erickson, A.; Donkelaar, A.V.; Martin, R.V.; Hystad, P.; Chen, H.; Finès, P.; et al. Associations between fine particulate matter and mortality in the 2001 Canadian Census Health and Environment Cohort. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Brauer, M.; Cohen, A.; Burnett, R.T.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Liang, R.; Wang, W.; Qi, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Long-term Fine Particulate Matter Exposure and Nonaccidental and Cause-specific Mortality in a Large National Cohort of Chinese Men. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 117002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.C.; Jerrett, M.; Pope, C.A., 3rd; Krewski, D.; Gapstur, S.M.; Diver, W.R.; Beckerman, B.S.; Marshall, J.D.; Su, J.; Crouse, D.L.; et al. Long-Term Ozone Exposure and Mortality in a Large Prospective Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesaroni, G.; Forastiere, F.; Stafoggia, M.; Andersen, Z.J.; Badaloni, C.; Beelen, R.; Caracciolo, B.; de Faire, U.; Erbel, R.; Eriksen, K.T.; et al. Long term exposure to ambient air pollution and incidence of acute coronary events: Prospective cohort study and meta-analysis in 11 European cohorts from the ESCAPE Project. BMJ 2014, 348, f7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafic, H.; Jabre, P.; Caussin, C.; Murad, M.H.; Escolano, S.; Tafflet, M.; Périer, M.C.; Marijon, E.; Vernerey, D.; Empana, J.P.; et al. Main air pollutants and myocardial infarction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2012, 307, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.K.; Spath, N.; Miller, M.R.; Mills, N.L.; Shah, A.S.V. Short-term exposure to carbon monoxide and myocardial infarction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, K.; Hoffmann, B.; Andersen, Z.J.; Atkinson, R.W.; Bauwelinck, M.; Bellander, T.; Brandt, J.; Brunekreef, B.; Cesaroni, G.; Chen, J.; et al. Long-term exposure to low-level ambient air pollution and incidence of stroke and coronary heart disease: A pooled analysis of six European cohorts within the ELAPSE project. Lancet Planet Health 2021, 5, e620–e632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, J.D.; Adar, S.D.; Barr, R.G.; Budoff, M.; Burke, G.L.; Curl, C.L.; Daviglus, M.L.; Diez Roux, A.V.; Gassett, A.J.; Jacobs, D.R.; et al. Association between air pollution and coronary artery calcification within six metropolitan areas in the USA (the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis and Air Pollution): A longitudinal cohort study. Lancet 2016, 388, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañeras, J.; Ferreira-González, I.; Marsal, J.R.; Barrabés, J.A.; Ribera, A.; Lidón, R.M.; Domingo, E.; Martí, G.; García-Dorado, D.; Codi IAM Registry investigators. Short-term exposure to air pollutants increases the risk of ST elevation myocardial infarction and of infarct-related ventricular arrhythmias and mortality. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 250, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, D.E.R.; Bredin, S.S.D.; Shellington, E.M.; Cole, C.; de Faye, A.; Harris, J.; Kim, D.D.; Abelsohn, A. A Systematic Review of the Short-Term Health Effects of Air Pollution in Persons Living with Coronary Heart Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhou, T.; Song, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, H.; Hu, Y.; Heianza, Y.; Qi, L. Joint exposure to various ambient air pollutants and incident heart failure: A prospective analysis in UK Biobank. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 1582–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Lin, Z.; He, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Huang, K.; Cao, J.; et al. Effect of Air Pollution on Heart Failure: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 76001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, W.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, H. Air Pollution and Cardiac Arrhythmias: From Epidemiological and Clinical Evidences to Cellular Electrophysiological Mechanisms. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 736151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.S.; Yang, P.S.; Lee, J.; Yu, H.T.; Kim, T.H.; Uhm, J.S.; Pak, H.N.; Lee, M.H.; Joung, B. Long-term exposure of fine particulate matter air pollution and incident atrial fibrillation in the general population: A nationwide cohort study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 283, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folino, F.; Buja, G.; Zanotto, G.; Marras, E.; Allocca, G.; Vaccari, D.; Gasparini, G.; Bertaglia, E.; Zoppo, F.; Calzolari, V.; et al. Association between air pollution and ventricular arrhythmias in high-risk patients (ARIA study): A multicentre longitudinal study. Lancet Planet Health 2017, 1, e58–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, A.P.; Khiew, Y.C.; Duffy, E.; O’Connell, J.; Brown, E.; Auwaerter, P.G.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Schwartz, B.S.; McEvoy, J.W. Climate change and the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022, 12, 100391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkoudian, N. Skin blood flow in adult human thermoregulation: How it works, when it does not, and why. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2003, 78, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessler, D.I. Thermoregulatory defense mechanisms. Crit. Care. Med. 2009, 37 (Suppl. 7), S203–S210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowell, L.B. Cardiovascular aspects of human thermoregulation. Circ. Res. 1983, 52, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowell, L.B.; Brengelmann, G.L.; Blackmon, J.R.; Murray, J.A. Redistribution of blood flow during sustained high skin temperature in resting man. J. Appl. Physiol 1970, 28, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowell, L.B.; Brengelmann, G.L.; Murray, J.A. Cardiovascular responses to sustained high skin temperature in resting man. J. Appl. Physiol. 1969, 27, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karjalainen, J.; Viitasalo, M. Fever and cardiac rhythm. Arch. Intern. Med. 1986, 146, 1169–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.D.; Haykowsky, M.J.; Petersen, S.R.; DeLorey, D.S.; Cheng-Baron, J.; Thompson, R.B. Increased left ventricular twist, untwisting rates, and suction maintain global diastolic function during passive heat stress in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 298, H930–H937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunes, J.; Tremblay, J.; Bellavance, F.; Hamet, P. Influence of environmental temperature on the blood pressure of hypertensive patients in Montréal. Am J Hypertens. 1991, 4, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, T.; Ogihara, T.; Maruyama, A.; Mikami, H.; Nakamaru, M.; Naka, T.; Kumahara, Y.; Nugent, C.A. The seasonal variation of blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension. Clin. Exp. Hypertens A 1982, 4, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, G. Seasonal variation in blood pressure in man. Nature 1961, 189, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, Y.; Tanaka, A.; Taruya, A.; Kashiwagi, M.; Nishiguchi, T.; Ozaki, Y.; Shiono, Y.; Shimamura, K.; Kitabata, H.; Kubo, T.; et al. Increased plaque rupture forms peak incidence of acute myocardial infarction in winter. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 320, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z. Cardiovascular responses to cold exposure. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed.) 2010, 2, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Guo, P. Effects of moderate strength cold air exposure on blood pressure and biochemical indicators among cardiovascular and cerebrovascular patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 2472–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, B.; Zhang, S.; Ma, S.; Zhou, J.; Wang, B. Effects of cold air on cardiovascular disease risk factors in rat. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 2312–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yavar, Z.; Sun, Q. Cardiovascular response to thermoregulatory challenges. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 309, H1793–H1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, S.; Keates, A.K.; Redfern, A.; McMurray, J.J.V. Seasonal variations in cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.H.; Kim, H.; Hong, Y.C. Variation in mortality of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes in relation to high temperature. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2013, 57, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gostimirovic, M.; Novakovic, R.; Rajkovic, J.; Djokic, V.; Terzic, D.; Putnik, S.; Gojkovic-Bukarica, L. The influence of climate change on human cardiovascular function. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health. 2020, 75, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Su, H. Effects of climatic temperature stress on cardiovascular diseases. Eur. J. Intern Med. 2010, 21, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrer, M.J.; Natale, A.M. Effect of hypothermia on the coagulation cascade. Crit. Care Med. 1992, 20, 1402–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.H.; Park, M.S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.; Hong, Y.C. Effects of cold and hot temperature on dehydration: A mechanism of cardiovascular burden. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2015, 59, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, L.; Winquist, A.; Klein, M.; O’Lenick, C.; Grundstein, A.; Ebelt Sarnat, S. Susceptibility to Heat-Related Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance Emergency Department Visits in Atlanta, Georgia, USA. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covino, B.G.; D’Amato, H.E. Mechanism of ventricular fibrillation in hypothermia. Circ. Res. 1962, 10, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, S.U.; Delaney, K.A.; Hoffman, R.S.; Slater, W.; Goldfrank, L.R. A prospective evaluation of the electrocardiographic manifestations of hypothermia. Acad. Emerg. Med. 1999, 6, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darocha, T.; Sobczyk, D.; Kosiński, S.; Jarosz, A.; Gałązkowski, R.; Nycz, K.; Drwiła, R. Electrocardiographic Changes Caused by Severe Accidental Hypothermia. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2015, 29, e83–e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudio, F.G.; Grissom, C.K. Cooling Methods in Heat Stroke. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 50, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, Y.; Yanovich, R. Heatstroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2449–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Xu, Z.; Bambrick, H.; Prescott, V.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Su, H.; Tong, S.; Hu, W. Cardiorespiratory effects of heatwaves: A systematic review and meta-analysis of global epidemiological evidence. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Guo, Y.; Barnett, A.G.; Tong, S.; Phung, D.; Chu, C.; Dear, K.; Wang, X.; Huang, C. Environmental ambient temperature and blood pressure in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 575, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halonen, J.I.; Zanobetti, A.; Sparrow, D.; Vokonas, P.S.; Schwartz, J. Outdoor temperature is associated with serum HDL and LDL. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunker, A.; Wildenhain, J.; Vandenbergh, A.; Henschke, N.; Rocklöv, J.; Hajat, S.; Sauerborn, R. Effects of Air Temperature on Climate-Sensitive Mortality and Morbidity Outcomes in the Elderly; a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Epidemiological Evidence. EBioMedicine 2016, 6, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Yin, P.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Niu, Y.; Wang, W.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Qi, J.; et al. Association between ambient temperature and mortality risk and burden: Time series study in 272 main Chinese cities. BMJ 2018, 363, k4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Eurowinter Group. Cold exposure and winter mortality from ischaemic heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, respiratory disease, and all causes in warm and cold regions of Europe. Lancet 1997, 349, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmad, B.; Khraishah, H.; Royé, D.; Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; Guo, Y.; Papatheodorou, S.I.; Achilleos, S.; Acquaotta, F.; Armstrong, B.; Bell, M.L.; et al. Associations Between Extreme Temperatures and Cardiovascular Cause-Specific Mortality: Results From 27 Countries. Circulation 2023, 147, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Breitner, S.; Wolf, K.; Hampel, R.; Meisinger, C.; Heier, M.; von Scheidt, W.; Kuch, B.; Peters, A.; Schneider, A.; et al. Temporal variations in the triggering of myocardial infarction by air temperature in Augsburg, Germany, 1987–2014. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 1600–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Chen, C.; Xu, D.; Li, T. Effects of ambient temperature on myocardial infarction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Armstrong, B.; Jaakkola, J.J.; Tong, S.; Pan, X. Extremely cold and hot temperatures increase the risk of ischaemic heart disease mortality: Epidemiological evidence from China. Heart 2013, 99, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Lavigne, E.; Gasparrini, A.; Copes, R.; Yagouti, A.; Burnett, R.T.; Goldberg, M.S.; Cakmak, S.; et al. Increased coronary heart disease and stroke hospitalisations from ambient temperatures in Ontario. Heart 2018, 104, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglis, S.C.; Clark, R.A.; Shakib, S.; Wong, D.T.; Molaee, P.; Wilkinson, D.; Stewart, S. Hot summers and heart failure: Seasonal variations in morbidity and mortality in Australian heart failure patients (1994–2005). Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2008, 10, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Yu, I.T.; Tse, L.A.; Tian, L.; Wang, X.; Wong, T.W. Is greater temperature change within a day associated with increased emergency hospital admissions for heart failure? Circ. Heart Fail. 2013, 6, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, H. Influence of ambient temperature and diurnal temperature range on incidence of cardiac arrhythmias. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2017, 61, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinn, L.; Hajat, S.; Wilkinson, P.; Armstrong, B.; Anderson, H.R.; Monk, V.; Harrison, R. Ambient temperature and activation of implantable cardioverter defibrillators. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2013, 57, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserman, E.B.; Zareba, W.; Utell, M.J.; Oakes, D.; Hopke, P.K.; Frampton, M.; Chalupa, D.; Beckett, W.; Rich, D.Q. Acute Changes in Ambient Temperature Are Associated with Adverse Changes in Cardiac Rhythm. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2014, 7, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranc, H.; Novack, V.; Shtein, A.; Sherman, R.; Novack, L. Extreme temperature and out-of-hospital-cardiac-arrest. Nationwide study in a hot climate country. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanobetti, A.; Coull, B.A.; Kloog, I.; Sparrow, D.; Vokonas, P.S.; Gold, D.R.; Schwartz, J. Fine-scale spatial and temporal variation in temperature and arrhythmia episodes in the VA Normative Aging Study. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, R.P.; Heisel, A.G.; Jung, J.K.; Schieffer, H.J. Circannual variation of malignant ventricular tachyarrhythmias in patients with implantable cardioverter-defibrillators and either coronary artery disease or idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Cardiol. 1997, 79, 1194–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.; Grüdtner, L.; Zimerman, L.I. Seasonal variation of ventricular tachycardia registered in 24-hour Holter monitoring. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2006, 87, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picano, E.; Mangia, C.; D’Andrea, A. Climate Change, Carbon Dioxide Emissions, and Medical Imaging Contribution. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 12, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogelj, J.; den Elzen, M.; Höhne, N.; Fransen, T.; Fekete, H.; Winkler, H.; Schaeffer, R.; Sha, F.; Riahi, K.; Meinshausen, M. Paris Agreement climate proposals need a boost to keep warming well below 2 °C. Nature 2016, 534, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Lledó, A.; Rodríguez-Martín, S.; Tobías, A.; Alonso-Martín, J.; Ansede-Cascudo, J.C.; de Abajo, F.J. Heat waves, ambient temperature, and risk of myocardial infarction: An ecological study in the Community of Madrid. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2020, 73, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryti, N.R.; Guo, Y.; Jaakkola, J.J. Global Association of Cold Spells and Adverse Health Effects: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajat, S.; O’Connor, M.; Kosatsky, T. Health effects of hot weather: From awareness of risk factors to effective health protection. Lancet 2010, 375, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.R.; Choi, S.; Kim, K.; Chang, J.; Kim, S.M.; Cho, Y.; Oh, Y.H.; Lee, G.; Son, J.S.; Kim, K.H.; et al. Association of the combined effects of air pollution and changes in physical activity with cardiovascular disease in young adults. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 2487–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.C.; Hayes, R.B.; Ahn, J.; Shao, Y.; Silverman, D.T.; Jones, R.R.; Thurston, G.D. Mediterranean Diet and the Association Between Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Risk. Circulation 2019, 139, 1766–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, J.; Green, R.; Dangour, A.D.; Haines, A.; Chalabi, Z.; Spadaro, J.; Markandya, A.; Wilkinson, P. Health effects of adopting low greenhouse gas emission diets in the UK. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e007364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layton, J.B.; Li, W.; Yuan, J.; Gilman, J.P.; Horton, D.B.; Setoguchi, S. Heatwaves, medications, and heat-related hospitalization in older Medicare beneficiaries with chronic conditions. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Vita, A.; Belmusto, A.; Di Perna, F.; Tremamunno, S.; De Matteis, G.; Franceschi, F.; Covino, M., on behalf of the CLIMPS Group. The Impact of Climate Change and Extreme Weather Conditions on Cardiovascular Health and Acute Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 759. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030759
De Vita A, Belmusto A, Di Perna F, Tremamunno S, De Matteis G, Franceschi F, Covino M on behalf of the CLIMPS Group. The Impact of Climate Change and Extreme Weather Conditions on Cardiovascular Health and Acute Cardiovascular Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(3):759. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030759
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Vita, Antonio, Antonietta Belmusto, Federico Di Perna, Saverio Tremamunno, Giuseppe De Matteis, Francesco Franceschi, and Marcello Covino on behalf of the CLIMPS Group. 2024. "The Impact of Climate Change and Extreme Weather Conditions on Cardiovascular Health and Acute Cardiovascular Diseases" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 3: 759. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030759
APA StyleDe Vita, A., Belmusto, A., Di Perna, F., Tremamunno, S., De Matteis, G., Franceschi, F., & Covino, M., on behalf of the CLIMPS Group. (2024). The Impact of Climate Change and Extreme Weather Conditions on Cardiovascular Health and Acute Cardiovascular Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(3), 759. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030759






