Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Hip Revision Surgery and Cerclage Wires Fixation for Vancouver B2 and B3 Fractures: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol
2.1.1. Preoperative Planning
2.1.2. Surgical Technique
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
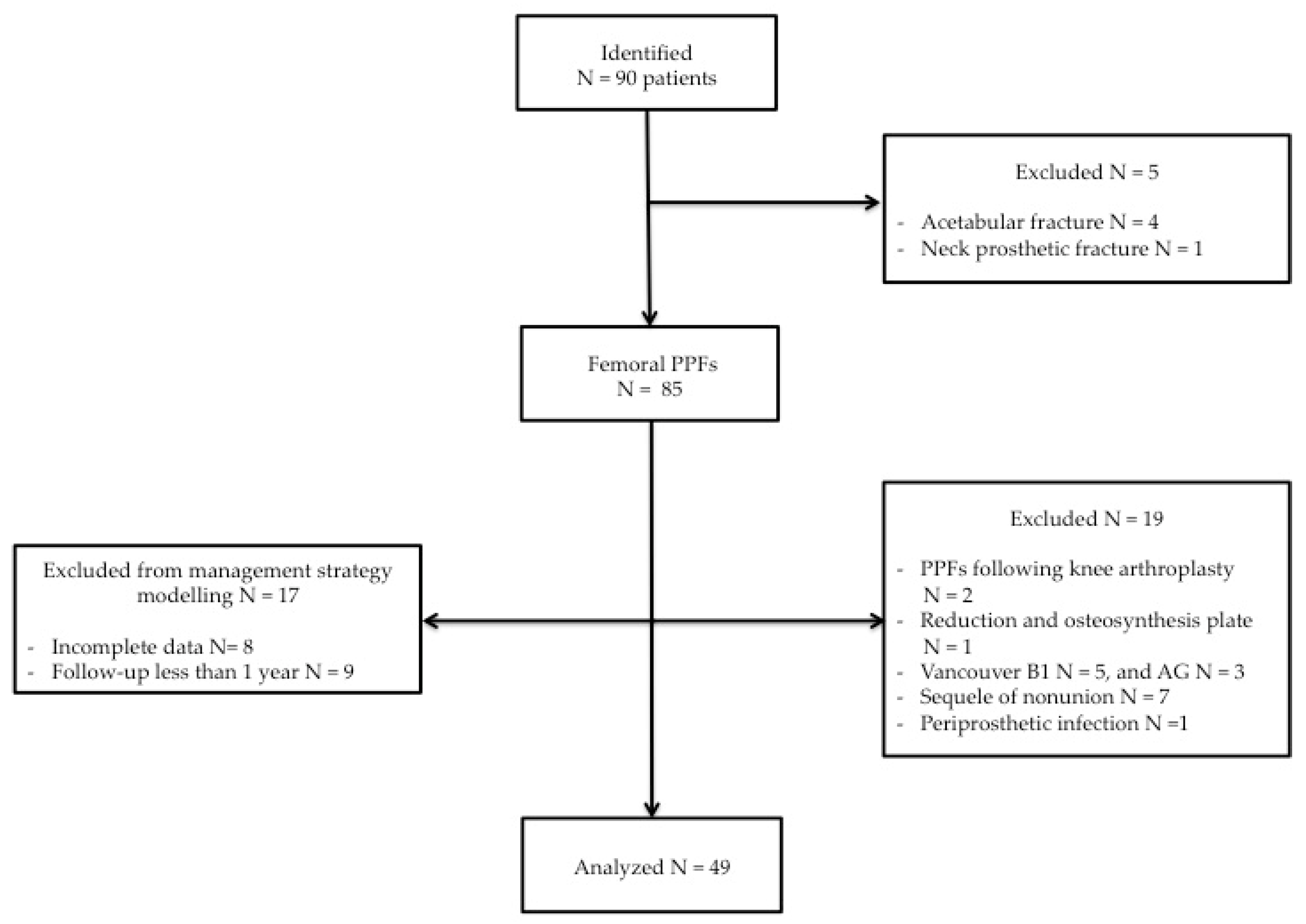
3.1. Selection of Study Population
3.2. Characteristics of Study Population
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pabinger, C.; Lothaller, H.; Portner, N.; Geissler, A. Projections of Hip Arthroplasty in OECD Countries up to 2050. Hip Int. 2018, 28, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernlund, E.; Svedbom, A.; Ivergård, M.; Compston, J.; Cooper, C.; Stenmark, J.; McCloskey, E.V.; Jönsson, B.; Kanis, J.A. Osteoporosis in the European Union: Medical Management, Epidemiology and Economic Burden: A Report Prepared in Collaboration with the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industry Associations (EFPIA). Arch. Osteoporos. 2013, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Ong, K.; Lau, E.; Mowat, F.; Halpern, M. Projections of Primary and Revision Hip and Knee Arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2007, 89, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel, M.P.; Watts, C.D.; Houdek, M.T.; Lewallen, D.G.; Berry, D.J. Epidemiology of Periprosthetic Fracture of the Femur in 32 644 Primary Total Hip Arthroplasties: A 40-Year Experience. Bone Joint J. 2016, 98-B, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kärrholm, J. The Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register (www.shpr.se). Acta Orthop. 2010, 81, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, C.P.; Haddad, F.S. The Unified Classification System (UCS): Improving Our Understanding of Periprosthetic Fractures. Bone Joint J. 2014, 96, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaunay, C.; Hamadouche, M.; Girard, J.; Duhamel, A.; SoFCOT Group. What Are the Causes for Failures of Primary Hip Arthroplasties in France? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013, 471, 3863–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, H.; Malchau, H.; Herberts, P.; Garellick, G. Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures: Classification and Demographics of 1049 Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures from the Swedish National Hip Arthroplasty Register. J. Arthroplast. 2005, 20, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidler-Maier, C.C.; Waddell, J.P. Incidence and Predisposing Factors of Periprosthetic Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Literature Review. Int. Orthop. (SICOT) 2015, 39, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thien, T.M.; Chatziagorou, G.; Garellick, G.; Furnes, O.; Havelin, L.I.; Mäkelä, K.; Overgaard, S.; Pedersen, A.; Eskelinen, A.; Pulkkinen, P.; et al. Periprosthetic Femoral Fracture within Two Years after Total Hip Replacement: Analysis of 437,629 Operations in the Nordic Arthroplasty Register Association Database. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2014, 96, e167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, W.; Sun, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. Risk Factors for the Periprosthetic Fracture after Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Scand. J. Surg. 2015, 104, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capone, A.; Congia, S.; Civinini, R.; Marongiu, G. Periprosthetic Fractures: Epidemiology and Current Treatment. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2017, 14, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The COMPOSE Study Team. Management and Outcomes of Femoral Periprosthetic Fractures at the Hip: Data from the Characteristics, Outcomes and Management of Periprosthetic Fracture Service Evaluation (COMPOSE) Cohort Study. Bone Jt. J. 2022, 104, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottle, A.; Griffiths, R.; White, S.; Wynn-Jones, H.; Aylin, P.; Moppett, I.; Chowdhury, E.; Wilson, H.; Davies, B.M. Periprosthetic Fractures: The next Fragility Fracture Epidemic? A National Observational Study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e042371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, O.H. The Reliability and Validity of the Vancouver Classification of Femoral Fractures After Hip Replacement. J. Arthroplast. 2000, 15, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, O.H.; Garbuz, D.S.; Masri, B.A.; Duncan, C.P. Classification of the HIP. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 1999, 30, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, J.; Rapuri, V.R.; Purtill, J.J.; Sharkey, P.F.; Rothman, R.H.; Hozack, W.J. Treatment Protocol for Proximal Femoral Periprosthetic Fractures. JBJS 2004, 86, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, D.J. Treatment of Vancouver B3 Periprosthetic Femur Fractures with a Fluted Tapered Stem. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2003, 417, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.M.; Moazen, M.; Leonidou, A.; Tsiridis, E. Locking Plate Fixation for Vancouver B1 Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures: A Critical Analysis of 135 Cases. J. Orthop. Sci. 2013, 18, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, E.; Behrend, C.; Bair, J.; Cram, P.; Kates, S. Mortality and Financial Burden of Periprosthetic Fractures of the Femur. Geriatr. Orthop. Surg. Rehabil. 2014, 5, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, J.M.; Griffin, W.L.; Odum, S.M.; Van Doren, B.; Weston, B.T.; Stryker, L.S. Survivorship After Periprosthetic Femur Fracture: Factors Affecting Outcome. J. Arthroplast. 2016, 31, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Matteo, V.; Di Pilla, M.; La Camera, F.; Morenghi, E.; Grappiolo, G.; Loppini, M. Perioperative Complications after Hip and Knee Revision Arthroplasty in the over 80 Years Old Population: A Retrospective Observational Case–Control Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetters, N.G.; Murray, T.G.; Moric, M.; Sporer, S.M.; Paprosky, W.G.; Della Valle, C.J. Risk Factors for Dislocation after Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013, 471, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Yang, Y.; An, B.; Yang, Y.; Shi, L.; Han, X.; Gao, S. Risk Factors for Dislocation after Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2017, 38, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.S.; Twaij, H.; Haddad, F.S. Two-Stage Revision for the Culture-Negative Infected Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Comparative Study. Bone Jt. J. 2018, 100, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dargel, J.; Oppermann, J.; Brüggemann, G.-P.; Eysel, P. Dislocation Following Total Hip Replacement. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2014, 111, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faldini, C.; Stefanini, N.; Fenga, D.; Neonakis, E.M.; Perna, F.; Mazzotti, A.; Pilla, F.; Triantafyllopoulos, I.K.; Traina, F. How to Prevent Dislocation after Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review of the Risk Factors and a Focus on Treatment Options. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2018, 19, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loppini, M.; Longo, U.G.; Caldarella, E.; Rocca, A.D.; Denaro, V.; Grappiolo, G. Femur First Surgical Technique: A Smart Non-Computer-Based Procedure to Achieve the Combined Anteversion in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.C.; Boddapati, V.; Gausden, E.B.; Samuel, A.M.; Russell, L.A.; Lane, J.M. Surgery for a Fracture of the Hip within 24 Hours of Admission Is Independently Associated with Reduced Short-Term Post-Operative Complications. Bone Joint J. 2017, 99-B, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, E.J.; Cash, D.J.W.; Kalra, S.; Hopgood, P.J. Time to Surgery and 30-Day Morbidity and Mortality of Periprosthetic Hip Fractures. Injury 2013, 44, 1949–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, V.N.; McCulloch, R.A.; Dhiman, P.; McGill, A.; Taylor, A.H.; Palmer, A.J.R.; Kendrick, B.J.L. Modifiable Risk Factors for Mortality in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty for Periprosthetic Fracture. Bone Jt. J. 2020, 102, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, W.W.; Egol, K.A.; Zuckerman, J.D.; Siu, A.L. Hip Fracture Management: Tailoring Care for the Older Patient. JAMA 2012, 307, 2185–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konow, T.; Baetz, J.; Melsheimer, O.; Grimberg, A.; Morlock, M. Factors Influencing Periprosthetic Femoral Fracture Risk: A German Registry Study. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Classification | Fracture Location | |
|---|---|---|
| A | AG | Greater trochanter fracture |
| AL | Lesser trochanter fracture | |
| B | B1 | Fracture around the prosthesis, stem well fixed |
| B2 | Fracture around the prosthesis, stem is loose | |
| B3 | Fracture around the prosthesis, loose stem, and poor proximal bone stock | |
| C | Fracture distal to tip of stem | |
| N | 49 |
|---|---|
| Age at surgery | 71.2 ± 2.3 (37–88) |
| Male | 15 (30.6%) |
| Female | 34 (69.4%) |
| Right | 29 (59.2%) |
| Left | 20 (40.8%) |
| PTHA | 43 (87.8%) |
| RTHA | 6 (12.2%) |
| Injury | |
| Major trauma | 6 (12.2%) |
| Minor trauma | 33 (67.3%) |
| Spontaneous | 10 (20.4%) |
| VB2 | 44 (89.8%) |
| VB3 | 5 (10.2%) |
| Time to Surgery (Days) | 3.9 ± 5.2 (0–30) |
|---|---|
| Operating time (minutes) | 104.6 ± 40.1 (45–224) |
| RA alone | 1 (2.0%) |
| RA and Fixation | 48 (98.0%) |
| Cerclage alone | 44 (91.7%) |
| Cerclage, screw and K-wire | 4 (8.3%) |
| Stem RA | 36 (73.4%) |
| RTHA | 13 (26.5%) |
| Uncemented stem | 46 (93.9%) |
| Wagner SL revision | 36 (78.3%) |
| Arcos Modular | 7 (15.2%) |
| Wagner Conus | 3 (6.5%) |
| Cemented stem | 3 (6.1%) |
| MS 30 | 3 (100.0%) |
| Augments | 1 (2.0%) |
| LOS (days) | 7.8 ± 5.4 (3–28) |
| Preoperative | Postoperative | Delta (95% CI) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HHS | 31.1 ± 7.7 (range 10 to 43) | 85.5 ± 14.8 (range 60 to 100) | 54.4 (range 49.6 to 59.2) | <0.001 |
| LLD | 14.6 ± 8.7 (range −39 to +10) | 5.5 ± 4.0 (range −17 to +15) | 12.4 (range 9.9 to 14.9) | <0.001 |
| Mechanical Complications | |
|---|---|
| Dislocation | 3 (6.1%) |
| Intra-operative fracture | 1 (2.0%) |
| Postoperative fracture | 0 (0.0%) |
| Non-union | 0 (0.0%) |
| Periprosthetic infection | 0 (0.0%) |
| Loosening | 0 (0.0%) |
| Eterometry | 1 (2.0%) |
| Failure of synthesis | 2 (4.1%) |
| Medical complications | |
| Superficial Wound infections | 2 (4.1%) |
| UTI | 1 (2.0%) |
| FA | 1 (2.0%) |
| Pneumonia (COPD) | 1 (2.0%) |
| Sciatic nerve palsy | 1 (2.0%) |
| Follow-up (mean (range)) | 63.4 (range 12–129) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Matteo, V.; La Camera, F.; Carfì, C.; Morenghi, E.; Grappiolo, G.; Loppini, M. Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Hip Revision Surgery and Cerclage Wires Fixation for Vancouver B2 and B3 Fractures: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030892
Di Matteo V, La Camera F, Carfì C, Morenghi E, Grappiolo G, Loppini M. Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Hip Revision Surgery and Cerclage Wires Fixation for Vancouver B2 and B3 Fractures: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(3):892. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030892
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Matteo, Vincenzo, Francesco La Camera, Carla Carfì, Emanuela Morenghi, Guido Grappiolo, and Mattia Loppini. 2024. "Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Hip Revision Surgery and Cerclage Wires Fixation for Vancouver B2 and B3 Fractures: A Retrospective Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 3: 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030892
APA StyleDi Matteo, V., La Camera, F., Carfì, C., Morenghi, E., Grappiolo, G., & Loppini, M. (2024). Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Hip Revision Surgery and Cerclage Wires Fixation for Vancouver B2 and B3 Fractures: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(3), 892. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13030892






