An Artificial Intelligence Analysis of Electrocardiograms for the Clinical Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Narrative Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
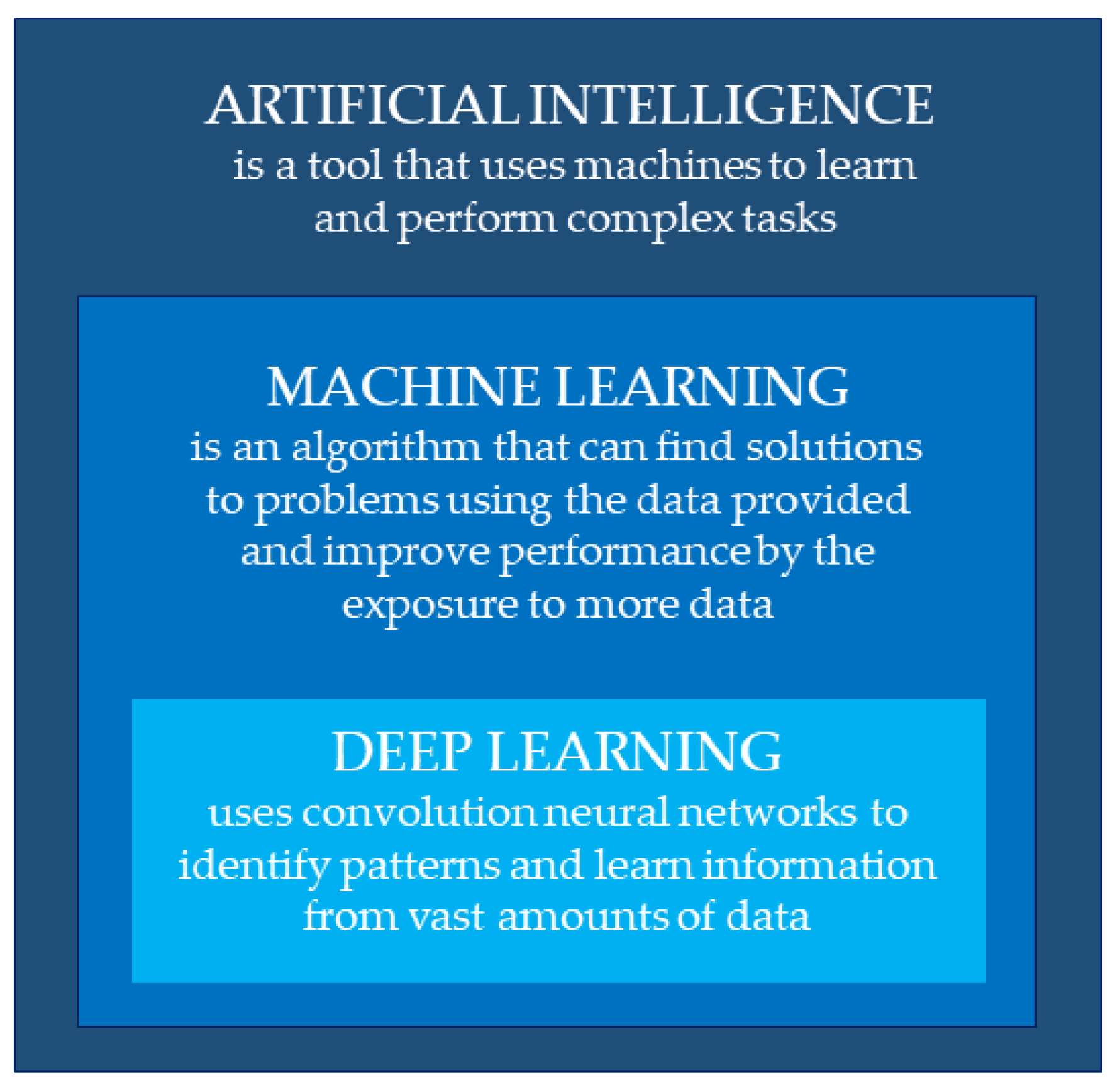
2. Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning
3. Application Fields in Electrocardiography
4. Atrial Fibrillation
5. Aortic Stenosis
6. Ventricular Dysfunction
7. Cardiomyopathies
8. Myocardial Infarction and Ischemic Cardiomyopathy
9. Electrolyte Abnormalities
10. Obstacles and Challenges to Overcome in Artificial Intelligence
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siontis, K.C.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Attia, Z.I.; Friedman, P.A. Artificial intelligence-enhanced electrocardiography in cardiovascular disease management. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Guo, W.; Zhao, L.; Huang, W.; Wang, L.; Sun, A.; Li, L.; Mo, F. Acute Myocardial Infarction Detection Using Deep Learning-Enabled Electrocardiograms. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 654515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bumgarner, J.M.; Lambert, C.T.; Hussein, A.A.; Cantillon, D.J.; Baranowski, B.; Wolski, K.; Lindsay, B.D.; Wazni, O.M.; Tarakji, K.G. Smartwatch Algorithm for Automated Detection of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2381–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserlauf, J.; You, C.; Patel, R.; Valys, A.; Albert, D.; Passman, R. Smartwatch Performance for the Detection and Quantification of Atrial Fibrillation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2019, 12, e006834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaccarotella, C.; Polimeni, A.; Mancuso, C.; Pelaia, G.; Esposito, G.; Indolfi, C. Assessment of Non-Invasive Measurements of Oxygen Saturation and Heart Rate with an Apple Smartwatch: Comparison with a Standard Pulse Oximeter. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaccarotella, C.A.M.; Migliarino, S.; Mongiardo, A.; Sabatino, J.; Santarpia, G.; De Rosa, S.; Curcio, A.; Indolfi, C. Measurement of the QT interval using the Apple Watch. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaccarotella, C.; Santarpia, G.; Curcio, A.; Indolfi, C. The smartwatch detects ECG abnormalities typical of Brugada syndrome. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 22, e24–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaccarotella, C.A.M.; Polimeni, A.; Migliarino, S.; Principe, E.; Curcio, A.; Mongiardo, A.; Sorrentino, S.; De Rosa, S.; Indolfi, C. Multichannel Electrocardiograms Obtained by a Smartwatch for the Diagnosis of ST-Segment Changes. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 1176–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Shelly, M.; I Attia, Z.; A Friedman, P.; Ito, S.; A Essayagh, B.; Ko, W.-Y.; Murphree, D.H.; Michelena, H.I.; Enriquez-Sarano, M.; E Carter, R.; et al. Electrocardiogram screening for aortic valve stenosis using artificial intelligence. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 2885–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somani, S.; Russak, A.J.; Richter, F.; Zhao, S.; Vaid, A.; Chaudhry, F.; De Freitas, J.K.; Naik, N.; Miotto, R.; Nadkarni, G.N.; et al. Deep learning and the electrocardiogram: Review of the current state-of-the-art. EP Eur. 2021, 23, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, H.; Ohlsson, M.; Peterson, C.; Edenbrandt, L. A confident decision support system for interpreting electrocardiograms: A confident decision support system. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 1999, 19, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogun, F.; Anh, D.; Kalahasty, G.; Wissner, E.; Serhal, C.B.; Bazzi, R.; Weaver, W.D.; Schuger, C. Misdiagnosis of atrial fibrillation and its clinical consequences. Am. J. Med. 2004, 117, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I Attia, Z.; Harmon, D.M.; Behr, E.R.; A Friedman, P. Application of artificial intelligence to the electrocardiogram. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 4717–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, S.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, P. Interpretable deep learning for automatic diagnosis of 12-lead electrocardiogram. iScience 2021, 24, 102373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, G.D.; Liu, C.; Moody, B.; Lehman, L.H.; Silva, I.; Li, Q.; Johnson, A.E.; Mark, R.G. AF Classification from a Short Single Lead ECG Recording: The PhysioNet/Computing in Cardiology Challenge 2017. In Proceedings of the 2017 Computing in Cardiology (CinC), Rennes, France, 24–27 September 2017; Volume 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Stiles, M.; Zhao, J. Robust ECG Signal Classification for the Detection of Atrial Fibrillation Using Novel Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 Computing in Cardiology Conference, Rennes, France, 24–27 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.-M.; Huang, C.-H.; Shih, E.S.; Hu, Y.-F.; Hwang, M.-J. Detection and Classification of Cardiac Arrhythmias by a Challenge-Best Deep Learning Neural Network Model. iScience 2020, 23, 100886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannun, A.Y.; Rajpurkar, P.; Haghpanahi, M.; Tison, G.H.; Bourn, C.; Turakhia, M.P.; Ng, A.Y. Cardiologist-level arrhythmia detection and classification in ambulatory electrocardiograms using a deep neural network. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Cheng, C.; Yin, H.; Li, X.; Zuo, P.; Ding, J.; Lin, F.; Wang, J.; Zhou, B.; Li, Y.; et al. Automatic multilabel electrocardiogram diagnosis of heart rhythm or conduction abnormalities with deep learning: A cohort study. Lancet Digit. Health 2020, 2, e348–e357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Wu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Shang, J.; Li, H.; Xie, J. ENCASE: An ENsemble ClASsifiEr for ECG Classification Using Expert Features and Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 Computing in Cardiology Conference, Rennes, France, 24–27 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I Attia, Z.; A Noseworthy, P.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Asirvatham, S.J.; Deshmukh, A.J.; Gersh, B.J.; E Carter, R.; Yao, X.; A Rabinstein, A.; Erickson, B.J.; et al. An artificial intelligence-enabled ECG algorithm for the identification of patients with atrial fibrillation during sinus rhythm: A retrospective analysis of outcome prediction. Lancet 2019, 394, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunath, S.; Pfeifer, J.M.; Ulloa-Cerna, A.E.; Nemani, A.; Carbonati, T.; Jing, L.; Vanmaanen, D.P.; Hartzel, D.N.; Ruhl, J.A.; Lagerman, B.F.; et al. Deep Neural Networks Can Predict New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation From the 12-Lead ECG and Help Identify Those at Risk of Atrial Fibrillation–Related Stroke. Circulation 2021, 143, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörr, M.; Nohturfft, V.; Brasier, N.; Bosshard, E.; Djurdjevic, A.; Gross, S.; Raichle, C.J.; Rhinisperger, M.; Stöckli, R.; Eckstein, J. The WATCH AF Trial: SmartWATCHes for Detection of Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2019, 5, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, T.; Liang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Yan, L.; Xing, Y.; Shi, H.; Li, S.; et al. Mobile Photoplethysmographic Technology to Detect Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 2365–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tison, G.H.; Sanchez, J.M.; Ballinger, B.; Singh, A.; Olgin, J.E.; Pletcher, M.J.; Vittinghoff, E.; Lee, E.S.; Fan, S.M.; Gladstone, R.A.; et al. Passive Detection of Atrial Fibrillation Using a Commercially Available Smartwatch. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Jeon, K.; Lee, Y.; Kim, K.; Park, J.; Oh, B.; Lee, M. Deep Learning–Based Algorithm for Detecting Aortic Stenosis Using Electrocardiography. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, D.M.; Malik, A.; Nishimura, R. Progression of Calcific Aortic Stenosis Detected by Artificial Intelligence Electrocardiogram. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2022, 97, 1211–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.-M.; Kim, K.-H.; Akkus, Z.; Jeon, K.-H.; Park, J.; Oh, B.-H. Artificial intelligence for detecting mitral regurgitation using electrocardiography. J. Electrocardiol. 2020, 59, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, Z.I.; Kapa, S.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; McKie, P.M.; Ladewig, D.J.; Satam, G.; Pellikka, P.A.; Enriquez-Sarano, M.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Munger, T.M.; et al. Screening for cardiac contractile dysfunction using an artificial intelligence–enabled electrocardiogram. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adedinsewo, D.; Carter, R.E.; Attia, Z.; Johnson, P.; Kashou, A.H.; Dugan, J.L.; Albus, M.; Sheele, J.M.; Bellolio, F.; Friedman, P.A.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Enabled ECG Algorithm to Identify Patients With Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction Presenting to the Emergency Department With Dyspnea. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2020, 13, e008437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaid, A.; Johnson, K.W.; Badgeley, M.A.; Somani, S.S.; Bicak, M.; Landi, I.; Russak, A.; Zhao, S.; Levin, M.A.; Freeman, R.S.; et al. Using Deep-Learning Algorithms to Simultaneously Identify Right and Left Ventricular Dysfunction from the Electrocardiogram. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 15, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, Q.A.; Tereshchenko, L.G.; Kongkatong, M.; Abraham, T.; Abraham, M.R.; Shatkay, H. Utilizing ECG-Based Heartbeat Classification for Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Identification. IEEE Trans. NanoBioscience 2015, 14, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, W.-Y.; Siontis, K.C.; Attia, Z.I.; Carter, R.E.; Kapa, S.; Ommen, S.R.; Demuth, S.J.; Ackerman, M.J.; Gersh, B.J.; Arruda-Olson, A.M.; et al. Detection of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Using a Convolutional Neural Network-Enabled Electrocardiogram. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tison, G.H.; Zhang, J.; Delling, F.N.; Deo, R.C. Automated and Interpretable Patient ECG Profiles for Disease Detection, Tracking, and Discovery. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2019, 12, e005289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, U.R.; Fujita, H.; Oh, S.L.; Hagiwara, Y.; Tan, J.H.; Adam, M. Application of deep convolutional neural network for automated detection of myocardial infarction using ECG signals. Inf. Sci. 2017, 415–416, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Huang, Q.; Chang, S.; Wang, H.; He, J. Multiple-feature-branch convolutional neural network for myocardial infarction diagnosis using electrocardiogram. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 45, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloglu, U.B.; Talo, M.; Yildirim, O.; Tan, R.S.; Acharya, U.R. Classification of myocardial infarction with multi-lead ECG signals and deep CNN. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 122, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALodhi, M.; Qureshi, A.N.; Sharif, U.; Ashiq, Z. A Novel Approach Using Voting from ECG Leads to Detect Myocardial Infarction. In Intelligent Systems and Applications; Arai, K., Kapoor, S., Bhatia, R., Eds.; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 869, pp. 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-W.; Wang, Y.-C.; Liu, M.-H.; Tsai, B.-Y.; Wu, M.-Y.; Hsieh, P.-H.; Wei, J.-T.; Shih, E.S.C.; Shiao, Y.-T.; Hwang, M.-J.; et al. Artificial intelligence-assisted remote detection of ST-elevation myocardial infarction using a mini-12-lead electrocardiogram device in prehospital ambulance care. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1001982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumpfer, N.; Grün, D.; Hannig, J.; Keller, T.; Guckert, M. Detecting myocardial scar using electrocardiogram data and deep neural networks. Biol. Chem. 2021, 402, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, C.D.; Valys, A.V.; Shreibati, J.B.; Treiman, D.L.; Petterson, F.L.; Gundotra, V.P.; Albert, D.E.; Attia, Z.I.; Carter, R.E.; Asirvatham, S.J.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep-Learning Model to Screen for Hyperkalemia From the Electrocardiogram. JAMA Cardiol. 2019, 4, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-S.; Fang, W.-H.; Hsu, C.-J.; Chen, S.-J.; Huang, K.-H.; Lin, W.-S.; Tsai, C.-S.; Kuo, C.-C.; Chau, T.; Yang, S.J.; et al. A Deep-Learning Algorithm (ECG12Net) for Detecting Hypokalemia and Hyperkalemia by Electrocardiography: Algorithm Development. JMIR Med. Inform. 2020, 8, e15931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, Z.I.; DeSimone, C.V.; Dillon, J.J.; Sapir, Y.; Somers, V.K.; Dugan, J.L.; Bruce, C.J.; Ackerman, M.J.; Asirvatham, S.J.; Striemer, B.L.; et al. Novel Bloodless Potassium Determination Using a Signal-Processed Single-Lead ECG. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.-A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siontis, K.C.; Gersh, B.J.; Killian, J.M.; Noseworthy, P.A.; McCabe, P.; Weston, S.A.; Roger, V.L.; Chamberlain, A.M. Typical, atypical, and asymptomatic presentations of new-onset atrial fibrillation in the community: Characteristics and prognostic implications. Heart Rhythm. 2016, 13, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladstone, D.J.; Spring, M.; Dorian, P.; Panzov, V.; Thorpe, K.E.; Hall, J.; Vaid, H.; O’Donnell, M.; Laupacis, A.; Côté, R.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Cryptogenic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2467–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopoulos, G.; Graff-Radford, J.; Lopez, C.L.; Yao, X.; Attia, Z.I.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Petersen, R.C.; Knopman, D.S.; Mielke, M.M.; Kremers, W.; et al. Artificial Intelligence–Electrocardiography to Predict Incident Atrial Fibrillation: A Population-Based Study. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2020, 13, e009355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Attia, Z.I.; Behnken, E.M.; Walvatne, K.; Giblon, R.E.; Liu, S.; Siontis, K.C.; Gersh, B.J.; Graff-Radford, J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; et al. Batch enrollment for an artificial intelligence-guided intervention to lower neurologic events in patients with undiagnosed atrial fibrillation: Rationale and design of a digital clinical trial. Am. Heart J. 2021, 239, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindricks, G.; Pokushalov, E.; Urban, L.; Taborsky, M.; Kuck, K.-H.; Lebedev, D.; Rieger, G.; Pürerfellner, H. Performance of a New Leadless Implantable Cardiac Monitor in Detecting and Quantifying Atrial Fibrillation Results of the XPECT Trial. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2010, 3, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hygrell, T.; Viberg, F.; Dahlberg, E.; Charlton, P.H.; Gudmundsdottir, K.K.; Mant, J.; Hörnlund, J.L.; Svennberg, E. An artificial intelligence–based model for prediction of atrial fibrillation from single-lead sinus rhythm electrocardiograms facilitating screening. EP Eur. 2023, 25, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, M.; Parker, D.; Weston, C.; Bowes, M. Screening for atrial fibrillation: Sensitivity and specificity of a new methodology. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2011, 61, 38–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Hedlin, H.; Rumsfeld, J.S.; Garcia, A.; Ferris, T.; Balasubramanian, V.; Russo, A.M.; Rajmane, A.; Cheung, L.; et al. Large-Scale Assessment of a Smartwatch to Identify Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindman, B.R.; Clavel, M.-A.; Mathieu, P.; Iung, B.; Lancellotti, P.; Otto, C.M.; Pibarot, P. Calcific aortic stenosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 16006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, C.M.; Prendergast, B. Aortic-Valve Stenosis—From Patients at Risk to Severe Valve Obstruction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polimeni, A.; Sorrentino, S.; De Rosa, S.; Spaccarotella, C.; Mongiardo, A.; Sabatino, J.; Indolfi, C. Transcatheter Versus Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement in Low-Risk Patients for the Treatment of Severe Aortic Stenosis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaccarotella, C.; Mongiardo, A.; De Rosa, S.; Indolfi, C. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation in patients at intermediate surgical risk. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 243, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagendorff, A.; Knebel, F.; Helfen, A.; Knierim, J.; Sinning, C.; Stöbe, S.; Fehske, W.; Ewen, S. Expert consensus document on the assessment of the severity of aortic valve stenosis by echocardiography to provide diagnostic conclusiveness by standardized verifiable documentation. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2020, 109, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.-H.; Park, S.-J.; Lee, S.-A.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, H.-K.; Yun, S.-C.; Hong, G.-R.; Song, J.-M.; Chung, C.-H.; et al. Early Surgery or Conservative Care for Asymptomatic Aortic Stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, R.; Rizzoli, G.; Stritoni, P.; Seminara, G.; Rubino, M.; Brumana, T. T-wave changes in patients with hemodynamic evidence of systolic or diastolic overload of the left ventricle: A retrospective study on 168 patients with isolated chronic aortic valve disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 1987, 14, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redfield, M.M.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Burnett, J.C.; Mahoney, D.W.; Bailey, K.R.; Rodeheffer, R.J. Burden of Systolic and Diastolic Ventricular Dysfunction in the Community: Appreciating the Scope of the Heart Failure Epidemic. JAMA 2003, 289, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omland, T.; Aakvaag, A.; Vik-Mo, H. Plasma cardiac natriuretic peptide determination as a screening test for the detection of patients with mild left ventricular impairment. Heart 1996, 76, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, T.T.; Kulecz, W.B.; Feiveson, A.H.; Greco, E.C.; DePalma, J.L.; Starc, V.; Vrtovec, B.; Rahman, M.A.; Bungo, M.W.; Hayat, M.J.; et al. Accuracy of advanced versus strictly conventional 12-lead ECG for detection and screening of coronary artery disease, left ventricular hypertrophy and left ventricular systolic dysfunction. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2010, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; McCoy, R.G.; Friedman, P.A.; Shah, N.D.; Barry, B.A.; Behnken, E.M.; Inselman, J.W.; Attia, Z.I.; Noseworthy, P.A. ECG AI-Guided Screening for Low Ejection Fraction (EAGLE): Rationale and design of a pragmatic cluster randomized trial. Am. Heart J. 2020, 219, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, R.; Goto, S.; Katsumata, Y.; A MacRae, C.; Deo, R.C. Importance of external validation and subgroup analysis of artificial intelligence in the detection of low ejection fraction from electrocardiograms. Eur. Heart J.-Digit. Health 2022, 3, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, S.; Hohenstein, S.; Nitsche, A.; Pellissier, V.; Leiner, J.; Stellmacher, L.; Hindricks, G.; Bollmann, A. Artificial intelligence-based identification of left ventricular systolic dysfunction from 12-lead electrocardiograms: External validation and advanced application of an existing model. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2023, ztad081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, P.M.; Gimeno, J.R.; Thaman, R.; Shah, J.; Ward, D.; Dickie, S.; Esteban, M.T.T.; McKenna, W.J. Historical trends in reported survival rates in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Heart 2005, 92, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Lipshultz, S.; Orav, E.J.; Wilkinson, J.D.; A Towbin, J.; E Messere, J.; Lowe, A.M.; A Sleeper, L.; Cox, G.F.; Hsu, D.T.; E Canter, C.; et al. Risk stratification at diagnosis for children with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: An analysis of data from the Pediatric Cardiomyopathy Registry. Lancet 2013, 382, 1889–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbelo, E.; Arbelo, E.; Protonotarios, A.; Protonotarios, A.; Gimeno, J.R.; Gimeno, J.R.; Arbustini, E.; Arbustini, E.; Barriales-Villa, R.; Barriales-Villa, R.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of cardiomyopathies. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3503–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Byrne, R.; Rossello, X.; Coughlan, J.J.; Barbato, E.; Berry, C.; Chieffo, A.; Claeys, M.J.; Dan, G.-A.; Dweck, M.R.; Galbraith, M.; et al. 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3720–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, R.K.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Pachori, R.B. Localization of Myocardial Infarction From Multi-Lead ECG Signals Using Multiscale Analysis and Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Sensors J. 2019, 19, 11437–11448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Hwang, H.-G.; Tseng, V.S. Convolutional neural network based automatic screening tool for cardiovascular diseases using different intervals of ECG signals. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 203, 106035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadesse, G.A.; Javed, H.; Weldemariam, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Zhu, T. DeepMI: Deep multi-lead ECG fusion for identifying myocardial infarction and its occurrence-time. Artif. Intell. Med. 2021, 121, 102192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Airhart, S.; Murali, S. Ischemic Cardiomyopathy. In Encyclopedia of Cardiovascular Research and Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2023 Focused Update of the 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3627–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.-M.; Jo, Y.-Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.-H. Artificial intelligence using electrocardiography: Strengths and pitfalls. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 2896–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Javadi, G.; Hamilton, A.; Sibley, S.; Laird, P.; Abolmaesumi, P.; Maslove, D.; Mousavi, P. Quantifying deep neural network uncertainty for atrial fibrillation detection with limited labels. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saporta, A.; Gui, X.; Agrawal, A.; Pareek, A.; Truong, S.Q.H.; Nguyen, C.D.T.; Ngo, V.-D.; Seekins, J.; Blankenberg, F.G.; Ng, A.Y.; et al. Benchmarking saliency methods for chest X-ray interpretation. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2022, 4, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, X. An Overview of Overfitting and its Solutions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1168, 022022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Zhou, S.; Trayanova, N.A. Optimal ECG-lead selection increases generalizability of deep learning on ECG abnormality classification. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2021, 379, 20200258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Hu, Y.; Foschini, L.; Chinitz, L.; Jankelson, L.; Ranganath, R. Deep learning models for electrocardiograms are susceptible to adversarial attack. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Field of Application | Authors | Disease Detected | AUC | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atrial fibrillation | Attia et al. [21] | Afib during sinus rhythm | 0.87 | 79 | 79 |
| Raghunath et al. [22] | New-Onset Afib | 0.85 | 69 | 81 | |
| Dorr et al. [23] | Afib using smart watch | 0.93 | 94 | 98 | |
| Guo et al. [24] | Afib using smart watch | - | 93 | 84 | |
| Tison et al. [25] | Afib using smart watch | 0.97 | 98 | 90 | |
| Valvulopathies | Cohen-Shelly et al. [9] | AS | 0.85 | 78 | 74 |
| Kwon et al. [26] | AS | 0.87 | 80 | 79 | |
| Harmon et al. [27] | AS progression | - | 78 | 74 | |
| Kwon et al. [28] | MR | 0.84 | 90 | 61 | |
| Ventricular dysfunction | Attia et al. [29] | HFrEF | 0.93 | 86 | 86 |
| Adedinsewo et al. [30] | HFrEF | 0.89 | 74 | 87 | |
| Vaid et al. [31] | LV/RV dysfunction | 0.84 | 76 | 76 | |
| Cardiomyopathies | Rahman et al. [32] | HCM | 0.85 | 90 | 90 |
| Ko et al. [33] | HCM | 0.96 | 87 | 91 | |
| Tison et al. [34] | HCM | 0.91 | - | - | |
| PAH | 0.94 | 80 | 90 | ||
| CA | 0.86 | - | - | ||
| MVP | 0.77 | - | - | ||
| Myocardial infarction | Acharya et al. [35] | MI | - | 95 | 94 |
| Liu et al. [36] | MI | - | 95 | 97 | |
| Baloglu et al. [37] | MI | - | 99 | - | |
| Lodhi et al. [38] | MI | - | 94 | 86 | |
| Chen et al. [39] | MI | 0,99 | - | 99 | |
| Ischemic cardiomyopathy | Gumpfer et al. [40] | Myocardial scar | 0.89 | 70 | 84 |
| Electrolyte abnormalities | Galloway et al. [41] | Hyperkalemia | 0.86 | 90 | 58 |
| Lin et al. [42] | Hyperkalemia | 0.96 | 83 | 98 | |
| Hypokalemia | 0.93 | 97 | 93 | ||
| Attia et al. [43] | Bloodless K+ Determination | - | - | - |
| Explainability | Uncertainty | Robustness | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Obstacle | The inability to monitor the mechanism of black boxes and correct the risk of unreasonable decisions leads to important ethical problems. | Uncertainty error is related to the use of raw data, which increases the amount of noise. Overfitting occurs when input data are not generalizable to the entire population and are more specific than a single location where they were collected. | Misinterpretation of misleading data that are misclassified. |
| Challenge | Explainable artificial intelligence would make the machine’s decision-making process known, allowing ethical problems to be overcome. | The quantification of uncertainty is crucial to increase confidence in the results obtained. | Robust model of correct recognition of contradictory input for accurate and correct classification. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Costanzo, A.; Spaccarotella, C.A.M.; Esposito, G.; Indolfi, C. An Artificial Intelligence Analysis of Electrocardiograms for the Clinical Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13041033
Di Costanzo A, Spaccarotella CAM, Esposito G, Indolfi C. An Artificial Intelligence Analysis of Electrocardiograms for the Clinical Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(4):1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13041033
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Costanzo, Assunta, Carmen Anna Maria Spaccarotella, Giovanni Esposito, and Ciro Indolfi. 2024. "An Artificial Intelligence Analysis of Electrocardiograms for the Clinical Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Narrative Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 4: 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13041033
APA StyleDi Costanzo, A., Spaccarotella, C. A. M., Esposito, G., & Indolfi, C. (2024). An Artificial Intelligence Analysis of Electrocardiograms for the Clinical Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(4), 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13041033






