Effect of Multi-Dose Dispensing on Medication Regimen Complexity: A Real-World Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
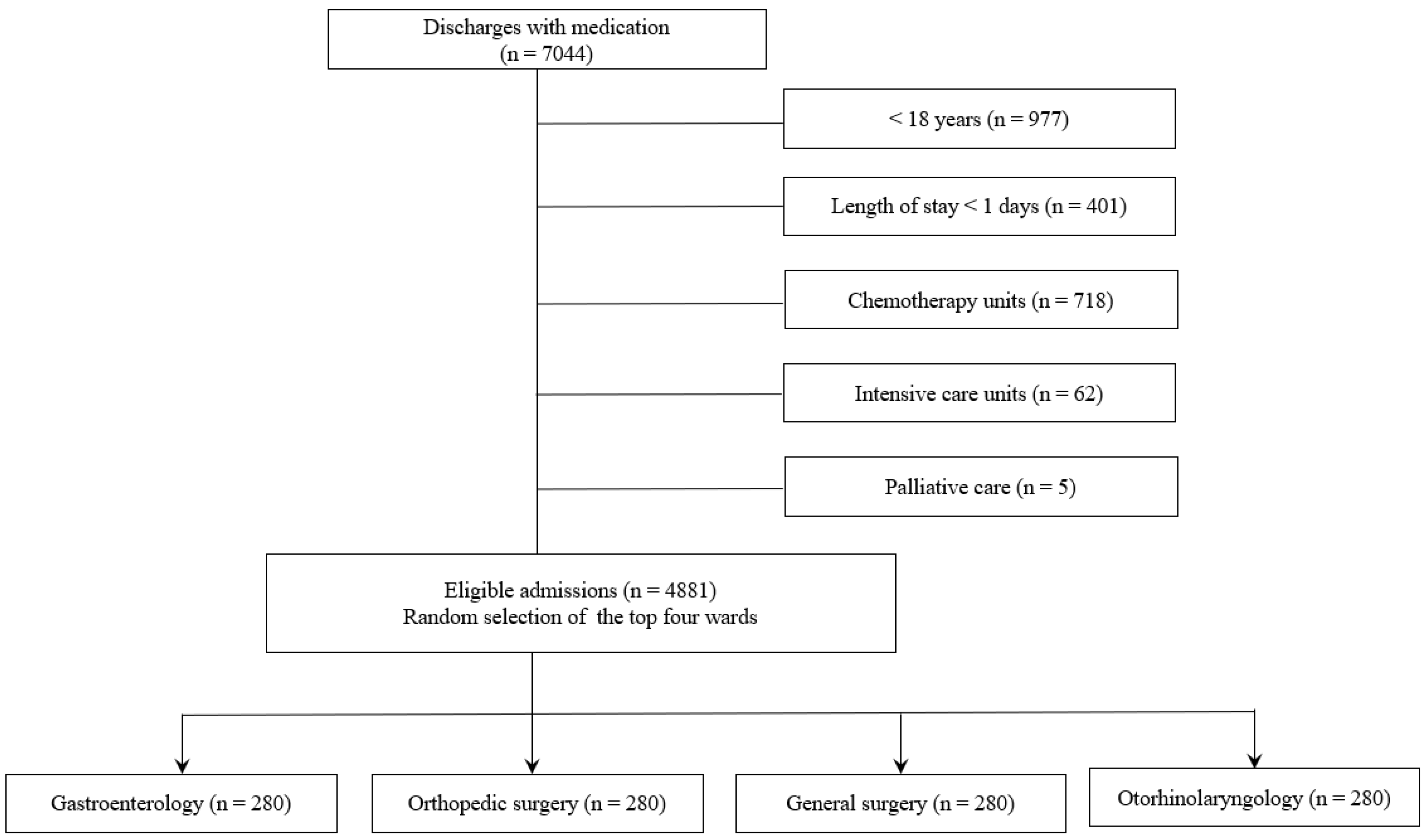
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. Data Collection
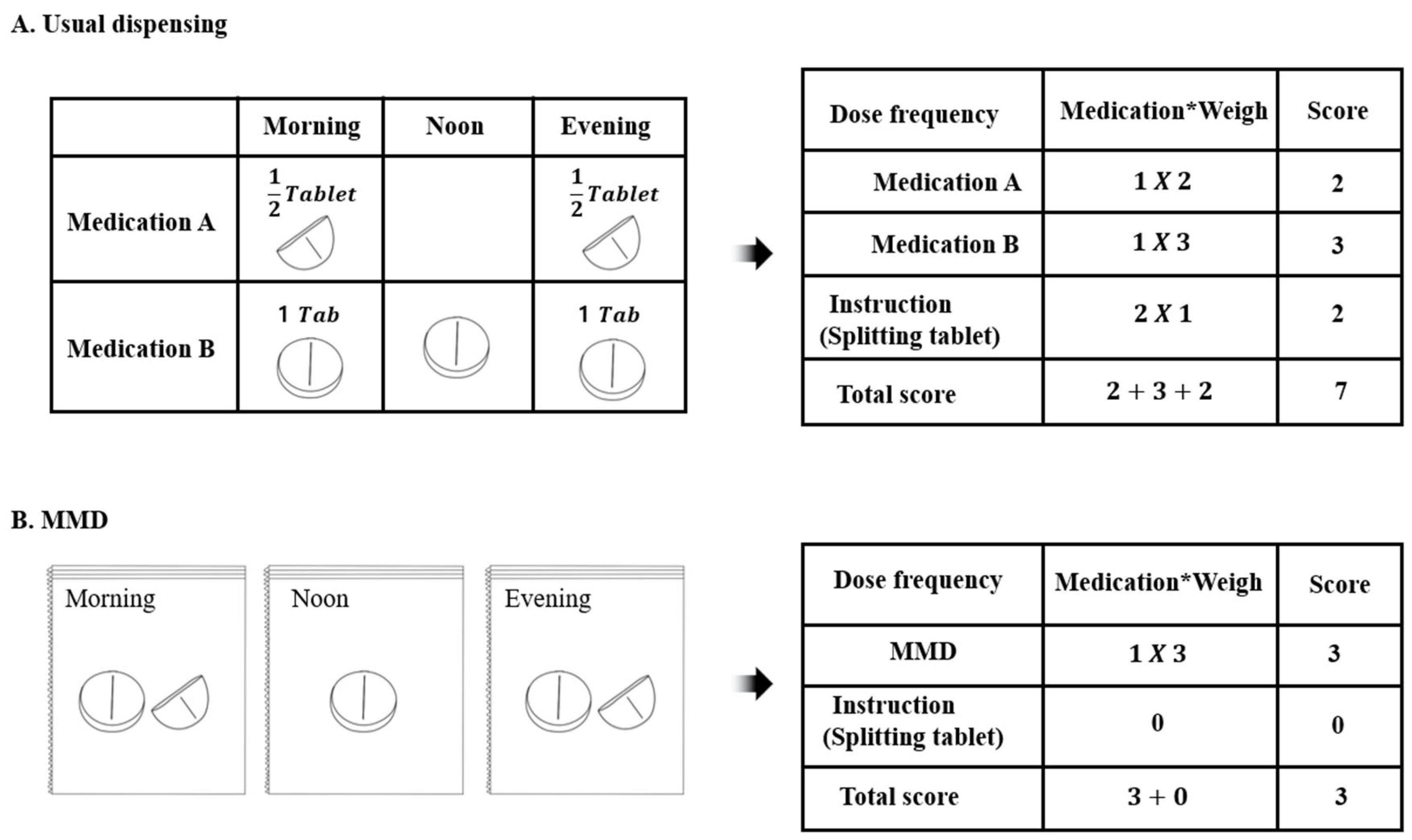
2.3. Study Outcome
Multi-Dose Dispensing (MMD)
2.4. MRCI Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
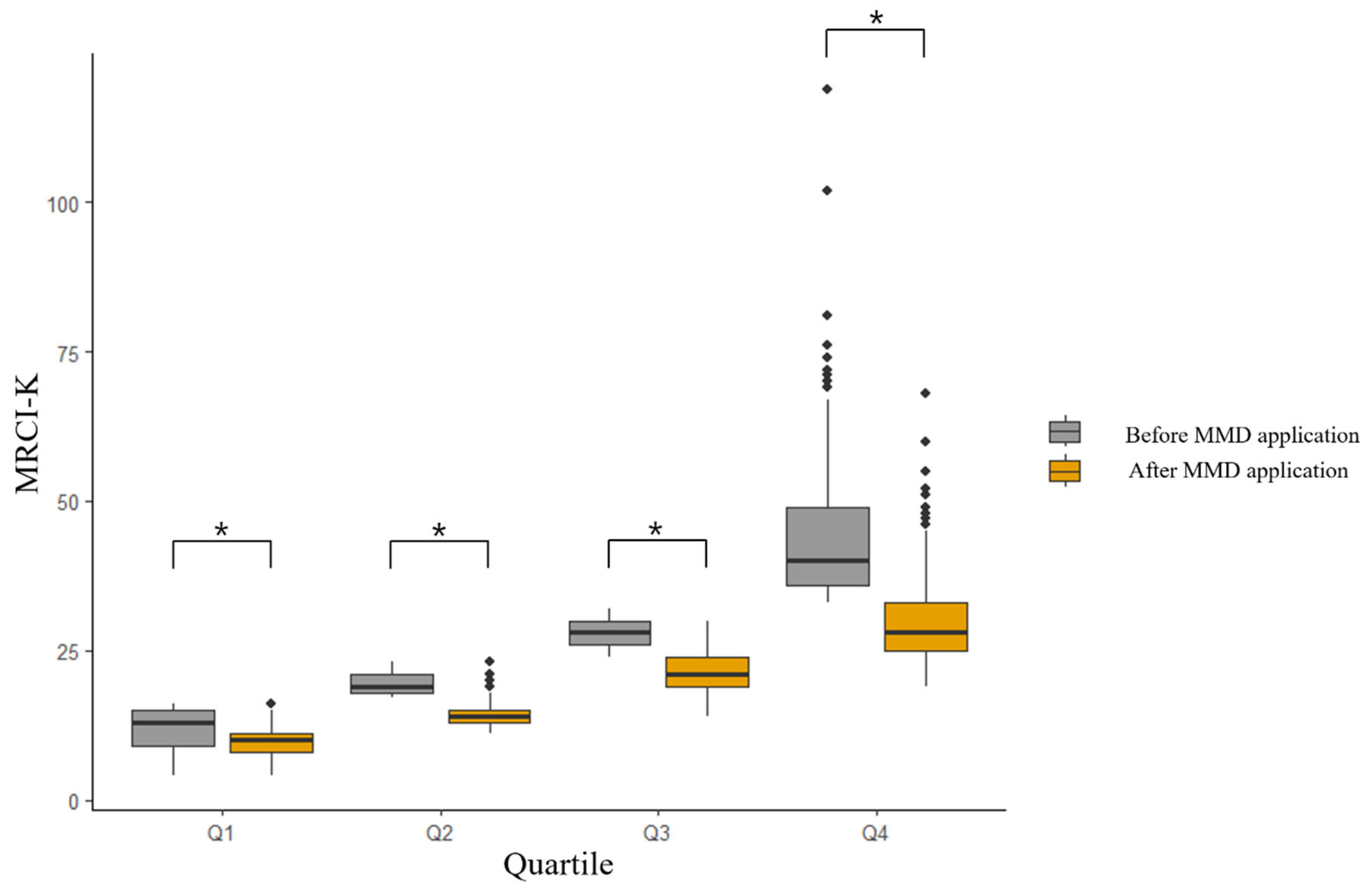
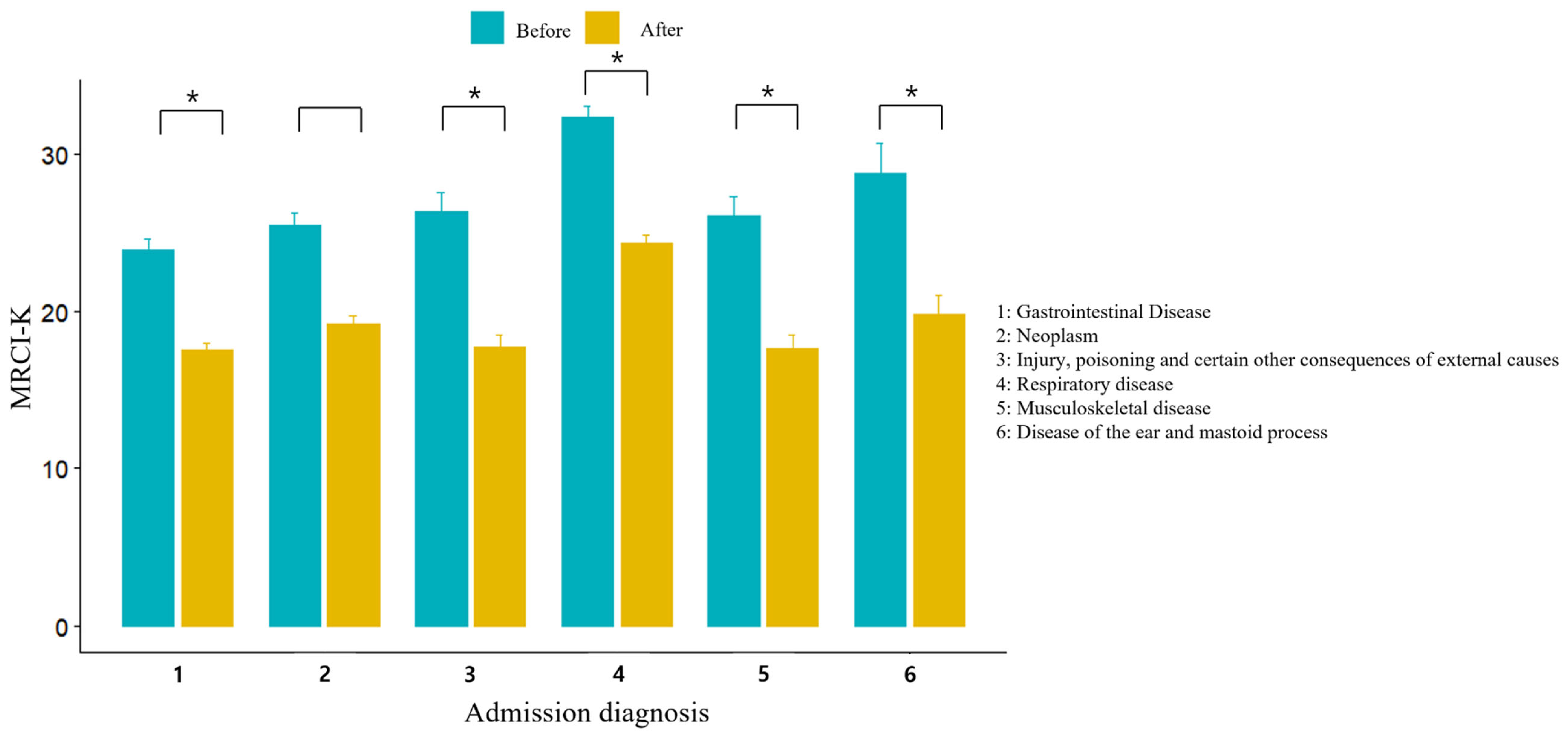
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mansur, N.; Weiss, A.; Beloosesky, Y. Looking beyond polypharmacy: Quantification of medication regimen complexity in the elderly. Am. J. Geriatr. Pharmacother. 2012, 10, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantuzza, L.L.; Ceccato, M.D.G.B.; Silveira, M.R.; Junqueira, L.M.R.; Reis, A.M.M. Association between medication regimen complexity and pharmacotherapy adherence: A systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 73, 1475–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sluggett, J.K.; Chen, E.Y.; Ilomäki, J.; Corlis, M.; Hilmer, S.N.; Van Emden, J.; Ooi, C.E.; Nguyen, K.-H.; Comans, T.; Hogan, M. Simplification of Medications Prescribed to Long-term care Residents (SIMPLER): Study protocol for a cluster randomised controlled trial. Trials 2018, 19, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paquin, A.M.; Zimmerman, K.M.; Kostas, T.R.; Pelletier, L.; Hwang, A.; Simone, M.; Skarf, L.M.; Rudolph, J.L. Complexity perplexity: A systematic review to describe the measurement of medication regimen complexity. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2013, 12, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, J.; Phun, Y.-T.; Bailey, M.J.; Kong, D.C.; Stewart, K. Development and validation of the medication regimen complexity index. Ann. Pharmacother. 2004, 38, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, J.D.; Metz, K.R.; Hosokawa, P.W.; Libby, A.M. Validation of a patient-level medication regimen complexity index as a possible tool to identify patients for medication therapy management intervention. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2014, 34, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stange, D.; Kriston, L.; Langebrake, C.; Cameron, L.K.; Wollacott, J.D.; Baehr, M.; Dartsch, D.C. Development and psychometric evaluation of the German version of the Medication Regimen Complexity Index (MRCI-D). J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2012, 18, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jang, J.; Yang, S.; Hahn, J.; Min, K.L.; Jung, E.H.; Oh, K.S.; Cho, R.; Chang, M.J. Development and validation of the Korean version of the medication regimen complexity index. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantuzza, L.L.; Ceccato, M.D.G.B.; Silveira, M.R.; Pinto, I.V.; Reis, A.M.M. Validation and standardization of the Brazilian version of the Medication Regimen Complexity Index for older adults in primary care. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2018, 18, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwint, H.-F.; Faber, A.; Gussekloo, J.; Bouvy, M.L. Effects of medication review on drug-related problems in patients using automated drug-dispensing systems: A pragmatic randomized controlled study. Drugs Aging 2011, 28, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallerstedt, S.M.; Fastbom, J.; Johnell, K.; Sjöberg, C.; Landahl, S.; Sundström, A. Drug treatment in older people before and after the transition to a multi-dose drug dispensing system–a longitudinal analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Coleman, C.I.; Limone, B.; Sobieraj, D.M.; Lee, S.; Roberts, M.S.; Kaur, R.; Alam, T. Dosing frequency and medication adherence in chronic disease. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2012, 18, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.T.; Kowalski, S.R.; Sorich, W.; Alderman, C.P. Medication regimen complexity and prevalence of potentially inappropriate medicines in older patients after hospitalisation. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2017, 39, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stange, D.; Kriston, L.; Baehr, M.; Dartsch, D. Simplification of medication regimens ñ a novel aspect of pharmaceutical care in hospital. Eur. J. Hosp. Pharm. Sci. Pract. 2012, 19, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, A.M.; Fish, D.N.; Hosokawa, P.W.; Linnebur, S.A.; Metz, K.R.; Nair, K.V.; Saseen, J.J.; Griend, J.P.V.; Vu, S.P.; Hirsch, J.D. Patient-level medication regimen complexity across populations with chronic disease. Clin. Ther. 2013, 35, 385–398.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellostas-Muñoz, L.; Díez-Manglano, J. Complexity of the medication regimen for polypathological patients. Rev. Clín. Española (Engl. Ed.) 2018, 218, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krska, J.; Corlett, S.A.; Katusiime, B. Complexity of medicine regimens and patient perception of medicine burden. Pharmacy 2019, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falch, C.; Alves, G. Pharmacists’ role in older adults’ medication regimen complexity: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, R.A.; O’Callaghan, C.; Paul, E.; George, J. Impact of an intervention to reduce medication regimen complexity for older hospital inpatients. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2013, 35, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouranayatihosseinabad, M.; Zaidi, T.S.; Peterson, G.; Nishtala, P.S.; Hannan, P.; Castelino, R. The impact of residential medication management reviews (RMMRs) on medication regimen complexity. Postgrad. Med. 2018, 130, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linnebur, S.A.; Griend, J.P.V.; Metz, K.R.; Hosokawa, P.W.; Hirsch, J.D.; Libby, A.M. Patient-level medication regimen complexity in older adults with depression. Clin. Ther. 2014, 36, 1538–1546.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moczygemba, L.R.; Barner, J.C.; Gabrillo, E.R. Outcomes of a Medicare Part D telephone medication therapy management program. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2012, 52, e144–e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Medical Wards | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Total (n = 1120) | Gastroenterology (n = 280) | Orthopedic Surgery (n = 280) | General Surgery (n = 280) | Otorhinolaryngology (n = 280) | p-Value |
| Age, years, mean ± SD | 58.8 ± 18.6 | 67.1 ± 15.4 | 56.8 ± 20.0 | 59.9 ± 17.0 | 51.3 ± 18.1 | <0.001 |
| Sex female, n (%) | 459 (40.9) | 99 (35.3) | 133 (47.5) | 113 (40.3) | 114 (40.7) | 0.03 |
| Primary diagnosis, n (%) | ||||||
| Gastrointestinal diseases | 316 (28.2) | 124 (44.2) | 0 (0.0) | 173 (61.7) | 19 (6.7) | <0.001 |
| Neoplasms | 260 (23.2) | 128 (45.7) | 12 (4.2) | 76 (27.1) | 44 (15.7) | <0.001 |
| Injury, poisoning, and certain other consequences of external causes | 141 (12.5) | 1 (0.3) | 130 (46.4) | 8 (2.8) | 2 (0.7) | <0.001 |
| Respiratory diseases | 112 (10.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 112 (40.0) | <0.001 |
| Musculoskeletal diseases | 88 (7.8) | 0 (0.0) | 88 (31.4) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 |
| Ear, nose, and throat diseases | 62 (5.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 62 (22.1) | <0.001 |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue diseases | 22 (1.9) | 0 (0.0) | 7 (2.5) | 1 (0.3) | 14 (5.0) | <0.001 |
| Cardiovascular diseases | 18 (1.6) | 4 (1.4) | 1 (0.3) | 13 (4.6) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 |
| Endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases | 5 (0.4) | 2 (0.7) | 3 (1.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 |
| Others | 96 (8.9) | 21 (7.7) | 39 (14.2) | 9 (3.5) | 27 (3.5) | <0.001 |
| Length of stay (days), mean ± SD | 7.2 ± 7.9 | 6.1 ± 5.2 | 8.3 ± 8.9 | 9.9 ± 10.3 | 4.5 ± 4.9 | <0.001 |
| Number of diagnoses except for principal diagnosis *, mean ± SD | 1.0 ± 1.5 | 2.0 ± 1.8 | 0.7 ± 1.2 | 0.9 ± 1.6 | 0.5 ± 0.8 | <0.001 |
| Destination after discharge, n (%) | ||||||
| Home | 1034 (92.3) | 267 (95.4) | 217 (77.5) | 273 (97.5) | 277 (98.9) | <0.001 |
| Transferred to another hospital | 64 (5.7) | 10 (3.5) | 51 (18.2) | 2 (0.714) | 1 (0.357) | <0.001 |
| Nursing home | 22 (1.9) | 3 (1.0) | 12 (4.2) | 5 (1.7) | 2 (0.7) | <0.001 |
| Number of medication | 5.7 ± 3.2 | 5.8 ± 3.8 | 5.9 ± 3.4 | 5.1 ± 2.8 | 5.8 ± 2.6 | 0.021 |
| Section A | 2.4 ± 1.9 | 2.3 ± 1.5 | 1.6 ± 1.2 | 1.3 ± 0.8 | 4.5 ± 2.2 | <0.001 |
| Section B | 11.2 ± 5.6 | 11.5 ± 7.1 | 11.2 ± 5.2 | 10.0 ± 4.7 | 12.1 ± 4.6 | <0.001 |
| Section C | 12.5 ± 7.4 | 12.3 ± 8.5 | 12.6 ± 7.3 | 10.6 ± 6.0 | 14.5 ± 7.1 | <0.001 |
| A + B + C | 26.2 ± 13.4 | 26.2 ± 16.1 | 25.5 ± 12.6 | 21.9 ± 10.6 | 31.1 ± 11.9 | <0.001 |
| Wards | Dose Frequency | Instructions | MRCI-K | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | −6.2 (4.6) | −0.8 (1.3) | −7.3(5.4) | <0.001 |
| Gastrointestinal medicine | −5.4 (5.6) | −0.8 (1.4) | −6.2 (6.5) | |
| Orthopedic surgery | −7.6 (4.7) | −0.8 (0.8) | −8.5 (5.1) | |
| General surgery | −5.6 (4.2) | −0.3 (0.8) | −6 (4.6) | |
| Otorhinolaryngology | −6.3 (3.4) | −1.2 (1.9) | −8.4 (4.8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Hahn, J.; Kim, H.; Chang, M.J. Effect of Multi-Dose Dispensing on Medication Regimen Complexity: A Real-World Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051205
Lee S, Hahn J, Kim H, Chang MJ. Effect of Multi-Dose Dispensing on Medication Regimen Complexity: A Real-World Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(5):1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051205
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sunmin, Jongsung Hahn, Heungjo Kim, and Min Jung Chang. 2024. "Effect of Multi-Dose Dispensing on Medication Regimen Complexity: A Real-World Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 5: 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051205
APA StyleLee, S., Hahn, J., Kim, H., & Chang, M. J. (2024). Effect of Multi-Dose Dispensing on Medication Regimen Complexity: A Real-World Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(5), 1205. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051205






