The Safety and Effectiveness of Apixaban in Patients with End-Stage Kidney Disease on Dialysis: A Retrospective Observational Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Design and Settings
2.2. Study Outcomes
2.3. Statistical Analysis
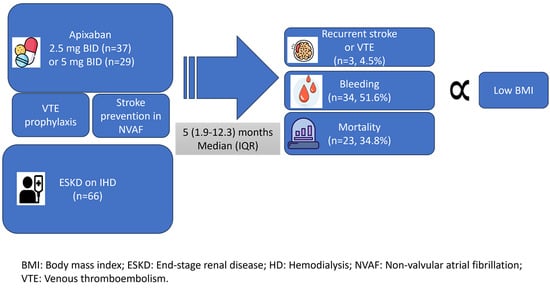
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, A.; Stecker, E.; Warden, B.A. Direct Oral Anticoagulant Use: A Practical Guide to Common Clinical Challenges. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e017559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, C.F.; Schmidt, M.; Lamberg, A.L.; Horváth-Puhó, E.; Baron, J.A.; Jespersen, B.; Sørensen, H.T. Kidney disease and risk of venous thromboembolism: A nationwide population-based case-control study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 1449–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.M.; Ademi, Z.; Doehner, W.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Mark, P.; Toyoda, K.; Wong, C.X.; Sarnak, M.; Cheung, M.; Herzog, C.A.; et al. Chronic Kidney Disease and Cerebrovascular Disease: Consensus and Guidance From a KDIGO Controversies Conference. Stroke 2021, 52, e328–e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Eck Van der Sluijs, A.; Abrahams, A.C.; Rookmaaker, M.B.; Verhaar, M.C.; Bos, W.J.W.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Dekker, F.W.; Van Diepen, M.; Ocak, G. Bleeding risk of haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girerd, S.; Girerd, N.; Frimat, L.; Holdaas, H.; Jardine, A.G.; Schmieder, R.E.; Fellström, B.; Settembre, N.; Malikov, S.; Rossignol, P.; et al. Arteriovenous fistula thrombosis is associated with increased all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in haemodialysis patients from the AURORA trial. Clin. Kidney J. 2020, 13, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhousani, M.; Malik, S.U.; Abu-Hashyeh, A.; Poznanski, N.J.; Al-Hasan, S.; Roth, D.F.; Alsharedi, M.; Mustafa, B. Using oral anticoagulants among chronic kidney disease patients to prevent recurrent venous thromboembolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb. Res. 2021, 198, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.Y.S.; Parikh, J.; Farrell, A.; Lefebvre, M.; Summa-Sorgini, C.; Battistella, M. Direct Oral Anticoagulant Use in Chronic Kidney Disease and Dialysis Patients With Venous Thromboembolism: A Systematic Review of Thrombosis and Bleeding Outcomes. Ann. Pharmacother. 2021, 55, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siontis, K.C.; Zhang, X.; Eckard, A.; Bhave, N.; Schaubel, D.E.; He, K.; Tilea, A.; Stack, A.G.; Balkrishnan, R.; Yao, X.; et al. Outcomes Associated With Apixaban Use in Patients With End-Stage Kidney Disease and Atrial Fibrillation in the United States. Circulation 2018, 138, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Ou, S.-H.; Huang, C.-W.; Lee, P.-T.; Chou, K.-J.; Lin, P.-C.; Su, Y.-C. Efficacy and Safety of Direct Oral Anticoagulants vs Warfarin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Dialysis Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Drug Investig. 2021, 41, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deal, E.N.; Pope, H.; Ross, W. Apixaban Use Among Patients With Severe Renal Impairment. Ann. Pharmacother. 2014, 48, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellenbogen, M.I.; Ardeshirrouhanifard, S.; Segal, J.B.; Streiff, M.B.; Deitelzweig, S.B.; Brotman, D.J. Safety and effectiveness of apixaban versus warfarin for acute venous thromboembolism in patients with end-stage kidney disease: A national cohort study. J. Hosp. Med. 2022, 17, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, D.; Palkimas, S.; Hockman, R.; Abraham, S.; Le, T.; Maitland, H. Safety and effectiveness of apixaban compared to warfarin in dialysis patients. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 2, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfar, S.; Elzeiny, S.M.; Ismail, H.; Makkeyah, Y.; Ibrahim, M. Direct Oral Anticoagulants vs. Warfarin in Hemodialysis Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 847286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarratt, S.C.; Nesbit, R.; Moye, R. Safety Outcomes of Apixaban Compared With Warfarin in Patients With End-Stage Renal Disease. Ann. Pharmacother. 2017, 51, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welander, F.; Renlund, H.; Dimény, E.; Holmberg, H.; Själander, A. Direct oral anticoagulants versus warfarin in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and CKD G3–G5D. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Gomes, T.; Wells, P.S.; Pequeno, P.; Johnson, A.; Sholzberg, M. Evaluation of definitions for oral anticoagulant-associated major bleeding: A population-based cohort study. Thromb. Res. 2022, 213, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.E.; Giugliano, R.P.; Patel, M.R.; Abramson, S.; Jardine, M.; Zhao, S.; Perkovic, V.; Maddux, F.W.; Piccini, J.P. Nonvitamin K Anticoagulant Agents in Patients With Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease or on Dialysis With AF. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 2888–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshogran, O.Y. Warfarin Dosing and Outcomes in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Closer Look at Warfarin Disposition. CDM 2019, 20, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vio, R.; Proietti, R.; Rigato, M.; Calò, L.A. Clinical Evidence for the Choice of the Direct Oral Anticoagulant in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation According to Creatinine Clearance. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanni, C.; Petrovitch, E.; Ali, M.; Gibson, W.; Giuliano, C.; Holzhausen, J.; Makowski, C.; Pallisco, A.; Patel, N.; Sutter, D.; et al. Outcomes associated with apixaban vs warfarin in patients with renal dysfunction. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 2366–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anouassi, Z.; Atallah, B.; Alsoud, L.O.; El Nekidy, W.; Al Mahmeed, W.; AlJaabari, M.; Almuti, K. Appropriateness of the Direct Oral Anticoagulants Dosing in the Middle East Gulf Region. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2021, 77, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, A.R.; Shakowski, C.; Trujillo, T.C.; Wright, G.C.; Mueller, S.W.; Kiser, T.H. Evaluation of safety and efficacy outcomes of direct oral anticoagulants versus warfarin in normal and extreme body weights for the treatment of atrial fibrillation or venous thromboembolism. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2022, 54, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netley, J.; Howard, K.; Wilson, W. Effects of body mass index on the safety and effectiveness of direct oral anticoagulants: A retrospective review. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2019, 48, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, A.F.; Jain, S.; Masri, A.; Alkukhun, L.; Senussi, M.; Sezer, A.; Wang, Y.; Thoma, F.; Bhonsale, A.; Saba, S.; et al. Outcomes of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Atrial Fibrillation Patients Across Different Body Mass Index Categories. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 7, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisters, R.; Lane, D.A.; Nieuwlaat, R.; De Vos, C.B.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; Lip, G.Y.H. A Novel User-Friendly Score (HAS-BLED) To Assess 1-Year Risk of Major Bleeding in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. Chest 2010, 138, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.; Maddox, W.; Nahman, S.; Diamond, M.; Sorrentino, R.; Guha, A.; Waller, J. Abstract 12014: Modified HASBLED Bleeding Risk Score in Dialysis Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation 2015, 132, A12014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocak, G.; Ramspek, C.; Rookmaaker, M.B.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Verhaar, M.C.; Bos, W.J.W.; Dekker, F.W.; Van Diepen, M. Performance of bleeding risk scores in dialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- January, C.T.; Wann, L.S.; Calkins, H.; Chen, L.Y.; Cigarroa, J.E.; Cleveland, J.C.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Field, M.E.; Furie, K.L.; et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS Focused Update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 104–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Baseline Characteristics | Total (n = 66) | No Bleeding (n = 32) | Bleeding (n = 34) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males n (%) | 33 (50) | 14 (43.8) | 19 (55.9) | 0.325 | ||
| Median Age (IQR)years | 71 (63.5–82) | 68.5 (59.5–76.5) | 75.5 (66.8–83.3) | 0.039 | ||
| Median Weight (IQR) kg | 70.5 (59.5–86.25) | 71.0 (60.0–88.0) | 66.5 (55.3–79.0) | 0.12 | ||
| BMI (Kg/m2) | N (%) | >25 | 37 (56.1) | 21 (65.6) | 16 (47.1) | 0.21 |
| 18–24.9 | 24 (36.4) | 10 (31.3) | 14 (41.2) | |||
| <18 | 5 (7.6) | 1(3.1) | 4 (11.8) | |||
| Median BMI (IQR) | 28.3 (22.6–32.8) | 29.9 (23.9–34.1) | 24.8 (20.7–30.3) | 0.037 | ||
| Apixaban Daily Dose | n (%) | 5 mg | 37 (56.1) | 17 (53.1) | 20 (58.8) | 0.64 |
| 10 mg | 29 (43.9) | 15 (46.9) | 14 (41.2) | |||
| Median (IQR) | 5 (5–10) | - | - | 0.66 | ||
| DVT/PE n (%) | 13 (19.7) | 6 (18.8) | 7 (20.6) | 0.85 | ||
| Atrial Fibrillation n (%) | 54 (81.8) | 26 (81.3) | 28 (82.4) | 0.91 | ||
| Diabetes n (%) | 60 (90.9) | 31(96.9) | 29 (85.3) | 0.20 | ||
| Dyslipidemia n (%) | 60 (92.3) | 30 (96.8) | 30 (88.2) | 0.36 | ||
| Stent n (%) | 33 (50) | 15 (46.9) | 18 (52.9) | 0.81 | ||
| CABG Within 12 Months n (%) | 19 (28.8) | 11(34.4) | 8 (23.5) | 0.33 | ||
| Liver Disease n (%) | 14 (21.2) | 7 (21.9) | 7 (20.6) | 0.90 | ||
| Malignancy n (%) | 4 (6.1) | 2 (6.3) | 2 (5.9) | 1.00 | ||
| Hypertension n (%) | 60 (90.9) | 30 (93.8) | 30 (88.2) | 0.673 | ||
| CAD/ACS Within 12 Months n (%) | 19 (28.8) | 11 (34.4) | 8 (23.5) | 0.41 | ||
| LV Thrombus n (%) | 3 (4.5) | 1 (3.1) | 2 (5.9) | 1.00 | ||
| Smoking n (%) | 16 (24.2) | 6 (18.8) | 10 (29.4) | 0.31 | ||
| Heart Failure n (%) (HFrEF, and HFpEF) | 47 (71.2) | 23 (71.9) | 24 (70.6) | 0.91 | ||
| Aortic Valve Stenosis n (%) | Mild | 11 (16.7) | 7 (21.9) | 4 (11.8) | 0.18 | |
| Moderate | 5 (7.6) | 4 (12.5) | 1(2.9) | |||
| Severe | 5 (7.6) | 1 (3.1) | 4 (11.8) | |||
| LVAD n (%) | 4 (6.1) | 0 (0) | 4 (11.8) | 0.11 | ||
| Stroke n (%) | Ischemic | 7 (10.6) | 2 (6.3) | 5 (14.7) | ||
| Hemorrhagic | 1 (1.5) | 1 (3.1) | 0 (0) | 0.33 | ||
| Concomitant Antiplatelet n (%) | 1 Antiplatelet | 26 (39.4) | 9 (28.1) | 17(50) | 0.14 | |
| 2 Antiplatelets | 16 (24.2) | 8 (25) | 8 (23.5) | |||
| Adherent (no more than 30 days between refills) n (%) | 56 (84.8) | 26 (81.3) | 30 (88.2) | 0.51 | ||
| Duration With Medication (months) Median (IQR) | 5 (1.9–12.3) | 3.5 (1.1–8.6) | 5 (2.0–14.8) | 0.22 | ||
| Outcomes | Total (n = 66) | No Bleeding (n = 32) | Bleeding (n = 34) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose appropriateness n (%) | 41(62.1) | 21 (65.6) | 20 (58.8) | 0.57 | |
| Dose appropriateness n (%) | Low | 19 (28.8) | 9 (28.1) | 10 (29.4) | 0.71 |
| Appropriate | 41(62.1) | 21 (65.6) | 20 (58.8) | ||
| High | 6 (9.1) | 2 (6.3) | 4 (11.8) | ||
| DVT/PE during follow-up n (%) | 3 (4.5) | 0 (0) | 3 (8.8) | 0.29 | |
| Stroke during follow-up n (%) | 3 (4.5) | 1(3.1) | 2 (5.9) | 1.00 | |
| Mortality n (%) | 23 (34.8) | 9 (28.1) | 14 (41.2) | 0.27 | |
| INR Median (IQR) | 1.3 (1.1–1.5) | 1.3 (1.1–1.5) | 1.25 (1.1–1.5) | 0.87 | |
| CHA2DS2_VASc Score Median (IQR) | 5.0 (4.0–6.0) | 5.0 (4.0–6.0) | 5 (4.0–6.3) | 0.59 | |
| B | Odds Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apixaban daily dose (mg) | 0.061 | 1.06 (0.85–1.33) | 0.591 |
| Age (Years) | 0.036 | 1.04 (0.99–1.08) | 0.104 |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | −0.103 | 0.9 (0.8–0.99) | 0.023 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Nekidy, W.; Abidi, E.; Nabil, S.; Kendakji, S.; Ali, M.; Aburuz, S.; Atallah, B.; Hijazi, F.; Mallat, J.; Akour, A. The Safety and Effectiveness of Apixaban in Patients with End-Stage Kidney Disease on Dialysis: A Retrospective Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051351
El Nekidy W, Abidi E, Nabil S, Kendakji S, Ali M, Aburuz S, Atallah B, Hijazi F, Mallat J, Akour A. The Safety and Effectiveness of Apixaban in Patients with End-Stage Kidney Disease on Dialysis: A Retrospective Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(5):1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051351
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Nekidy, Wasim, Emna Abidi, Said Nabil, Saba Kendakji, Moatasem Ali, Salahdein Aburuz, Bassam Atallah, Fadi Hijazi, Jihad Mallat, and Amal Akour. 2024. "The Safety and Effectiveness of Apixaban in Patients with End-Stage Kidney Disease on Dialysis: A Retrospective Observational Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 5: 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051351
APA StyleEl Nekidy, W., Abidi, E., Nabil, S., Kendakji, S., Ali, M., Aburuz, S., Atallah, B., Hijazi, F., Mallat, J., & Akour, A. (2024). The Safety and Effectiveness of Apixaban in Patients with End-Stage Kidney Disease on Dialysis: A Retrospective Observational Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(5), 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051351