Effect of Whole-Body Vibration Exercise on Pain, Disability, Balance, Proprioception, Functional Performance and Quality of Life in People with Non-Specific Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Registration
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Study Selection Criteria
2.5. Methodological Quality Assessment
2.6. Certainty of Evidence
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Dealing with Missing Data
3. Results
3.1. Study Identifications
3.2. Participants
3.3. Description of Interventions and Protocols
3.4. Outcome Measures
3.5. Risk of Bias across Outcomes
3.6. PEDro Quality Assessment of Study Methodology
| Variables | Eligibility Criteria | Randomized Allocation | Concealed Allocation | Comparable at Baseline | Blinding of the Subjects | Blinding of the Therapist | Blinding of Assessors | Adequate Follow Up | Intention to Treat Analysis | Comparison between Groups | Point Estimates and Variability | Total Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ruger et al., 2023 [45] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Cigdem Karacay et al., 2022 [18] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Micke et al., 2021 [44] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9 |
| Jung et al., 2020 [41] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Wang et al., 2019 [23] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| Wegner et al., 2019 [46] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Sajadi et al., 2019 * [49] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Kaeding et al., 2017 [42] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Maddlozzo et al., 2016 [43] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Yang et al., 2015 [47] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| del Pozo-Cruz et al., 2011 [16] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Rittweger et al., 2002 * [48] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
3.7. Findings of Certainty of Evidence
3.8. Effects of Intervention
3.9. Quantitative Analysis (Data Synthesis)
3.9.1. Pain
3.9.2. Disability
3.10. Balance and Proprioception
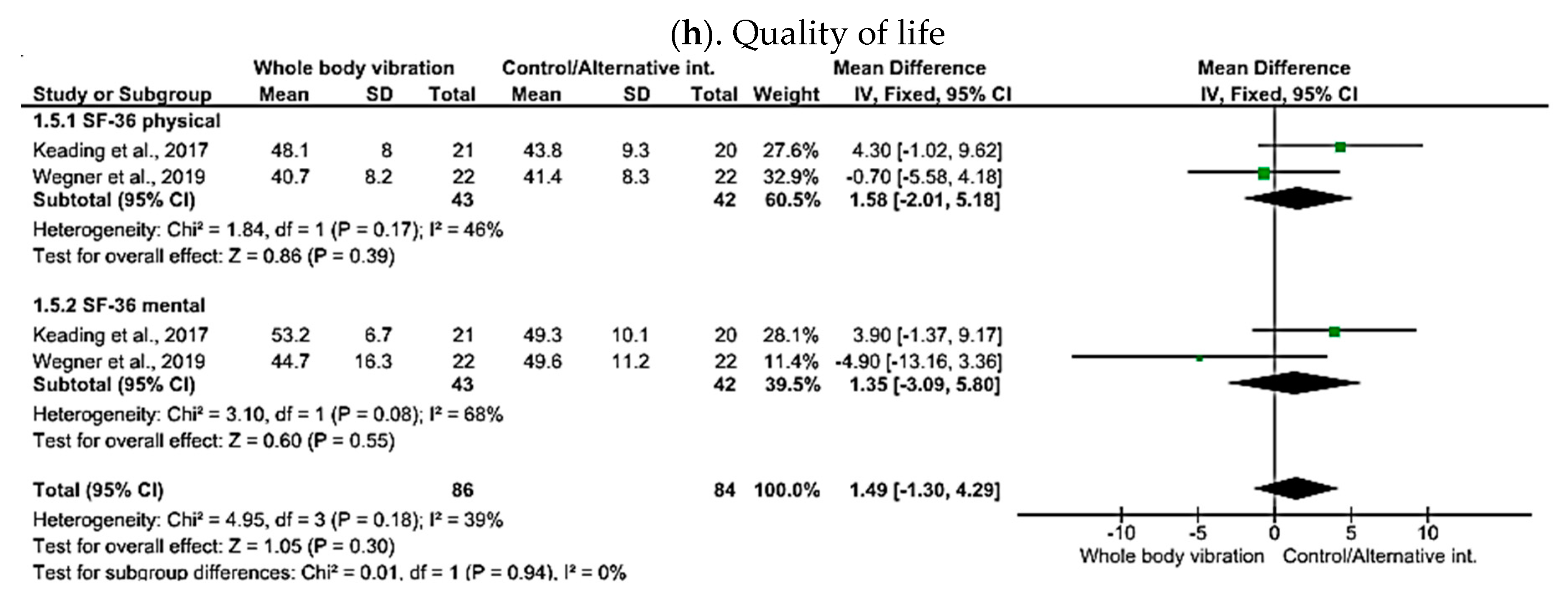
3.11. Functional Performance and Quality of Life
4. Discussion
4.1. Pain
4.2. Disability
4.3. Quality of Life
4.4. Balance and Proprioception
4.5. Functional Capacity
4.6. Strength and Limitation
5. Future Perspective
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, A.; March, L.; Zheng, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Blyth, F.M.; Smith, E.; Buchbinder, R.; Hoy, D. Global low back pain prevalence and years lived with disability from 1990 to 2017: Estimates from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapp, W.; Weinberger, M.; Erk, S.; Fuchs, B.; Mueller, M.; Gallhofer, B.; Hajak, G.; Kübler, A.; Lautenbacher, S. A brief intervention utilising visual feedback reduces pain and enhances tactile acuity in CLBP patients. J. Back Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2015, 28, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchikanti, L.; Singh, V.; Falco, F.J.; Benyamin, R.M.; Hirsch, J.A. Epidemiology of low back pain in adults. Neuromodulation 2014, 17 (Suppl. S2), 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, R.; Takamjani, I.E.; Dadgoo, M.; Sarrafzadeh, J.; Ahmadi, A.; Pourahmadi, M.R.; Jafarpisheh, A.S. A protocol for clinical trial study of the effect of core stabilization exercises on spine kinematics during gait with and without load in patients with non-specific chronic low back pain. Chiropr. Man. Ther. 2017, 25, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, M.; Deckers, K.; Eldabe, S.; Kiesel, K.; Gilligan, C.; Vieceli, J.; Crosby, P. Muscle Control and Non-specific Chronic Low Back Pain. Neuromodulation 2018, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokouhyan, S.M.; Davoudi, M.; Hoviattalab, M.; Abedi, M.; Bervis, S.; Parnianpour, M.; Brumagne, S.; Khalaf, K. Distinction of non-specific low back pain patients with proprioceptive disorders from healthy individuals by linear discriminant analysis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1078805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manojlović, M. The efficiency of proprioceptive training in preventing injuries to team athletes: A systematic review. EQOL J. 2021, 13, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M.; Eshghi, S.; Hosseinzadeh, M. The effect of a shoulder injury prevention programme on proprioception and dynamic stability of young volleyball players; a randomized controlled trial. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, M.L.; Vrana, A.; Schweinhardt, P. Low Back Pain: The Potential Contribution of Supraspinal Motor Control and Proprioception. Neuroscientist 2019, 25, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dieën, J.H.; Reeves, N.P.; Kawchuk, G.; van Dillen, L.R.; Hodges, P.W. Motor Control Changes in Low Back Pain: Divergence in Presentations and Mechanisms. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2019, 49, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.H.; Mousavi, S.J.; Kiers, H.; Ferreira, P.; Refshauge, K.; van Dieën, J. Is there a relationship between lumbar proprioception and low back pain? A systematic review with meta-analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 120–136.e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamkhar, L.; Kahlaee, A.H. Pain and Pain-Related Disability Associated With Proprioceptive Impairment in Chronic Low Back Pain Patients: A Systematic Review. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2019, 42, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X. Effect of Whole-Body Vibration Training on Muscle Activation for Individuals with Knee Osteoarthritis. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6671390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittweger, J. Vibration as an exercise modality: How it may work, and what its potential might be. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 877–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, M.; Bosco, C. The use of vibration as an exercise intervention. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2003, 31, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Pozo-Cruz, B.; Hernández Mocholí, M.A.; Adsuar, J.C.; Parraca, J.A.; Muro, I.; Gusi, N. Effects of whole body vibration therapy on main outcome measures for chronic non-specific low back pain: A single-blind randomized controlled trial. J. Rehabil. Med. 2011, 43, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afridi, B.; Khan, H.; Akkol, E.K.; Aschner, M. Pain Perception and Management: Where do We Stand? Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cigdem Karacay, B.; Sahbaz, T.; Gurtekin, B.; Yildiz, S.; Ozcan, E. Effectiveness of whole-body vibration exercise and core stabilization exercise in chronic non-specific low back pain: A randomized-controlled study. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 68, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X.; Cai, H.; Sun, J. Does whole-body vibration training have a positive effect on balance and walking function in patients with stroke? A meta-analysis. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1076665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sá-Caputo, D.; Paineiras-Domingos, L.L.; Francisca-Santos, A.; Dos Anjos, E.M.; Reis, A.S.; Neves, M.F.T.; Oigman, W.; Oliveira, R.; Brandão, A.; Machado, C.B.; et al. Whole-body vibration improves the functional parameters of individuals with metabolic syndrome: An exploratory study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartley, E.J.; Palit, S.; Fillingim, R.B.; Robinson, M.E. Multisystem Resiliency as a Predictor of Physical and Psychological Functioning in Older Adults With Chronic Low Back Pain. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhu, W.; He, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Ding, H. Correlation between functional disability and quality of life among rural elderly in Anhui province, China: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Gu, W.; Chen, B.L.; Wang, X.; Hu, H.Y.; Zheng, Y.L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, P.J. Effects of whole-body vibration exercise for non-specific chronic low back pain: An assessor-blind, randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2019, 33, 1445–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Dong, Y.; Guo, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Effects of Whole-Body Vibration on Lumbar-Abdominal Muscles Activation in Healthy Young Adults: A Pilot Study. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, P.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Vibration therapy to improve pain and function in patients with chronic low back pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Lin, W.; Li, X.; Andersen, L.L.; Wang, Y. Efficacy of whole body vibration therapy on pain and functional ability in people with non-specific low back pain: A systematic review. BMC Complement Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remer, F.; Keilani, M.; Kull, P.; Crevenna, R. Effects of whole-body vibration therapy on pain, functionality, postural stability, and proprioception in patients with subacute and chronic non-specific low back pain: A systematic review. Wien Med. Wochenschr 2023, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazeri, A.; Mousavi, S.J. Quality of Life and Low Back Pain. In Handbook of Disease Burdens and Quality of Life Measures; Preedy, V.R., Watson, R.R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 3979–3994. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, G.M.; Dila, K.A.S.; Mohamed, M.Y.F.; Tam, D.N.H.; Kien, N.D.; Ahmed, A.M.; Huy, N.T. A step by step guide for conducting a systematic review and meta-analysis with simulation data. Trop. Med. Health 2019, 47, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolucci, T.; Attanasi, C.; Cecchini, W.; Marazzi, A.; Capobianco, S.V.; Santilli, V. Chronic low back pain and postural rehabilitation exercise: A literature review. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balagué, F.; Mannion, A.F.; Pellisé, F.; Cedraschi, C. Non-specific low back pain. Lancet 2012, 379, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, L.J.; Milanese, S.F.; Grimmer-Somers, K.A. Epidemiology of adolescent spinal pain: A systematic overview of the research literature. Spine 2007, 32, 2630–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseley, A.M.; Rahman, P.; Wells, G.A.; Zadro, J.R.; Sherrington, C.; Toupin-April, K.; Brosseau, L. Agreement between the Cochrane risk of bias tool and Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro) scale: A meta-epidemiological study of randomized controlled trials of physical therapy interventions. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cashin, A.G.; McAuley, J.H. Clinimetrics: Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro) Scale. J. Physiother. 2020, 66, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schünemann, H.; Brożek, J.; Guyatt, G.; Oxman, A. GRADE Handbook for Grading Quality of Evidence and Strength of Recommendations. Updated October 2013. The GRADE Working Group. 2013. Available online: https://www.rama.mahidol.ac.th/ceb/sites/default/files/public/pdf/journal_club/2017/GRADE%20handbook.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Hultcrantz, M.; Rind, D.; Akl, E.A.; Treweek, S.; Mustafa, R.A.; Iorio, A.; Alper, B.S.; Meerpohl, J.J.; Murad, M.H.; Ansari, M.T. The GRADE Working Group clarifies the construct of certainty of evidence. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2017, 87, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, J.J.; Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Group, C.S.M. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Cochrane: London, UK, 2019; pp. 241–284. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, K.S.; Jung, J.H.; In, T.S.; Cho, H.Y. The Effectiveness of Trunk Stabilization Exercise Combined with Vibration for Adolescent Patients with Nonspecific Low Back Pain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaeding, T.S.; Karch, A.; Schwarz, R.; Flor, T.; Wittke, T.C.; Kück, M.; Böselt, G.; Tegtbur, U.; Stein, L. Whole-body vibration training as a workplace-based sports activity for employees with chronic low-back pain. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2017, 27, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddalozzo, G.F.; Kuo, B.; Maddalozzo, W.A.; Maddalozzo, C.D.; Galver, J.W. Comparison of 2 Multimodal Interventions With and Without Whole Body Vibration Therapy Plus Traction on Pain and Disability in Patients With Nonspecific Chronic Low Back Pain. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Micke, F.; Weissenfels, A.; Wirtz, N.; von Stengel, S.; Dörmann, U.; Kohl, M.; Kleinöder, H.; Donath, L.; Kemmler, W. Similar Pain Intensity Reductions and Trunk Strength Improvements Following Whole-Body Electromyostimulation vs. Whole-Body Vibration vs. Conventional Back-Strengthening Training in Chronic Non-specific Low Back Pain Patients: A Three-Armed Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 664991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüger, A.; Laudner, K.; Delank, K.S.; Schwesig, R.; Steinmetz, A. Effects of Different Forms of Sensorimotor Training on Postural Control and Functional Status in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegener, V.; Rarack, S.; Tiffe, T.; Grill, E.; Melcher, C.; Birkenmaier, C.; Jansson, V.; Wegener, B. Effects of Whole Body Vibration Therapy and Classic Physiotherapy on Postural Stability in People With Back Pain: A Randomized Trial. Clin. Spine Surg. 2019, 32, E214–E220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Seo, D. The effects of whole body vibration on static balance, spinal curvature, pain, and disability of patients with low back pain. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rittweger, J.; Just, K.; Kautzsch, K.; Reeg, P.; Felsenberg, D. Treatment of chronic lower back pain with lumbar extension and whole-body vibration exercise: A randomized controlled trial. Spine 2002, 27, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajadi, N.; Bagheri, R.; Amiri, A.; Maroufi, N.; Shadmehr, A.; Pourahmadi, M. Effects of Different Frequencies of Whole Body Vibration on Repositioning Error in Patients With Chronic Low Back Pain in Different Angles of Lumbar Flexion. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2019, 42, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzack, R.; Wall, P.D. Pain mechanisms: A new theory. Science 1965, 150, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comitato, A.; Bardoni, R. Presynaptic Inhibition of Pain and Touch in the Spinal Cord: From Receptors to Circuits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfering, A.; Burger, C.; Schade, V.; Radlinger, L. Stochastic resonance whole body vibration increases perceived muscle relaxation but not cardiovascular activation: A randomized controlled trial. World J. Orthop. 2016, 7, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfering, A.; Zahno, J.; Taeymans, J.; Blasimann, A.; Radlinger, L. Acute effects of stochastic resonance whole body vibration. World J. Orthop. 2013, 4, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kwon, B.S.; Park, J.W.; Lee, H.; Nam, K.; Park, T.; Cho, Y.; Kim, T. Effect of Whole Body Horizontal Vibration Exercise in Chronic Low Back Pain Patients: Vertical Versus Horizontal Vibration Exercise. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 42, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, M.F.; Loh, Y.C.; Tan, C.S.; Khadijah Adam, S.; Abdul Manan, N.; Basir, R. General Pathways of Pain Sensation and the Major Neurotransmitters Involved in Pain Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, A.A.; Bhojraj, S.Y.; Deshmukh, M.; Kalkotwar, S.; Joshi, V.R.; Yarmal, T.; Kalkonde, Y.; Bang, A.T. Activity limitation and disability due to pain in back and extremities in rural population: A community-based study during a period of twelve months in rural Gadchiroli, India. J. Glob. Health 2021, 11, 12003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonanni, R.; Cariati, I.; Romagnoli, C.; D’Arcangelo, G.; Annino, G.; Tancredi, V. Whole Body Vibration: A Valid Alternative Strategy to Exercise? J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2022, 7, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasti, E.; Rojhani-Shirazi, Z.; Ebrahimi, N.; Sobhan, M.R. Effects of whole body vibration with exercise therapy versus exercise therapy alone on flexibility, vertical jump height, agility and pain in athletes with patellofemoral pain: A randomized clinical trial. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittweger, J.; Mutschelknauss, M.; Felsenberg, D. Acute changes in neuromuscular excitability after exhaustive whole body vibration exercise as compared to exhaustion by squatting exercise. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2003, 23, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, N.; Khan, Z.; Veqar, Z. Effect of Whole-Body Vibration on Balance or Proprioception in Nonspecific Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review. J. Chiropr. Med. 2023, 22, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, L.; Huang, Q.; Sertic, J.V.L.; Konczak, J. The Effectiveness of Proprioceptive Training for Improving Motor Performance and Motor Dysfunction: A Systematic Review. Front. Rehabil. Sci. 2022, 3, 830166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lou, T.; Shen, X. Correlation Between Proprioceptive Impairment and Motor Deficits After Stroke: A Meta-Analysis Review. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 688616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lins, L.; Carvalho, F.M. SF-36 total score as a single measure of health-related quality of life: Scoping review. SAGE Open Med. 2016, 4, 2050312116671725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Wu, Z.; Sun, L.; Zhou, L.; Wang, G.; Xiao, L.; Wang, H. The Effects and Mechanisms of Exercise on the Treatment of Depression. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 705559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, D.X.; Aguiñaga, S.; Vásquez, P.M.; Conroy, D.E.; Erickson, K.I.; Hillman, C.; Stillman, C.M.; Ballard, R.M.; Sheppard, B.B.; Petruzzello, S.J.; et al. A systematic review of physical activity and quality of life and well-being. Transl. Behav. Med. 2020, 10, 1098–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahindru, A.; Patil, P.; Agrawal, V. Role of Physical Activity on Mental Health and Well-Being: A Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e33475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.J.; MacCarron, P.; Cohen, E. Social reward and support effects on exercise experiences and performance: Evidence from parkrun. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blecher, R.; Heinemann-Yerushalmi, L.; Assaraf, E.; Konstantin, N.; Chapman, J.R.; Cope, T.C.; Bewick, G.S.; Banks, R.W.; Zelzer, E. New functions for the proprioceptive system in skeletal biology. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20170327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.-y.; Cho, Y.-j.; Chen, R.-s. The Effect of Whole-Body Vibration on Proprioception and Motor Function for Individuals with Moderate Parkinson Disease: A Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Occup. Ther. Int. 2021, 2021, 9441366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Waddington, G.; Adams, R.; Anson, J.; Liu, Y. Assessing proprioception: A critical review of methods. J. Sport Health Sci. 2016, 5, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aman, J.E.; Elangovan, N.; Yeh, I.L.; Konczak, J. The effectiveness of proprioceptive training for improving motor function: A systematic review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaoğlu, E.; Faruk Bucak, Ö.; Kökçe, M.; Özkan, M.; Çetin, M.; Atasoy, M.; Aytüre, L.; Karacan, İ. High-frequency whole-body vibration activates tonic vibration reflex. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 69, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanenko, Y.; Gurfinkel, V.S. Human Postural Control. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminian-Far, A.; Hadian, M.R.; Olyaei, G.; Talebian, S.; Bakhtiary, A.H. Whole-body vibration and the prevention and treatment of delayed-onset muscle soreness. J. Athl. Train. 2011, 46, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, T.G.; Barnes, D.; Nichols, G.; Kishino, N.D.; Coval, K.; Piel, B.; Hoshino, D.; Gatchel, R.J. Progressive isoinertial lifting evaluation. II. A comparison with isokinetic lifting in a disabled chronic low-back pain industrial population. Spine 1988, 13, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torvinen, S.; Kannus, P.; Sievänen, H.; Järvinen, T.A.; Pasanen, M.; Kontulainen, S.; Järvinen, T.L.; Järvinen, M.; Oja, P.; Vuori, I. Effect of four-month vertical whole body vibration on performance and balance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Liu, X. Effects of whole-body vibration training combined with KAATSU training on lower limb joint muscle strength in older women. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1231088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yan, L.; Hou, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.; Yan, C.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Ding, X. Exercise intervention for patients with chronic low back pain: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1155225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Search Terms | Articles Found in Databases | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PubMed | CENTRAL | Web of Science | Scopus | |
| “Whole-body vibration” | 2812 | 1523 | 4798 | 4779 |
| “Whole-body vibration exercise” | 532 | 892 | 1911 | 1906 |
| “Whole-body vibration exercise” OR “Whole-body vibration” | 709 | 1482 | 4797 | 4779 |
| “Whole-body vibration exercise” AND “low back pain” | 31 | 36 | 104 | 105 |
| “Whole-body vibration” AND “chronic low back pain” | 31 | 29 | 58 | 57 |
| “Whole-body vibration “AND “chronic low back pain” AND “disability” | 13 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| “Whole-body vibration” AND “chronic low back pain” AND “balance” | 5 | 8 | 8 | 7 |
| “Whole-body vibration” AND “chronic low back pain” AND “proprioception” | 5 | 6 | 7 | 6 |
| “Whole-body vibration” AND “chronic low back pain” AND “functional performance” | 1 | 9 | 4 | 4 |
| “Whole-body vibration” AND “chronic low back pain” AND “quality of life” | 3 | 6 | 10 | 9 |
| Total | 4142 | 4009 | 11,715 | 11,670 |
| Study | Total Participants/Follow up | Diagnosis | Intervention and Comparator (Dosages) | Outcome Measures | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ruger et al., 2023 [45] | N = 75/ Baseline and at 2nd week | NSCLBP above age of 18 year | Sensorimotor physiotherapy training Gallileo training Posturomed training 15 min/session, 6 total sessions | ODI, Posturography, | Statistically significant changes in ODI but no improvement in postural stability. |
| Cigdem Karacay et al., 2022 [18] | N = 74/ Baseline, 8 weeks and 20 weeks. | NSCLBP, 24 to 64 years of age | WBVE in 3 positions for 3 days/week for 8 weeks + classic lumbar home exercise Core stabilization + classic lumbar home exercise—3 days/week × 8 weeks William–Mckenzie home exercise—3 days/week × 8 weeks | VAS, RMDQ, PILE | Statistically significant difference in WBV group for VAS, RMDQ and PILE. |
| Micke et al., 2021 [44] | N = 240/ Baseline and 12 weeks | NSCLBP, ages 40–70 years | Electromyostimulation—1 day/week × 12 weeks WBVE—2 days/week for 12 weeks Warm up and circuit training for 1 day/week for 12 weeks | NPRS | Statistically significant and moderate improvement in NPRS all groups. |
| Jung et al., 2020 [41] | N = 50/ Baseline and after 12 weeks | NSCLBP aged between 10 and 19 years | Vibration—25 min/day, 3 day/week for 12 weeks Placebo: trunk stabilization exercise for same amount of time | Repositioning error, Lumbar kinematics Lumbar hip coordination NPRS | There was significant improvement in NPRS, Repositioning error. |
| Wang et al., 2019 [23] | N = 89/ Baseline and 12 weeks | NSCLBP from 3 months, pain score below 8 | WBVE 3 times/week for 12 weeks Same exercise programme without vibration 3 times/week for 12 weeks | Visual analog scale Oswestry Disability Index Lumbar joint position sense SF-36 | Statistically significant improvement in VAS, ODI, lumbar joint position sense, SF-36. |
| Wegener et al., 2019 [46] | N = 44/ Baseline and after the intervention | NSCLBP with age above 50 years | WBV Classic physiotherapy training All exercise were performed for 2 days/week for 6 weeks | Postural disability, ODI, SF-36 | No significant improvement in ODI, SF-36. |
| Kaeding et al., 2017 [42] | N = 41/ Baseline and after 3 months | Chronic low back pain with minimum age of 18 year | WBVE 2.5 times/week for 3 months Control | RMDQ ODI, SF-36, static posturography | Significant improvement in RMDQ ODI and SF-36. |
| Maddalozzo et al., 2016 [43] | N = 125/ Baseline and end of the intervention | NSCLBP | Mckenzie exercise + WBV + traction Mckenzie exercise | ODI NPRS | Statistically significant improvement in both groups. However, more improvement in WBV+ traction group. |
| Yang et al., 2015 [47] | N = 40/ Baseline and 6 weeks. | CLBP with no neurological deficit from 12 weeks | WBV + 25 lumbar stability 3 days/week for 6 weeks 30 lumbar stability—3 days/week for 6 weeks | VAS KODI Static balance-fall index, posturography and postural sway | Significant improvement in WBV group for the fall index, VAS score, and ODI score. Spinal balance, VAS scale, and ODI score more improved in the control group than WBV. |
| del Pozo-Cruz et al., 2011 [16] | N = 50/ Baseline and 12 weeks. | Diagnosis of NSCLBP and minimum of 6 months of symptom | WBVE 2 times/week for 12 weeks Control | PILE RMDQ ODI VAS Biodex balance system | Statistically significant improvement in AP stability index, ODI, RMDQ, VAS, and PILE. |
| Authors and Year | Position of Application | Frequency (Hz) | Amplitude | Duration | Rest Time | Repetitions | Total Duration | Frequency of Sessions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ruger et al., 2023 [45] | X | 5–30 Hz | 4.5 mm | X | X | X | 15 min | Six sessions within 2 weeks |
| Cigdem Karacay et al., (2022) [18] | Knee bent to 120 Bridge Push up | 25 Hz | 2 mm | 30 sec in 0–4 weeks 60 s in 4–8 week | 30 s | 2 | 4.5 min WBVE + 10 min warm up & cool down—0–4 weeks 7.5 min WBVE + 10 min warm up & cool down—0–4 weeks | 3 days/week for 8 weeks |
| Micke et al., 2021 [44] | Dynamic cable squats Squats with arm extension Calf raises Static squats with arm movement, Static cable squats with calf raises | 5–6 Hz 7–8 Hz 10 Hz 8–10 Hz 8 Hz | 9 mm | 60 s of oscillation | 30 s | 5–8 reps, 2 sets | 15 min | 2 days/week for 12 weeks |
| Jung et al., 2020 [41] | Single bridge Bridge Knee flex Plank Squat Bridge Side bridge | 15 Hz | 2 mm | 60 s 60 s 60 s 60 s 90 s 90 s 90 s | 30 s break after each exercise | X | 5 min warm-up, 15 min whole-body vibration exercise and 5 min cool down | 3 days/week for 12 weeks |
| Wang et al., 2019 [23] | Squat Kneeling Bridge Bridge with leg lift Bridge Knee flex Back release | 9 Hz | X | 90 s 60 s 90 s 60 s 60 s 90 s | 30 30 30 30 30 30 | 2 2 2 2 2 2 | 5 min warm-up, 15 min whole-body vibration exercise and 5 min cool down | 3 days/week for 12 weeks |
| Wegener et al., 2019 [46] | 5 trunk stability exercises | 5–12 Hz 12–20 20 | X | 1 min 1.5 min 2 min | X | X | Twice a week for 6 weeks | |
| Kaeding et al., 2017 [42] | Basic position | 10–30 Hz | 1.5–3.5 mm | X | 60 s | 5 | X | 2.5/week for 3 months |
| Maddalozzo et al., 2016 [43] | Wall squats squats, and lunges + WBV traction | WBV traction table—20–30 Hz WBV platform—40–50 Hz | 0.6–1.2 mm | X | X | X | X | X |
| Yang et al., 2015 [47] | Standing with slight flexion of knee joint and lumbar lordosis | 18 Hz | X | 5 min | X | X | 5 min WBVE + 25 min lumbar stability training | 3 days/week for 6 weeks |
| del Pozo-Cruz et al., 2011 [16] | Standing with the knee set at 120° | 20 Hz | X | 60 s 120 s180 s 240 s 360 s | 30 s 30 s 30 s 30 s 0 s | 6 3 2 2 1 | 6 min 6 min 6 min 8 min 6 min | 2 days/week for 12 weeks |
| NPRS | VAS | ODI | RMDQ | Balance | Proprioception | QoL | PILE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ruger et al., 2023 [45] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Cigdem Karacay et al., 2022 [18] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Micke et al., 2021 [44] | ✓ | |||||||
| Jung et al., 2020 [41] | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Wang et al., 2019 [23] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Wegner et al., 2019 [46] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Kaeding et al., 2017 [42] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Maddlozzo et al., 2016 [43] | ✓ | |||||||
| Yang et al., 2015 [47] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| del Pozo-Cruz et al., 2011 [16] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Certainty Assessment | Summary of Findings | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants (Studies) Follow-Up | Risk of Bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Publication Bias | Overall Certainty of Evidence | Study Event Rates (%) | Relative Effect (95% CI) | Anticipated Absolute Effects | ||
| With Control/Alternnate | With Whole-Body Vibration | Risk with Control/Alternnate | Risk Difference with Whole-Body Vibration | ||||||||
| ODI | |||||||||||
| 488 (7 RCTs) | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | none | ⨁⨁⨁⨁ High | 235 | 253 | - | MD 3.78 SD lower (5.27 lower to 2.29 lower) | |
| VAS | |||||||||||
| 228 (4 RCTs) | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | none | ⨁⨁⨁⨁ High | 113 | 115 | - | - | SMD 0.81 SD lower (1.11 lower to 0.5 lower) |
| RMDQ | |||||||||||
| 329 (3 RCTs) | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | none | ⨁⨁⨁⨁ High | 162 | 167 | - | MD 1.43 SD lower (2.04 lower to 0.82 lower) | |
| Repositioning error | |||||||||||
| 228 (2 RCTs) | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | none | ⨁⨁⨁⨁ High | 113 | 115 | - | - | SMD 4.2 lower (7.5 lower to 0.89 lower) |
| PILE | |||||||||||
| 449 (2 RCTs) | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | none | ⨁⨁⨁⨁ High | 224 | 225 | - | - | SMD 0.25 higher (0.07 lower to 0.58 higher) |
| Balance | |||||||||||
| 242 (3 RCTs) | not serious | serious | not serious | not serious | none | ⨁⨁⨁◯ Moderate | 120 | 122 | - | - | SMD 0.21 lower (0.46 lower to 0.04 higher) |
| SF-36 | |||||||||||
| 170 (2 RCTs) | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | none | ⨁⨁⨁⨁ High | 84 | 86 | - | MD 1.49 SD higher (1.3 lower to 4.29 higher) | |
| NPRS | |||||||||||
| 85 (2 RCTs) | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | none | ⨁⨁⨁⨁ High | 80 | 95 | - | SMD 1.14 higher (2.40 higher to 0.12 lower) | |
| Outcome Measure | Systematic Review | Meta-Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| NPRS | 3/3 studies showed improvement | Large insignificant improvement |
| VAS | 4/4 studies showed improvement | Significant large improvement |
| ODI | 6/7 studies showed improvement | Significant large improvement |
| RMDQ | 3/3 studies showed improvement | Significant large improvement |
| Balance | 3/5 studies showed improvement | Significant moderate improvement |
| Proprioception | 2/2 studies showed improvement | Significant large improvement |
| Quality of life (SF-36) | 2/3 studies showed improvement | Not improved |
| PILE | 1/2 studies showed improvement | Not improved |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zafar, T.; Zaki, S.; Alam, M.F.; Sharma, S.; Babkair, R.A.; Nuhmani, S.; Pandita, S. Effect of Whole-Body Vibration Exercise on Pain, Disability, Balance, Proprioception, Functional Performance and Quality of Life in People with Non-Specific Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061639
Zafar T, Zaki S, Alam MF, Sharma S, Babkair RA, Nuhmani S, Pandita S. Effect of Whole-Body Vibration Exercise on Pain, Disability, Balance, Proprioception, Functional Performance and Quality of Life in People with Non-Specific Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(6):1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061639
Chicago/Turabian StyleZafar, Tasneem, Saima Zaki, Md Farhan Alam, Saurabh Sharma, Reem Abdullah Babkair, Shibili Nuhmani, and Sujata Pandita. 2024. "Effect of Whole-Body Vibration Exercise on Pain, Disability, Balance, Proprioception, Functional Performance and Quality of Life in People with Non-Specific Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 6: 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061639
APA StyleZafar, T., Zaki, S., Alam, M. F., Sharma, S., Babkair, R. A., Nuhmani, S., & Pandita, S. (2024). Effect of Whole-Body Vibration Exercise on Pain, Disability, Balance, Proprioception, Functional Performance and Quality of Life in People with Non-Specific Chronic Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(6), 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061639







