Effective Treatment of Rosacea and Other Vascular Lesions Using Intense Pulsed Light System Emitting Vascular Chromophore-Specific Wavelengths: A Clinical and Dermoscopical Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
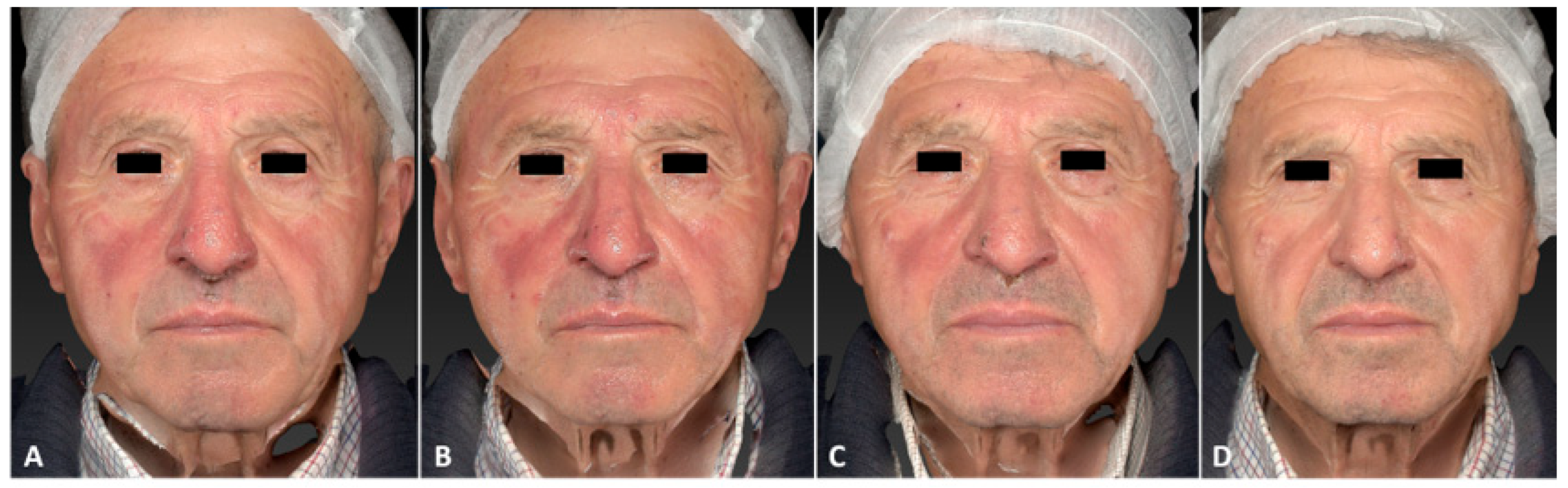
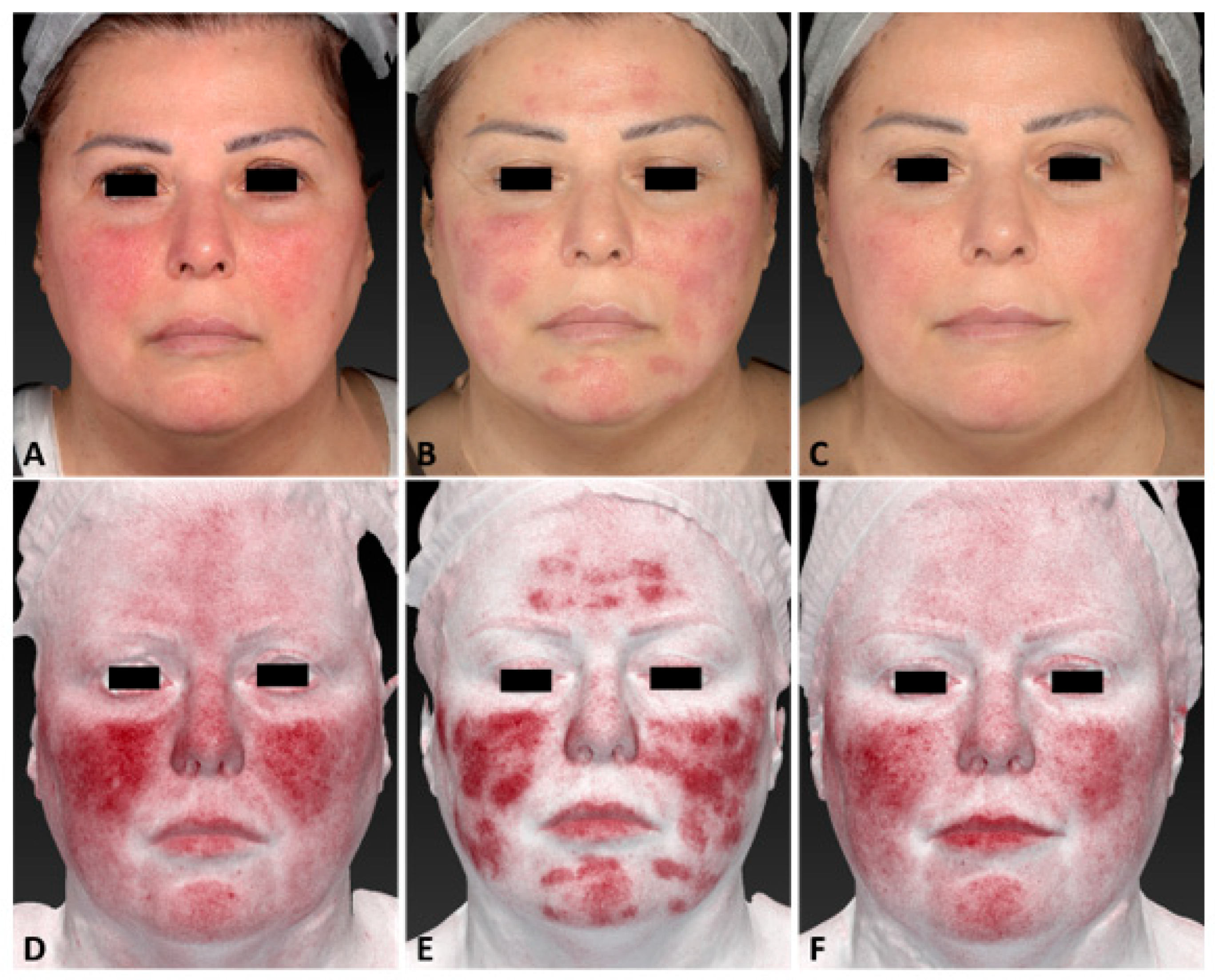
3. Results
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rainer, B.M.; Kang, S.; Chien, A.L. Rosacea: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. Derm. Endocrinol. 2017, 9, e1361574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gether, L.; Overgaard, L.; Egeberg, A.; Thyssen, J. Incidence and prevalence of rosacea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Thiboutot, D.; Anderson, R.; Cook-Bolden, F.; Draelos, Z.; Gallo, R.L.; Granstein, R.D.; Kang, S.; Macsai, M.; Gold, L.S.; Tan, J. Standard management options for rosacea: The 2019 update by the National Rosacea Society Expert Committee. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parodi, A.; Paolino, S.; Greco, A.; Drago, F.; Mansi, C.; Rebora, A.; Parodi, A.; Savarino, V. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in rosacea: Clinical effectiveness of its eradication. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 6, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meki´c, S.; Hamer, M.; Wigmann, C.; Gunn, D.; Kayser, M.; Jacobs, L.; Schikowski, T.; Nijsten, T.; Pardo, L. Epidemiology and determinants of facial telangiectasia: A cross-sectional study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Two, A.M.; Wu, W.; Gallo, R.L.; Hata, T.R.; Rosacea, J. Rosacea: Part I. Introduction, categorization, histology, pathogenesis, and risk factors. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 72, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoulis, A.C.; Stavrianeas, N.G.; Georgala, S.; Bozi, E.; Kalogeromitros, D.; Koumantaki, E.; Katsambas, A.D. Poikiloderma of Civatte: A clinical and epidemiological study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2005, 19, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vissing, A.-C.E.; Dierickx, C.; Karmisholt, K.E.; Haedersdal, M. Topical brimonidine reduces IPL-induced erythema without affecting efficacy: A randomized controlled trial in patients with facial telangiectasias. Lasers Surg. Med. 2018, 50, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, E.V.; Smirnov, M.; Pankratov, M.; Altshuler, G. Intense Pulsed Light and Laser Treatment of Facial Telangiectasias and Dyspigmentation: Some Theoretical and Practical Comparisons. Dermatol. Surg. 2006, 31, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, S.; Miceli, A.; Krishnamurthy, K. Treatment of Facial Telangiectases with Glycerin Sclerotherapy. Dermatol. Surg. 2019, 45, 950–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.; Kuceki, G.; Birdsall, M.; Sahni, D.R.; Sahni, V.N.; Hull, C.M. Rosacea: Practical Guidance and Challenges for Clinical Management. Rev. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, F.H.X.; Kumarasinghe, S.P. Brimonidine for treatment of telangiectasia of dermatomyositis. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2017, 59, e220–e221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello Netto, B.A.S.D.; Beiriz, Y.D.R.; Bonatto, A.C.; Maciel, G.S.B.; de Almeida, L.R.; Corassa, J.M. Uso de tartarato de brimonidina para resolução de matting telangiectásico: Relato de caso. J. Vasc. Bras. 2020, 19, e20190159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maliyar, K.; Abdulla, S.J. Dermatology: How to manage rosacea in skin of colour. Drugs Context 2022, 11, 2021-11-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Zuuren, E.J.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Tan, J.; van der Linden, M.M.; Arents, B.W.; Carter, B.; Charland, L. Interventions for rosacea based on the phenotype approach: An updated systematic review including GRADE assessments. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yepuri, V.; Patil, A.D.; Fritz, K.; Salavastru, C.; Kroumpouzos, G.; Nisticò, S.P.; Piccolo, D.; Sadek, A.; Badawi, A.; Kassir, M.; et al. Light-Based Devices for the Treatment of Facial Erythema and Telangiectasia. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, M.P.; Eckhouse, S. Photothermal sclerosis of leg veins. ESC medical systems, LTD photoderm VL Cooperative Study Group. Dermatol. Surg. 1996, 22, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.Y.; Moon, H.-R.; Ryu, H.J. Comparative efficacy of short-pulsed intense pulsed light and pulsed dye laser to treat rosacea. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2018, 21, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapicioglu, Y.; Sarac, G.; Cenk, H. Treatment of erythema to telangiectatic rosacea, facial erythema, and facial telangiectasia with a 577-nm pro-yellow laser: A case series. Lasers Med. Sci. 2019, 34, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stier, M.F.; Glick, S.A.; Hirsch, R.J. Laser treatment of pediatric vascular lesions: Port wine stains and hemangiomas. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 58, 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babilas, P.; Schreml, S.; Szeimies, R.-M.; Landthaler, M. Intense Pulsed Light (IPL): A Review. Lasers Surg. Med. 2010, 42, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistico, S.P.; Silvestri, M.; Zingoni, T.; Tamburi, F.; Bennardo, L.; Cannarozzo, G. Combination of Fractional CO2 Laser and Rhodamine-Intense Pulsed Light in Facial Rejuvenation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Photobiomodul. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2021, 39, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, D.; Di Marcantonio, D.; Crisman, G.; Cannarozzo, G.; Sannino, M.; Chiricozzi, A.; Chimenti, S. Unconventional use of intense pulsed light. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 618206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzengruber, F.; Czernielewski, J.; Conrad, C.; Feldmeyer, L.; Yawalkar, N.; Häusermann, P.; Cozzio, A.; Mainetti, C.; Goldblum, D.; Läuchli, S.; et al. Swiss S1 guideline for the treatment of rosacea. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 1775–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoppin, H.H.H.; Goldberg, D.J. Laser Treatment of Facial Telangiectases: An Update. Dermatol. Surg. 2010, 36, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammirati, C.T.; Carniol, P.J.; Hruza, G.J. Laser Treatment of Facial Vascular Lesions. Facial Plast. Surg. 2001, 17, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vladimir, F.; Jorgaqi, E.; Byzhyti, M. Our experience in the treatment of hemangioma with intense pulsed light laser: A 10 year study in Albania. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14880. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, J.D.; Friedmann, D.P.; Abdo, K.; Cahana, Z. Efficacy and Safety of Intense Pulsed Light With a KTP/PDLlike Filter for the Treatment of Facial Telangiectasias. J. Drugs Dermatol. JDD 2020, 19, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccolo, D.; Crisman, G.; Kostaki, D.; Cannarozzo, G.; Sannino, M.; Chimenti, S. Rhodamine intense pulsed light versus conventional intense pulsed light for facial telangiectasias. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2016, 18, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, M.P.; Weiss, R.A.; Weiss, M.A. Intense pulsed light as a nonablative approach to photoaging. Dermatol. Surg. 2005, 31, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeter, C.A.; Haaf-von Below, S.; Neumann, H.A.M. Effective treatment of rosacea using intense pulsed light systems. Dermatol. Surg. 2005, 31, 1285–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennardo, L.; Patruno, C.; Zappia, E.; Tamburi, F.; Sannino, M.; Negosanti, F.; Nisticò, S.P.; Cannarozzo, G. Combination of Specific Vascular Lasers and Vascular Intense Pulsed Light Improves Facial Telangiectasias and Redness. Medicina 2022, 58, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, Z.; Alster, T.S. The role of lasers and intense pulsed light technology in dermatology. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 9, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, M.J.; Torstensson, P.A. Thermal relaxation times: An outdated concept in photothermal treatments. Lasers Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raulin, C.; Greve, B.; Grema, H. IPL technology: A review. Lasers Surg. Med. 2003, 32, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunoda, K.; Akasaka, K.; Akasaka, T.; Amano, H. Successful treatment of erythematotelangiectatic rosacea with intense pulsed light: Report of 13 cases. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 1113–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gade, A.; Vasile, G.F.; Rubenstein, R. Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) Therapy; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bjerring, P.; Christiansen, K.; Troilius, A. Intense pulsed light source for treatment of facial telangiectasias. J. Cutan. Laser Ther. 2001, 3, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, N.M.; Rajabi-Estarabadi, A.; Aigen, A.R. Use of Intense Pulsed Light Versus Pulsed-Dye Laser in the Treatment of Truncal Telangiectasia. Dermatol. Surg. 2020, 47, 862–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanghetti, E.A. Split-face randomized treatment of facial telangiectasia comparing pulsed dye laser and an intense pulsed light handpiece. Lasers Surg. Med. 2011, 44, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campolmi, P.; Bonan, P.; Cannarozzo, G.; Bruscino, N.; Troiano, M.; Prignano, F.; Lotti, T. Intense pulsed light in the treatment of non-aesthetic facial and neck vascular lesions: Report of 85 cases. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2011, 25, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, H.; Yue, B.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z. Treatment of facial telangiectasia with narrow-band intense pulsed light in Chinese patients. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2018, 20, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Luan, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Zhou, N. Improved telangiectasia and reduced recurrence rate of rosacea after treatment with 540 nm-wavelength intense pulsed light: A prospective randomized controlled trial with a 2-year follow-up. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 3543–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsiwala, S.Z.; Arsiwala, N. Role of Dermoscopy in Laser Therapy. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2023, 14, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onizuka, K.; Tsuneda, K.; Shibata, Y.; Ito, M.; Sekine, I. Efficacy of flashlamp-pumped pulsed dye laser therapy for port wine stains: Clinical assessment and histopathological characteristics. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1995, 48, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiskerstrand, E.J.; Svaasand, L.O.; Kopstad, G.; Dalaker, M.; Norvang, L.T.; Volden, G. Laser treatment of port wine stains: Therapeutic outcome in relation to morphological parameters. Br. J. Dermatol. 1996, 134, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angermeier, M.C. Treatment of facial vascular lesions with intense pulsed light. J. Cutan. Laser Ther. 1999, 1, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retamar, R.A.; Chames, C.; Pellerano, G. Treatment of linear and spider telangiectasia with an intense pulsed light source. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2014, 3, 197–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Han, J.; Hu, D.; Cheng, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, T.; Zhao, W. Intense pulsed light is effective in treating postburn hyperpigmentation and telangiectasia in Chinese patients. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2018, 20, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piccolo, D.; Fusco, I.; Zingoni, T.; Conforti, C. Effective Treatment of Rosacea and Other Vascular Lesions Using Intense Pulsed Light System Emitting Vascular Chromophore-Specific Wavelengths: A Clinical and Dermoscopical Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061646
Piccolo D, Fusco I, Zingoni T, Conforti C. Effective Treatment of Rosacea and Other Vascular Lesions Using Intense Pulsed Light System Emitting Vascular Chromophore-Specific Wavelengths: A Clinical and Dermoscopical Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(6):1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061646
Chicago/Turabian StylePiccolo, Domenico, Irene Fusco, Tiziano Zingoni, and Claudio Conforti. 2024. "Effective Treatment of Rosacea and Other Vascular Lesions Using Intense Pulsed Light System Emitting Vascular Chromophore-Specific Wavelengths: A Clinical and Dermoscopical Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 6: 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061646
APA StylePiccolo, D., Fusco, I., Zingoni, T., & Conforti, C. (2024). Effective Treatment of Rosacea and Other Vascular Lesions Using Intense Pulsed Light System Emitting Vascular Chromophore-Specific Wavelengths: A Clinical and Dermoscopical Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(6), 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13061646





