Evaluation of Aligners and Root Resorption: An Overview of Systematic Reviews
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Protocol
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Information Sources, Search Strategy, and Study Selection
2.4. Data Items and Collection
2.5. Quality Assessment
2.6. Data Synthesis
3. Results
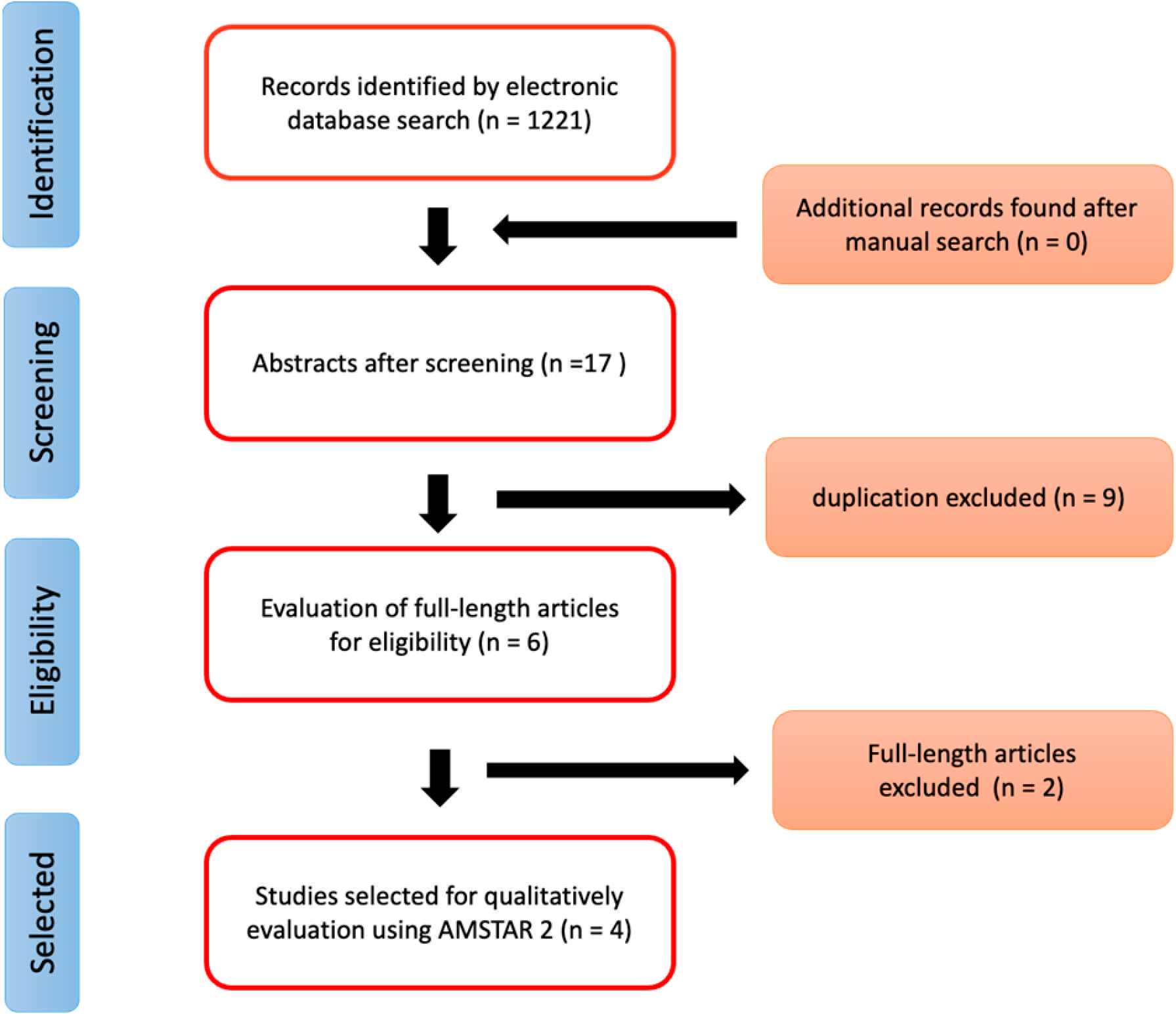
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Quality of Evidence from the Data Synthesis
3.4. Data Synthesis
3.5. Root Resorption According to the Detection Method
3.6. Root Resorption in CAT versus Pre-Adjusted Edgewise Appliances (PEA)
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weltman, B.; Vig, K.W.; Fields, H.W.; Shanker, S.; Kaizar, E.E. Root resorption associated with orthodontic tooth movement: A systematic review. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2010, 137, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldeeri, A.; Alhammad, L.; Alduham, A.; Ghassan, W.; Shafshak, S.; Fatani, E. Association of orthodontic clear aligners with root resorption using three-dimension measurements: A systematic review. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2018, 19, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassir, Y.A.; McIntyre, G.T.; Bearn, D.R. Orthodontic treatment and root resorption: An overview of systematic reviews. Eur. J. Orthod. 2021, 43, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sameshima, G.T.; Iglesias-Linares, A. Orthodontic root resorption. J. World Fed. Orthod. 2021, 10, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azaripour, A.; Weusmann, J.; Mahmoodi, B.; Peppas, D.; Gerhold-Ay, A.; Van Noorden, C.J.F.; Willershausen, B. Braces versus Invisalign®: Gingival parameters and patients’ satisfaction during treatment: A cross-sectional study. BMC Oral Health 2015, 15, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meade, M.J.; Ng, E.; Weir, T. Digital treatment planning and clear aligner therapy: A retrospective cohort study. J. Orthod. 2023, 50, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brezniak, N.; Wasserstein, A. Root resorption following treatment with aligners. Angle Orthod. 2008, 78, 111–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias-Linares, A.; Sonnenberg, B.; Solano, B.; Yañez-Vico, R.-M.; Solano, E.; Lindauer, S.J.; Flores-Mir, C. Orthodontically induced external apical root resorption in patients treated with fixed appliances vs removable aligners. Angle Orthod. 2017, 87, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissa, O.; Carlyle, T.; El-Bialy, T. Evaluation of root length following treatment with clear aligners and two different fixed orthodontic appliances. A pilot study. J. Orthod. Sci. 2018, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, V.; Mehta, S.; Gauthier, M.; Mu, J.; Kuo, C.-L.; Nanda, R.; Yadav, S. Comparison of external apical root resorption with clear aligners and pre-adjusted edgewise appliances in non-extraction cases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Orthod. 2021, 43, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samandara, A.; Papageorgiou, S.N.; Ioannidou-Marathiotou, I.; Kavvadia-Tsatala, S.; A Papadopoulos, M. Evaluation of orthodontically induced external root resorption following orthodontic treatment using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Orthod. 2019, 41, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponder, S.N.; Benavides, E.; Kapila, S.; Hatch, N.E. Quantification of external root resorption by low- vs high-resolution cone-beam computed tomography and periapical radiography: A volumetric and linear analysis. Am. J. Orthodont. Dentofac. Orthoped. 2013, 143, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadauskaitė, U.; Berlin, V. Orthodontic treatment with clear aligners and apical root resorption. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 35–47. [Google Scholar]
- Elhaddaoui, R.; Qoraich, H.S.; Bahije, L.; Zaoui, F. Orthodontic aligners and root resorption: A systematic review. Int. Orthod. 2017, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: A critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 2017, 358, j4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. The PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir-Behghadami, M.; Janati, A. Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes and Study (PICOS) design as a framework to formulate eligibility criteria in systematic reviews. Emerg. Med. 2020, 37, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Qi, R.; Liu, C. Root resorption in orthodontic treatment with clear aligners: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2019, 22, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laux, M.; Abbott, P.V.; Pajarola, G.; Nair, P.N.R. Apical inflammatory root resorption: A correlative radiographic and histological assessment. Int. Endod. J. 2000, 33, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezniak, N.; Wasserstein, A. Orthodontically induced inflammatory root resorption. Part I: The basic science aspects. Angle Orthod. 2002, 72, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hohmann, A.; Wolfram, U.; Geiger, M.; Boryor, A.; Kober, C.; Sander, C.; Sander, F.G. Correspondences of hydrostatic pressure in periodontal ligament with regions of root resorption: A clinical and a finite element study of the same human teeth. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. Update 2009, 93, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jacox, L.A.; Little, S.H.; Ko, C.C. Orthodontic tooth movement: The biology and clinical implications. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2018, 34, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brezniak, N.; Wasserstein, A. Orthodontically induced inflammatory root resorption. Part II: The clinical aspects. Angle Orthod. 2002, 72, 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.L.; Hua, X.M. Root Resorption of Clear Aligner Treatment. J. Oral Sci. 2019, 35, 1115–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.Y.; Feng, Y.X. Clinical research advances of root resorption during orthodontic treatment with aligners. J. Pract. Stomatol. 2019, 12, 756–759. [Google Scholar]
- Currell, S.D.; Liaw, A.; Grant, P.D.B.; Esterman, A.; Nimmo, A. Orthodontic mechanotherapies and their influence on external root resorption: A systematic review. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2019, 155, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Hikida, T.; Yoshino, T.; Kikuta, J.; Shimizu, M.; Takahashi, M.; Kasai, K. Jiggling force aggravates orthodontic root resorption via TNF-α during rat experimental tooth movement. Int. J. Oral-Med. Sci. 2016, 14, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, T. Evaluation of root resorption after comprehensive orthodontic treatment using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT): A meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health 2018, 18, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inchingolo, F.; Inchingolo, A.M.; Palmieri, G.; Di Pede, C.; Garofoli, G.; de Ruvo, E.; Inchingolo, A.D.; Palermo, A.; Mancini, A.; Di Venere, D.; et al. Root Resorption during Orthodontic Treatment with Clear Aligners vs. Fixed Appliances-A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, L.J.; Jones, A.S.; Petocz, P.; Darendeliler, M.A. Physical properties of root cementum: Part 10. Comparison of the effects of invisible removable thermoplastic appliances with light and heavy orthodontic forces on premolar cementum. A microcomputed-tomography study. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 133, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marina, G.R.; Josete, B.C.M.; Paolo, M.C. Association of orthodontic force system and root resorption: A systematic review. Am J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2015, 147, 610–626. [Google Scholar]
- Shea, B.J.; Hamel, C.; Wells, G.A.; Bouter, L.; Kristjansson, E.; Grimshaw, J.; Henry, D.; Boers, M. AMSTAR is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherrard, J.F.; Rossouw, P.E.; Benson, B.W.; Carrillo, R.; Buschang, P.H. Accuracy and reliability of tooth and root lengths measured on cone-beam computed tomographs. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2010, 137, S100–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, B.; Holly, M.; Paine, M.; Sameshima, G. A Comparison of Root Resorption between Invisalign Treatment and Contemporary Orthodontic Treatment. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 1–91. [Google Scholar]

| Database | Search Strategy | Sum |
|---|---|---|
| 1 MEDLINE (via Pubmed) | (root or tooth or apical) * resorption and (aligners or invisalign) and orthodontics | 159 |
| 2 Google Scholar | (root or tooth or apical) * resorption and (aligners or invisalign) and orthodontics | 678 |
| 3 ScienceDirect | ((root or tooth or apical) * resorption) and (aligners or invisalign) | 55 |
| 4 Web of Science | (root resorption) and orthodontics | 39 |
| 5 Embase | (‘root resorption’/exp OR ‘root resorption’ OR ((‘root’/exp OR root) AND (‘resorption’/exp OR resorption))) AND (aligners OR ‘invisalign’/exp OR invisalign) | 251 |
| 6 Scopus | (root or tooth or apical) * resorption and (aligners or invisalign) and orthodontics | error |
| 7 LIVIVO | root resorption and aligner and review | 36 |
| 8 LILACS | (root or tooth or apical) * resorption and (aligners or invisalign) and orthodontics | 3 |
| Total | 1221 |
| Author | Year | Study Design | No. of Study | No. of Participants | Type of Study | Period of Search | Journal | Objective | Quality of Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaibhav Gandhi et al. [10] | 2021 | systematic review and meta-analysis | 16 | 523 | 4 prospective, 12 retrospective | up to 31 December 2019 | Eur J Orthod | tTo evaluate and compare the amount of EARR observed during the orthodontic treatment with PEA or CAT and with 2D or 3D methods | Low |
| Sadauskaitė U, Berlin V. [13] | 2020 | systematic review | 6 | 686 | 2 retrospective, 1 prospective, 1 pilot, 1 case-control, 1 NRCT | 2009 to 2019 | Med. Sci | To evaluate the link between clear aligner therapy and EARR and to the amount of EARR using clear aligner therapy and fixed orthodontic treatment | Critically low |
| Xuanwei Fang et al. [18] | 2019 | systematic review and meta-analysis | 11 | 828 | 6 before-and-after, 4 cohort | up to December 2018 | Orthod Craniofac Res | To investigate the EARR in participants receiving CAT and it with PEA | Low |
| Rajae Elhaddaoui et al. [14] | 2016 | systematic review | 3 | 217 | 1 NRCT, 1 retrospective, 1 RCT | up to December 2015 | Int orthod | To assess the incidence and severity of RR following CAT and associated factors, a comparative analysis also made with fixed multi-bracket treatments | Critically low |
| Meeting the Criteria | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | Partial Yes | No | |
| 1. Did the research questions and inclusion criteria for the review include the components of PICO? | 4 | ||
| 2. Did the report of the review contain an explicit statement that the review methods were established prior to the conduct of the review and did the report justify any significant deviations from the protocol? | 2 | 2 | |
| 3. Did the review authors explain their selection of the study designs for inclusion in the review? | 4 | ||
| 4. Did the review authors use a comprehensive literature search strategy? | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 5. Did the review authors perform study selection in duplicate? | 2 | 2 | |
| 6. Did the review authors perform data extraction in duplicate? | 2 | 2 | |
| 7. Did the review authors provide a list of excluded studies and justify the exclusions? | 1 | 3 | |
| 8. Did the review authors describe the included studies in adequate detail? | 4 | ||
| 9. Did the review authors use a satisfactory technique for assessing the risk of bias in individual studies that were included in the review? | 2 | 2 | |
| 10. Did the review authors report on the sources of funding for the studies included in the review? | 1 | 3 | |
| 11. If meta-analysis was performed did the review authors use appropriate methods for statistical combination of results? | 1 | 1 | |
| 12. If meta-analysis was performed, did the review authors assess the potential impact of risk of bias in individual studies on the results of the meta-analysis or other evidence synthesis? | 2 | 2 | |
| 13. Did the review authors account for risk of bias in individual studies when interpreting/discussing the results of the review? | 1 | 3 | |
| 14. Did the review authors provide a satisfactory explanation for, and discussion of, any heterogeneity observed in the results of the review? | 2 | ||
| 15. If they performed quantitative synthesis did the review authors carry out an adequate investigation of publication bias (small study bias) and discuss its likely impact on the results of the review? | 3 | 1 | |
| 16. Did the review authors report any potential sources of conflict of interest, including any funding they received for conducting the review? | 2 | 2 | |
| [10] | [13] | [18] | [14] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Did the research questions and inclusion criteria for the review include the components of PICO? | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 2. Did the report of the review contain an explicit statement that the review methods were established prior to the conduct of the review and did the report justify any significant deviations from the protocol? | Y | N | Y | N |
| 3. Did the review authors explain their selection of the study designs for inclusion in the review? | N | N | N | N |
| 4. Did the review authors use a comprehensive literature search strategy? | Y | N | PY | PY |
| 5. Did the review authors perform study selection in duplicate? | Y | N | Y | N |
| 6. Did the review authors perform data extraction in duplicate? | Y | N | Y | N |
| 7. Did the review authors provide a list of excluded studies and justify the exclusions? | N | N | Y | N |
| 8. Did the review authors describe the included studies in adequate detail? | PY | PY | PY | PY |
| 9. Did the review authors use a satisfactory technique for assessing the risk of bias in individual studies that were included in the review? | Y | N | Y | N |
| 10. Did the review authors report on the sources of funding for the studies included in the review? | N | Y | N | N |
| 11. If meta-analysis was performed did the review authors use appropriate methods for statistical combination of results? | Y | NM | N | NM |
| 12. If meta-analysis was performed, did the review authors assess the potential impact of risk of bias in individual studies on the results of the meta-analysis or other evidence synthesis? | N | NM | N | NM |
| 13. Did the review authors account for risk of bias in individual studies when interpreting/discussing the results of the review? | Y | N | Y | N |
| 14. Did the review authors provide a satisfactory explanation for, and discussion of, any heterogeneity observed in the results of the review? | Y | N | Y | N |
| 15. If they performed quantitative synthesis did the review authors carry out an adequate investigation of publication bias (small study bias) and discuss its likely impact on the results of the review? | Y | NM | N | N |
| 16. Did the review authors report any potential sources of conflict of interest, including any funding they received for conducting the review? | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Quality of evidence | Low Critically | Low Critically | low | low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Zhang, P.; Koh, J.-T.; Oh, M.-H.; Cho, J.-H. Evaluation of Aligners and Root Resorption: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13071950
Zhang M, Zhang P, Koh J-T, Oh M-H, Cho J-H. Evaluation of Aligners and Root Resorption: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(7):1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13071950
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Meiling, Peng Zhang, Jeong-Tae Koh, Min-Hee Oh, and Jin-Hyoung Cho. 2024. "Evaluation of Aligners and Root Resorption: An Overview of Systematic Reviews" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 7: 1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13071950
APA StyleZhang, M., Zhang, P., Koh, J.-T., Oh, M.-H., & Cho, J.-H. (2024). Evaluation of Aligners and Root Resorption: An Overview of Systematic Reviews. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(7), 1950. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13071950







