Effect of Monosodium Urate Crystal Deposition on Atherosclerotic Carotid Plaques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Ethics
2.2. Study Design and Population
2.3. Demographic Data and Laboratory Data
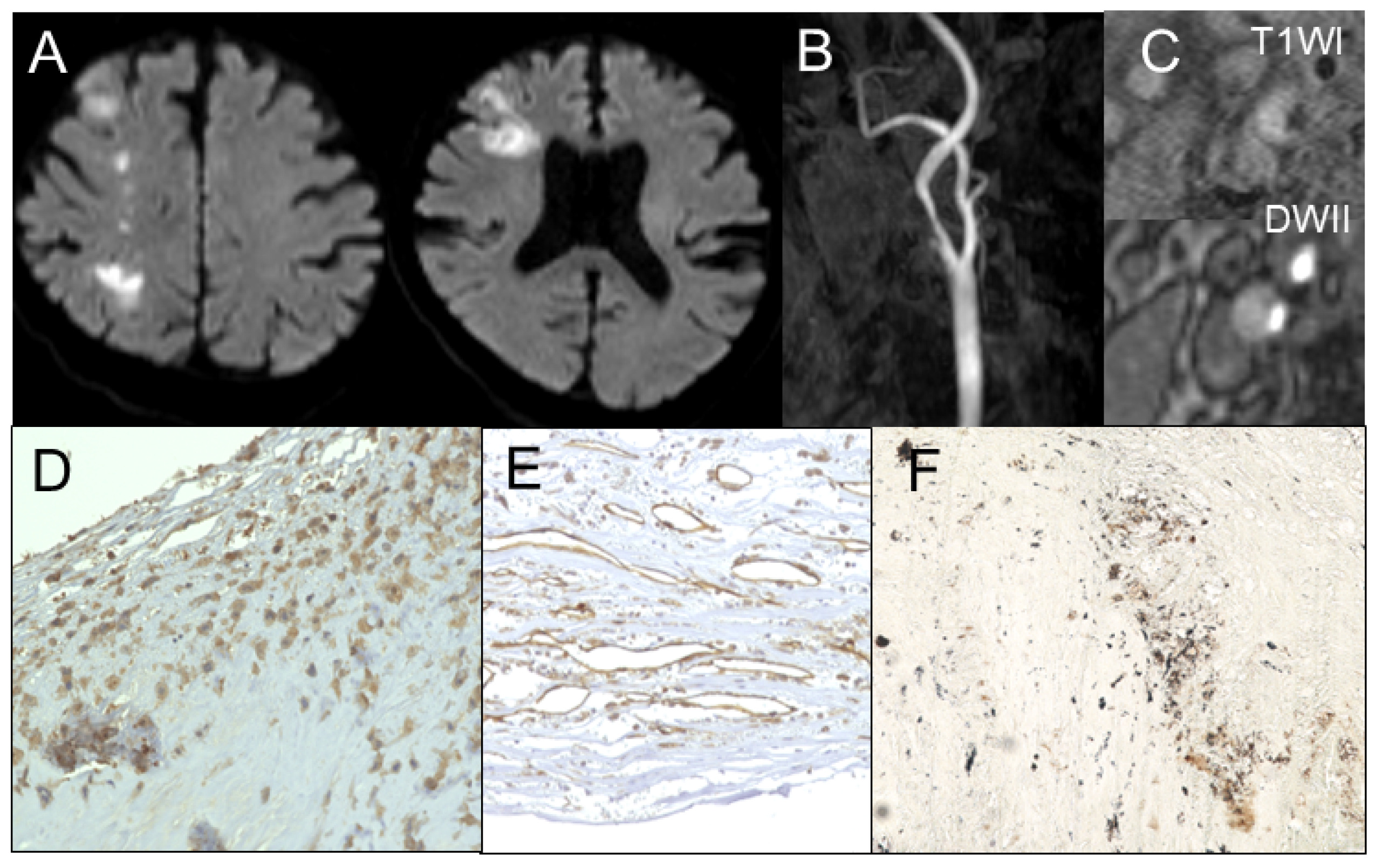
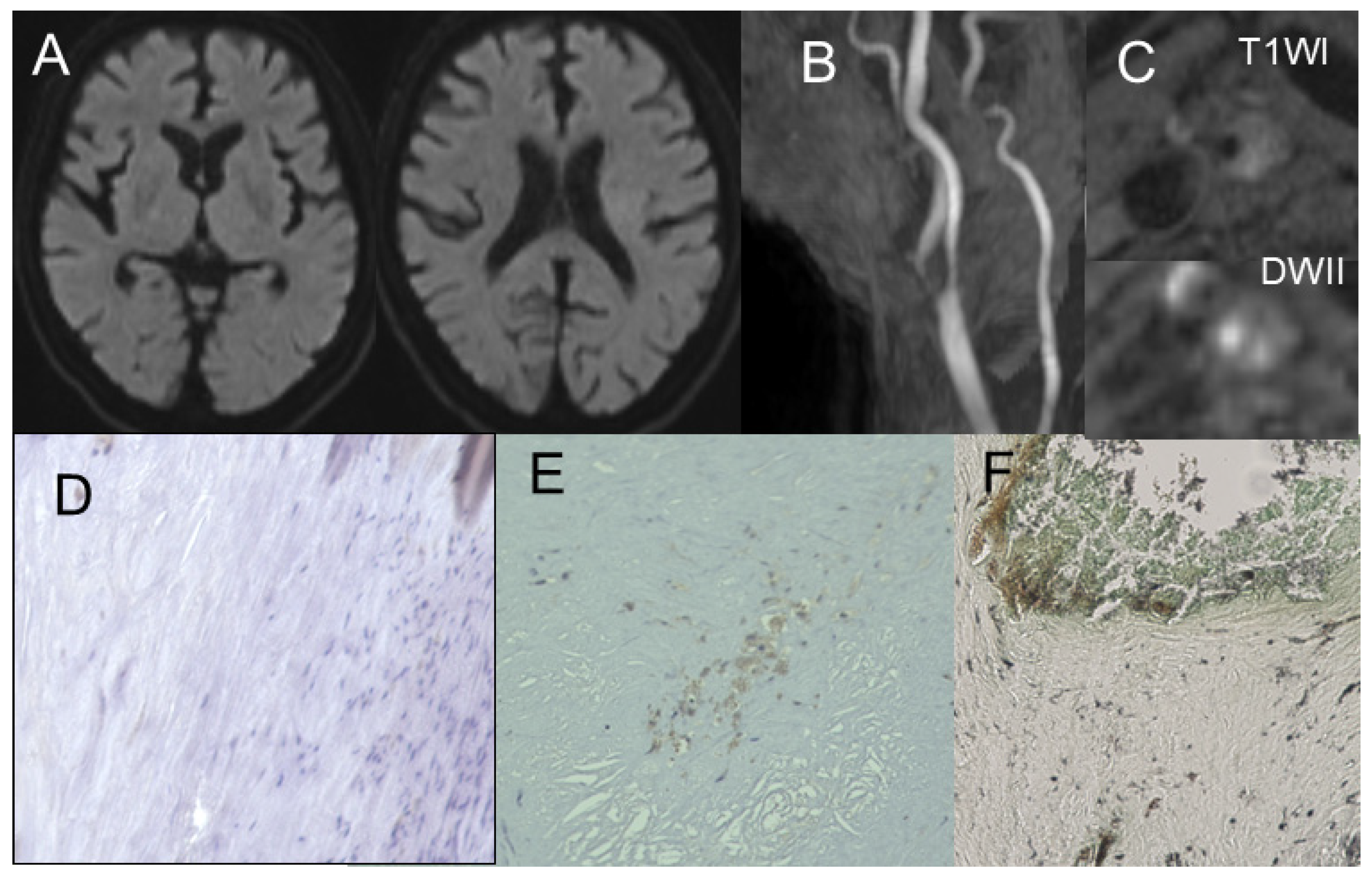
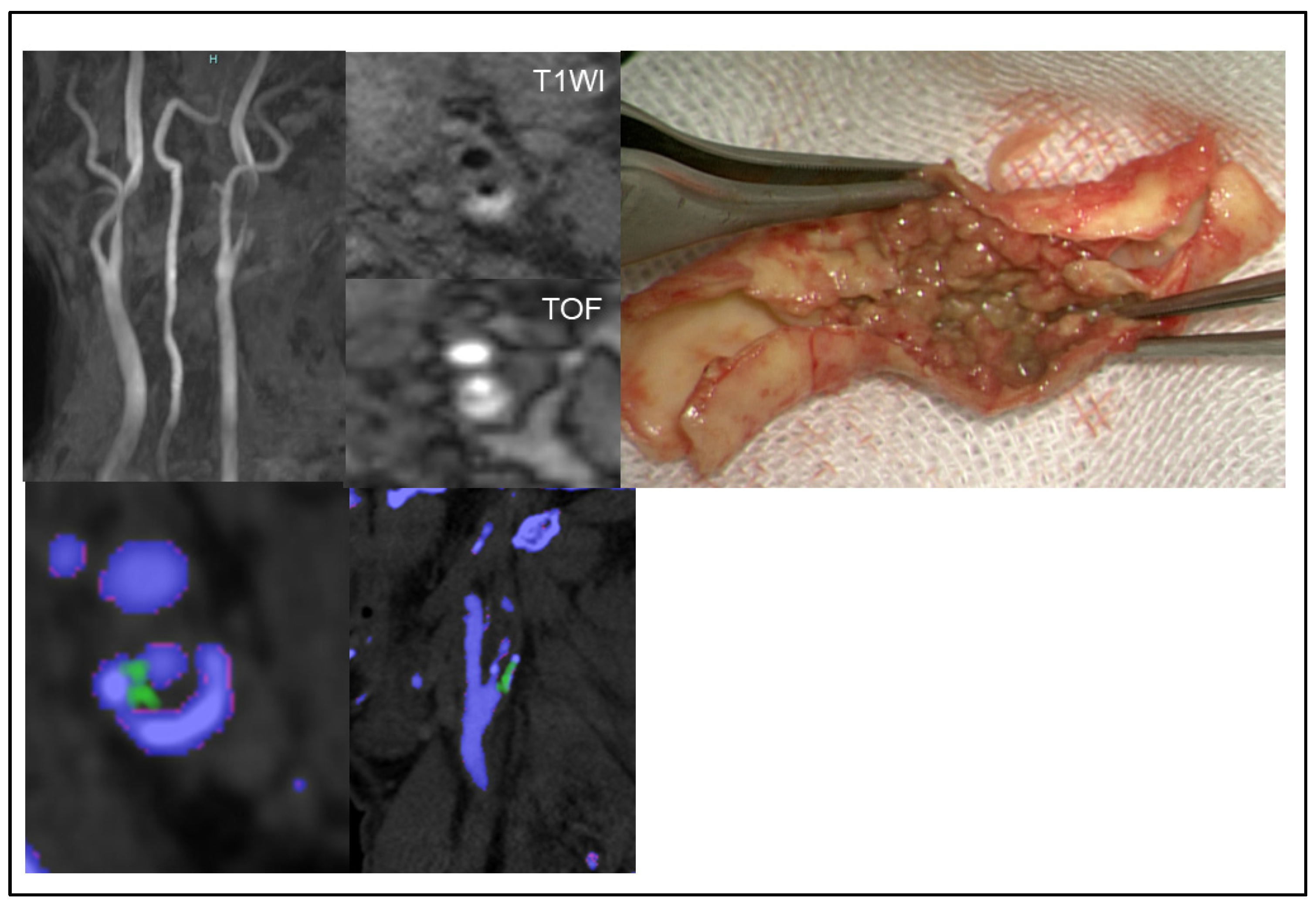
2.4. Assessing MSU Deposits in Plaque and Stenosis Degree Using DECT
2.5. Assessing Plaque Composition Using MR Imaging
2.6. Immunohistochemistry for Urate Crystal
2.7. Blood Sampling
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Gomori’s Methenamine Silver and HE Staining
3.3. Correlation Between Radiological Findings and Plaque Pathology
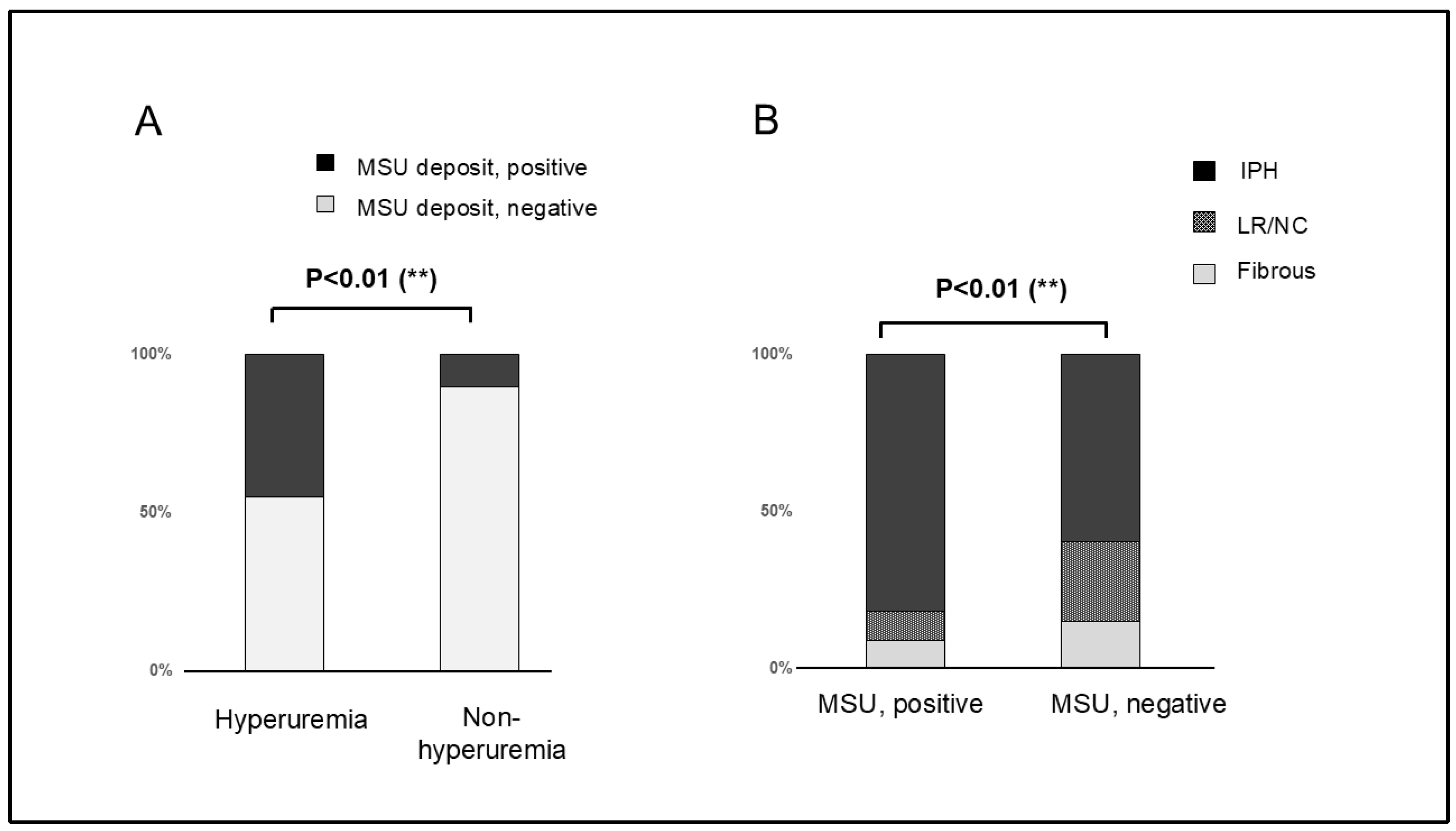
3.4. MSU Deposits Detected Using DECT and Its Accuracy
4. Discussion
4.1. Correlation Between Plaque Composition, Inflammation, and MSU Crystal Deposition
4.2. MSU Crystal Deposits Detected Using DECT
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Easton, J.D.; Saver, J.L.; Albers, G.W.; Alberts, M.J.; Chaturvedi, S.; Feldmann, E.; Hatsukami, T.S.; Higashida, R.T.; Johnston, S.C.; Kidwell, C.S.; et al. Definition and evaluation of transient ischemic attack: A scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council; Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and the Interdisciplinary Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease. The American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this statement as an educational tool for neurologists. Stroke 2009, 40, 2276–2293. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Savastano, L.; Brinjikji, W.; Lutsep, H.; Chen, H.; Chaturvedi, S. Symptomatic Nonstenotic Carotids: A Topical Review. Stroke 2024, 55, 2921–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patetsios, P.; Song, M.; Shutze, W.P.; Pappas, C.; Rodino, W.; Ramirez, J.A.; Panetta, T.F. Identification of uric acid and xanthine oxidase in atherosclerotic plaque. Am. J. Cardiol. 2001, 88, 188–191, A6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosla, U.M.; Zharikov, S.; Finch, J.L.; Nakagawa, T.; Roncal, C.; Mu, W.; Krotova, K.; Block, E.R.; Prabhakar, S.; Johnson, R.J. Hyperuricemia induces endothelial dysfunction. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 1739–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.F.; Grainge, M.J.; Zhang, W.; Doherty, M. Global epidemiology of gout: Prevalence, incidence and risk factors. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.K.; Al-Arfaj, A.M.; Eftekhari, A.; Munk, P.L.; Shojania, K.; Reid, G.; Nicolaou, S. Dual energy computed tomography in tophaceous gout. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1609–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richette, P.; Doherty, M.; Pascual, E.; Barskova, V.; Becce, F.; Castaneda, J.; Coyfish, M.; Guillo, S.; Jansen, T.; Janssens, H.; et al. 2018 updated European League Against Rheumatism evidence-based recommendations for the diagnosis of gout. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalbeth, N.; House, M.E.; Aati, O.; Tan, P.; Franklin, C.; Horne, A.; Gamble, G.D.; Stamp, L.K.; Doyle, A.J.; McQueen, F.M. Urate crystal deposition in asymptomatic hyperuricaemia and symptomatic gout: A dual energy CT study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 908–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuchtner, G.M.; Plank, F.; Beyer, C.; Schwabl, C.; Held, J.; Bellmann-Weiler, R.; Weiss, G.; Gruber, J.; Widmann, G.; Klauser, A.S. Monosodium Urate Crystal Deposition in Coronary Artery Plaque by 128-Slice Dual-Energy Computed Tomography: An Ex Vivo Phantom and In Vivo Study. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2021, 45, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patetsios, P.; Rodino, W.; Wisselink, W.; Bryan, D.; Kirwin, J.D.; Panetta, T.F. Identification of uric acid in aortic aneurysms and atherosclerotic artery. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1996, 800, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stary, H.C.; Chandler, A.B.; Dinsmore, R.E.; Fuster, V.; Glagov, S.; Insull, W.; Rosenfeld, M.E., Jr.; Schwartz, C.J.; Wagner, W.D.; Wissler, R.W. A definition of advanced types of atherosclerotic lesions and a histological classification of atherosclerosis. A report from the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis, American Heart Association. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1995, 15, 1512–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, V.; Franchi, F.; Prasad, M.; Fatica, E.M.; Alexander, M.P.; Bois, M.C.; Lam, J.; Singh, R.J.; Meyer, F.B.; Lanzino, G.; et al. Uric Acid Expression in Carotid Atherosclerotic Plaque and Serum Uric Acid Are Associated With Cerebrovascular Events. Hypertension 2022, 79, 1814–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Ogino, K.; Igawa, G.; Matsuura, T.; Kaetsu, Y.; Sugihara, S.; Matsubara, K.; Miake, J.; Hamada, T.; Yoshida, A.; et al. Allopurinol reduces neointimal hyperplasia in the carotid artery ligation model in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertens. Res. 2006, 29, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kimura, Y.; Yanagida, T.; Onda, A.; Tsukui, D.; Hosoyamada, M.; Kono, H. Soluble Uric Acid Promotes Atherosclerosis via AMPK (AMP-Activated Protein Kinase)-Mediated Inflammation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwazaki, D.; Koh, M.; Uchino, H.; Akioka, N.; Kuwayama, N.; Noguchi, K.; Kuroda, S. Hypoxia accelerates intraplaque neovascularization derived from endothelial progenitor cells in carotid stenosis. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 131, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omoumi, P.; Becce, F.; Racine, D.; Ott, J.G.; Andreisek, G.; Verdun, F.R. Dual-Energy CT: Basic Principles, Technical Approaches, and Applications in Musculoskeletal Imaging (Part 1). Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2015, 19, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dawson, P.A.; Hubbert, M.L.; Rao, A. Getting the mOST from OST: Role of organic solute transporter, OSTalpha-OSTbeta, in bile acid and steroid metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallinson, P.I.; Coupal, T.; Reisinger, C.; Chou, H.; Munk, P.L.; Nicolaou, S.; Ouellette, H. Artifacts in dual-energy CT gout protocol: A review of 50 suspected cases with an artifact identification guide. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 203, W103–W109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| With Hyperuricemia | Without Hyperuricemia | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | n = 31 (34.8%) | n = 58 (65.2%) | |
| Age (years) | 72.2 ± 9.2 | 71.3 ± 8.4 | 0.54 |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 27 | 51 | 0.92 |
| Female | 4 | 7 | |
| Medical comorbidity | |||
| Hypertension | 25 | 46 | 0.48 |
| Diabetetes | 15 | 27 | 0.52 |
| Hypercholesterolemia | 18 | 30 | 0.27 |
| Coronary artery disease | 12 | 18 | 0.49 |
| Aortic disease | 6 | 10 | 0.78 |
| ASO | 5 | 9 | 0.98 |
| Chronic renal failure | 12 | 18 | 0.45 |
| History of stroke | |||
| Ischemic stroke | 8 | 13 | 0.79 |
| Ipsilateral ischemic stroke | 5 | 8 | 0.76 |
| Contra- or posterior circulation | 3 | 5 | 0.98 |
| Hemorrhagic stroke | 2 | 4 | 0.95 |
| Medical therapy prior to CEA | |||
| Hyperuricemia | 25 | 12 | <0.01 |
| HT | 24 | 42 | 0.8 |
| HL statin | 18 | 26 | 0.27 |
| HL other | 5 | 7 | 0.74 |
| DM | 13 | 20 | 0.49 |
| Antiplatelet | 11 | 15 | 0.81 |
| Anticoaglunt | 2 | 5 | 0.95 |
| Radiological findings | |||
| Degree of stenosis(%) | 71.0 ± 11.3 | 69.5 ± 11.3 | 0.48 |
| Plaque unceration presence | 17 | 22 | 0.19 |
| Ipsilateral intracranial atherosclerosis | 5 | 11 | 0.97 |
| Plaque composition | |||
| Fibrous | 2 | 4 | 0.86 |
| LR/NC | 8 | 11 | |
| IPH | 21 | 43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kashiwazaki, D.; Maruyama, K.; Hamada, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Hori, E.; Akioka, N.; Noguchi, K.; Kuroda, S. Effect of Monosodium Urate Crystal Deposition on Atherosclerotic Carotid Plaques. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020518
Kashiwazaki D, Maruyama K, Hamada S, Yamamoto S, Hori E, Akioka N, Noguchi K, Kuroda S. Effect of Monosodium Urate Crystal Deposition on Atherosclerotic Carotid Plaques. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(2):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020518
Chicago/Turabian StyleKashiwazaki, Daina, Kunitaka Maruyama, Saori Hamada, Shusuke Yamamoto, Emiko Hori, Naoki Akioka, Kyo Noguchi, and Satoshi Kuroda. 2025. "Effect of Monosodium Urate Crystal Deposition on Atherosclerotic Carotid Plaques" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 2: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020518
APA StyleKashiwazaki, D., Maruyama, K., Hamada, S., Yamamoto, S., Hori, E., Akioka, N., Noguchi, K., & Kuroda, S. (2025). Effect of Monosodium Urate Crystal Deposition on Atherosclerotic Carotid Plaques. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(2), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14020518






