Differences in Artificial Intelligence-Based Macular Fluid Parameters Between Clinical Stages of Diabetic Macular Edema and Their Relationship with Visual Acuity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. The Neural Network for MF Segmentation
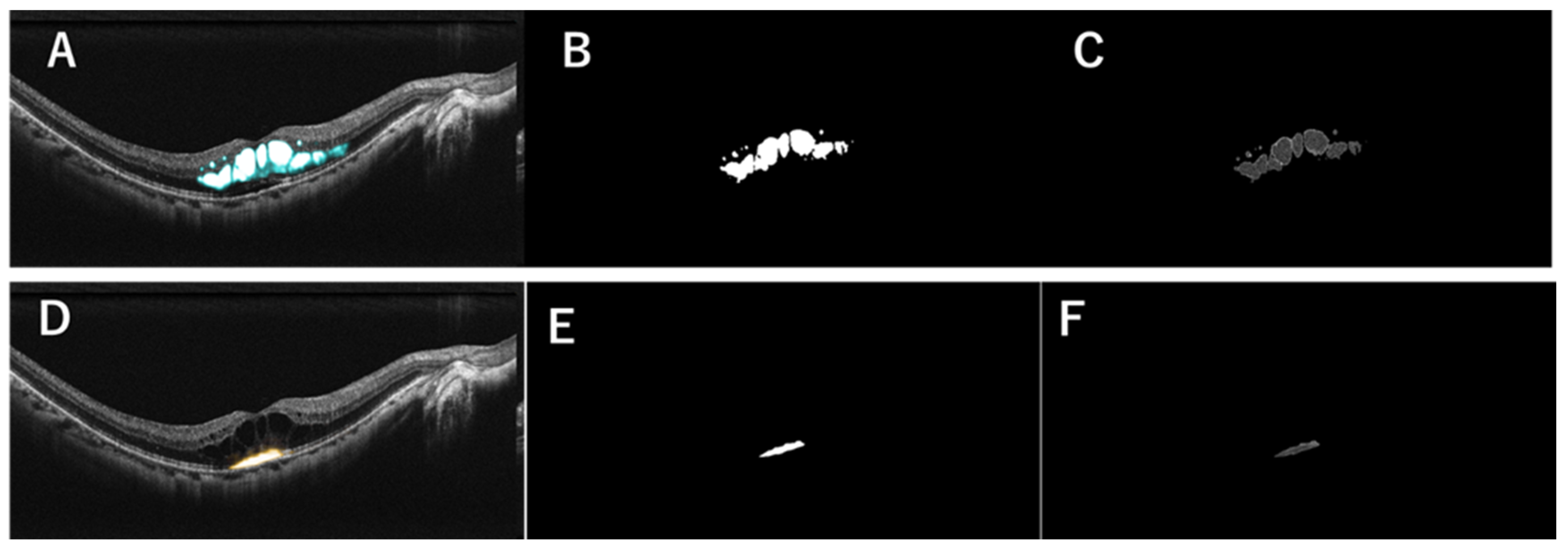
2.3. Generation of MF Images in a Representative Case
2.4. Endpoints and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Background
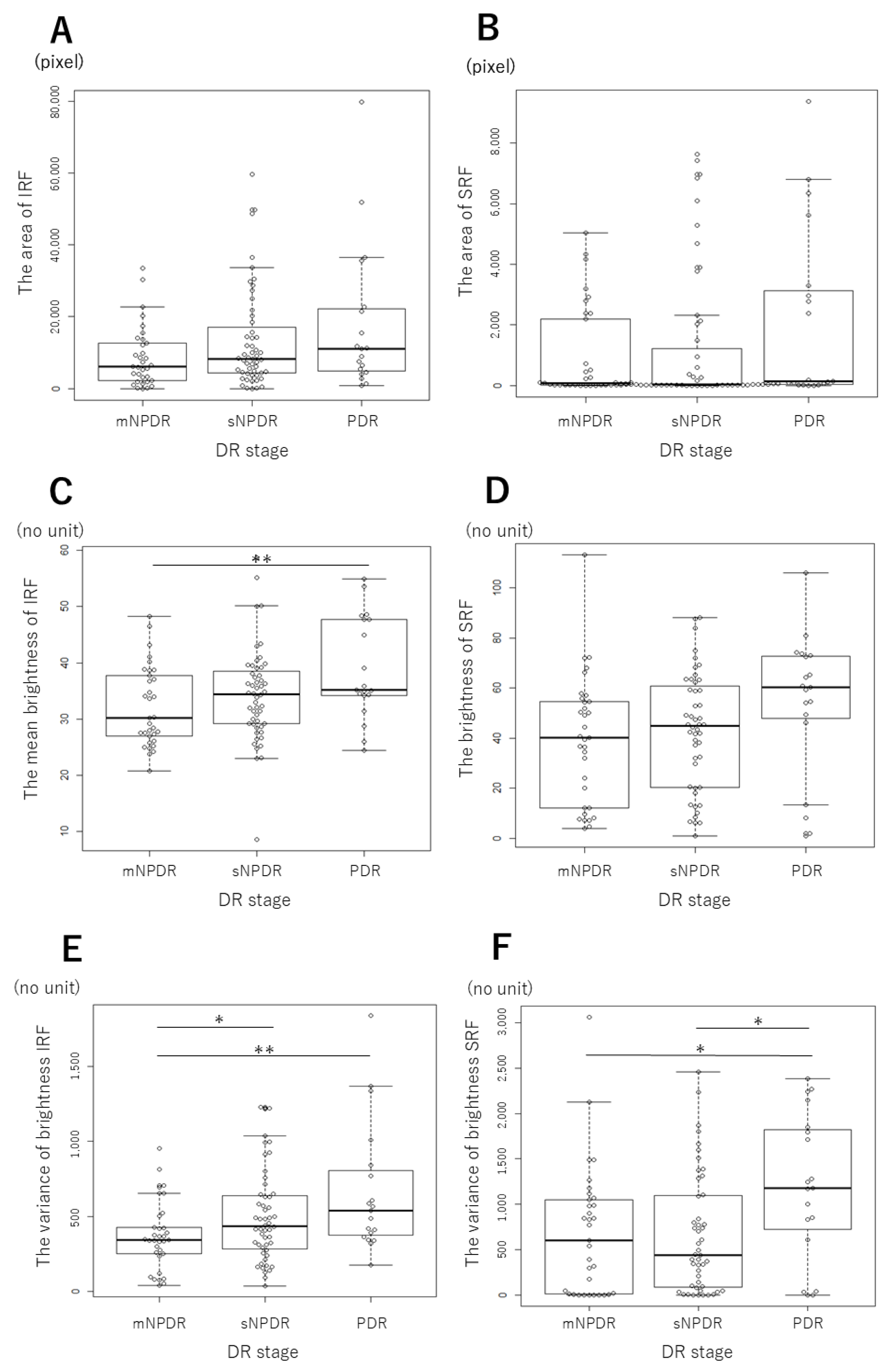
3.2. Changes in the MF Parameters Depending on DR Stages
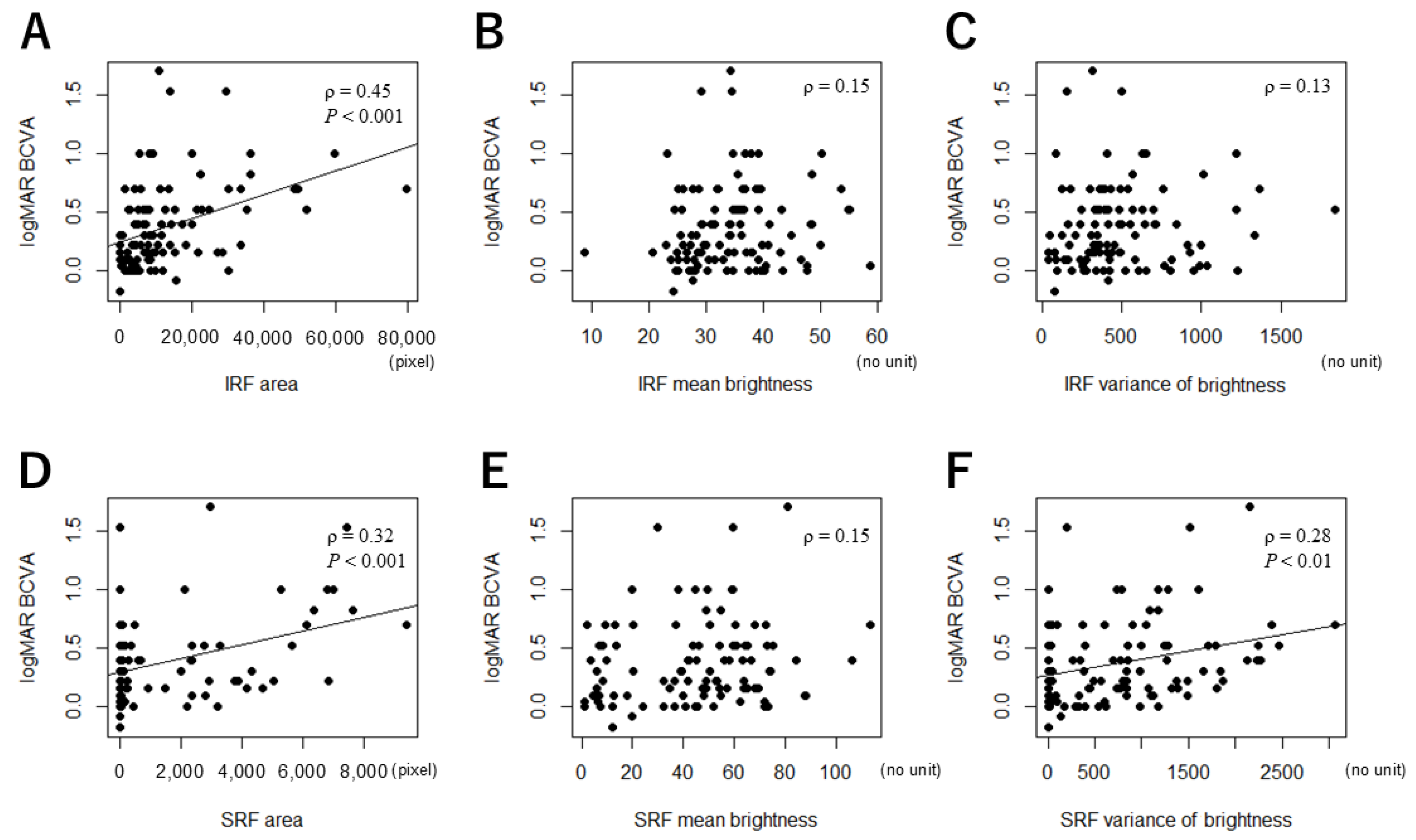
3.3. Correlations Between the MF Parameters and logMAR BCVA
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Do, D.V.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Boyer, D.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Brown, D.M.; Vitti, R.; Berliner, A.J.; Gao, B.; Zeitz, O.; Ruckert, R.; et al. One-Year Outcomes of the DA VINCI Study of VEGF Trap-Eye in Eyes with Diabetic Macular Edema. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 1658–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlegl, T.; Waldstein, S.M.; Bogunovic, H.; Endstraßer, F.; Sadeghipour, A.; Philip, A.-M.; Podkowinski, D.; Gerendas, B.S.; Langs, G.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U. Fully Automated Detection and Quantification of Macular Fluid in OCT Using Deep Learning. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alryalat, S.A.; Al-Antary, M.; Arafa, Y.; Azad, B.; Boldyreff, C.; Ghnaimat, T.; Al-Antary, N.; Alfegi, S.; Elfalah, M.; Abu-Ameerh, M. Deep Learning Prediction of Response to Anti-VEGF among Diabetic Macular Edema Patients: Treatment Response Analyzer System (TRAS). Diagnostics 2022, 12, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-Y.; Chou, Y.-B.; Jheng, Y.-C.; Kao, Z.-K.; Huang, H.-Y.; Chen, H.-R.; Hwang, D.-K.; Chen, S.-J.; Chiou, S.-H.; Wu, Y.-T. Automatic Segmentation of Retinal Fluid and Photoreceptor Layer from Optical Coherence Tomography Images of Diabetic Macular Edema Patients Using Deep Learning and Associations with Visual Acuity. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.S.; Tyring, A.J.; Deruyter, N.P.; Wu, Y.; Rokem, A.; Lee, A.Y. Deep-learning based, automated segmentation of macular edema in optical coherence tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 3440–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilla-Pantoja, F.D.; Sanchez, Y.D.; Quijano-Nieto, B.A.; Perdomo, O.J.; Gonzalez, F.A. Etiology of Macular Edema Defined by Deep Learning in Optical Coherence Tomography Scans. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2022, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Chen, H.-R.; Huang, H.-Y.; Hsiao, Y.-I.; Kao, Z.-K.; Chang, K.-J.; Lin, T.-C.; Yang, C.-H.; Kao, C.-L.; Chen, P.-Y.; et al. Deep learning to infer visual acuity from optical coherence tomography in diabetic macular edema. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1008950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michl, M.; Fabianska, M.; Seeböck, P.; Sadeghipour, A.; Najeeb, B.H.; Bogunovic, H.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U.M.; Gerendas, B.S. Automated quantification of macular fluid in retinal diseases and their response to anti-VEGF therapy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 106, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitamura, M.; Saito, M.; Hirooka, K.; Dong, Z.; Ando, R.; Kase, S.; Ishida, S. AI-based analysis of surgical outcomes in vitrectomy with and without cystotomy for refractory cystoid diabetic macular edema. 2024; preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.K.B.; Cowie, C.C. Epidemiology of Ocular Functions and Diseases in Persons with Diabetes. In Diabetes in America, 3rd ed.; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2018; Chapter 21. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, M.L.; Nunes, S.G.; Cunha-Vaz, J.G. Microaneurysm Turnover at the Macula Predicts Risk of Development of Clinically Significant Macular Edema in Persons with Mild Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, T.; Yoshimura, N. Structural Changes in Individual Retinal Layers in Diabetic Macular Edema. J. Diabetes Res. 2013, 2013, 920713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daruich, A.; Matet, A.; Moulin, A.; Kowalczuk, L.; Nicolas, M.; Sellam, A.; Rothschild, P.-R.; Omri, S.; Gélizé, E.; Jonet, L.; et al. Mechanisms of macular edema: Beyond the surface. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2018, 63, 20–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, H.; Kase, S.; Takahashi, M.; Ito, Y.; Sonoda, S.; Sakoguchi, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Katsuta, S.; Ishida, S.; Kase, M. Stratified choroidal vascular structure in treatment-naïve diabetic retinopathy. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 60, e73–e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horii, T.; Murakami, T.; Nishijima, K.; Akagi, T.; Uji, A.; Arakawa, N.; Muraoka, Y.; Yoshimura, N. Relationship between Fluorescein Pooling and Optical Coherence Tomographic Reflectivity of Cystoid Spaces in Diabetic Macular Edema. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthelmes, D.; Sutter, F.K.P.; Gillies, M.C. Differential Optical Densities of Intraretinal Spaces. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 3529–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velaga, S.B.N.M.; Parinitha, B. Correlation between retinal sensitivity and cystoid space characteristics in diabetic macular edema. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 64, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Kase, S.; Saito, M.; Hirose, I.; Murata, M.; Takakuwa, E.; Ishida, S. Clinicopathological findings in refractory diabetic macular edema: A case report. Biomed. Rep. 2024, 20, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Kang, K.E.; Chung, H.; Kim, H.C. Three-dimensional analysis of morphologic changes and visual outcomes in diabetic macular edema. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 63, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Gao, K.; He, S.; Zhong, X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shao, H.; Shen, L. Artificial Intelligence-Based Quantification of Central Macular Fluid Volume and VA Prediction for Diabetic Macular Edema Using OCT Images. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2023, 12, 2441–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboi, K.Y.Q.; Guo, Y. Association Between Fluid Volume in Inner Nuclear Layer and Visual Acuity in Diabetic Macular Edema. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 237, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, P.K.; Vogl, W.D.; Gerendas, B.S.; Glassman, A.R.; Bogunovic, H.; Jampol, L.M.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U.M. Quantification of Fluid Resolution and Visual Acuity Gain in Patients with Diabetic Macular Edema Using Deep Learning: A Post Hoc Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2020, 138, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| mNPDR (n = 33) | sNPDR (n = 52) | PDR (n = 19) | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All the 3 Groups | mNPDR vs. sNPDR | mNPDR vs. PDR | sNPDR vs. PDR | ||||
| Age (years) | 66.3 ± 9.6 | 64.5 ± 11.3 | 59.8 ± 6.0 | <0.01 ☨ | 0.90 ☨☨ | <0.01 ☨☨ | <0.05 ☨☨ |
| logMAR BCVA | 0.27 ± 0.29 | 0.37 ± 0.37 | 0.57 ± 0.36 | <0.01 ☨ | 0.41 ☨☨ | <0.01 ☨☨ | <0.05 ☨☨ |
| Pseudophakic eye (%) | 15 (45.5%) | 14 (26.9%) | 3 (15.8%) | 0.058 # | NA | NA | NA |
| PRP (%) | 3 (9.1%) | 25 (48.1%) | 7 (36.8%) | <0.001 # | <0.001 ## | 0.052 ## | 0.43 ## |
| ERM (%) | 6 (18.2%) | 10 (19.2%) | 1 (5.2%) | 0.35 # | NA | NA | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mitamura, M.; Saito, M.; Hirooka, K.; Dong, Z.; Ando, R.; Kase, S.; Ishida, S. Differences in Artificial Intelligence-Based Macular Fluid Parameters Between Clinical Stages of Diabetic Macular Edema and Their Relationship with Visual Acuity. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14031007
Mitamura M, Saito M, Hirooka K, Dong Z, Ando R, Kase S, Ishida S. Differences in Artificial Intelligence-Based Macular Fluid Parameters Between Clinical Stages of Diabetic Macular Edema and Their Relationship with Visual Acuity. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(3):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14031007
Chicago/Turabian StyleMitamura, Mizuho, Michiyuki Saito, Kiriko Hirooka, Zhenyu Dong, Ryo Ando, Satoru Kase, and Susumu Ishida. 2025. "Differences in Artificial Intelligence-Based Macular Fluid Parameters Between Clinical Stages of Diabetic Macular Edema and Their Relationship with Visual Acuity" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 3: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14031007
APA StyleMitamura, M., Saito, M., Hirooka, K., Dong, Z., Ando, R., Kase, S., & Ishida, S. (2025). Differences in Artificial Intelligence-Based Macular Fluid Parameters Between Clinical Stages of Diabetic Macular Edema and Their Relationship with Visual Acuity. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(3), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14031007





