Automatic Segmentation of the Nasolacrimal Canal: Application of the nnU-Net v2 Model in CBCT Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
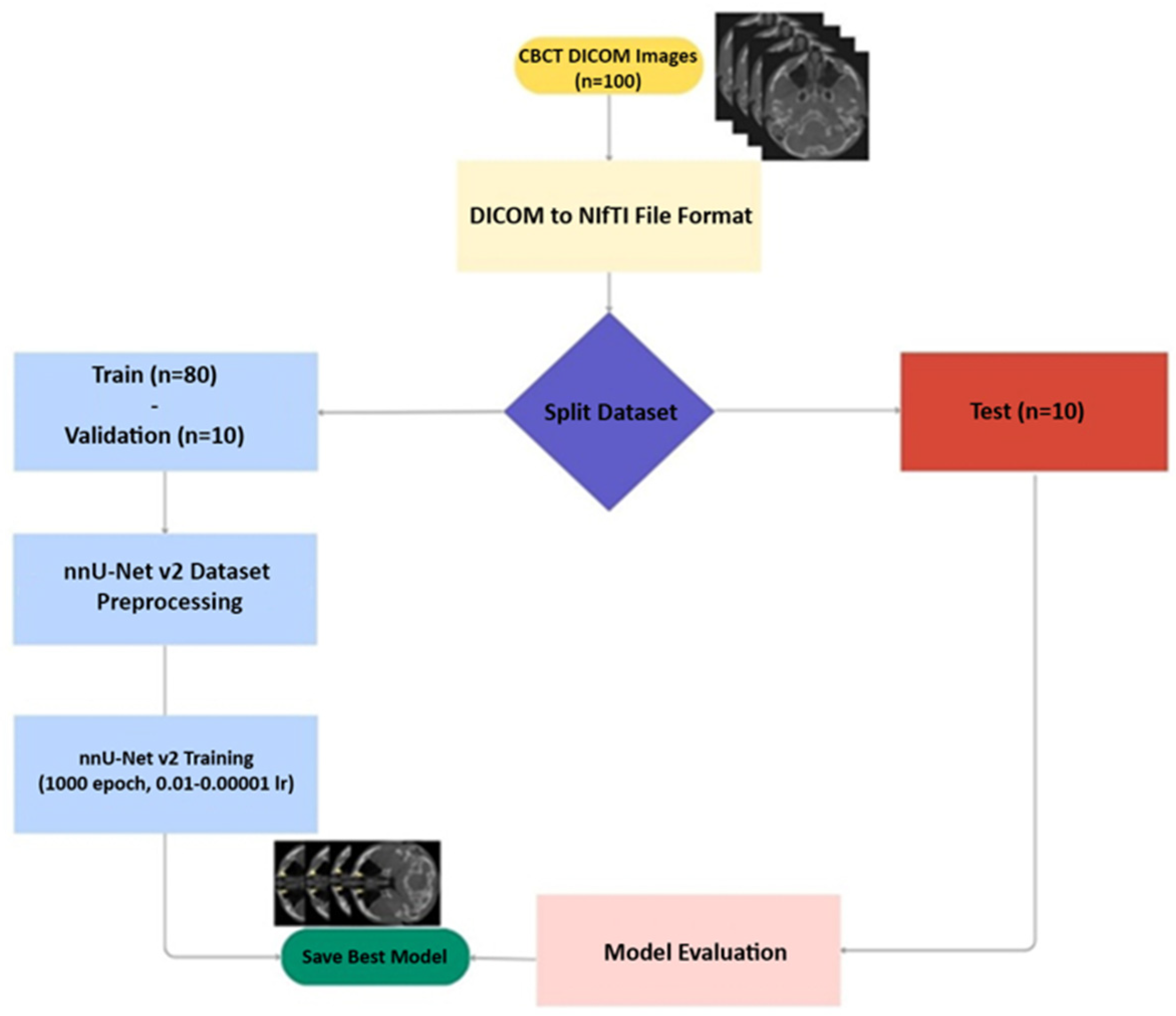
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data
- Individuals over 18 years of age.
- Individuals without any syndrome or bone disease.
- Clearly identified images of NLC’s bone boundaries.
- Individuals with known pre-existing infection, neoplasm and malformations associated with NLC.
- Individuals who have undergone surgical operations and trauma involving the maxillofacial region and NLC.
- Images with motion or metal artifacts that prevent NLC from being displayed and degrade diagnostic quality.
2.3. Obtaining and Evaluating CBCT Images
2.4. Ground Truth
2.5. Testing Data
2.6. Model
2.7. Evaluation
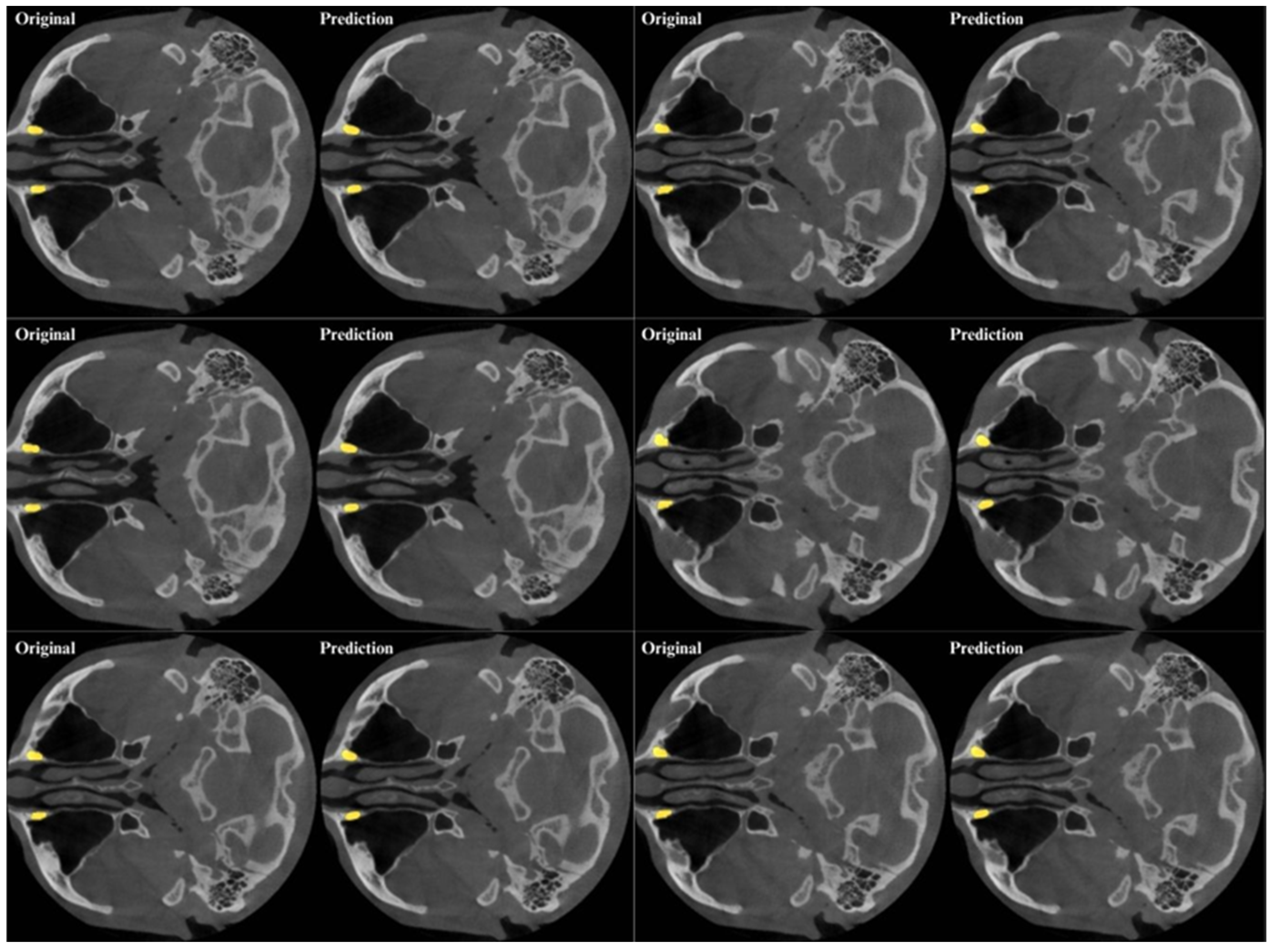
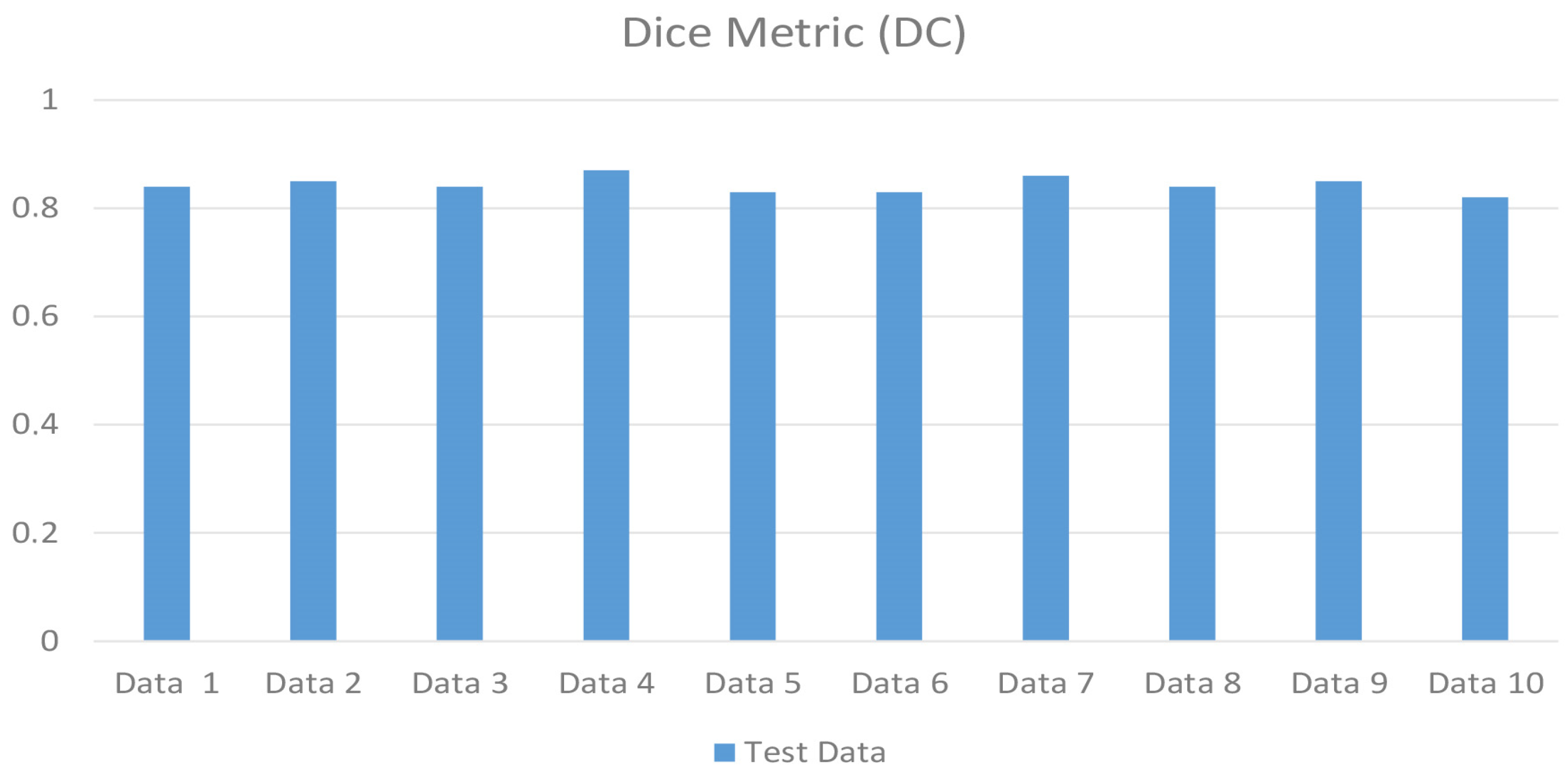
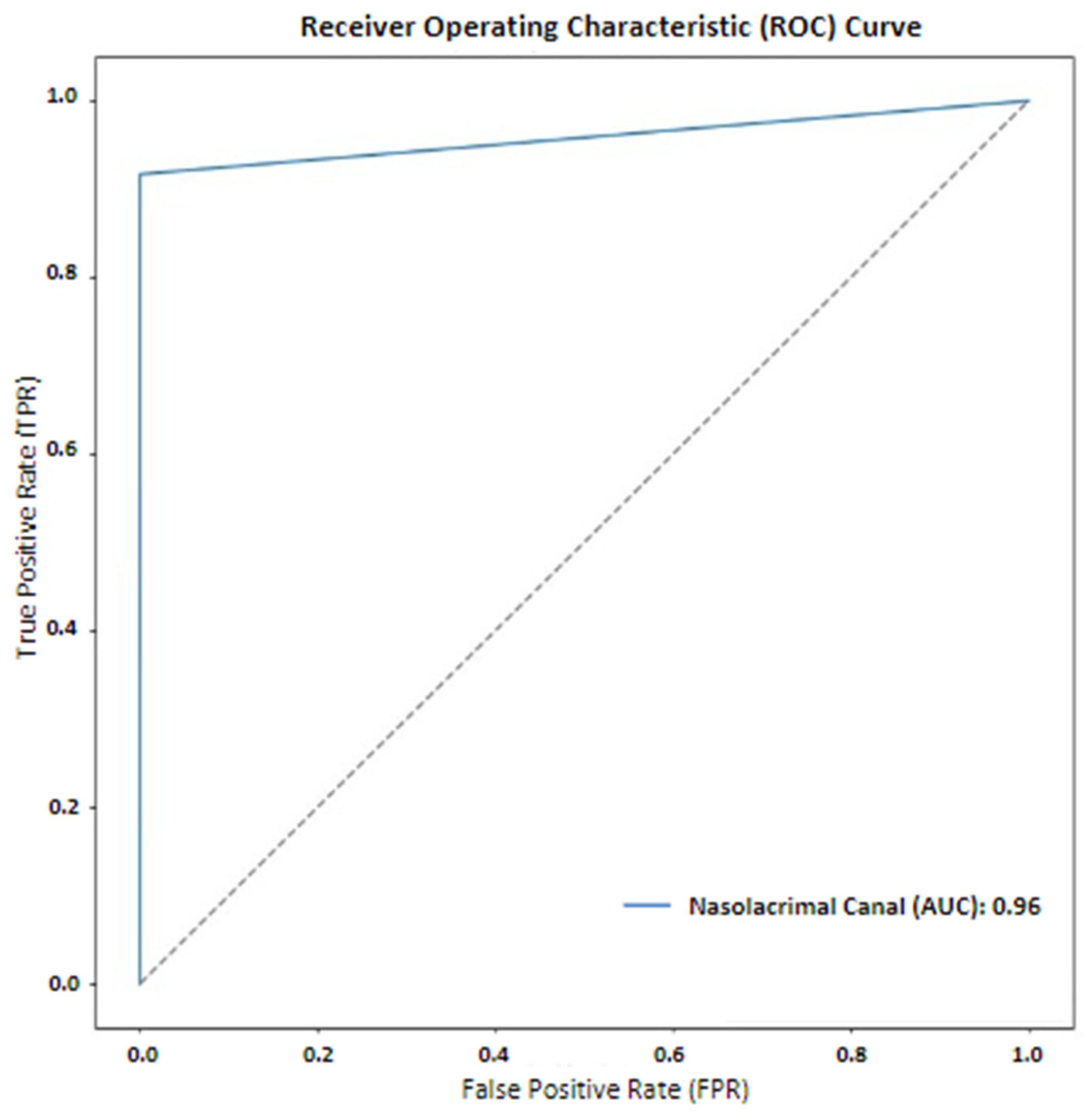
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, S.; Lee, U.Y.; Yang, S.W.; Lee, W.J.; Kim, D.H.; Youn, K.H.; Kim, Y.S. 3D morphological classification of the nasolacrimal duct: Anatomical study for planning treatment of tear drainage obstruction. Clin. Anat. 2021, 34, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jañez-Garcia, L.; Saenz-Frances, F.; Ramirez-Sebastian, J.M.; Toledano-Fernandez, N.; Urbasos-Pascual, M.; Jañez-Escalada, L. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the bony nasolacrimal canal by automated segmentation of computed tomography images. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maliborski, A.; Różycki, R. Diagnostic imaging of the nasolacrimal drainage system. Part I. Radiological anatomy of lacrimal pathways. Physiology of tear secretion and tear outflow. Med. Sci. Monit. 2014, 20, 628. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Czyz, C.N.; Bacon, T.S.; Stacey, A.W.; Cahill, E.N.; Costin, B.R.; Karanfilov, B.I.; Cahill, K.V. Nasolacrimal system aeration on computed tomographic imaging: Sex and age variation. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 32, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atum, M.; Alagöz, G. Blood cell ratios in patients with primary acquired nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Ophthalmol. J. 2020, 5, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousoubris, P.D.; Rosman, D.A. Radiologic evaluation of lacrimal and orbital disease. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2006, 39, 865–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, S.A.; Pak, J.; Shields, M. Pathology and imaging of the lacrimal drainage system. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2005, 15, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, F.; Carvalho, A.; Francisco, V.; Francisco, M.; Neto, G. Evaluation of 1000 lacrimal ducts by dacryocystography. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 91, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, G.; Gauba, V.; Tsangaris, P.; Tharmaseelan, K. Digital subtraction dacryocystography and syringing in the management of epiphora. Orbit 2007, 26, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.J.; Singh, S.; Naik, M.N.; Kaliki, S.; Dave, T.V. Interactive navigation-guided ophthalmic plastic surgery: The utility of 3D CT-DCG-guided dacryolocalization in secondary acquired lacrimal duct obstructions. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2016, 11, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, B.; Ilgit, E.; Onal, B.; Konuk, O.; Erbas, G. MR dacryocystography in the evaluation of patients with obstructive epiphora treated by means of interventional radiologic procedures. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, J.; Kamao, T.; Mitani, A.; Mizuki, N.; Shiraishi, A. Analysis of lacrimal duct morphology from cone-beam computed tomography dacryocystography in a Japanese population. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2022, 16, 2057–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, A.G.; Mansour, K.; Bos, J.J.; Castelijns, J.A. Diameter of the bony lacrimal canal: Normal values and values related to nasolacrimal duct obstruction: Assessment with CT. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2001, 22, 845–850. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, I.; Virdee, S.; Sharp, I.; Sulh, J. Postoperative complications following LeFort 1 maxillary advancement surgery in cleft palate patients: A 5-year retrospective study. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2018, 55, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumussoy, I.; Duman, S.B. Morphometric analysis of occipital condyles using alternative imaging technique. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2020, 42, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdolali, F.; Zoroofi, R.A.; Otake, Y.; Sato, Y. Automatic segmentation of maxillofacial cysts in cone beam CT images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2016, 72, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, D.; Mazen, S.; Tsujiko, S.; Otake, Y.; Sato, Y.; Numajiri, T. Deep-learning-based automatic facial bone segmentation using a two-dimensional U-Net. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 52, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Kim, D.-h.; Jeong, S.-N.; Choi, S.-H. Diagnosis and prediction of periodontally compromised teeth using a deep learning-based convolutional neural network algorithm. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2018, 48, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Jeong, S.-N.; Choi, S.-H. Detection and diagnosis of dental caries using a deep learning-based convolutional neural network algorithm. J. Dent. 2018, 77, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setzer, F.C.; Shi, K.J.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, H.; Yoon, H.; Mupparapu, M.; Li, J. Artificial intelligence for the computer-aided detection of periapical lesions in cone-beam computed tomographic images. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widiasri, M.; Arifin, A.Z.; Suciati, N.; Fatichah, C.; Astuti, E.R.; Indraswari, R.; Putra, R.H.; Za’in, C. Dental-yolo: Alveolar bone and mandibular canal detection on cone beam computed tomography images for dental implant planning. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 101483–101494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kök, H.; Acilar, A.M.; İzgi, M.S. Usage and comparison of artificial intelligence algorithms for determination of growth and development by cervical vertebrae stages in orthodontics. Prog. Orthod. 2019, 20, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Li, Z.-B.; Li, Z. Predicting postoperative facial swelling following impacted mandibular third molars extraction by using artificial neural networks evaluation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Lv, J.; Xu, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, G.; Ai, K. Advancements in oral and maxillofacial surgery medical images segmentation techniques: An overview. J. Dent. 2023, 138, 104727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koç, U.; Sezer, E.A.; Özkaya, Y.A.; Yarbay, Y.; Beşler, M.S.; Taydaş, O.; Yalçın, A.; Evrimler, Ş.; Kızıloğlu, H.A.; Kesimal, U.; et al. Elevating healthcare through artificial intelligence: Analyzing the abdominal emergencies data set (Tr_Abdomen_Rad_Emergency) At Teknofest-2022. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 3588–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, F.; Çetinel, G.; Gül, S. A fully-automated computer-aided breast lesion detection and classification system. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 62, 102157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Kayikcioglu, T.; Kayipmaz, S. Computer-aided diagnosis of periapical cyst and keratocystic odontogenic tumor on cone beam computed tomography. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2017, 146, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolielo, L.F.P.; Van Dessel, J.; Van Lenthe, G.H.; Lambrichts, I.; Jacobs, R. Computer-based automatic classification of trabecular bone pattern can assist radiographic bone quality assessment at dental implant site. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20180437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdolali, F.; Zoroofi, R.A.; Otake, Y.; Sato, Y. Automated classification of maxillofacial cysts in cone beam CT images using contourlet transformation and Spherical Harmonics. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2017, 139, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, S.N. Diagnosis of cystic lesions using panoramic and cone beam computed tomographic images based on deep learning neural network. Oral Dis. 2020, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isensee, F.; Jäger, P.F.; Kohl, S.A.; Petersen, J.; Maier-Hein, K.H. Automated design of deep learning methods for biomedical image segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.08128. [Google Scholar]
- Bayrakdar, I.S.; Elfayome, N.S.; Hussien, R.A.; Gulsen, I.T.; Kuran, A.; Gunes, I.; Al-Badr, A.; Celik, O.; Orhan, K. Artificial intelligence system for automatic maxillary sinus segmentation on cone beam computed tomography images. DentoMaxilloFacial Radiol. 2024, 53, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, part III 18. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Razavi, M.; Shams, N.; Afshari, F.; Nanai, S. Investigating the Morphology of the Nasolacrimal Canal in Cone Beam Computed Tomography Images and Its Relationship with Age and Gender. Maedica 2024, 19, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, S.B.; Gumussoy, İ. Assesment of Prelacrimal Recess in Patients With Maxillary Sinus Hypoplasia Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2021, 35, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmen, D.; Veerasigamani, N.; Briner, H.R.; Jones, N.; Schuknecht, B. Anterior maxillary wall and lacrimal duct relationship-CT analysis for prelacrimal access to the maxillary sinus. Rhinology 2017, 55, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, B.; Taspinar, Y.S.; Koklu, M.; Tassoker, M. Automatic segmentation of the maxillary sinus on cone beam computed tomographic images with U-Net deep learning model. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2024, 281, 6111–6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaskari, J.; Sahlsten, J.; Järnstedt, J.; Mehtonen, H.; Karhu, K.; Sundqvist, O.; Hietanen, A.; Varjonen, V.; Mattila, V.; Kaski, K. Deep learning method for mandibular canal segmentation in dental cone beam computed tomography volumes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, N.; Van Gerven, A.; Smolders, A.; de Faria Vasconcelos, K.; Willems, H.; Jacobs, R. Convolutional neural network for automatic maxillary sinus segmentation on cone-beam computed tomographic images. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preda, F.; Morgan, N.; Van Gerven, A.; Nogueira-Reis, F.; Smolders, A.; Wang, X.; Nomidis, S.; Shaheen, E.; Willems, H.; Jacobs, R. Deep convolutional neural network-based automated segmentation of the maxillofacial complex from cone-beam computed tomography: A validation study. J. Dent. 2022, 124, 104238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-K.; Lim, H.-K.; Lee, S.; Cho, Y.; Song, I.-S. Deep active learning for automatic segmentation of maxillary sinus lesions using a convolutional neural network. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obuchowicz, R.; Strzelecki, M.; Piórkowski, A. Clinical Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging and Image Processing—A Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damilakis, J.; Stratakis, J. Descriptive overview of AI applications in x-ray imaging and radiotherapy. J. Radiol. Prot. 2024, 44, 041001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Gao, G.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, T.; Zeng, W.; Guo, J.; Tang, W. Automatic classification and segmentation of multiclass jaw lesions in cone-beam CT using deep learning. DentoMaxilloFacial Radiol. 2024, 53, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yağmur, Ü.S.; Namdar, P.F. Evaluation of the mandibular canal by CBCT with a deep learning approach. Balk. J. Dent. Med. 2024, 28, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asci, E.; Kilic, M.; Celik, O.; Cantekin, K.; Bircan, H.B.; Bayrakdar, İ.S.; Orhan, K. A Deep Learning Approach to Automatic Tooth Caries Segmentation in Panoramic Radiographs of Children in Primary Dentition, Mixed Dentition, and Permanent Dentition. Children 2024, 11, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Icoz, D.; Terzioglu, H.; Ozel, M.A.; Karakurt, R. Evaluation of an artificial intelligence system for the diagnosis of apical periodontitis on digital panoramic images. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2023, 8, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Yong, T.H.; Shin, N.Y.; Jang, B.G.; Kim, J.E.; Huh, K.H.; Lee, S.-S.; Heo, M.-S.; Choi, S.-C.; et al. Deep Learning Hybrid Method to Automatically Diagnose Periodontal Bone Loss and Stage Periodontitis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, K.; Zhang, F.; Yu, F.; Shi, K.; Sun, Z.; et al. Artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of dental diseases on panoramic radiographs: A preliminary study. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Lin, G.; Bao, R.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, J.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Zuo, X.; Feng, Q.; Liu, S. An automated method for assessing condyle head changes in patients with skeletal class II malocclusion based on Cone-beam CT images. DentoMaxilloFacial Radiol. 2024, 53, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Jeon, K.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Ha, E.-G.; Lee, C.; Han, S.-S. Deep learning-based fully automatic segmentation of the maxillary sinus on cone-beam computed tomographic images. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, L. Study on iris segmentation algorithm based on dense U-Net. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 123959–123968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Metrics | Metric Formula | Metric Value |
|---|---|---|
| True Positive | 16,297.7 | |
| False Positive | 4214.2 | |
| False Negative | 1624.5 | |
| Precision | TP/(TP + FP) | 0.7888 |
| Recall (Sensitivity) | TP/(TP + FN) | 0.9168 |
| Dice Coefficients (DC) | (2 × T P)/(2 × T P + F P + F N) | 0.8465 |
| Intersection over Union (IoU) | (|A∩B|)/(|A∪B|) | 0.7341 |
| F1-Score | 2 × (Precision × Recall)/(Precision + Recall) | 0.8480 |
| 95% Hausdorff Distance (95%HD) mm | dH95(A, B) = max(d95(A, B), d95(A, B)) | 0.9460 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Model | NnU-Net v2 |
| Epoch | 1000 |
| Batch Size | 2 |
| Learning Rate | 0.00001 |
| Optimization | ADAM |
| Activation | ReLU |
| Authors | Aim | Sample | Segmentation Model | Imaging Method | Evaluation Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ozturk [37] | The aim of this study is to develop a deep learning-based method to perform maxillary sinus segmentation using CBCT images. | 100 Scans | U-Net | CBCT | F-1 Score: 0.9784 IoU: 0.9275 |
| Preda et al. [40] | This present study investigated the accuracy, consistency and time-efficiency of a novel deep convolutional neural network (CNN)-based model for the automated maxillofacial bone segmentation from CBCT images. | 144 Patients | U-Net | CBCT | DC: 0.926 %95 HD: 0.621 IoU: 0.862 |
| Shi et al. [44] | This study proposes an automated method to measure condylar changes in patients with skeletal class II malocclusion following surgical orthodontic treatment. | 48 Patients | nnU-Net | CBCT | Maxilla DC: 0.9263 Mandible DC: 0.9387 Condyle DC: 0.971 |
| Yağmur et al. [45] | The aim of this study is to evaluate the mandibular canal with CBCT using a deep learning approach. | 300 Patients | nnU-Net v2 | CBCT | DC: 0.76 |
| Ascı et al. [46] | The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of dental caries segmentation on the panoramic radiographs taken from children in primary dentition, mixed dentition and permanent dentition with AI models developed using the deep learning method. | 6075 Patients | U-Net | Panoramic Radiographs | Sensitivity: 0.8269 Precision: 0.9123 F-1 Score: 0.8675 |
| İçöz et al. [47] | The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of an AI system in the detection of roots with apical periodontitis on digital panoramic radiographs. | 306 Scans | YOLOv3 | Panoramic Radiographs | Sensitivity: 98% Specificity: 56% F-1 Score: 71% |
| Chang et al. [48] | The aim of this study was to develop an automated method for diagnosing periodontal bone loss for staging periodontitis on dental panoramic radiographs using the deep learning hybrid method for the first time. | 340 Scans | Mask R-CNN | Panoramic Radiographs | Periodontal Bone Level IoU: 0.88 Accuracy: 0.92 DC: 0.93 Cementoenamel Junction Level IoU: 0.84 Accuracy: 0.87 DC: 0.91 Teeth and Implants IoU: 0.83 Accuracy: 0.87 DC: 0.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haylaz, E.; Gumussoy, I.; Duman, S.B.; Kalabalik, F.; Eren, M.C.; Demirsoy, M.S.; Celik, O.; Bayrakdar, I.S. Automatic Segmentation of the Nasolacrimal Canal: Application of the nnU-Net v2 Model in CBCT Imaging. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030778
Haylaz E, Gumussoy I, Duman SB, Kalabalik F, Eren MC, Demirsoy MS, Celik O, Bayrakdar IS. Automatic Segmentation of the Nasolacrimal Canal: Application of the nnU-Net v2 Model in CBCT Imaging. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(3):778. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030778
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaylaz, Emre, Ismail Gumussoy, Suayip Burak Duman, Fahrettin Kalabalik, Muhammet Can Eren, Mustafa Sami Demirsoy, Ozer Celik, and Ibrahim Sevki Bayrakdar. 2025. "Automatic Segmentation of the Nasolacrimal Canal: Application of the nnU-Net v2 Model in CBCT Imaging" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 3: 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030778
APA StyleHaylaz, E., Gumussoy, I., Duman, S. B., Kalabalik, F., Eren, M. C., Demirsoy, M. S., Celik, O., & Bayrakdar, I. S. (2025). Automatic Segmentation of the Nasolacrimal Canal: Application of the nnU-Net v2 Model in CBCT Imaging. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(3), 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030778








